Poster Presentation
Diunggah oleh
api-300786566Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Poster Presentation
Diunggah oleh
api-300786566Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Alexis
Johnson
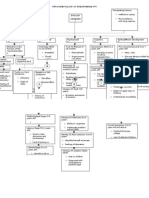
Review of Literature
Cognitive
Schlaug,Norton, Overy and Winner (2005) Studies show that
students who participated in early Music training showed a
Research
Ques+ons
greater increase in developmental abilities, math, reading, writing,
language, than those who did not.
1. How can engaging students - There was a greater activation of the posterior inferior and
in the music classroom help middle frontal gyrus, the portion of the brain that’s associated
students develop social and with language, in students who studied music.
emotional skills?
Emotional
Giles, Cogan and Cox (1991): Research has proven that New Age
music and Disney Music are both effective at altering negative
2. How will starting students moods in students. Different genres are used to help alter the
in music engagement early moods of patients in mental institutions. Teachers can use specific
affect their cognitive genres of music to help students address stress and any negative
development? emotions they may be feeling.
Social
Hargreaves, Marshall and North (2003): Research has shown that
engaging in music can helps students create relationships with
other people. Music training and performance can give students
How hhhfjf
Recommenda+ons
for
Research
the confidence that will transfer to other parts of their lives.
-More research on how music Turner (33): Child-centered learning allows students to guide their
and different music genres can own learning. This can help them with communication because
help students cope with stress they have to discuss what they are interested in and want to learn
and anxiety more about.
- What aspects of music Prac+cal Applica+on abili*es
education (rhythm, solfege, -‐ Song-‐ wri*ng : Teachers can -‐ Foster experiences and lessons
note reading, etc.) are the most facilitate experiences where that allow students to engage
effective at helping develop students are crea*ng works and communicate with each
students cognitive abilities. that help them express their other. This will help them
emo*ons. develop confidence,
communica*on, and social
-‐ Rhythm, Solfege, and note skills they can use in other
reading exercises that aspects of life.
engance students cogni*ve
Hargreaves, D. J., Marshall, N. A., & North, A. C. (2003). Music education in the twenty-
Literature
cited
first century: a psychological perspective. British Journal of Music Education, 20(2),
Gerry, D., Unrau, A., & Trainor, L. J. (2012). Active music classes in infancy 147-163.
enhance musical, communicative and social development. Developmental
science, 15(3), 398-407. Higgins, L. (2012). Community music : in theory and in practice. New York : Oxford
University Press.
Giles, M. M., Cogan, D., & Cox, C. (1991). A music and art program to
promote emotional health in elementary school children. Journal of Music Rickard, N. S., Toukhsati, S. R., & Field, S. E. (2005). The effect of music on cognitive
Therapy, 28(3), 135–148. performance: Insight from neurobiological and animal studies. Behavioral and Cognitive
Hallam, S. (8/23/10). The power of music: Its impact on the intellectual, Neuroscience Reviews, 4(4), 235-261.
social and personal development of children and young people.
International Journal of Music Education, Volume 28 (3). Retrieved from: Schlaug, G., Norton, A., Overy, K., & Winner, E. (2005). Effects of music training on the
http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/0255761410370658 child's brain and cognitive development. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences,
1060(1), 219-230.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Can Music Help Special Education Students Control Negative Behavior in the Classroom?Dari EverandCan Music Help Special Education Students Control Negative Behavior in the Classroom?Belum ada peringkat
- WEEKS, K. 2014 - Vowels - Sonic Gems of Emotion For Social Communication Practical Singing Strategies For Non-Musician Teachers With Developmentally Diverse Young ChildrenDokumen8 halamanWEEKS, K. 2014 - Vowels - Sonic Gems of Emotion For Social Communication Practical Singing Strategies For Non-Musician Teachers With Developmentally Diverse Young ChildrenClara de LannaBelum ada peringkat
- Academic Performance and Music PreferenceDokumen33 halamanAcademic Performance and Music PreferencePrecious Heiress MarasiganBelum ada peringkat
- Annotated BibliographyDokumen3 halamanAnnotated Bibliographyapi-272805272Belum ada peringkat
- Effect of music on college student gradesDokumen4 halamanEffect of music on college student grades33 Siddhant JainBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2Dokumen11 halamanChapter 2Aaron James MabuyoBelum ada peringkat
- Usic Lessons Emotional Intelligence andDokumen11 halamanUsic Lessons Emotional Intelligence andRicardo MolleapazaBelum ada peringkat
- GerryUnrauTrainor 2012 PDFDokumen11 halamanGerryUnrauTrainor 2012 PDFLaura F MerinoBelum ada peringkat
- Robert S. Legutko (2012)Dokumen10 halamanRobert S. Legutko (2012)yantiBelum ada peringkat
- Final For DefenseDokumen33 halamanFinal For DefenseRALPH JOSEPH SANTOSBelum ada peringkat
- Making Music in A Group: Synchronization and Shared ExperienceDokumen4 halamanMaking Music in A Group: Synchronization and Shared ExperiencemoiBelum ada peringkat
- Musical Activities in Primary SchoolsDokumen7 halamanMusical Activities in Primary SchoolsYossy Eka NandaBelum ada peringkat
- Evaluation of The Dalcroze Rhythmic Approach in First Steps of Music EducationDokumen6 halamanEvaluation of The Dalcroze Rhythmic Approach in First Steps of Music EducationpapuenteBelum ada peringkat
- The Effect of Listening To Music On The Academic Performance of The Student in Grade 12 Ict and Humms 12 On GrpmhsDokumen14 halamanThe Effect of Listening To Music On The Academic Performance of The Student in Grade 12 Ict and Humms 12 On GrpmhsTavera Jericho De LunaBelum ada peringkat
- The Effect of Hindustani Classical Instrumental Music Santoor in Improving Writing Skills of Students With Learning DisabilityDokumen6 halamanThe Effect of Hindustani Classical Instrumental Music Santoor in Improving Writing Skills of Students With Learning DisabilityinventionjournalsBelum ada peringkat
- Does Learning Music Affects Study Habits of LearnersDokumen8 halamanDoes Learning Music Affects Study Habits of Learnerstulikabansal_gie100% (1)
- Introduction CH 1Dokumen12 halamanIntroduction CH 1Chelsie ColifloresBelum ada peringkat
- Music Lessons Enchance IQ SchellenbergDokumen5 halamanMusic Lessons Enchance IQ SchellenbergClarissa Dewi100% (1)
- Gloria Stahl: 807169939 (I Don't Know What The Unit Code Is)Dokumen6 halamanGloria Stahl: 807169939 (I Don't Know What The Unit Code Is)Gloria StahlBelum ada peringkat
- Art-Habibi Et Al-Music Training and Child Development-2018Dokumen9 halamanArt-Habibi Et Al-Music Training and Child Development-2018Birgita Solange SantosBelum ada peringkat
- Texto InglesDokumen4 halamanTexto InglesRaimundo LimaBelum ada peringkat
- Mus 785 Article Review 2Dokumen7 halamanMus 785 Article Review 2api-624478936Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1: Introduction 1.1 Background of The TopicDokumen5 halamanChapter 1: Introduction 1.1 Background of The TopicFatimah SamadBelum ada peringkat
- Music in The Classroom and Its Impact On GradesDokumen1 halamanMusic in The Classroom and Its Impact On GradesTravis GrimesBelum ada peringkat
- Creative Music Listening PDFDokumen7 halamanCreative Music Listening PDFTees ThingsBelum ada peringkat
- Intergrating Music & Movement in LessonsDokumen74 halamanIntergrating Music & Movement in Lessonsaleem_80Belum ada peringkat
- Articole MeloterapieDokumen46 halamanArticole MeloterapiePatricia Andreea BerbecBelum ada peringkat
- Engage Young English Learners with Songs and MovementDokumen13 halamanEngage Young English Learners with Songs and Movementestefi paulozzoBelum ada peringkat
- Psychological Science: Music Lessons Enhance IQDokumen5 halamanPsychological Science: Music Lessons Enhance IQSoporte CeffanBelum ada peringkat
- Title Music and Cognitive ImprovementDokumen3 halamanTitle Music and Cognitive ImprovementTravis GrimesBelum ada peringkat
- Utilizing Music in Teaching MathematicsDokumen6 halamanUtilizing Music in Teaching MathematicsPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalBelum ada peringkat
- Hedden 2007Dokumen12 halamanHedden 2007Sofia GatoBelum ada peringkat
- Fnbeh 13 00172Dokumen9 halamanFnbeh 13 00172Matías RodriguezBelum ada peringkat
- Competency 2 AY 2023 2024 TEACHING MUSICDokumen14 halamanCompetency 2 AY 2023 2024 TEACHING MUSICchaibalinBelum ada peringkat
- Musical Independence in Secondary Music Ensembles: Annotated BibliographyDokumen14 halamanMusical Independence in Secondary Music Ensembles: Annotated Bibliographyapi-557621519Belum ada peringkat
- Stem 1 Group 8Dokumen40 halamanStem 1 Group 8Dianne VillanuevaBelum ada peringkat
- The Role of Music Education in ChildhoodDokumen20 halamanThe Role of Music Education in ChildhoodCarlos MuñozBelum ada peringkat
- From Child To Musician Skill Development During The Begining Stages of Learning An InstrumentDokumen31 halamanFrom Child To Musician Skill Development During The Begining Stages of Learning An InstrumentHeidy Carvajal GarcíaBelum ada peringkat
- Carol Hayward - Sight Reading PDFDokumen11 halamanCarol Hayward - Sight Reading PDFMatthew Moore100% (1)
- Scholarship FinalDokumen8 halamanScholarship Finalapi-455953247Belum ada peringkat
- Scholarship Annotated BibliographyDokumen4 halamanScholarship Annotated Bibliographyapi-329930090Belum ada peringkat
- Music Educates and SoothesDokumen5 halamanMusic Educates and Soothesapi-697411513Belum ada peringkat
- PosterdesignDokumen1 halamanPosterdesignapi-372033975Belum ada peringkat
- Annotated Bibliography: Krivanek 1Dokumen5 halamanAnnotated Bibliography: Krivanek 1api-356431883Belum ada peringkat
- Ed332447 PDFDokumen17 halamanEd332447 PDFJuanero, Reyean IñigoBelum ada peringkat
- The Effect of Music Genres (Pop & Classical) On Critical Thinking of Grade 10 Students of Marian College.Dokumen22 halamanThe Effect of Music Genres (Pop & Classical) On Critical Thinking of Grade 10 Students of Marian College.Gift Cyrl SilabayBelum ada peringkat
- Jigsaw PDFDokumen15 halamanJigsaw PDFapi-460332539Belum ada peringkat
- Jkuebler Action ResearchDokumen24 halamanJkuebler Action Researchapi-317364001Belum ada peringkat
- Improvisation and Music Education BeyondDokumen3 halamanImprovisation and Music Education BeyondxiongtuBelum ada peringkat
- SUTELA, K. 2019 - Applying Music and Movement To Promote Agency Development in Music Education. A Case Study in A Special SchoolDokumen15 halamanSUTELA, K. 2019 - Applying Music and Movement To Promote Agency Development in Music Education. A Case Study in A Special SchoolClara de LannaBelum ada peringkat
- CHAPTERS 1 5 With AppendicesDokumen93 halamanCHAPTERS 1 5 With AppendicesTiktok TrendsBelum ada peringkat
- ImportanceOfMusicinECEDokumen10 halamanImportanceOfMusicinECEdasaiyahslb957Belum ada peringkat
- (Notes:: Why Music Is Important For Academic Development?Dokumen8 halaman(Notes:: Why Music Is Important For Academic Development?Gloria StahlBelum ada peringkat
- Benefits of Music Education 1Dokumen9 halamanBenefits of Music Education 1api-442336215Belum ada peringkat
- Movement Activities in The General Music Classroom 1Dokumen7 halamanMovement Activities in The General Music Classroom 1Robert Mago Cabusao Jr.Belum ada peringkat
- Foundations of Music LiteracyDokumen13 halamanFoundations of Music LiteracyMike BrodowskiBelum ada peringkat
- Music and IQDokumen10 halamanMusic and IQh.kaviani88Belum ada peringkat
- An Instrument To Measure Engagement in MusicDokumen19 halamanAn Instrument To Measure Engagement in MusicIrina CusnirBelum ada peringkat
- An Empirical Study On Teaching Urban Young ChildreDokumen13 halamanAn Empirical Study On Teaching Urban Young ChildreJaba PriyaBelum ada peringkat
- The Effects of Listening To Music On The Academic Performance of The Selected Senior High School Students of Saint Bernadette College of AlabangDokumen19 halamanThe Effects of Listening To Music On The Academic Performance of The Selected Senior High School Students of Saint Bernadette College of AlabangMa Doreen GuiwanonBelum ada peringkat
- Resume - Alexis Johnson FinalDokumen3 halamanResume - Alexis Johnson Finalapi-300786566Belum ada peringkat
- Cover LetterDokumen1 halamanCover Letterapi-300786566Belum ada peringkat
- Student Background BDokumen2 halamanStudent Background Bapi-300786566Belum ada peringkat
- 6th Grade Saxophone 2Dokumen2 halaman6th Grade Saxophone 2api-300786566Belum ada peringkat
- Student Impact ProjectDokumen8 halamanStudent Impact Projectapi-300786566Belum ada peringkat
- Unit ProjectDokumen9 halamanUnit Projectapi-300786566Belum ada peringkat
- Technology ProjectDokumen2 halamanTechnology Projectapi-300786566Belum ada peringkat
- Video Feedback 2Dokumen2 halamanVideo Feedback 2api-300786566Belum ada peringkat
- Symphonic Band 4Dokumen1 halamanSymphonic Band 4api-300786566Belum ada peringkat
- Video Reflection OneDokumen2 halamanVideo Reflection Oneapi-300786566Belum ada peringkat
- Symphonic Band 4Dokumen1 halamanSymphonic Band 4api-300786566Belum ada peringkat
- Student Background ADokumen2 halamanStudent Background Aapi-300786566Belum ada peringkat
- 380 Research PaperDokumen10 halaman380 Research Paperapi-300786566Belum ada peringkat
- 5th Grade Clarinet Lesson 2Dokumen3 halaman5th Grade Clarinet Lesson 2api-300786566Belum ada peringkat
- Mued 231 Ukulele Curriculum 2017Dokumen54 halamanMued 231 Ukulele Curriculum 2017api-300790514Belum ada peringkat
- Elementary Lesson PlanDokumen1 halamanElementary Lesson Planapi-300786566Belum ada peringkat
- Real Repertoire ListDokumen2 halamanReal Repertoire Listapi-300786566Belum ada peringkat
- Stone Spring Music Night Lexi and ErinDokumen3 halamanStone Spring Music Night Lexi and Erinapi-300786566Belum ada peringkat
- Real Performance ListDokumen1 halamanReal Performance Listapi-300786566Belum ada peringkat
- Star Wars TeachingDokumen3 halamanStar Wars Teachingapi-300786566Belum ada peringkat
- Research PaperDokumen9 halamanResearch Paperapi-300786566Belum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan ProjectDokumen2 halamanLesson Plan Projectapi-300786566Belum ada peringkat
- Experience Design 1Dokumen3 halamanExperience Design 1api-300786566Belum ada peringkat
- Philosophy of Education PaperDokumen6 halamanPhilosophy of Education Paperapi-300786566Belum ada peringkat
- Semester ReflectionDokumen3 halamanSemester Reflectionapi-300786566Belum ada peringkat
- Experimental Design 380Dokumen3 halamanExperimental Design 380api-300786566Belum ada peringkat
- Brass Tech Lesson OnDokumen3 halamanBrass Tech Lesson Onapi-300786566Belum ada peringkat
- Research ProposalDokumen1 halamanResearch Proposalapi-300786566Belum ada peringkat
- Pattern Movement Chart TemplateDokumen2 halamanPattern Movement Chart Templateapi-300786566Belum ada peringkat
- REFERENCESDokumen33 halamanREFERENCESJovilyn DuranBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of AnxietyDokumen3 halamanAnatomy of AnxietykhnumdumandfullofcumBelum ada peringkat
- Autism Adolescents FrenchDokumen6 halamanAutism Adolescents FrenchEla AndreicaBelum ada peringkat
- 15-Minute Psychiatric Screening AssessmentDokumen65 halaman15-Minute Psychiatric Screening AssessmentUnedited revealations100% (1)
- Group PsychotherapyDokumen22 halamanGroup PsychotherapyRENJULAL100% (5)
- The Risk Need Responsivity RNR Model Does Adding The Good Lives Model Contribute To Effective Crime PreventionDokumen22 halamanThe Risk Need Responsivity RNR Model Does Adding The Good Lives Model Contribute To Effective Crime PreventionJennifer Latapiá0% (1)
- Broken Family and How Does It Affects Student's Academic PerformanceDokumen1 halamanBroken Family and How Does It Affects Student's Academic Performancesei gosaBelum ada peringkat
- Is It Executive Function Disorder PDFDokumen13 halamanIs It Executive Function Disorder PDFRza_Sharp100% (3)
- The Three Ego StatesDokumen9 halamanThe Three Ego StatesAnkur PrabhakarBelum ada peringkat
- Review Article-Psychiatric Epidemiology PDFDokumen10 halamanReview Article-Psychiatric Epidemiology PDFM I Singh SethiBelum ada peringkat
- Daily Lesson Log APPLIED SUBJECT - GAS - Discipline and Ideas in The Social ScienceDokumen4 halamanDaily Lesson Log APPLIED SUBJECT - GAS - Discipline and Ideas in The Social ScienceHannae pascua100% (1)
- Children With Learning Difficulties and Conditions of School Inclusion - A Brief Report and A Constant Challenge of Inclusive EducationDokumen7 halamanChildren With Learning Difficulties and Conditions of School Inclusion - A Brief Report and A Constant Challenge of Inclusive EducationYo MonterrosasBelum ada peringkat
- Levenson's LOCDokumen2 halamanLevenson's LOCnesumaBelum ada peringkat
- Aaron Beck's CBT & NATsDokumen4 halamanAaron Beck's CBT & NATsAj AquinoBelum ada peringkat
- Client A Psychological ReportDokumen5 halamanClient A Psychological ReportNica MangampatBelum ada peringkat
- Social Support and Burnout: A Meta-Analysis of Correlation CoefficientsDokumen16 halamanSocial Support and Burnout: A Meta-Analysis of Correlation CoefficientsAprilia SeasariBelum ada peringkat
- The Discipline of Counseling ExplainedDokumen43 halamanThe Discipline of Counseling ExplainedErnie Ronel Tirol MabahagueBelum ada peringkat
- Mood Disorders: A Closer Look at Psychological DisordersDokumen25 halamanMood Disorders: A Closer Look at Psychological DisordersManoj Bala100% (1)
- ADHD (Oxford American Psychiatry Library) 2014Dokumen146 halamanADHD (Oxford American Psychiatry Library) 2014Antonio DoniniBelum ada peringkat
- Psychopathology Paranoid SchizophreniaDokumen2 halamanPsychopathology Paranoid SchizophreniaPrincess Joy T. Catral57% (7)
- PDDDokumen113 halamanPDDJacqueline AgustinBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical and Social Factors Associated With Violent Behavior in Persons With Schizophrenia Spectrum DisordersDokumen6 halamanClinical and Social Factors Associated With Violent Behavior in Persons With Schizophrenia Spectrum DisordersIJAR JOURNALBelum ada peringkat
- Anorexia Nervosa: Understanding the Mental Health ConditionDokumen11 halamanAnorexia Nervosa: Understanding the Mental Health Conditionsahraahmedali100% (1)
- No Suicide ContractsDokumen9 halamanNo Suicide Contractsprfsc13Belum ada peringkat
- Adolescent HealthDokumen19 halamanAdolescent Healthhou1212!67% (3)
- Mental Health Concepts, Therapies, Studies, and PoliciesDokumen1 halamanMental Health Concepts, Therapies, Studies, and PoliciesNikki MacarayoBelum ada peringkat
- Developmental DelayDokumen15 halamanDevelopmental DelayYian FaustoBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 14Dokumen26 halamanChapter 14slg233Belum ada peringkat
- Legalized MarijuanaDokumen4 halamanLegalized Marijuanaapi-372183039Belum ada peringkat
- How parents' language impacts childrenDokumen4 halamanHow parents' language impacts childrenChandra Kant100% (2)