Must Choose Adjacent Relative Volatilities As Key Components
Diunggah oleh
Gastón Miranda GarcíaDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Must Choose Adjacent Relative Volatilities As Key Components
Diunggah oleh
Gastón Miranda GarcíaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Simple shortcut methods for a quaternary system, easily modifie **See NIST Webbook
**Ideal VLE *Must choose adjacent relative volatilities as key components Antoine's constants (So
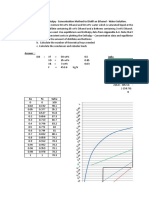
feed rate, F (mol/min) = 100 feed liquid fract, q = 1 zF1 = 0.25974026 log(p*
theoretical stages, Nideal = 16.305 P column (mm Hg) = 6205.77 z F2
= 0.350649351 compound
Distillate recovery of key components **Setup for recovery of species 1 & 2 zF3 = 0.25974026 methane
Feed overall mole fractions: Distillate 1 = 97.1% z F4
= 0.12987013 ethane
Sum = 1 Distillate 2 = 1.0% n-propane
n-butane
Preliminary Calculations Based on Light and Heavy Key Components to Estimate aij n-pentane
species i xF xFF Recovery xDD yD xBB xB n-hexane
n-butane 1 0.25974026 25.974 97.1% 25.22078 0.986287 0.7532468 0.0101 n-heptane
n-pentane 2 0.350649351 35.065 1.0% 0.350649 0.013713 34.714286 0.4664 n-octane
n-hexane 3 0.25974026 25.974 0 0 0 25.974026 0.3490 n-nonane
n-heptane 4 0.12987013 12.987 0 0 0 12.987013 0.1745 methanol
sum 1 100 25.57143 1 74.428571 1 methanol
i-propanol
Antoine Equation Constants: log(p*(torr))=A-B/(T(deg C) + C) Feed Temperature Calculation sec-butanol
T (C) = 110.53 Bottoms water
species A B C Tb (C) pi* (torr) Ki aFij KixF water
n-butane 6.8089557 935.8611791 238.73 0 13472.14 2.171 2.428 0.564 glycerin
n-pentane 6.85221 1064.63 232 0 5547.731 0.894 1.000 0.313
n-hexane 6.87601 1171.17 224.41 69 2395.533 0.386 0.432 0.100
n-heptane 6.89677 1264.9 216.54 98.4 1070.18 0.172 0.193 0.022
1.0000
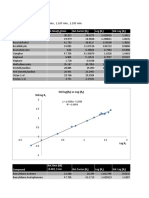
Top Tray Dew Point Calculation Reboiler Bubble-Point Calculation
T (C) = 72.61 Distillate T (C) = 135.33 Bottoms
species pi* (torr) Ki aDij yD/Ki pi* (torr) Ki aBij KixB
n-butane 6353.314 1.024 2.792 0.963 ### 3.268 2.255 0.033
n-pentane 2275.628 0.367 1.000 0.037 8993.051 1.449 1.000 0.676
n-hexane 856.811 0.138 0.377 0.000 4172.511 0.672 0.464 0.235
n-heptane 332.7811 0.054 0.146 0.000 2004.305 0.323 0.223 0.056
sum = 1.001 1.0000
Relative Volatilities Hengstebeck-Geddes Eq
species <a> xDD xD xBB xB => log (di/bi) = a + b log (ai)
n-butane 2.48 25.22 0.99 0.75 0.01 a= -1.996
n-pentane 1.00 0.35 0.01 34.71 0.47 b= 8.917
n-hexane 0.42 0.00 0.00 25.97 0.35
n-heptane 0.18 0.00 0.00 12.99 0.17
25.57 1.00 74.43 1.00 guess f = 1.580933276
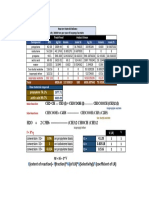
species Eq 22.29 Eq. 22.30 Calculate Optimal R from Olujics Eq
i term(i) term(i) Y= 1.120
1 0.72 2.72 X= 3.343
2 -0.60 -0.02 Ropt/Rmin= 1.293
3 -0.09 0.00 Ropt = 2.189
4 -0.02 0.00 Needed to fit plates
SaixDi/(ai-f) = 0.00 2.69 = SaixDi/(ai-f) factor = 1.163 R/Rmin
sum - (1-q) = 0.00 1.69 = Rmin R= 2.546 => 1.503440968
Calc Nmin from Fenske Eq 22.13 Nmin+1 = 8.917
Calculate N from Gilliland Correlation Fig 22.5
X= 0.24 Y= 0.43 => Nideal = 16.30
Calculate optimum feed stage location from Kirkbride equation
m/p = 1.169711988
m = 8.790110183 Optimum feed stage = 7.514765
NIST Webbook for more chemical data as needed: http://webbook.nist.gov/
e's constants (Some taken from Lange's Handbook of Chemistry and Felder & Rousseau)
log(p*, mm Hg) = A - B/(T (deg C) + C)
A B C Tb (C) range
6.6118294808 259.6386 265.99 ln(mmHg), K
6.8026584762 656.4014 255.99 ln(mmHg), K
6.8297150224 813.199 247.99 ln(mmHg), K
6.8089557462 935.8612 238.73 ln(mmHg), K
6.85221 1064.63 232
6.87601 1171.17 224.41 69.0 -25 to 92
6.89677 1264.90 216.54 98.4 -2 to 124
6.91868 1351.99 209.15 125.7 19 to 152
6.93893 1431.82 202.01 150.8 39 to 179
7.8975 1474.08 229.13 65.0 -14 to 65
7.97328 1515.14 232.85 65.0 64 to 110
8.11778 1580.92 219.61 82.4 0 to 101
7.47431 1314.19 186.55 99.5 25 to 120
8.10765 1750.29 235.00 100.0 0 to 60
7.96681 1668.21 228.00 100.0 60 to 150
6.8239002047 1411.53 72.58 285.4
1,2,3, propanetriol = glycerin methanol
DHvap (kJ/mol) = 91.7 ± 0.9 37.83
Tbp (K) = 560 ± 40 65
CpL (J/mol-K) = 218.9 79.5
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- DC SIM+User+GuideDokumen115 halamanDC SIM+User+GuideSegundopqBelum ada peringkat
- Elliott Centrifugal CompressorDokumen2 halamanElliott Centrifugal Compressorionutlaur86Belum ada peringkat
- 1081ch8 37 PDFDokumen14 halaman1081ch8 37 PDFArkn KikiBelum ada peringkat
- Fish Bone DiagramDokumen60 halamanFish Bone DiagramSaurabh RaiBelum ada peringkat
- Applying Advanced Control To A VCM Unit (PTQ - Q1 2007)Dokumen5 halamanApplying Advanced Control To A VCM Unit (PTQ - Q1 2007)yliangcaBelum ada peringkat
- Distillation Tower DesignDokumen65 halamanDistillation Tower DesignAntonio SilvaBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Report Experiment 5 Chm421Dokumen9 halamanLab Report Experiment 5 Chm421aremyrah AzlanBelum ada peringkat
- Extractive Distillation ReportDokumen17 halamanExtractive Distillation ReportAmanda Brown100% (1)
- 2009 - Prof Eng - WWTP Design ExcelDokumen9 halaman2009 - Prof Eng - WWTP Design ExcelLinh PhamBelum ada peringkat
- Hall Yarborough ZDokumen3 halamanHall Yarborough ZicaBelum ada peringkat
- Technologies For The Design and Operation of Phosphate Fertilizer & Sulfuric Acid PlantsDokumen12 halamanTechnologies For The Design and Operation of Phosphate Fertilizer & Sulfuric Acid PlantsJavier Alejandro RodriguezBelum ada peringkat
- Sop Edited CeuticsDokumen33 halamanSop Edited Ceuticsbandameedi.ramu2819Belum ada peringkat
- (18994741 - Polish Journal of Chemical Technology) Process Simulation of Dimethyl Ether Synthesis Via Methanol Vapor Phase DehydrationDokumen6 halaman(18994741 - Polish Journal of Chemical Technology) Process Simulation of Dimethyl Ether Synthesis Via Methanol Vapor Phase DehydrationGlacier RamkissoonBelum ada peringkat
- Komponen: Chart TitleDokumen15 halamanKomponen: Chart TitleALdi Dota2Belum ada peringkat
- Destilasi Binner & Multi KomponenDokumen8 halamanDestilasi Binner & Multi KomponenApril Rianto BaktiarBelum ada peringkat
- PB Mod 2 1 Homework 1 LL 2016 HRDokumen8 halamanPB Mod 2 1 Homework 1 LL 2016 HRAntonio ChissanoBelum ada peringkat
- Metode Short CutDokumen5 halamanMetode Short CutNabilla Putri AndiniBelum ada peringkat
- Flash Vaporization (Tugas Kita Bersama)Dokumen13 halamanFlash Vaporization (Tugas Kita Bersama)Hanna HerdayunitaBelum ada peringkat
- Hall Yarborough ZDokumen3 halamanHall Yarborough Zvictor javier nuñezBelum ada peringkat
- Hall Yarborough ZDokumen3 halamanHall Yarborough ZicaBelum ada peringkat
- T T T T T: PC G NDokumen3 halamanT T T T T: PC G NSig BahaBelum ada peringkat
- Hall Yarborough ZDokumen4 halamanHall Yarborough ZDanny MoralesBelum ada peringkat
- Hall Yarborough ZDokumen3 halamanHall Yarborough ZTy LeBelum ada peringkat
- Multikomponen DistilasiDokumen24 halamanMultikomponen DistilasiBunga Rajhana Ragil GayatriBelum ada peringkat
- Multi Komponen DistilasiDokumen3 halamanMulti Komponen DistilasiCitra Desiana ErinBelum ada peringkat
- Retention Time of CH 1.111 Min, 1.107 Min, 1.105 Min: Calibration Curve For 60 ̊CDokumen2 halamanRetention Time of CH 1.111 Min, 1.107 Min, 1.105 Min: Calibration Curve For 60 ̊CMadhushi BandaraBelum ada peringkat
- Distillation Column: Bubble Point ComputationDokumen11 halamanDistillation Column: Bubble Point ComputationChua RhickBelum ada peringkat
- Che61 At11Dokumen9 halamanChe61 At11Michael Alex MabaoBelum ada peringkat
- New Tutorial 8 With SolutionDokumen5 halamanNew Tutorial 8 With SolutionNaveed AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- Distillation ColumnDokumen10 halamanDistillation ColumnPrajapati HarshBelum ada peringkat
- Distribution of Components: F F D D W WDokumen7 halamanDistribution of Components: F F D D W Wsamtech007Belum ada peringkat
- TPP Excel BaruDokumen7 halamanTPP Excel BaruAtika HapsatiBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment # 3 - Problem # 3 in TutorialDokumen21 halamanAssignment # 3 - Problem # 3 in TutorialmahmoudBelum ada peringkat
- Termo 12,18,34Dokumen17 halamanTermo 12,18,34salma de la rosaBelum ada peringkat
- Latihan Soal PAP MDDokumen6 halamanLatihan Soal PAP MDvalianamgrhyBelum ada peringkat
- Concentracion Naoh Concentracion HCL Density Methyl Acetate Masa M Acetate MethyDokumen6 halamanConcentracion Naoh Concentracion HCL Density Methyl Acetate Masa M Acetate MethypochagatoBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas OPB (Fadiya Salwa Zaizafun 1700020130)Dokumen12 halamanTugas OPB (Fadiya Salwa Zaizafun 1700020130)Fadiya Salwa ZaizafunBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas 1 Tekprodgas Cheasar Septian Dwi Cahyo071002200065Dokumen21 halamanTugas 1 Tekprodgas Cheasar Septian Dwi Cahyo071002200065Cheasar SeptianBelum ada peringkat
- P MMHG: Constantes de Antoine Parámetros Binarios: (G - G) (Cal/Mol K) Parámetros Binarios: AlfaDokumen14 halamanP MMHG: Constantes de Antoine Parámetros Binarios: (G - G) (Cal/Mol K) Parámetros Binarios: AlfaXiime WalburgBelum ada peringkat
- Solution Excel Probem 1.2Dokumen6 halamanSolution Excel Probem 1.2Az-yBelum ada peringkat
- Komponen Acetone Methanol (LK) 2-Propanol (HK) 1-Propanol TolueneDokumen17 halamanKomponen Acetone Methanol (LK) 2-Propanol (HK) 1-Propanol TolueneDheyana SariBelum ada peringkat
- Homework 3Dokumen12 halamanHomework 3Trung Kỹ PhạmBelum ada peringkat
- Newton-Raphson (Z)Dokumen5 halamanNewton-Raphson (Z)Carlos Ubillas AlcaldeBelum ada peringkat
- Cooler (2 Juli 2023)Dokumen293 halamanCooler (2 Juli 2023)habbibrachmanBelum ada peringkat
- 1 ReactorDokumen69 halaman1 ReactorBahrulUlumBelum ada peringkat
- Homework 4 Problem 1: Estimate The Density of A 0.8-Specific Gravity Dead Oil at 40Dokumen8 halamanHomework 4 Problem 1: Estimate The Density of A 0.8-Specific Gravity Dead Oil at 40Trung Kỹ PhạmBelum ada peringkat
- Gas Natural1Dokumen12 halamanGas Natural1ISRAEL RODRIGUEZBelum ada peringkat
- Mass Tra AssDokumen3 halamanMass Tra AssRoahliza NalazaBelum ada peringkat
- Calor Lat Vap Chopey - Djra Mipg20Dokumen11 halamanCalor Lat Vap Chopey - Djra Mipg20Dan JefteBelum ada peringkat
- Gas Processors Suppliers Association GPSA Eng (Bookos - Org) - 701-821-1!60!41-60Dokumen20 halamanGas Processors Suppliers Association GPSA Eng (Bookos - Org) - 701-821-1!60!41-60Karen VlBelum ada peringkat
- DataDokumen3 halamanDataEduardo Paulini VillanuevaBelum ada peringkat
- HW1 SolutionDokumen3 halamanHW1 SolutionMohammad Iqbal Mahamad Amir100% (2)
- Distillation Column 1 - (D01)Dokumen20 halamanDistillation Column 1 - (D01)Patricia MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 1 - Tables and GraphsDokumen9 halamanLab 1 - Tables and GraphsDarleen PeraltaBelum ada peringkat
- Calculos Del Rri: TOP HYP HYPDokumen5 halamanCalculos Del Rri: TOP HYP HYPLuis Alberto MendezBelum ada peringkat
- (ρm-ρcamp) / (ρm-ρet)Dokumen7 halaman(ρm-ρcamp) / (ρm-ρet)Tsara ParamitahBelum ada peringkat
- OTK KristiantyDokumen9 halamanOTK KristiantyDewi RatnasariBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment of SHMTDokumen10 halamanAssignment of SHMTZohaib AliBelum ada peringkat
- Reactor Material BalaneDokumen1 halamanReactor Material BalaneAsad RazaBelum ada peringkat
- 2023 TPM351ppyDokumen7 halaman2023 TPM351ppyJenyver LappyBelum ada peringkat
- QuizDokumen21 halamanQuizIhaw HalimBelum ada peringkat
- I Componente A B C Psat (Kpa)Dokumen3 halamanI Componente A B C Psat (Kpa)Katerine Ostos ArellanoBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas 1 40040117060067 SyadilalutfimDokumen6 halamanTugas 1 40040117060067 SyadilalutfimSyadila LutfiBelum ada peringkat
- Colburn's Method - Solve For Hydrocarbons SystemDokumen16 halamanColburn's Method - Solve For Hydrocarbons Systemumair saleemBelum ada peringkat
- Newton RahpsonDokumen1 halamanNewton RahpsonElvis CoronelBelum ada peringkat
- Taking Hexane RefrenceDokumen6 halamanTaking Hexane RefrencePravin KaleBelum ada peringkat
- TH206 B3aDokumen9 halamanTH206 B3aDivyanshu SumanBelum ada peringkat
- Multistage Distillation - Multicomponent: Assignment 5 - Mass Transfer OperationsDokumen10 halamanMultistage Distillation - Multicomponent: Assignment 5 - Mass Transfer OperationsGaddy KhalfaniBelum ada peringkat
- Metanol A OleafinasDokumen7 halamanMetanol A OleafinasGastón Miranda GarcíaBelum ada peringkat
- Etherificacion Del GlicerolDokumen8 halamanEtherificacion Del GlicerolGastón Miranda GarcíaBelum ada peringkat
- Glycerol InvestigationDokumen13 halamanGlycerol InvestigationGastón Miranda GarcíaBelum ada peringkat
- Práctica - Voz PasivaDokumen2 halamanPráctica - Voz PasivaGastón Miranda García50% (2)
- Perry's Chemical Engineers' Handbook (McGrawHill-8thEd-2008) - about&URLDokumen2 halamanPerry's Chemical Engineers' Handbook (McGrawHill-8thEd-2008) - about&URLMuhammad Andrifar Empatpuluhlima0% (1)
- Lab Report 6 Isolation of Eugenol From Cloves by DistillationDokumen4 halamanLab Report 6 Isolation of Eugenol From Cloves by DistillationMyeeka HammondBelum ada peringkat
- Distillation: Enthalpy Concentration Methods (HX) Diagram or Ponchon Savarit MethodDokumen9 halamanDistillation: Enthalpy Concentration Methods (HX) Diagram or Ponchon Savarit MethodRose Dane Escobedo DiestaBelum ada peringkat
- Patchouli OilsDokumen5 halamanPatchouli OilsbudiliaBelum ada peringkat
- Us 8450543Dokumen36 halamanUs 8450543Areva FateehaBelum ada peringkat
- G&T-Tasting AuswertungDokumen8 halamanG&T-Tasting AuswertungoscompBelum ada peringkat
- Menu Drinks Asador 9Dokumen6 halamanMenu Drinks Asador 9dominic2299Belum ada peringkat
- 2020-ptq-q 2Dokumen120 halaman2020-ptq-q 2Forcus onBelum ada peringkat
- Astm D-5322 PDFDokumen3 halamanAstm D-5322 PDFGisella Mariel RubilarBelum ada peringkat
- Designation: D 4176 - 93 (Reapproved 1997)Dokumen6 halamanDesignation: D 4176 - 93 (Reapproved 1997)David CazorlaBelum ada peringkat
- Extraction of Oil From Eucalyptus Camadulensis Using Water Distillation MethodDokumen7 halamanExtraction of Oil From Eucalyptus Camadulensis Using Water Distillation MethodSergio CBBelum ada peringkat
- Organic Chemistry Different TestDokumen5 halamanOrganic Chemistry Different TestNera AyonBelum ada peringkat
- 5.characterization of Petroleum FractionsDokumen65 halaman5.characterization of Petroleum FractionsNatalia AguilarBelum ada peringkat
- EaglesDisobey 01Dokumen115 halamanEaglesDisobey 01Anonymous xKkcNEyGBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis of Soil Samples From Various Areas of PunjabDokumen3 halamanAnalysis of Soil Samples From Various Areas of PunjabDikshaBelum ada peringkat
- Distillation Model Rev1Dokumen9 halamanDistillation Model Rev1mehul1094167% (3)
- 0610 0620 0625 Planning v1Dokumen34 halaman0610 0620 0625 Planning v1ganesh mukhia50% (2)
- AsphaltDokumen5 halamanAsphaltJenny Lyn SemineBelum ada peringkat
- Essay On Childrens DayDokumen6 halamanEssay On Childrens Dayoqzunxbaf100% (1)
- Multi Component DistillationDokumen94 halamanMulti Component DistillationMayur J Mehta60% (5)
- Pump AroundDokumen3 halamanPump AroundAshrafMostafaBelum ada peringkat