Gcse Waves
Diunggah oleh
DanKimberley0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
4 tayangan1 halamanThis document defines key terms related to waves including amplitude, wavelength, time period, frequency, and defines transverse and longitudinal waves. It distinguishes between electromagnetic, mechanical, transverse and longitudinal waves. It also covers topics in optics such as refraction, refractive index, Snell's law, focal point, and total internal reflection. Refraction describes how light changes speed and direction when passing from one medium to another. Snell's law defines the relationship between angles of incidence and refraction based on the refractive indices of the materials.
Deskripsi Asli:
Gcse Waves
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniThis document defines key terms related to waves including amplitude, wavelength, time period, frequency, and defines transverse and longitudinal waves. It distinguishes between electromagnetic, mechanical, transverse and longitudinal waves. It also covers topics in optics such as refraction, refractive index, Snell's law, focal point, and total internal reflection. Refraction describes how light changes speed and direction when passing from one medium to another. Snell's law defines the relationship between angles of incidence and refraction based on the refractive indices of the materials.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
4 tayangan1 halamanGcse Waves
Diunggah oleh
DanKimberleyThis document defines key terms related to waves including amplitude, wavelength, time period, frequency, and defines transverse and longitudinal waves. It distinguishes between electromagnetic, mechanical, transverse and longitudinal waves. It also covers topics in optics such as refraction, refractive index, Snell's law, focal point, and total internal reflection. Refraction describes how light changes speed and direction when passing from one medium to another. Snell's law defines the relationship between angles of incidence and refraction based on the refractive indices of the materials.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 1
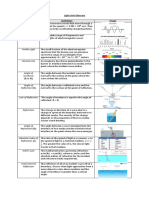
GCSE Waves
Amplitude – greatest displacement from equilibrium. (m)
Wavelength – distance between the same point on two consecutive waves. (m)
Time period – time taken for one oscillation. (s)
Frequency – how many complete waves pass a certain point per second = 1/T.
Transverse – oscillations perpendicular to direction of wave propagation.
Longitudinal – oscillations parallel to direction of wave propagation.
Wave – transfer of energy through vibrations without the net movement of particles.
WAVES Transverse Longitudinal
Electromagnetic All of them !
Mechanical S, Water, String, Guitar P, Sound, Ultrasound,
Infrasound
Refraction
Light going from air to glass
Refractive index measures optical density. N = c / v where v is the speed of light in material.
Focal point – the point at which all parallel rays meet.
Snell’s Law
N1 refractive index of starting medium. α1 = angle of incidence.
N2 refractive index of second medium, α2 = angle of reflection
N1 sin α1 =N2 sin α2
Total Internal Reflection
When going from something more dense to less dense.
Sin of critical angle = n2/n1
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsDari EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsBelum ada peringkat
- FAL (2022-23) FRESHERS PHY1008 ETH AP2022234000319 Reference Material I 18-Oct-2022 Fundamental of OpticsDokumen13 halamanFAL (2022-23) FRESHERS PHY1008 ETH AP2022234000319 Reference Material I 18-Oct-2022 Fundamental of OpticsPritam PatraBelum ada peringkat
- Quantum Mechanics 5: Entanglement, EPR, Teleportation, & Advanced TopicsDari EverandQuantum Mechanics 5: Entanglement, EPR, Teleportation, & Advanced TopicsPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (3)
- Physics Topic 4 Study GuideDokumen8 halamanPhysics Topic 4 Study GuideSai 0235Belum ada peringkat
- Notes - Unit 8 - Waves, Sound, and LightDokumen58 halamanNotes - Unit 8 - Waves, Sound, and Lightsonu4672Belum ada peringkat
- Waves PPDokumen21 halamanWaves PPMacha LaraBelum ada peringkat
- OCR A Physics A-Level: Topic 4.4: WavesDokumen7 halamanOCR A Physics A-Level: Topic 4.4: WavesjmsonlBelum ada peringkat
- Properties of WavesDokumen34 halamanProperties of WavesNuraini SeptyaningrumBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 22.1 4Dokumen34 halamanChapter 22.1 4Richard Renz VillafuerteBelum ada peringkat
- IGCSE Waves Definitions and ConceptsDokumen2 halamanIGCSE Waves Definitions and ConceptsMohamad Rizal MukhtarBelum ada peringkat
- CN 1Dokumen51 halamanCN 1Umar FarooqBelum ada peringkat
- Waves and ThermodynamicsDokumen23 halamanWaves and Thermodynamicsvineethkatakam06Belum ada peringkat
- Mechanical Waves and SoundDokumen46 halamanMechanical Waves and SoundPortia A. Egken100% (1)
- Dispersion and Snells LawDokumen5 halamanDispersion and Snells Lawklerni07Belum ada peringkat
- IX. Waves, Sounds and FluidsDokumen66 halamanIX. Waves, Sounds and FluidsMa Angelica Shane Navarro0% (1)
- Properties of WaveDokumen61 halamanProperties of WavePASSAWAT BOONCHITSIRIKULBelum ada peringkat
- Waves Changing Behaviour of Light (Theory)Dokumen2 halamanWaves Changing Behaviour of Light (Theory)Anushka SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Light GlossaryDokumen1 halamanLight Glossaryapi-668691050Belum ada peringkat
- PhysicsDokumen8 halamanPhysicsHeather SimpsonBelum ada peringkat
- Edexcel As Physics Unit 2 Revision PowerpointDokumen92 halamanEdexcel As Physics Unit 2 Revision PowerpointAnonymous tlSLEPRRe92% (12)
- Notes On Waves Reflk N RefrkDokumen3 halamanNotes On Waves Reflk N RefrkrhubeshBelum ada peringkat
- Mendecki 2013 - Mine Seismology Glossary of Selected TermsDokumen29 halamanMendecki 2013 - Mine Seismology Glossary of Selected TermsCatalina Andrea Badilla QuiñonesBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1 AQA Physics - WavesDokumen2 halamanUnit 1 AQA Physics - WavesAlex KingstonBelum ada peringkat
- sg24 Waves 1Dokumen2 halamansg24 Waves 1api-317469538Belum ada peringkat
- Ip PythonDokumen30 halamanIp PythonFelipe Quezada CastañedaBelum ada peringkat
- HSC Physics Module 3: Waves & ThermodynamicsDokumen30 halamanHSC Physics Module 3: Waves & ThermodynamicswillBelum ada peringkat
- FAL (2021-22) PHY1010 ETH AP2021222000083 Reference Material I 18-Aug-2021 Wave Optics-InterferenceDokumen53 halamanFAL (2021-22) PHY1010 ETH AP2021222000083 Reference Material I 18-Aug-2021 Wave Optics-Interferencetejas paiBelum ada peringkat
- WavesDokumen24 halamanWavesHarveen Kaur AnandBelum ada peringkat
- 2 Sound Wave - USDokumen29 halaman2 Sound Wave - USCharlotte gamingBelum ada peringkat
- Waves and Optics SummaryDokumen10 halamanWaves and Optics Summaryandrew.mooreBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 2 As EdexcelDokumen91 halamanUnit 2 As Edexcelsadika sabaBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 3 Properties of Waves Including Light and Sound: What Is Wave Motion?Dokumen11 halamanTopic 3 Properties of Waves Including Light and Sound: What Is Wave Motion?PichakornBelum ada peringkat
- Light As An Electromagnetic Wave: Handout: 2Dokumen1 halamanLight As An Electromagnetic Wave: Handout: 2Saurabh BhansaliBelum ada peringkat
- The Nature of Light PDFDokumen15 halamanThe Nature of Light PDFthinaBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Physics PHY-109 Waves-1: Quantum MechanicsDokumen16 halamanEngineering Physics PHY-109 Waves-1: Quantum MechanicsShivanshu PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- WavesDokumen11 halamanWavesdilsharakaviBelum ada peringkat
- WavesDokumen11 halamanWavesIfrah ZiaBelum ada peringkat
- Basics of Seismic ProspectingDokumen68 halamanBasics of Seismic Prospectingshubham panchalBelum ada peringkat
- Radio Wave PropagationDokumen63 halamanRadio Wave PropagationMike FinezaBelum ada peringkat
- The Nature and Properties of WavesDokumen24 halamanThe Nature and Properties of WavesMeryl PalenciaBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Placement Physics Waves and Optics: SoundDokumen6 halamanAdvanced Placement Physics Waves and Optics: SoundMartín FigueroaBelum ada peringkat
- Handout 8 WavesDokumen6 halamanHandout 8 WavesMary Grace AcostaBelum ada peringkat
- WavesDokumen31 halamanWavesArchana MallaBelum ada peringkat
- Reflection, Refraction, and DiffractionDokumen18 halamanReflection, Refraction, and Diffractionjaymart villartaBelum ada peringkat
- X PhysicsDokumen4 halamanX PhysicsTapas BanerjeeBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Wave PhenomenaDokumen43 halamanBasic Wave Phenomena李彊Belum ada peringkat
- Aqa A Level Physics Required PracticalsDokumen8 halamanAqa A Level Physics Required PracticalsLouisBelum ada peringkat
- Waves Notes Physics o LevelDokumen20 halamanWaves Notes Physics o Levelkwikiriza safiruBelum ada peringkat
- Quantum Photonics: Optoelectronics and Photonics: Wave Nature of LightDokumen31 halamanQuantum Photonics: Optoelectronics and Photonics: Wave Nature of Lightgafeer fableBelum ada peringkat
- Phy WavesDokumen18 halamanPhy WavesAndy HungBelum ada peringkat
- Weekly Learning Activity Sheets General Physics 1 Grade 12, Quarter 2, Week 4Dokumen4 halamanWeekly Learning Activity Sheets General Physics 1 Grade 12, Quarter 2, Week 4Shekaina Faith Cuizon Lozada100% (2)
- Physics2 Model AnswersDokumen11 halamanPhysics2 Model AnswersMoeezBelum ada peringkat
- Waves and Wave EffectsDokumen18 halamanWaves and Wave EffectsShadyBelum ada peringkat
- V Speed of Light in A Given MaterialDokumen4 halamanV Speed of Light in A Given MaterialbeaulajenishBelum ada peringkat
- Interference of Light by Mr. Charis Israel AnchaDokumen11 halamanInterference of Light by Mr. Charis Israel AnchaCharis Israel Ancha100% (1)
- Physics 11: Chapter 17: Reflection and RefractionDokumen4 halamanPhysics 11: Chapter 17: Reflection and Refractionclim3953Belum ada peringkat
- فيزياء لغات - 2 ثانوي - ترم 1 - مذكرة 1 - ذاكروليDokumen30 halamanفيزياء لغات - 2 ثانوي - ترم 1 - مذكرة 1 - ذاكروليKerlos SaeedBelum ada peringkat
- TG Science 9Dokumen41 halamanTG Science 9Norweena QuinonesBelum ada peringkat
- IGCSE Physics NotesDokumen15 halamanIGCSE Physics NotesOmkar Bhupesh RaneBelum ada peringkat
- Seismic Refraction Method - Lecture - 21Dokumen24 halamanSeismic Refraction Method - Lecture - 21ramatokadar60Belum ada peringkat
- On Festivals and FastingDokumen4 halamanOn Festivals and FastingOrangeGuitaristBelum ada peringkat
- Waking Up: Author Finished? TopicsDokumen2 halamanWaking Up: Author Finished? TopicsDanKimberleyBelum ada peringkat
- Kalam Cosmological ArgumentDokumen1 halamanKalam Cosmological ArgumentDanKimberleyBelum ada peringkat
- Indoctrination of ChildrenDokumen1 halamanIndoctrination of ChildrenDanKimberleyBelum ada peringkat
- Lord of The Flies: Author Date Read Fiction / Non-Fiction Rating /10 TopicsDokumen1 halamanLord of The Flies: Author Date Read Fiction / Non-Fiction Rating /10 TopicsDanKimberleyBelum ada peringkat
- The Problem of EvilDokumen1 halamanThe Problem of EvilDanKimberleyBelum ada peringkat
- Pascal's WagerDokumen1 halamanPascal's WagerDanKimberleyBelum ada peringkat
- StamitzDokumen2 halamanStamitzDanKimberleyBelum ada peringkat
- Paper 3 Things: Means Add Raw Uncertainty, Multiply or Divide Means Add Percentage UncertaintyDokumen1 halamanPaper 3 Things: Means Add Raw Uncertainty, Multiply or Divide Means Add Percentage UncertaintyDanKimberleyBelum ada peringkat
- Force Against Velocity: Circular MotionDokumen1 halamanForce Against Velocity: Circular MotionDanKimberleyBelum ada peringkat
- Errors and UncertaintyDokumen1 halamanErrors and UncertaintyDanKimberleyBelum ada peringkat
- Waves 2Dokumen1 halamanWaves 2DanKimberleyBelum ada peringkat
- Adding ForcesDokumen1 halamanAdding ForcesDanKimberleyBelum ada peringkat
- Core Practical 11 - Dan KimberleyDokumen1 halamanCore Practical 11 - Dan KimberleyDanKimberleyBelum ada peringkat
- Fluorescent TubesDokumen1 halamanFluorescent TubesDanKimberleyBelum ada peringkat
- Practical 9Dokumen2 halamanPractical 9DanKimberleyBelum ada peringkat
- Adding ForcesDokumen2 halamanAdding ForcesDanKimberleyBelum ada peringkat
- Gravitational and Kinetic EnergiesDokumen1 halamanGravitational and Kinetic EnergiesDanKimberleyBelum ada peringkat
- Adding ForcesDokumen2 halamanAdding ForcesDanKimberleyBelum ada peringkat
- Spreadsheet 5Dokumen3 halamanSpreadsheet 5DanKimberleyBelum ada peringkat
- Core Practical 5Dokumen3 halamanCore Practical 5DanKimberley100% (1)
- Practical 9 Take 2Dokumen3 halamanPractical 9 Take 2DanKimberleyBelum ada peringkat
- Core Practical 9Dokumen4 halamanCore Practical 9DanKimberleyBelum ada peringkat
- Core Practical 2: Measuring Resistivity: 1 PreparationDokumen3 halamanCore Practical 2: Measuring Resistivity: 1 PreparationDanKimberleyBelum ada peringkat
- Power in Electric CircuitsDokumen1 halamanPower in Electric CircuitsDanKimberleyBelum ada peringkat
- Core Practical 4Dokumen4 halamanCore Practical 4DanKimberleyBelum ada peringkat
- Power in Electric CircuitsDokumen4 halamanPower in Electric CircuitsDanKimberleyBelum ada peringkat
- Semiconductors: Semiconductors Are Generally Solid Materials With Small Numbers of Delocalised Electrons Free ToDokumen2 halamanSemiconductors: Semiconductors Are Generally Solid Materials With Small Numbers of Delocalised Electrons Free ToDanKimberleyBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid Movement: Laminar FlowDokumen2 halamanFluid Movement: Laminar FlowDanKimberleyBelum ada peringkat