Skin Morphology 1/16
Diunggah oleh
Indiana USMJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Skin Morphology 1/16
Diunggah oleh
Indiana USMHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Class Notes
Skin Morphology 1/16
A. Key Terms
a. Erosion – Focal loss of epidermis, does not penetrate below DEJ (NO SCAR)
b. Ulcer – focal loss of epidermis and dermis
c. Excoriation – erosion caused by scratching
d. Fissure- linear loss of epidermis and dermis (sharp) defined
e. Atrophy – depression in skin due to loss of epidermis & dermis
f. Comedone – plug of sebaceous and keratinaceous debris
g. Lithification- thickened epidermis induced by scratching (surfers)
h. Burrow – narrow elevated channels in skin (Parasite)
i. Milia – small cysts with walls containing epidermis
j. Petechiae & Purpura – bloss <0.5 or > 0.5
1/16 Scaling Dermatology
A) Psoriasis
a. Inflammatory eruption with increased epidermal proliferation (increased turnover)
b. Silvery Scale + Nail pitting (Onychosis – nail separation)
c. Koebner Phenomena – lesions at site of trauma
d. Parakeratosis & Acanthocytosis
B) Pityriasis Rosea
a. Herald Patch – Christmas Tree –
b. Common among young people
i. Spares face and palms
c. Red – yellow thin plaques
d. Self Limiting – Leads to melanin scaring in blacks
C) Secondary Syphilis
a. Contagious – Spirochetes
b. VLDR test
c. Copper coin on palm and soles
D) Lichen Planus
a. 6 P’s Plague and papules and Pruritic (mad itching)
b. Wishcow Striate
c. Horrible Itching
d. Koebner Phenomenon
E) Atopic Dermatitis
a. IGE asthma – allergy
b. Lichenification – thickening (due to repeated trauma)
F) Chronic Dermatitis (Atopic + Seborrheic)
a. Seborrheic – Pitrosporum – AIDS
G) Statis Dermatitis
a. No blood flow – leads to ulceration abd edena
H) Ichtyosis
a. Fish skin – white/brown
b. No itching
c. Genetic with lack of inflammation
d. Sudden onset – Red flag for leukemia/lymphoma
I) Tinea Capitis and Tinea Corporisis
a. Very itchy due to fungi
Calclum and Phosphate Chemical
A) Calcium
a. Lab
i. Albumin binds to CA
ii. Acidosis increased Calcium
b. Hormones
i. PTH & 1,252 Vit D
ii. Influence – Diet, bone, renal
iii. PTH
1. Fall in Ca (Calcium sensing receptor) Increase PTH
2. PTH will increase CA reabsorption
3. Increase active 1-25 OH D (Active) = increase interstitial calcium
a. 1-25Oh D will inhibit PTH
4. PTH activates osteoclast increase CA
iv. Calcitonin
1. Hormone made at thyroid gland
2. Opposite of Parathyroid in everywhere
B) Hypercalcemia
a. PTH-RP
i. Tumor secretion of PTH like hormone
b. Hypercalcemia
i. High PTH
ii. Primary hyperparathryoidtis
iii. Lithium
c. Familial Hypocalciruic Hypercalcemia
i. CaSR less sensitive to calcium
d. Hyperparathyroidism
C) Hypocalcemia
a. Pseudohypoparathyroidism
i. GNAS gene mutation
ii. Albright Hereditary Osteodystrophy phenotype
D) Vitamin D
a. Rickets/Hypermalacia
b. Barriers to Vitamind D – Sunscreen/aging/season/clothes
E) Phosphate
a. Ubiqutious in western diet
b.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Navle Master ListDokumen60 halamanNavle Master Listhari krishnaa athotaBelum ada peringkat
- Dental MCQDokumen22 halamanDental MCQPinpointq0% (1)
- Clinical Medicine and SurgeryDokumen134 halamanClinical Medicine and SurgeryEthar MahmoodBelum ada peringkat
- 8 Integumentary System (FINAL)Dokumen11 halaman8 Integumentary System (FINAL)kath-kathBelum ada peringkat
- DermDokumen10 halamanDermyassrmarwaBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiology PDFDokumen27 halamanCardiology PDFNada AKBelum ada peringkat
- Dermatology LE1 PDFDokumen17 halamanDermatology LE1 PDFCearlene GalleonBelum ada peringkat
- Krok Made SimpleDokumen16 halamanKrok Made SimplePrashant Singh100% (1)
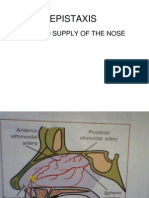
- EPISTAXISDokumen24 halamanEPISTAXISKelechi OtamiriBelum ada peringkat
- E. A. D. A.: Gastrointestinal SystemDokumen9 halamanE. A. D. A.: Gastrointestinal SystemDominic ReambonanzaBelum ada peringkat
- Nosocomial FungiDokumen8 halamanNosocomial Fungiapi-3712326Belum ada peringkat
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDokumen8 halamanChronic Kidney Diseaseampogison08Belum ada peringkat
- Parasitic - Toxic SummaryDokumen9 halamanParasitic - Toxic Summaryakilesh hardowarBelum ada peringkat
- Hema, Onco, Cardiology Review NotesDokumen9 halamanHema, Onco, Cardiology Review Notesjeshema100% (1)
- Test - 4 MCQsDokumen3 halamanTest - 4 MCQsعايشاة زارينBelum ada peringkat
- A Burdizzo Is Used For: A. Branding B. Dehorning C. Castration D. All of The AboveDokumen54 halamanA Burdizzo Is Used For: A. Branding B. Dehorning C. Castration D. All of The AboveMac Dwayne CarpesoBelum ada peringkat
- Medsurg ElearningDokumen46 halamanMedsurg ElearningNathaniel PulidoBelum ada peringkat
- Krok Hacks 1: 1.) HelminthsDokumen8 halamanKrok Hacks 1: 1.) HelminthsMoatasem AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Grand Test May 6 Question PaperDokumen48 halamanGrand Test May 6 Question PaperSonalBelum ada peringkat
- IOM PG 2014 EntranceDokumen18 halamanIOM PG 2014 EntrancePrashant BasukalaBelum ada peringkat
- T & D - DERMATOLOGY - 2022 - QuestionDokumen6 halamanT & D - DERMATOLOGY - 2022 - QuestionVyserionBelum ada peringkat
- Tests Dermatology 1Dokumen23 halamanTests Dermatology 1Donya GholamiBelum ada peringkat
- 3y1s Surgpath Lec 8. Liver&gb (Agb) SamplexDokumen1 halaman3y1s Surgpath Lec 8. Liver&gb (Agb) SamplexCRUZ Jill EraBelum ada peringkat
- Gastrointestinal SystemDokumen8 halamanGastrointestinal Systemtheglobalnursing100% (1)
- Shigella and CholeraDokumen1 halamanShigella and Choleramohamed mowafeyBelum ada peringkat
- Biochem 2Dokumen7 halamanBiochem 2Aleena KarimBelum ada peringkat
- Information 1Dokumen2 halamanInformation 1Nazish RafiqueBelum ada peringkat
- JC DermaDokumen32 halamanJC DermashreemathyBelum ada peringkat
- DermaDokumen20 halamanDermaALSA MAHEK0% (1)
- Iron Deficiency AnemiaDokumen4 halamanIron Deficiency AnemiaWiljohn de la CruzBelum ada peringkat
- 12.5 PTH DNDokumen11 halaman12.5 PTH DNDanny NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- Omsb Part I - 2010Dokumen10 halamanOmsb Part I - 2010Firyal Balushi100% (1)
- Bovine Board ReviewDokumen30 halamanBovine Board ReviewNayara PataroBelum ada peringkat
- Iii RD Professional - Part - Ii Syllabus: Theory PracticalDokumen5 halamanIii RD Professional - Part - Ii Syllabus: Theory Practicalsravanidasari1707Belum ada peringkat
- AVNecz 2024Dokumen19 halamanAVNecz 2024aheraaaheraBelum ada peringkat
- Veterinary PathologyDokumen48 halamanVeterinary PathologyNitin Kale100% (1)
- STOMADokumen3 halamanSTOMAShafiq ZahariBelum ada peringkat
- MCQ Dermatology (Dr. Asaf K.)Dokumen31 halamanMCQ Dermatology (Dr. Asaf K.)Dinesh JadhavBelum ada peringkat
- Strepto ClassDokumen34 halamanStrepto ClassAbcdefg HijklBelum ada peringkat
- Vibrio VulnificusDokumen2 halamanVibrio VulnificusDerek Miguel SmithBelum ada peringkat
- Dr. Talwar - MCQ - 11.08.2015Dokumen10 halamanDr. Talwar - MCQ - 11.08.2015Adab NadafBelum ada peringkat
- Derma FinalDokumen5 halamanDerma FinalMr.FantasthiccBelum ada peringkat
- NCM 112 Lesson2Dokumen5 halamanNCM 112 Lesson2Trisha LopezBelum ada peringkat
- Dermat Questions 252Dokumen72 halamanDermat Questions 252Srirupa BiswasBelum ada peringkat
- Git SystemDokumen16 halamanGit SystemedithlucnasBelum ada peringkat
- Quiz Questions On AnemiaDokumen2 halamanQuiz Questions On AnemiaSlooma100% (1)
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDokumen60 halamanFluid and ElectrolytesAlgene AnnBelum ada peringkat
- 1) Commonest Type of Stone in UTI IsDokumen3 halaman1) Commonest Type of Stone in UTI IsRatan YadavBelum ada peringkat
- 6TH Grade Science QuestionnaireDokumen4 halaman6TH Grade Science QuestionnaireSantiago VegaBelum ada peringkat
- MCQ IN PAEDO by @ubanidrDokumen70 halamanMCQ IN PAEDO by @ubanidrUbani Prince CBelum ada peringkat
- Ashiq - S Rock The KrokDokumen31 halamanAshiq - S Rock The KrokJack frimpongBelum ada peringkat
- Hematology I Final Study GuideDokumen28 halamanHematology I Final Study GuideLauren Napoli100% (1)
- UWorld Peds Study GuideDokumen20 halamanUWorld Peds Study GuideAriana SheridanBelum ada peringkat
- Acid-Base Balance and Oxygenation: Blood GasesDokumen5 halamanAcid-Base Balance and Oxygenation: Blood GasesMarcus, RN100% (6)
- INICET JULY 2021 Solved Paper PDF PathologyDokumen36 halamanINICET JULY 2021 Solved Paper PDF Pathologysusan291Belum ada peringkat
- Тесты По Предмету Патофизиология, Клиническая Патофизиология Для Студентов, Обучающихся На Английском ЯзыкеDokumen41 halamanТесты По Предмету Патофизиология, Клиническая Патофизиология Для Студентов, Обучающихся На Английском ЯзыкеTerry LXRDBelum ada peringkat
- FGHFGJHTFH: Taenia MulticepsDokumen4 halamanFGHFGJHTFH: Taenia MulticepssnehalBelum ada peringkat
- ACVPM Toxicology ReviewDokumen21 halamanACVPM Toxicology ReviewShamely CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Parasitic Protozoa: Toxoplasma, Cryptosporidia, Pneumocystis, And MicrosporidiaDari EverandParasitic Protozoa: Toxoplasma, Cryptosporidia, Pneumocystis, And MicrosporidiaBelum ada peringkat
- Micro AlbDokumen2 halamanMicro AlbDinesh SreedharanBelum ada peringkat
- Diagnostic Report: Client Code: Client'S Name and AddressDokumen6 halamanDiagnostic Report: Client Code: Client'S Name and AddressShubhamBelum ada peringkat
- ThyrotoxicosisDokumen42 halamanThyrotoxicosisShaw Khan100% (7)
- The Princeton Club Waiver of Liability Relating To Covid-19Dokumen2 halamanThe Princeton Club Waiver of Liability Relating To Covid-19Tim StackBelum ada peringkat
- Icu Drug StudyDokumen23 halamanIcu Drug StudyApril LebrilloBelum ada peringkat
- Unit Nouns: To PenicillinDokumen5 halamanUnit Nouns: To PenicillinMayra NapaBelum ada peringkat
- Top 10 Papers in Dyslipidemias 2023Dokumen3 halamanTop 10 Papers in Dyslipidemias 2023Bubu ToBelum ada peringkat
- 1 - Kanno - J Oral Rehab - 2006 CópiaDokumen13 halaman1 - Kanno - J Oral Rehab - 2006 CópiaYvelisse LoraBelum ada peringkat
- Financial Times Europe August 222020Dokumen46 halamanFinancial Times Europe August 222020HoangBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Psychology ReportDokumen33 halamanClinical Psychology Reportiqra-j75% (4)
- Asbestos Contamination in Talc-Based Cosmetics: An Invisible Cancer RiskDokumen3 halamanAsbestos Contamination in Talc-Based Cosmetics: An Invisible Cancer RiskAlexia GonzalezBelum ada peringkat
- 4.factors Affecting Growth and Survival of Microorganisms in Foods PDFDokumen17 halaman4.factors Affecting Growth and Survival of Microorganisms in Foods PDFKumkum CrBelum ada peringkat
- Ventricular Tachycardia Bsn3b-Grp1Dokumen35 halamanVentricular Tachycardia Bsn3b-Grp1Jessica RamosBelum ada peringkat
- Anaesthetic EmergenciesDokumen11 halamanAnaesthetic EmergenciesSivasankaryBelum ada peringkat
- Research: Objective Main Outcome MeasuresDokumen11 halamanResearch: Objective Main Outcome Measureslakshminivas PingaliBelum ada peringkat
- Vestibular Neuritis HandoutDokumen3 halamanVestibular Neuritis HandoutPrisilia QurratuAiniBelum ada peringkat
- Holy Infant College Tacloban City NSTP - Cwts Unit First AidDokumen40 halamanHoly Infant College Tacloban City NSTP - Cwts Unit First AidWinsley RazBelum ada peringkat
- Lymphoma Case StudyDokumen16 halamanLymphoma Case Studyapi-622273373Belum ada peringkat
- Impaired Tissue PerfusionDokumen2 halamanImpaired Tissue PerfusionLeo Mar MakilanBelum ada peringkat
- Hrpyc81 Final Assignment 62Dokumen32 halamanHrpyc81 Final Assignment 62Tiffany SmithBelum ada peringkat
- Psych History ScriptDokumen8 halamanPsych History ScriptRyan Loyd MarquezBelum ada peringkat
- Approach To Renal BiopsyDokumen77 halamanApproach To Renal BiopsySandeep Kumar VushikamallaBelum ada peringkat
- MBBS Programme Handbook Revised Sep 2011 Distribution Version PDFDokumen150 halamanMBBS Programme Handbook Revised Sep 2011 Distribution Version PDFlathaBelum ada peringkat
- IVIg Seminar Slide - 高雄榮總Dokumen41 halamanIVIg Seminar Slide - 高雄榮總黃仕儒Belum ada peringkat
- Group 5 Research Paper 22the Causes of The Increasing Anxiety Amongst The Grade 10 Student of Maligaya Highschool22 1Dokumen3 halamanGroup 5 Research Paper 22the Causes of The Increasing Anxiety Amongst The Grade 10 Student of Maligaya Highschool22 1Lean De MesaBelum ada peringkat
- God of Small Things EssayDokumen6 halamanGod of Small Things EssaydunqfacafBelum ada peringkat
- Dental HygieneDokumen3 halamanDental Hygieneapi-507354264Belum ada peringkat
- Health of Newly Arrived Immigrants in Canada and The United StatesDokumen10 halamanHealth of Newly Arrived Immigrants in Canada and The United StatesRafael AlfradiqueBelum ada peringkat
- Care Plan Worksheet Mental Health 2022Dokumen3 halamanCare Plan Worksheet Mental Health 2022tahani.mah147Belum ada peringkat
- Life Fitness 95t Manual Do UtilizadorDokumen22 halamanLife Fitness 95t Manual Do UtilizadorOliver SilvaBelum ada peringkat