Gas Pipe Sizing Guide
Diunggah oleh
Mike AdvinculaDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Gas Pipe Sizing Guide
Diunggah oleh
Mike AdvinculaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
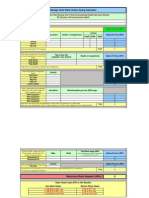
Gas Pipe Line Calculation Sizing
USING CPC PIPE SIZING TABLE (PROPANE)
This handout will guide you thru the basic, most common method for sizing a propane piping system for
residential or commercial application. There are other methods available for sizing these systems by
either a complex formulaic method described in the California Plumbing Code, or the system can be
engineered by a qualified professional.
The information below is paraphrased from the California Plumbing Code and is provided as an aid.
Sizing of Gas Piping Systems.
Gas piping systems shall be of such size and so installed as to provide a supply of gas to meet the
maximum demand and supply gas to each appliance inlet at not less than the minimum supply pressure
required by the appliance.
Required Gas Supply.
Volume. The hourly volume of gas required at each piping outlet shall be taken as not less than the
maximum hourly BTU rating as specified by the manufacturer of the appliance or appliances to be
connected to each such outlet. Where the rating of the gas appliance(s) to be installed in unknown,
Table 1 shall be permitted to be used to estimate the requirements of typical appliances.
Longest Length Method. The size of each section of gas piping shall be determined using the total
length of piping from the meter to the most remote outlet and the load of that section (see calculation
example in “Figure A” use steps 1- 6 below:
Sizing of Piping Sections. To determine the size of each section of pipe in any system using piping
specific table*, and proceed as follows:
(1) Measure the length of the pipe from the gas meter location to the most remote outlet on the
system.
(2) Locate that total length in the left-hand column of sizing table*, or the next longer distance where
the table does not give the exact length.
(3) Starting at the most remote outlet, find in the row just selected the gas demand for the outlet.
Where the exact figure of demand is not shown, choose the next larger figure in the row.
(4) At the top of this column will be found the correct size of pipe.
(5) Using this same row, proceed in a similar manner for each section of pipe serving this outlet. For
each section of pipe, determine the total gas demand supplied by that section.
(6) Size each section of branch piping not previously sized by measuring the distance from the gas
meter location to the most remote outlet in that branch and follow the procedures of steps 2, 3, 4, and
5 above. Size branch piping in the order of their distance from the meter location, beginning with the
most distant outlet not previously sized.
*See Pipe Specific Tables on pages 4, 5, and 6.
TABLE 1
APPROXIMATE GAS INPUT FOR TYPICAL APPLIANCES
APPLIANCE INPUT Btu/h. Cubic Feet of Gas
(Approx.) Per Hour
Space Heating Units
Warm air furnaces:
Single family 100,000 91
Multifamily, per unit 60,000 55
Hydronic boilers:
Single family 100,000 91
Multifamily, per unit 60,000 55
Space and Water-Heating Units
Hydronic boilers:
Single family 120,000 109
Multifamily, per unit 75,000 68
Water-Heating Appliances
Water heater, automatic:
Storage 30 to 40 gal. tank 35,000 32
Water heater, automatic
Storage 50 gal. tank 50,000 45
Water heater, automatic instantaneous:
Capacity at 2 gal./minute 142,800 130
Capacity at 4 gal./minute 285,000 259
Capacity at 6 gal./minute 428,400 389
Water heater, domestic
Circulation or side-arm 35,000 32
Cooking Appliances
Range, freestanding, domestic 65,000 59
Built-in oven/ broiler, domestic 25,000 23
Built-in counter-top range, domestic 40,000 36
Other Appliances
Clothes dryer, domestic 35,000 32
Gas fireplace – direct vent 40,000 36
Gas log unit 80,000 73
Barbecue 40,000 36
Gas Refrigerator 3,000 2
For SI units: 1 Btu per hour = .0293 W
Method for determining correct pipe sizing per 1216.1.1:
(1) Compute BTU demand for all appliances
Maximum gas demand of outlet A:
35,000
Maximum gas demand of outlet B:
3,000
Maximum gas demand of outlet C:
65,000
Maximum gas demand of outlet D:
150,000
Total BTU demand 253,000 BTU (35,000 + 3,000 + 65,000 + 150,000)
(2) Determine the length of pipe from the gas meter to the most remote outlet (outlet A) is 60 feet.
Sec 1 (10) + Sec 2 (10) + Sec 3 (30) = 60
(3) Using the length in feet column row marked 60 feet in Table sizing table:
Outlet A, supplying 32 cubic feet per hour, requires ½ inch pipe.
Section 1, supplying outlets A and B, or 35 cubic feet per hour requires ½ inch pipe.
Section 2, supplying outlets A, B, and C, or 94 cubic feet per hour requires 1/2 inch pipe.
Section 3, supplying outlets A, B, C, and D, or 230 cubic feet per hour, requires 3/4 inch pipe.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Dwelling Unit Feeder - Service Conductor Calculations NECDokumen10 halamanDwelling Unit Feeder - Service Conductor Calculations NECRudanekBelum ada peringkat
- Stavanger Tourist SpotDokumen96 halamanStavanger Tourist Spotregupathi6413Belum ada peringkat
- Electrical Resedential Amp Commercial Calculations PDFDokumen50 halamanElectrical Resedential Amp Commercial Calculations PDFBenj LucioBelum ada peringkat
- Watson McDaniel EngineeringDataDokumen61 halamanWatson McDaniel EngineeringDataViswanathan DamodaranBelum ada peringkat
- Legend & Symbol: Joint DetailDokumen5 halamanLegend & Symbol: Joint DetailMike Advincula100% (1)
- 00 BLANK - Hot and Cold Water LU Calculation SheetDokumen17 halaman00 BLANK - Hot and Cold Water LU Calculation SheetmaxmorekBelum ada peringkat
- Calculation ReportDokumen29 halamanCalculation Reportvictor.sBelum ada peringkat
- PNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGDari EverandPNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGBelum ada peringkat
- NTPC (National Thermal Power Corporation) Sipat Boiler-Haxxo24 I IDokumen88 halamanNTPC (National Thermal Power Corporation) Sipat Boiler-Haxxo24 I Ihaxxo24100% (1)
- Gas Pipe Line Sizing PDFDokumen4 halamanGas Pipe Line Sizing PDFCandraBelum ada peringkat
- SSP - CMR For July To December 2017 SSPDokumen6 halamanSSP - CMR For July To December 2017 SSPMike Advincula100% (1)
- SSP - CMR For July To December 2017 SSPDokumen6 halamanSSP - CMR For July To December 2017 SSPMike Advincula100% (1)
- PermittingHazardous PDFDokumen35 halamanPermittingHazardous PDFMike AdvinculaBelum ada peringkat
- Vents For Plumbing System PDFDokumen47 halamanVents For Plumbing System PDFIrfanshah2013Belum ada peringkat
- LPG Handbook PDFDokumen50 halamanLPG Handbook PDFAhmed Sherif100% (1)
- Boiler Design and Operation ParametersDokumen88 halamanBoiler Design and Operation ParametersKrishnan Santhanaraj100% (3)
- Buffer Tank Hydraulic SeparatorDokumen4 halamanBuffer Tank Hydraulic SeparatorJohn MoreBelum ada peringkat
- Gaspipe SizingDokumen15 halamanGaspipe SizingmaxxhaloBelum ada peringkat
- Steam-Calc-Medina 500 Bed - Rev2Dokumen8 halamanSteam-Calc-Medina 500 Bed - Rev2alialavi2Belum ada peringkat
- Closed Expansion TankDokumen4 halamanClosed Expansion Tanka_salehiBelum ada peringkat
- ReticulationDokumen118 halamanReticulationIzzul Hazim100% (1)
- Boiler Operation TTPSDokumen137 halamanBoiler Operation TTPSChetanPrajapati100% (3)
- MATH8-Relations and Functions Worksheet AnswersDokumen15 halamanMATH8-Relations and Functions Worksheet AnswersRhealyn Joy Narciso100% (2)
- Air Source Heat Pump Technical ManualDokumen28 halamanAir Source Heat Pump Technical ManualWayne Grey100% (3)
- Gas Pipe Sizing (Natural)Dokumen6 halamanGas Pipe Sizing (Natural)kuraimundBelum ada peringkat
- Stories of Prophets - 2Dokumen19 halamanStories of Prophets - 2Hadis MusaBelum ada peringkat
- Domestic Gas Planning and SizingDokumen2 halamanDomestic Gas Planning and SizingBoab DingwallBelum ada peringkat
- High-Rise Design - Hot Water Recirculations and General Pumping PracticesDokumen156 halamanHigh-Rise Design - Hot Water Recirculations and General Pumping PracticesAnonymous PCsoNCt0mFBelum ada peringkat
- 660 MW Sipat BoilerDokumen88 halaman660 MW Sipat BoilerTochi Krishna Abhishek100% (4)
- Boiler Design and Operation ParametersDokumen88 halamanBoiler Design and Operation ParametersNavneet SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Process Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersDari EverandProcess Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersBelum ada peringkat
- TSD CogenDokumen5 halamanTSD CogenGaurav SushrutBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 - Gas Piping Installations PDFDokumen14 halamanChapter 4 - Gas Piping Installations PDFGeorge_Wabag_2014Belum ada peringkat
- Versant ModifiedDokumen57 halamanVersant ModifiedAryan Kharadkar100% (3)
- CAMERON Indirect HeatingDokumen4 halamanCAMERON Indirect Heatingأصلان أصلان100% (1)
- Bill No. 1 - General Items PreliminariesDokumen24 halamanBill No. 1 - General Items PreliminariesNorazreen NorAzharBelum ada peringkat
- JSW Energy Plant Maintenance BBPDokumen46 halamanJSW Energy Plant Maintenance BBPSandeep Kumar PraharajBelum ada peringkat
- Gas Load Calculations: City of Vacaville Community Development Building DivisionDokumen2 halamanGas Load Calculations: City of Vacaville Community Development Building DivisionHammad MalikBelum ada peringkat
- Residential Gas Installation Sizing GuideDokumen3 halamanResidential Gas Installation Sizing GuideLamHotBelum ada peringkat
- LP Gas Fisher Handbook Serviceman Inst PDFDokumen52 halamanLP Gas Fisher Handbook Serviceman Inst PDFEden Frias100% (1)
- Properly size gas lines for tankless water heatersDokumen6 halamanProperly size gas lines for tankless water heatersJames LoewenBelum ada peringkat
- Keston 30C ManualDokumen80 halamanKeston 30C Manualstainless12Belum ada peringkat
- 45 Export - Acetylene PlantDokumen8 halaman45 Export - Acetylene PlantBilel AzzouniBelum ada peringkat
- Calculation For Steam and Hot Water Consumption For: Sun Rise CharmingDokumen4 halamanCalculation For Steam and Hot Water Consumption For: Sun Rise CharmingYasser FathiBelum ada peringkat
- Ideal Mexico Slimline RS40 ManualDokumen40 halamanIdeal Mexico Slimline RS40 ManualszodonnellBelum ada peringkat
- Biscuit SpecificationsDokumen19 halamanBiscuit SpecificationsmohammadBelum ada peringkat
- Saunier Duval Thema C23 Installation ManualDokumen20 halamanSaunier Duval Thema C23 Installation ManualZmarandoiu SorinaBelum ada peringkat
- Bosch Greenstar ZWBR 7-25 A23 Gcno.46-311-44 Boiler Installation and Service ManualDokumen36 halamanBosch Greenstar ZWBR 7-25 A23 Gcno.46-311-44 Boiler Installation and Service ManualMerlin1950Belum ada peringkat
- Contoh Bangunan Gedung Di JakartaDokumen46 halamanContoh Bangunan Gedung Di Jakartabudi budihardjoBelum ada peringkat
- Copy of Power Plant Plate-A Revised ENGLISH VersionDokumen3 halamanCopy of Power Plant Plate-A Revised ENGLISH VersionMariel MirafloresBelum ada peringkat
- Boiler Feed Pumps and Standard Values For Boiler Feed and Circulating WaterDokumen3 halamanBoiler Feed Pumps and Standard Values For Boiler Feed and Circulating WaterAshrafMostafaBelum ada peringkat
- Manualul Pentru Incalzire Danfoss - Chapter8Dokumen25 halamanManualul Pentru Incalzire Danfoss - Chapter8valicanBelum ada peringkat
- Vivadens MCR: Wall-Hung Gas Condensing BoilersDokumen12 halamanVivadens MCR: Wall-Hung Gas Condensing BoilersIsmael Llamelo PerezBelum ada peringkat
- Gas - Adding or Extending Piping: Permit RequirementsDokumen3 halamanGas - Adding or Extending Piping: Permit RequirementsAndrian WicaksonoBelum ada peringkat
- Service Procedure: Airflow MeasurementDokumen44 halamanService Procedure: Airflow MeasurementzebidiansBelum ada peringkat
- Installation and Servicing Instructions For Highflow 400 BF Manufactured After 1997Dokumen48 halamanInstallation and Servicing Instructions For Highflow 400 BF Manufactured After 1997Tom GuthrieBelum ada peringkat
- Hot Water GP H CalculatorDokumen112 halamanHot Water GP H CalculatorYaseen MallickBelum ada peringkat
- A.O. Smith Servicing Guide 320991-000Dokumen72 halamanA.O. Smith Servicing Guide 320991-000ToMBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 3Dokumen18 halamanLecture 3KHALID SERAGALDINBelum ada peringkat
- Improved Forced Draft Biomass Cookstove PerformanceDokumen8 halamanImproved Forced Draft Biomass Cookstove PerformanceRikkinBelum ada peringkat
- MitsubishiDokumen10 halamanMitsubishiPrabhat Kisku100% (1)
- Domestic Gas PipingDokumen2 halamanDomestic Gas Pipingvalentinlupascu33Belum ada peringkat
- Bosch HGS70Dokumen1 halamanBosch HGS70PurcellMurrayBelum ada peringkat
- Catalogue Heat PumpDokumen38 halamanCatalogue Heat Pumpdongta123Belum ada peringkat
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesDari EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesBelum ada peringkat
- 00 Electrical Residential Caloocan GeneralDokumen1 halaman00 Electrical Residential Caloocan GeneralMike AdvinculaBelum ada peringkat
- Proposal For Flores ResidenceDokumen1 halamanProposal For Flores ResidenceMike AdvinculaBelum ada peringkat
- Laudry Shop Plumbing PlanDokumen1 halamanLaudry Shop Plumbing PlanMike AdvinculaBelum ada peringkat
- 00 Electrical Residential Caloocan GeneralDokumen1 halaman00 Electrical Residential Caloocan GeneralMike AdvinculaBelum ada peringkat
- Whitner, Contingency Planning For The Household Hazardous Waste FacilityDokumen17 halamanWhitner, Contingency Planning For The Household Hazardous Waste FacilityMike AdvinculaBelum ada peringkat
- Plumbing ClientDokumen1 halamanPlumbing ClientMike AdvinculaBelum ada peringkat
- Pormida Panel BoardDokumen1 halamanPormida Panel BoardMike AdvinculaBelum ada peringkat
- S QC - SAGULLO S4 FRAMING PLAN S4bDokumen1 halamanS QC - SAGULLO S4 FRAMING PLAN S4bMike AdvinculaBelum ada peringkat
- General Notes Material Specification: Proposed 3-Storey Commercial BuildingDokumen1 halamanGeneral Notes Material Specification: Proposed 3-Storey Commercial BuildingMike AdvinculaBelum ada peringkat
- Price Materials ElectricalDokumen4 halamanPrice Materials ElectricalMike AdvinculaBelum ada peringkat
- Shangri-La Salcedo Place: August 12, 2021Dokumen6 halamanShangri-La Salcedo Place: August 12, 2021Mike AdvinculaBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Notes: Perspective View: LegendDokumen1 halamanElectrical Notes: Perspective View: LegendMike AdvinculaBelum ada peringkat
- September 2020 Schedule Maintenance ScheduleDokumen1 halamanSeptember 2020 Schedule Maintenance ScheduleMike AdvinculaBelum ada peringkat
- Bid Form - Trees - T3 - Electrical and Auxiliary WorksDokumen1 halamanBid Form - Trees - T3 - Electrical and Auxiliary WorksMike AdvinculaBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Status For Manual Pool StationDokumen1 halamanEngineering Status For Manual Pool StationMike AdvinculaBelum ada peringkat
- Explanation LetterDokumen1 halamanExplanation LetterMike AdvinculaBelum ada peringkat
- Water Dynamic LoadDokumen27 halamanWater Dynamic LoadsolarpolBelum ada peringkat
- GensetDokumen1 halamanGensetMike AdvinculaBelum ada peringkat
- GensetDokumen1 halamanGensetMike AdvinculaBelum ada peringkat
- Macea Engineering Activity (Emission Test 3.14.18)Dokumen1 halamanMacea Engineering Activity (Emission Test 3.14.18)Mike AdvinculaBelum ada peringkat
- b676 Boysen Quick Drying Enamel OrangeDokumen10 halamanb676 Boysen Quick Drying Enamel OrangeMike Advincula100% (1)
- Me RalcoDokumen1 halamanMe RalcoMike AdvinculaBelum ada peringkat
- BE Industrial Fans Fans PUBL 7588Dokumen8 halamanBE Industrial Fans Fans PUBL 7588Mike AdvinculaBelum ada peringkat
- Delta - Flexdrive 2017 104 One Roxas1Dokumen1 halamanDelta - Flexdrive 2017 104 One Roxas1Mike AdvinculaBelum ada peringkat
- The Grey Nomads Guide To AustraliaDokumen3 halamanThe Grey Nomads Guide To AustraliaFreerangecamping60% (5)
- 37th APSDC Scientific PresentationsDokumen7 halaman37th APSDC Scientific PresentationsSatyendra KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Causes and Effects of PollutionDokumen6 halamanCauses and Effects of PollutionNhư NgọcBelum ada peringkat
- Causes of DyspneaDokumen9 halamanCauses of DyspneaHanis Afiqah Violet MeowBelum ada peringkat
- Meningitis & EncephalitisDokumen7 halamanMeningitis & EncephalitisABAKADABelum ada peringkat
- Manual Del GVMapper v3 3 PDFDokumen102 halamanManual Del GVMapper v3 3 PDFguanatosBelum ada peringkat
- Pentecostal Ecclesiology: Simon K.H. Chan - 978-90-04-39714-9 Via Free AccessDokumen156 halamanPentecostal Ecclesiology: Simon K.H. Chan - 978-90-04-39714-9 Via Free AccessStanley JohnsonBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Composite Materials Design EngineeringDokumen19 halamanAdvanced Composite Materials Design EngineeringpanyamnrBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Variable Cramers Rule PDFDokumen4 halaman3 Variable Cramers Rule PDFElton DiocsonBelum ada peringkat
- Hairpin tube arrangements and multiple-bend designs for superheatersDokumen2 halamanHairpin tube arrangements and multiple-bend designs for superheatersMArifHidayahBelum ada peringkat
- Time and Work Assignments PDFDokumen8 halamanTime and Work Assignments PDFpavan0% (1)
- Chapter 4 Cost MinimizationDokumen6 halamanChapter 4 Cost MinimizationXavier Hetsel Ortega BarraganBelum ada peringkat
- Shapes FlashcardsDokumen5 halamanShapes FlashcardsHome Organising by JRBelum ada peringkat
- 44 Sounds Aus EnglishDokumen2 halaman44 Sounds Aus EnglishAlfie Arabejo Masong LaperaBelum ada peringkat
- P&id BoilerDokumen1 halamanP&id BoilerBagus AryowibowoBelum ada peringkat
- Kingspan Spectrum™: Premium Organic Coating SystemDokumen4 halamanKingspan Spectrum™: Premium Organic Coating SystemNikolaBelum ada peringkat
- Progressing Cavity Pump Overhaul GuideDokumen5 halamanProgressing Cavity Pump Overhaul Guidesdsds-54Belum ada peringkat
- Sensor Controlled Animatronic Hand: Graduation Project PresentationDokumen24 halamanSensor Controlled Animatronic Hand: Graduation Project PresentationAnonymous D2FmKSxuuBelum ada peringkat
- H. Bateman, A. Erdélyi Et Al. - Higher Transcendental Functions 3 (1955, McGraw-Hill)Dokumen310 halamanH. Bateman, A. Erdélyi Et Al. - Higher Transcendental Functions 3 (1955, McGraw-Hill)ITALO HERRERA MOYABelum ada peringkat
- Cooling System Exhaust System: RadiatorDokumen2 halamanCooling System Exhaust System: RadiatorMd ShBelum ada peringkat
- NASA Technical Mem Randum: E-Flutter N78Dokumen17 halamanNASA Technical Mem Randum: E-Flutter N78gfsdg dfgBelum ada peringkat
- Rincon Dueling RigbyDokumen5 halamanRincon Dueling Rigbytootalldean100% (1)
- r05320202 Microprocessors and Micro ControllersDokumen7 halamanr05320202 Microprocessors and Micro ControllersSri LalithaBelum ada peringkat
- Product CataloguepityDokumen270 halamanProduct CataloguepityRaghuRags100% (1)