Summary Engineering Economics Formulator
Diunggah oleh
Zaid Tariq AlabiryHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Summary Engineering Economics Formulator
Diunggah oleh
Zaid Tariq AlabiryHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
lOMoARcPSD|2843453
Summary Engineering Economics: - Formulary
Engineering Economics (University of Manitoba)
StuDocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university
Downloaded by Zaid Alabiry (zaidalabiry@hotmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|2843453
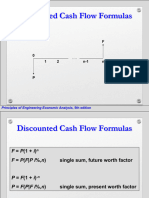
Simple interest: F = P(1+iN)
Compound interest: F = P ( 1+i )N
Factor To Find Given Formula
Compound amount F P (F/P, i%, N) (1+i) N
Present worth P F (P/F, i%, N) 1
(1+i) N
Sinking funds A F (A/F, i%, N) i
(1+i) N −1
N
Series compound amount F A (F/A, i%, N) (1+i) −1
i
Capital recovery A P (A/P, i%, N) i(1+i) N
(1+i) N −1
N
Series present worth P A (P/A, i%, N) (1+i) −1
i(1+i) N
Arithmetic gradient conversion A G (A/G, i%, N)
Factor relationships
(F/P, i%, N) = i(F/A, i%, N) + 1
(P/F, i%, N) = 1 – (P/A, i%, N)i
(A/F, i%, N) = (A/P, i%, N) – i
i
(A/P, i%, N) =
1−( P/ F ,i % , N )
Gradient Calculations
Name To Find Given Equation
Future worth of gradient series (F/G, i%, N) F G F 1
= [
G i
N
(1+i) −1
- N]
i
Uniform series worth of a gradient series (A/G, i%, N) A G A 1
= -
G i
N
N
(1+i) −1
Present worth of a gradient series (P/G, i%, N) P G P 1
= [
G i
(1+i) N −1
-
i(1+i) N
N
N ]
(1+i)
Only (A/G, i%, N) from tables
Downloaded by Zaid Alabiry (zaidalabiry@hotmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|2843453
When G > 0, A” = A’ + G(A/G, i%, N)
When G < 0, A” = A’ – G(A/G, i%, N)
When G is percentage:
g>i 1+g
i¿ = −1
1+i
g=i N A'
P=
(1+i)
g < i (most cases) 1+g A'
i¿ = −1 and P = (P/A, i¿ ,
1+i 1+g
N)
Interpolation: when N or i% is unknown
Find i% for P = 1,500, F = 4,500 , N = 8
F
= (F/P, i%, N)
P
4,500
= (F/P, i%, 8) = 3
1,500
From tables
(F/P, 14, 8) = 2.8525
(F/P, 15, 8) = 3.0590
3.0000−2.8525
i = 0.14 + 0.01
3.0590−2.8525
i = 0.147143
i = effective rate; r = nominal rate; m = number of compounding periods per year
r m
(1 + i) = (1+ )
m
N r mN
(1+i) = (1+ )
m
Continuous compounding
r
i= e -1
Payment periods differ from compounding periods
m = number of compounding periods per year
Downloaded by Zaid Alabiry (zaidalabiry@hotmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|2843453
k = number of periods per year
c = number of interest period
c
r r
Effective interest rate per period i = (1+ ) - 1 OR i = e k -1 for continues compounding
ck
Changing interest rate
F = P(1 + i1)(1 + i2)….(1 + in)
Loans
Balance with N-n payments remaining B n = A(P/A, i%, N-n)
Interest during period n In = ( B n−1 ¿ i = A(P/A, i%, N – n + 1)i
Pn = A - I n = A(1 – (P/A, i%, N – n + 1)i)
Pn = A(P/F, i%, N – n + 1)
Downloaded by Zaid Alabiry (zaidalabiry@hotmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|2843453
Continuous cash flow
rN r
(F/P, r, N) e ( e −1)
F=P r
re
r
(P/F, r, N) e −1
P=F rN
re
(A/F, r, N) r
A=F Rn
e −1
(F/A, r, N) er N −1
F=A
r
(A/P, r, N) r erN
A=P
erN −1
(P/A, r, N) erN −1
P=A
r erN
A
Perpetuities and Capitalized cost (uniform series forever): P =
i
A
Capitalized worth = -P +
i
Disbursements
When there is no revenues: Capitalized cost = P + ( Annualized )
i
Economic evaluators
Present Worth Evaluators
Net Present Value (NPV); present worth of cash inflows less present worth of cash outflows
N
C
NPV = ∑ (1+i)
t
t ;
t=0
Ct is positive for cash inflows and negative for cash outflow for the period t
i the discount rate per period
N number of periods
Present Worth of Annual Cost (PWAC)
Present Worth of Capital Expenditure (PWCE)
Annualized Evaluators
Equivalent Annual Cost (EAC) = (P – S) (A/P, i%, N) + Si ; where S: Salvage Value
Equivalent Annual Worth (EAW)
Economic Ratios
Downloaded by Zaid Alabiry (zaidalabiry@hotmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|2843453
PWCE ratios:
NPV
Net benefit as percentage of total capital
PWCE
NPV +PWCE
express gross benefit
PWCE
PWAC ratios
NPV
Net benefit as percentage of total capital
PWAC
NPV + PWAC
express gross benefit
PW A C
Rate of Return
N
C
Internal Rate of Return (IROR): is by definition when NPV = 0 = ∑ (1+i)
t
t ; we need to find i
t=0
1
NPV
Rate of Return on Capital (RORC) = (1 + i) ( +1) N –1
PWCE
Downloaded by Zaid Alabiry (zaidalabiry@hotmail.com)
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Engineering Economy Formulas: D A 2b 2b +K + 4 B C 2 BDokumen4 halamanEngineering Economy Formulas: D A 2b 2b +K + 4 B C 2 BCrystel ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- Compund Interest TablesDokumen18 halamanCompund Interest TablesAnna DewiBelum ada peringkat
- Compund Interest TablesDokumen18 halamanCompund Interest TablesCindy HosianiBelum ada peringkat
- FE Reference PagesDokumen7 halamanFE Reference PagesCarolyn BaezBelum ada peringkat
- Interest Factor Formulas: Compound AmountDokumen3 halamanInterest Factor Formulas: Compound AmountanjumjauherBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Economics Excerpt From FE Reference PDFDokumen7 halamanEngineering Economics Excerpt From FE Reference PDFBo Han HuangBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Economics: Factor Name Converts Symbol FormulaDokumen7 halamanEngineering Economics: Factor Name Converts Symbol FormulaJowel MercadoBelum ada peringkat
- TABLE 2.6 Summary of Discrete Compounding Interest Factors. To FindDokumen2 halamanTABLE 2.6 Summary of Discrete Compounding Interest Factors. To FindKarim HakimBelum ada peringkat
- TablesDokumen30 halamanTablesAhmed walidBelum ada peringkat
- Compound Interest Tables and FactorsDokumen18 halamanCompound Interest Tables and FactorsAbsoyoshi Joel Espinoza CondorBelum ada peringkat
- CH 03 Combining FactorsDokumen15 halamanCH 03 Combining Factorsalmosawi 17Belum ada peringkat
- Interest FormulasDokumen2 halamanInterest Formulasavinashf3Belum ada peringkat
- Bicol University College of Engineering Civil Engineering DepartmentDokumen4 halamanBicol University College of Engineering Civil Engineering DepartmentJannel Llanillo JamisolaBelum ada peringkat
- Formula Sheet - Quantitative FinanceDokumen1 halamanFormula Sheet - Quantitative FinanceInês SoaresBelum ada peringkat
- Formulae for Standard Compound Interest CalculationsDokumen2 halamanFormulae for Standard Compound Interest CalculationsAbubakar A N GBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Annuities - Engineering EconomyDokumen9 halamanTypes of Annuities - Engineering EconomySeungcheol ChoiBelum ada peringkat
- EE Formulas NCITDokumen8 halamanEE Formulas NCITYe FengBelum ada peringkat
- ENGR 371 Midterm July 1999Dokumen4 halamanENGR 371 Midterm July 1999amnesiannBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Economics FormulasDokumen2 halamanEngineering Economics FormulasBorja, Alexandra C.Belum ada peringkat
- Công TH CDokumen1 halamanCông TH Cminhndn21405Belum ada peringkat
- EquationsDokumen1 halamanEquationsbhavikrathodhiBelum ada peringkat
- Formula for Simple, Compound Interest, Annuities, Capital CostsDokumen2 halamanFormula for Simple, Compound Interest, Annuities, Capital CostsWYNDYLL ARTUZBelum ada peringkat
- Corrosion CalculationDokumen7 halamanCorrosion CalculationM Abdullah Khalid ArvgsmBelum ada peringkat
- IE 307 Engineering Economy Gradient Series and Amortization ScheduleDokumen8 halamanIE 307 Engineering Economy Gradient Series and Amortization ScheduleJayrMenes100% (1)
- MATH 01 FormulaDokumen3 halamanMATH 01 FormulaJae Bert UbisoftBelum ada peringkat
- Full download book Engineering Economy Pdf pdfDokumen41 halamanFull download book Engineering Economy Pdf pdfjohn.jackson254100% (7)
- EconomicsDokumen19 halamanEconomicsegBelum ada peringkat
- For MüllerDokumen2 halamanFor MüllerMehmet Kemal YükselBelum ada peringkat
- Formulas: F - Future Value P - Present/Principal ValueDokumen2 halamanFormulas: F - Future Value P - Present/Principal ValueJimuel Ace SarmientoBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Economics EquationDokumen2 halamanEngineering Economics EquationCeline Marie CervantesBelum ada peringkat
- Relations For Discrete Cash Flows With End-of-Period CompoundingDokumen1 halamanRelations For Discrete Cash Flows With End-of-Period Compoundingxiereo22Belum ada peringkat
- EC 314: Public and Private Investment Q2: Time Value: PeriodDokumen1 halamanEC 314: Public and Private Investment Q2: Time Value: PeriodJamie WoodsBelum ada peringkat
- SMP Machine Investment Analysis Using Present Worth, Annual Worth, and Uniform Series EquivalentsDokumen24 halamanSMP Machine Investment Analysis Using Present Worth, Annual Worth, and Uniform Series EquivalentsAjlan AlajlanBelum ada peringkat
- Formulas Ingenieria EconomicaDokumen1 halamanFormulas Ingenieria EconomicaNicolay GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- Formulas Ingeco PDFDokumen1 halamanFormulas Ingeco PDFJorge Alberto Duran silvaBelum ada peringkat
- Compound TableDokumen31 halamanCompound TableTeresa Agitha HerdinaBelum ada peringkat
- VPN FCL + + + Van Vai Vae VFN Vfi Vfe VFN VPN (1+i)Dokumen1 halamanVPN FCL + + + Van Vai Vae VFN Vfi Vfe VFN VPN (1+i)AngelDaniloAlvarezBarajasBelum ada peringkat
- Nilai Uang (Discounted Value) : By: A. Agung Gde Kartika, ST., M.Sc. Teknik Sipil ItsDokumen20 halamanNilai Uang (Discounted Value) : By: A. Agung Gde Kartika, ST., M.Sc. Teknik Sipil ItsSasqia MaulidyaBelum ada peringkat
- Economics 1Dokumen12 halamanEconomics 1jhozabethcarbonelBelum ada peringkat
- Extra Questions On Time Value of Money (Div-I)Dokumen5 halamanExtra Questions On Time Value of Money (Div-I)SHRADDHA BHOIRBelum ada peringkat
- Summary of FormulaDokumen1 halamanSummary of Formulakevin_ramos007Belum ada peringkat
- Ch02.part II - ModifiedDokumen34 halamanCh02.part II - Modifiedfaisal4420Belum ada peringkat
- Contemporary Engineering Economics SayfasıDokumen1 halamanContemporary Engineering Economics SayfasıMehmet Kemal YükselBelum ada peringkat
- EC 314: Public and Private Investment Q2: Time Value: PeriodDokumen1 halamanEC 314: Public and Private Investment Q2: Time Value: PeriodJamie WoodsBelum ada peringkat
- E ENGINEERING ECONOMICS ReviewDokumen16 halamanE ENGINEERING ECONOMICS ReviewJM CopinoBelum ada peringkat
- Formula SheetDokumen1 halamanFormula Sheetnick07052004Belum ada peringkat
- 04 B EPM 119 Midterm Spring2021Dokumen16 halaman04 B EPM 119 Midterm Spring2021KaRim El-BeGawiiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 Part 2 of 2 PDFDokumen60 halamanChapter 2 Part 2 of 2 PDFASAD ULLAHBelum ada peringkat
- Summary of Annuity FormulasDokumen1 halamanSummary of Annuity FormulasJames DabalosBelum ada peringkat
- FormelnDokumen1 halamanFormelnhanna.ericssonkleinBelum ada peringkat
- Formula Sheet Principles of FinanceDokumen6 halamanFormula Sheet Principles of FinanceSI PBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Economy ConceptsDokumen6 halamanEngineering Economy ConceptsJeremy Allan BartoloBelum ada peringkat
- P/ F, I%, NDokumen3 halamanP/ F, I%, NCheerag DuggalBelum ada peringkat
- Discounted Cash Flow FormulasDokumen34 halamanDiscounted Cash Flow FormulasnorahBelum ada peringkat
- Finding critical points of a function in multiple variablesDokumen5 halamanFinding critical points of a function in multiple variablesJoshua ThomasBelum ada peringkat
- CV 4252 Gradient Series FactorsDokumen25 halamanCV 4252 Gradient Series Factorszzz_monsterBelum ada peringkat
- DTFT VS CTFTDokumen1 halamanDTFT VS CTFTHansen LienardiBelum ada peringkat
- EC 314: Public and Private Investment Q2: Time ValueDokumen1 halamanEC 314: Public and Private Investment Q2: Time ValueJamie WoodsBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Economics Present and Future Worth FormulasDokumen4 halamanEngineering Economics Present and Future Worth FormulasNasser SABelum ada peringkat
- Dual-Duct Constant-Volume System AnalysisDokumen2 halamanDual-Duct Constant-Volume System AnalysisZaid Tariq AlabiryBelum ada peringkat
- Dual-duct constant-volume system analysis hot and cold air flowsDokumen3 halamanDual-duct constant-volume system analysis hot and cold air flowsZaid Tariq AlabiryBelum ada peringkat
- Selection of Round Ceiling DiffuserDokumen2 halamanSelection of Round Ceiling DiffuserZaid Tariq Alabiry0% (1)
- Fan and Duct System AnalysisDokumen3 halamanFan and Duct System AnalysisZaid Tariq AlabiryBelum ada peringkat
- Economizer Control AnalysisDokumen4 halamanEconomizer Control AnalysisZaid Tariq AlabiryBelum ada peringkat
- Torre14 114Dokumen1 halamanTorre14 114FABIAN YESID RAMIREZ LEONBelum ada peringkat
- RAC Lecture 10Dokumen18 halamanRAC Lecture 10api-373446667% (3)
- Asset Vs Maintenance 0812Dokumen4 halamanAsset Vs Maintenance 0812César Noriega MendozaBelum ada peringkat
- Ashrae Chart PDFDokumen2 halamanAshrae Chart PDFZaid Tariq AlabiryBelum ada peringkat
- HVAC Duct Sizing GuideDokumen91 halamanHVAC Duct Sizing GuidePrabir Bhowmik100% (1)
- Dual-Duct Constant-Volume System AnalysisDokumen3 halamanDual-Duct Constant-Volume System AnalysisZaid Tariq AlabiryBelum ada peringkat
- Eng Econ Formulas PDFDokumen2 halamanEng Econ Formulas PDFtrix337Belum ada peringkat
- Fan and Duct System AnalysisDokumen3 halamanFan and Duct System AnalysisZaid Tariq AlabiryBelum ada peringkat
- Forced-Air Natural Gas Furnace & Hot-Water Heating Coil Calculations PDFDokumen2 halamanForced-Air Natural Gas Furnace & Hot-Water Heating Coil Calculations PDFZaid Tariq AlabiryBelum ada peringkat
- Air-Conditioning System Design ProjectsDokumen95 halamanAir-Conditioning System Design ProjectsZaid Tariq AlabiryBelum ada peringkat
- Fan and Duct System AnalysisDokumen3 halamanFan and Duct System AnalysisZaid Tariq AlabiryBelum ada peringkat
- University of Toronto MIE 258F Midterm Exam QuestionsDokumen8 halamanUniversity of Toronto MIE 258F Midterm Exam QuestionsZaid Tariq AlabiryBelum ada peringkat
- Air-Conditioning System DesignDokumen1 halamanAir-Conditioning System DesignZaid Tariq AlabiryBelum ada peringkat
- Foundations of Engineering EconomyDokumen29 halamanFoundations of Engineering EconomyZaid Tariq AlabiryBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Economics Excerpt From FE Reference PDFDokumen7 halamanEngineering Economics Excerpt From FE Reference PDFBo Han HuangBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 01 Economy - 1Dokumen15 halamanChapter 01 Economy - 1Zaid Tariq AlabiryBelum ada peringkat
- Eng Econ Formulas PDFDokumen2 halamanEng Econ Formulas PDFtrix337Belum ada peringkat
- Air-Conditioning System Design ProjectsDokumen95 halamanAir-Conditioning System Design ProjectsZaid Tariq AlabiryBelum ada peringkat
- Effective Interest RatesDokumen2 halamanEffective Interest RatesZaid Tariq AlabiryBelum ada peringkat
- Foundations of Engineering EconomyDokumen29 halamanFoundations of Engineering EconomyZaid Tariq AlabiryBelum ada peringkat
- Effective Interest RatesDokumen2 halamanEffective Interest RatesZaid Tariq AlabiryBelum ada peringkat
- Foundations of Engineering EconomyDokumen29 halamanFoundations of Engineering EconomyZaid Tariq AlabiryBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Economic AnalysisDokumen5 halamanEngineering Economic AnalysisZaid Tariq AlabiryBelum ada peringkat
- What It Takes To Be An EntrepreneurDokumen3 halamanWhat It Takes To Be An EntrepreneurJose FrancisBelum ada peringkat
- ESICDokumen30 halamanESICLucKy PanditBelum ada peringkat
- BA5014 QB Entrepreneurship DevelopmentDokumen11 halamanBA5014 QB Entrepreneurship DevelopmentIndhuja MBelum ada peringkat
- Hamlin and Park DesignDokumen24 halamanHamlin and Park Designantonio1957Belum ada peringkat
- Anbu Employee Welfare Measure Project PPT PresentationDokumen12 halamanAnbu Employee Welfare Measure Project PPT PresentationVasanth KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Insurance Marketing in Indian EnvironmentDokumen6 halamanInsurance Marketing in Indian EnvironmentPurab MehtaBelum ada peringkat
- PFRS 8 Segment ReportingDokumen3 halamanPFRS 8 Segment ReportingAllaine ElfaBelum ada peringkat
- Agency (Nature)Dokumen8 halamanAgency (Nature)RicmcbolBelum ada peringkat
- Rapid Root Cause Investigations - Novartis 31.03.2010Dokumen19 halamanRapid Root Cause Investigations - Novartis 31.03.2010kumar_chemicalBelum ada peringkat
- Order ManagementDokumen49 halamanOrder ManagementpvlnraoBelum ada peringkat
- Industry Analysis FundamentalsDokumen21 halamanIndustry Analysis FundamentalsNarayanan SubramanianBelum ada peringkat
- AirwayBill 0NGKT15231058Dokumen1 halamanAirwayBill 0NGKT15231058halipzramlyzBelum ada peringkat
- Lean, But Not Yet Mean: Why Transformation Needs A Second ChapterDokumen8 halamanLean, But Not Yet Mean: Why Transformation Needs A Second ChapterAriana SánchezBelum ada peringkat
- Sharepoint User Guide 2010Dokumen12 halamanSharepoint User Guide 2010Marco BertoldiBelum ada peringkat
- Recession and DepressionDokumen5 halamanRecession and DepressionhirahBelum ada peringkat
- Contact Details: BSP DirectoryDokumen4 halamanContact Details: BSP DirectoryPondo AsensoBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Form Legal Opinion LetterDokumen2 halamanSample Form Legal Opinion LetterLindsay Mills100% (1)
- Cafe LagunaDokumen7 halamanCafe LagunaAmyRoseCruz100% (1)
- Percentage Exercise Hints Explanations PDFDokumen12 halamanPercentage Exercise Hints Explanations PDFGIRIDHARAN K MBelum ada peringkat
- Transfer Prices and Multiple Valuation ApproachesDokumen6 halamanTransfer Prices and Multiple Valuation Approachessampath0% (1)
- Spinny Intro DeckDokumen12 halamanSpinny Intro DeckVicky Choudhary100% (1)
- Andra Pradesh PDFDokumen50 halamanAndra Pradesh PDFMichael KSKSBelum ada peringkat
- Cassava ProductionDokumen44 halamanCassava ProductionLino Cuesta93% (14)
- BSRDokumen569 halamanBSRUpali Karunarathne100% (8)
- Radhakrishnan .P, Prasad .V, Gopalan .MDokumen2 halamanRadhakrishnan .P, Prasad .V, Gopalan .MPGDM IMSBelum ada peringkat
- Recent Trends in CompensationDokumen2 halamanRecent Trends in Compensationhasanshs12100% (1)
- Assignment Strategic ManagementDokumen3 halamanAssignment Strategic ManagementMr. Zahid MasoodBelum ada peringkat
- Signavio - BPMN Modeling ConventionsDokumen3 halamanSignavio - BPMN Modeling ConventionsleoaugBelum ada peringkat
- Credit Creation and Money SupplyDokumen27 halamanCredit Creation and Money SupplyPrasad LadBelum ada peringkat
- BB SMC-1Dokumen25 halamanBB SMC-1Suleman Saleh80% (10)