Material Science Exam
Diunggah oleh
Raymond Yabut100%(1)100% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (1 suara)
99 tayangan1 halamanMATERIAL SCIENCE COMPETENCY
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniMATERIAL SCIENCE COMPETENCY
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
100%(1)100% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (1 suara)
99 tayangan1 halamanMaterial Science Exam
Diunggah oleh
Raymond YabutMATERIAL SCIENCE COMPETENCY
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 1
TECHNOLOGICAL INSTITUTE OF THE PHILIPPINES - c.
increased strength and ductility
MANILA d. increased strength, decreased ductility
DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS COMPETENCY EXAM 10. LDPE undergoes extensive (0ver 100%) elongation prior to
NAME. _____________________Date: MARCH 5, 2018 rupture, while polystyrene undergoes only 1 – 2 % elongation.
Instructor: ENGR. L.A. CARRILLO What is the main reason for the difference?
ANSWER IN CHRONOLOGICAL ORDER. NO LOOSE a. The polyethyle is less dense.
SHEETS. DETAILED SOLUTIONS AND BOX YOUR b. More cross-linking occurs in the polystyrene.
ANSWERS. c. The large styrene groups in the polystyrene prvent slippage.
1. Which of the following statements regarding diffusion in a d. LDPE is less crystalline.
crystal structure is true? 11. Which best describe the glass transition temperature?
a. Solid interstitial atoms cannot diffuse through crystal structures I. It is the temperature at which the rate of volume contract
that lack vacancies. II. It is the temperature at which residual stresses in the glass can
b. It occurs only in alloys , never in pure crystals. be relieved.
c. It often uses an exchange or vacancy mechanism. III. It is the point where the material behaves more like a solid
d. It occurs primarily as a result of mechanical work. than a viscous liquid.
2. Which of the following are true about Fick’s Law of Diffusion? a. I only b. I and II only
I. The law states that the flux moves from high to low c. I and III only d. II and III only
concentration. 12. Given the following phase diagram, determine the % of liquid
II. It is only applicable to gases and liquids, not solids. remaining at 600°C that results from the equilibrium cooling of an
III. J, the flux, may be in units of cm3/ cm2-s. alloy containing 5% silicon and 95% aluminum.
A. I onlyB. II only 47%
C. I and III D. II and III only
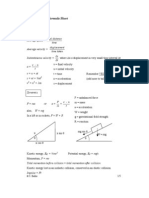
3 – 5. Given a stress –strain diagram for a material is shown.
3. B is identified as
a. lower yield point b. plastic deformation
c. elastic deformation d. elongation at fracture
4. A is defined as
a. lower yield point b. upper yield point
c. proportional limit d. fracture point
5. C is defined as
a. fracture point b. elastic limit
c. plastic limit d. proportional limit Figure 12 Figure 13
13. Using the given phase diagram, what are the relative weights
of phases α1 and α2 for an alloy of 70% B at temperature T1.
10%α1, 90% α2
14. For a completely corrosion-resistant stainless steel, what
minimum percentage of chromium in the alloy is required?
a. 1.2% b. 3.2% c. 11% d. 13%
15. Which of the following would most likely require a steel
containing 0.6% carbon that has been spheroidized, cold-drawn,
and slightly tempered?
a. a bridge beam b. a water pipe
Figure 3 c. a cutting tool d. a ball bearing
Figure 19 16. Which of the following statements is false?
6. Which of the following best describes the 0.2 % offset yield a. Stainless steels contain large amounts of chromium.
stress? b. There are three basic types of stainless steels: martensitic,
a. It is the elastic limit after which a measurable plastic strain has ferritic and austenitic.
occurred. c. The non-magnetic steels contain large amounts of nickel.
b. It is the stress at which the material plastically strains 0.2% d. Stabilization of the face-centered cubic crystal structure of
c. It is the stress at which the material elastically strains 0.2% stainless steels imparts a non-magnetic characteristic to the alloy.
d. It is 0.2% below the fracture point of the material. 17. Which of the following is not a structural class of steels.
7. It is possible to have plastic flow in a crystal at shear stress a. carbon b. high strength, low alloy
lower than the critical shear stress under conditions of very slow c. low alloy d. tool and die
deformation and high temperature. This phenomenon is called. 18. Which of the following phases of steel has a face-centered
a. slip b. twinning c. creep d. bending cubic structure?
8. Pick the proper relationship between the modulus of elasticity, a. ferrite b. cementite c. pearlite d. austenite
E, the Poisson ratio, v, and the bulk modulus of elasticity, K? 19. For 50%at 1275°C as shown, what is the relative amount of
a. E = K (1-2v) b. E = K (1-v) c. E = 3K/ (1-2v) each phase present? 60% Liquid and 40% solid
d. E = 3K ( 1- 2v) 20. Which of the following is a line defect in a lattice crystal
9. What are the effects of cold working a metal? structure?
a. decreased strength and ductility a. tilt boundary b. screw dislocation
b. decreased strength, increased ductility c. vacancy d. Schottky Imperfection
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Physics Exam Questions2Dokumen2 halamanPhysics Exam Questions2Amrita100% (1)
- FP Assignment 2Dokumen1 halamanFP Assignment 2Austin Phua Yun HockBelum ada peringkat
- Inorganic Chemistry Exam 20110505Dokumen3 halamanInorganic Chemistry Exam 20110505曾鈞浩Belum ada peringkat
- God'S Care International Academy: 24, Okota Road, Gideon Bus Stop, IsoloDokumen2 halamanGod'S Care International Academy: 24, Okota Road, Gideon Bus Stop, IsolosunliasBelum ada peringkat
- 238-Fall 2010Dokumen9 halaman238-Fall 2010DeepakBelum ada peringkat
- A .Grammar Choose The Correct Answer !: English QuizDokumen3 halamanA .Grammar Choose The Correct Answer !: English QuiznaylahusainBelum ada peringkat
- Basic PhysicsDokumen4 halamanBasic PhysicsDiane Marr Nicolas Dencio100% (1)
- Summmative Test: Description Ordinary Number Standard FormDokumen2 halamanSummmative Test: Description Ordinary Number Standard Formfadilah nurBelum ada peringkat
- HSEB Question Collection Series - Physics, New Course 2069 XI - HSEB NOTESDokumen1 halamanHSEB Question Collection Series - Physics, New Course 2069 XI - HSEB NOTESHSEB Notes100% (10)
- 2012 Vcaa Physics Exam 2 SolutionsDokumen2 halaman2012 Vcaa Physics Exam 2 SolutionspappadutBelum ada peringkat
- Material Science Question BankDokumen3 halamanMaterial Science Question BankSirish Chand PutlaBelum ada peringkat
- Question On Chemical Kinetics-MA 2022Dokumen12 halamanQuestion On Chemical Kinetics-MA 2022Sangay ChodenBelum ada peringkat
- Geometric FormulasDokumen7 halamanGeometric Formulasprince168Belum ada peringkat
- ALT Quiz in English 8Dokumen1 halamanALT Quiz in English 8Cath Casaway100% (1)
- Quiz #2 For IB1 Math StudiesDokumen2 halamanQuiz #2 For IB1 Math Studieshadukenryu9761Belum ada peringkat
- GCSE Bonding QuizDokumen1 halamanGCSE Bonding Quizs17m0582Belum ada peringkat
- Exam Strategy PhysicsDokumen1 halamanExam Strategy PhysicsAniket KhanBelum ada peringkat
- CP Physics Final Exam Review 2Dokumen25 halamanCP Physics Final Exam Review 2eltytanBelum ada peringkat
- Spectroscopy WorksheetDokumen24 halamanSpectroscopy Worksheetpokemon goBelum ada peringkat
- Multiple Question CHM 101Dokumen26 halamanMultiple Question CHM 101Emmanuella OffiongBelum ada peringkat
- CARAMAT Environmental Impact Assessment ExamDokumen2 halamanCARAMAT Environmental Impact Assessment ExamPopoyBelum ada peringkat
- Thermodynamics WorksheetDokumen13 halamanThermodynamics WorksheetHudsun HornetBelum ada peringkat
- Grad 5 Math QuizDokumen3 halamanGrad 5 Math QuizEkaSeptiyaniBelum ada peringkat
- Acid Base - Q - MSDokumen41 halamanAcid Base - Q - MSAnonymous ABelum ada peringkat
- PhysicsDokumen24 halamanPhysicsMayra FlorBelum ada peringkat
- Geometry Revision NotesDokumen2 halamanGeometry Revision NotesMr_limBelum ada peringkat
- Ce6306 Som PDFDokumen55 halamanCe6306 Som PDFHemakumar ManoharanBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 5 Review-PolynomialsDokumen9 halamanUnit 5 Review-Polynomialsapi-237494396Belum ada peringkat
- Geometry Revision NotesDokumen2 halamanGeometry Revision NotesMr_limBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5Dokumen8 halamanChapter 5api-201479236Belum ada peringkat
- CONS Orgchem WorksheetsDokumen18 halamanCONS Orgchem Worksheetssan_cdkeyBelum ada peringkat
- T.Y.B.Sc .-V Analytical-ChemistryDokumen9 halamanT.Y.B.Sc .-V Analytical-ChemistryVaibhav GadeBelum ada peringkat
- Gouy BalanceDokumen2 halamanGouy BalanceOvidiu Rotariu100% (1)
- Chemical Bond ObjbDokumen9 halamanChemical Bond Objbalvin2282Belum ada peringkat
- Physics Lab Practical Exam - 2018Dokumen1 halamanPhysics Lab Practical Exam - 2018IrfanBelum ada peringkat
- FinalExam B AnsKeyDokumen12 halamanFinalExam B AnsKeyDVRaoBelum ada peringkat
- Electrochemistry QuestionsDokumen2 halamanElectrochemistry Questionsshrutik7Belum ada peringkat
- 02 Linear FunctionDokumen11 halaman02 Linear FunctionLola CarolinaBelum ada peringkat
- (Reviewer) 1st Le Chem 16Dokumen3 halaman(Reviewer) 1st Le Chem 16Jay VeeBelum ada peringkat
- Lista de Exercícios 0 - Conceitos BásicosDokumen24 halamanLista de Exercícios 0 - Conceitos BásicosJoýce SilveiraBelum ada peringkat
- Student Profile WorksheetDokumen10 halamanStudent Profile WorksheetShaliniJainBelum ada peringkat
- Test Bank Chapter 3Dokumen10 halamanTest Bank Chapter 3mrbookoBelum ada peringkat
- Test BanksDokumen21 halamanTest Banksalex_flutistBelum ada peringkat
- Hydrogen NMR (Multiple Choice) QPDokumen4 halamanHydrogen NMR (Multiple Choice) QPheyitsmemuahBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 04tifDokumen45 halamanChapter 04tifNiyanthesh ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Notes 11Dokumen3 halamanPhysics Notes 11dkshepneaBelum ada peringkat
- 2013 As Chemistry Chapter 11 Review - GASESDokumen11 halaman2013 As Chemistry Chapter 11 Review - GASESbiancae697Belum ada peringkat
- Mcqs of Inorganic and Physical Chemistry by Malik XufyanDokumen29 halamanMcqs of Inorganic and Physical Chemistry by Malik XufyanMalikXufyanBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Nanoscience and Nanotechnology: A Workbook: M. Kuno August 22, 2005Dokumen370 halamanIntroduction To Nanoscience and Nanotechnology: A Workbook: M. Kuno August 22, 2005Saravanakumar RajagopalBelum ada peringkat
- Physics QuizDokumen2 halamanPhysics QuizVboy8Belum ada peringkat
- Molar Volume WsDokumen1 halamanMolar Volume WsAnnaReyes100% (1)
- Class Copy: Geometry Algebraic Proofs Foldable InstructionsDokumen1 halamanClass Copy: Geometry Algebraic Proofs Foldable InstructionsRobin A WilsonBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Accel Syllabus 2011-2012Dokumen3 halamanBiology Accel Syllabus 2011-2012Mike DeleonBelum ada peringkat
- Moving Charges FinalDokumen41 halamanMoving Charges FinalVinothBelum ada peringkat
- Che 323 Problem Set 6: Electrochemistry March 12, 2014 Engr. May V. Tampus ConceptsDokumen1 halamanChe 323 Problem Set 6: Electrochemistry March 12, 2014 Engr. May V. Tampus ConceptsLouie G NavaltaBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Semester 1 ExamDokumen2 halamanPhysics Semester 1 Examjnewman85Belum ada peringkat
- Oml 751-Tom MCQDokumen21 halamanOml 751-Tom MCQVijay KanthBelum ada peringkat
- ME 461 FirstExam-Fall 2015Dokumen7 halamanME 461 FirstExam-Fall 2015JaneBelum ada peringkat
- PTHT End SemDokumen11 halamanPTHT End SemCh PrasadBelum ada peringkat
- Elems 19Dokumen100 halamanElems 19Reynald de VeraBelum ada peringkat
- Size Reduction PartechDokumen33 halamanSize Reduction PartechRaymond YabutBelum ada peringkat
- Problem Set MidtermDokumen34 halamanProblem Set MidtermRaymond YabutBelum ada peringkat
- Ecological Solid Waste Management Act of 2000Dokumen3 halamanEcological Solid Waste Management Act of 2000Pablo VictoriaBelum ada peringkat
- "Chemical Engineering Design: What If? Analyzing The Uncertainty" JANUARY 8, 2019 ROOM C-106Dokumen1 halaman"Chemical Engineering Design: What If? Analyzing The Uncertainty" JANUARY 8, 2019 ROOM C-106Raymond YabutBelum ada peringkat
- Physical Chemistry ExamDokumen1 halamanPhysical Chemistry ExamRaymond Yabut100% (1)
- Chem QueastionsDokumen137 halamanChem QueastionsdjftBelum ada peringkat
- PhysChem ProblemsolvingDokumen10 halamanPhysChem ProblemsolvingTom WoolfordBelum ada peringkat
- Biotech Multiple Choice QuestionsDokumen33 halamanBiotech Multiple Choice QuestionsRaymond YabutBelum ada peringkat
- Methanol-Water Equilibrium Curve FINAL PDFDokumen1 halamanMethanol-Water Equilibrium Curve FINAL PDFRaymond YabutBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis of CSTRDokumen11 halamanAnalysis of CSTRRaymond YabutBelum ada peringkat
- Physical Chemistry Competency ExamDokumen2 halamanPhysical Chemistry Competency ExamRaymond YabutBelum ada peringkat
- Kinetics Prelim Take Home Exam December 25 2017Dokumen2 halamanKinetics Prelim Take Home Exam December 25 2017Michelle Mendoza100% (1)
- Anachem 2017-2018Dokumen1 halamanAnachem 2017-2018Raymond YabutBelum ada peringkat
- Urea ModelingDokumen20 halamanUrea ModelingekmagisBelum ada peringkat
- Competency Exam in Organic ChemistryDokumen4 halamanCompetency Exam in Organic ChemistryRaymond Yabut100% (1)
- Algebra 77 Problems PDFDokumen21 halamanAlgebra 77 Problems PDFRaymond YabutBelum ada peringkat
- Physical 11Dokumen2 halamanPhysical 11Rodriguez RommelBelum ada peringkat
- General-Chemistry Calculations January 2018Dokumen2 halamanGeneral-Chemistry Calculations January 2018Raymond Yabut100% (2)
- ChE ThermodynamicsDokumen10 halamanChE ThermodynamicsRaymond YabutBelum ada peringkat
- PS7 SolutionsDokumen5 halamanPS7 SolutionsYenhao Philip ChenBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 4b - Slender Columns: RJ AquinoDokumen35 halamanLecture 4b - Slender Columns: RJ AquinoEmanoAceBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture06 FEG Basics & Heat Capacity1Dokumen51 halamanLecture06 FEG Basics & Heat Capacity1lalitbickBelum ada peringkat
- 264 1118 Peerless 830669 SpecificationsDokumen1 halaman264 1118 Peerless 830669 Specificationsbk1313Belum ada peringkat
- Nav Gyro Error by Celestial 1Dokumen13 halamanNav Gyro Error by Celestial 1dpc876Belum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Fluid MechanicsDokumen77 halamanFundamentals of Fluid MechanicsvijaynieBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 4Dokumen76 halamanUnit 4Hemant TulsaniBelum ada peringkat
- MonorailDokumen13 halamanMonorailleodegarioporralBelum ada peringkat
- Higher Physics Formula Sheet: S. BakkeDokumen5 halamanHigher Physics Formula Sheet: S. BakkeAbid RedwanBelum ada peringkat
- Newtons Laws Discovery Stations 2018Dokumen7 halamanNewtons Laws Discovery Stations 2018api-314701419Belum ada peringkat
- Basic Laplace Fourier TransformsDokumen3 halamanBasic Laplace Fourier TransformsWayne LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Kisi AzizDokumen17 halamanKisi AzizRahmat WidodoBelum ada peringkat
- Position Measurement On Machine ToolsDokumen13 halamanPosition Measurement On Machine ToolsAriel GermainBelum ada peringkat
- PR-lecture 6-7Dokumen58 halamanPR-lecture 6-7المهندس عبدالرحمن السلويBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals Selection Installation and Maintenance of Gearboxes Gear Drives Part 1Dokumen61 halamanFundamentals Selection Installation and Maintenance of Gearboxes Gear Drives Part 1BorisBelum ada peringkat
- Optional Area Examination Analytical ChemistryDokumen4 halamanOptional Area Examination Analytical ChemistryMohamed DahmaneBelum ada peringkat
- Piglet ManualDokumen50 halamanPiglet ManualJonathan Wardrop100% (1)
- Final Report EditedDokumen17 halamanFinal Report Editedapi-309687389Belum ada peringkat
- PHGN100 EquationSheetDokumen1 halamanPHGN100 EquationSheetSamuel BangapadangBelum ada peringkat
- Gravitation and Central ForcesDokumen27 halamanGravitation and Central ForcesFaiza Nur LailaBelum ada peringkat
- The Bloch EquationsDokumen11 halamanThe Bloch EquationsShivam PhogatBelum ada peringkat
- Lect-IV Vector SpaceDokumen10 halamanLect-IV Vector SpaceAbhijit Kar GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis of Structural Member SystemsDokumen620 halamanAnalysis of Structural Member Systemskhiettrth100% (2)
- A Compendium of Spherical Astronomy, NewcombDokumen470 halamanA Compendium of Spherical Astronomy, Newcombandresmejia68100% (1)
- LQR For Rotating Inverted PendulumDokumen14 halamanLQR For Rotating Inverted PendulumValery GaulinBelum ada peringkat
- Gate Chemical 2008Dokumen12 halamanGate Chemical 2008Adil RiazBelum ada peringkat
- Ch-2 Forces On and in The BodyDokumen25 halamanCh-2 Forces On and in The BodyLindsey AdalsonBelum ada peringkat
- The Dual Nature of LightDokumen12 halamanThe Dual Nature of LightrkukgBelum ada peringkat
- L427-06i Pigment SuspensionDokumen3 halamanL427-06i Pigment SuspensionhugogaunaBelum ada peringkat