Concept Map
Diunggah oleh
Mel Izhra N. MargateHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Concept Map
Diunggah oleh
Mel Izhra N. MargateHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
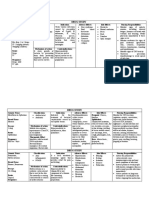
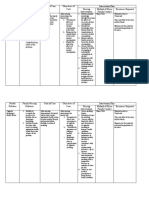
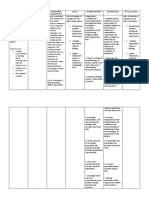
Environmental Factors:
Risk Factors:
Systemic Lupus Erythematusos Susceptibility to certain
Genetic
viruses
Predisposition
Hormonal Abnormality
Ultraviolet radiation
Medications
Pathophysiology Hydralazine
The immune system starts to develop Procainamide hydrochloride
antibodies to the nuclear antigen. B cells begin Penicillin
Clinical Manifestations: to overproduce antibodies and antigens with Isonicotonic acid hyrazide
the help of multiple cytokines such as B- Quinidine
Fever
lymphocyte stimulator, which is overexpressed
Malaise
in SLE. The antibodies and antigen antibody
Weight loss and anorexia
complexes and have the propensity to get
Subacute cutaneous
trapped in the capillaries of visceral structures.
erythematosus
Acute cutaneous lesion The antibodies also act to destroy host cells. It Diagnostic Findings:
consisting of a butterfly is thought that those two mechanisms are
shaped erythematusos responsible for majority of the clinical o Complete history and
rash across the bridge of manifestations of this disease process. It is physical examination
the nose and cheeks hypothesized that the immunoregulatory and blood tests.
Papulosquamous or disturbances is brought about by some o Anti-DNA – antibody that
annular lupus combination of four distinct factors: genetic, develops against DNA
erythematusos immunologic, hormonal, and environment. patient’s oeweqwn DNA
Arthralgia o Anti-ds DNA- antibody
Arthritis against DNA that is
Joint swelling, tenderness highly specific to SLE,
and pain on movement. which helps differentiate
Myocarditis it from drug induced
Hypertension lupus.
o Anti- Sm – antibody against
Sm, which is a specific
protein fround in the
nucleus.
o CBC may reveal anemia
Nursing Management:
Medical Management:
Educate the patient about the
importance of continuing Regular monitoring to assess disease activity and
prescribed medication. therapeutic effectiveness.
Nurse should also screen the Monoclonal antibodies, cortcicosteroids, antimalarial
patient for osteoporosis, agents.
because long term use of Belimumab- treatment for SLE.
corticosteroids increase the IV administration of corticosteroids is an alternative to
incidence of osteoporosis. traditional high doses administration.
Educating the patient regarding Anti malarial medications- Hydroxychloroquine, is an
calcium and Vitamin D effective for managing cutaneous musculoskeletal and
supplementation daily is mild systemic features of SLE.
encourage. NSAIDs- used for minor clinical manifestations are often
The patient is reminded of the used in conjuction with corticosteroid.
importance of monitoring Immunosuppressive agents used because of their effect on
because of increased risk of overall immune function.
systemic involvement
including renal and
cardiovascular effects.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Leukemia PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDokumen4 halamanLeukemia PATHOPHYSIOLOGYElle Rosales50% (2)
- PEDIA - Drug Study & NCPDokumen24 halamanPEDIA - Drug Study & NCPCzarina Mae Lomboy100% (1)
- FNCP (Cigarette Smoking, Faulty Eating Habits and Alcohol Drinking) BuiuibDokumen4 halamanFNCP (Cigarette Smoking, Faulty Eating Habits and Alcohol Drinking) BuiuibMel Izhra N. MargateBelum ada peringkat
- GB Syndrome..Dokumen13 halamanGB Syndrome..Shitaljit Irom100% (1)
- Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus: SGD B3Dokumen41 halamanCutaneous Lupus Erythematosus: SGD B3Che Haniff100% (2)
- B. 11 Situation - Care of Client With Problems in Inflammatory & Immunologic ResponseDokumen4 halamanB. 11 Situation - Care of Client With Problems in Inflammatory & Immunologic ResponseSOLEIL LOUISE LACSON MARBAS100% (1)
- Haematology Test Name Results Biological Reference Interval Units Specimen Test Method CBC - Complete Blood CountDokumen8 halamanHaematology Test Name Results Biological Reference Interval Units Specimen Test Method CBC - Complete Blood CountArun DheekshahBelum ada peringkat
- Immunologic (Autoimmune) Disorders: Risk Factors Diagnostic TestsDokumen7 halamanImmunologic (Autoimmune) Disorders: Risk Factors Diagnostic Testsfebie pachecoBelum ada peringkat
- MCQs + SEQs Medical Physics Midterm Exam Paper-Fall 2020Dokumen3 halamanMCQs + SEQs Medical Physics Midterm Exam Paper-Fall 2020Ali Nouman100% (1)
- (Walter Podolny, JR., John B. Scalzi) Construction PDFDokumen354 halaman(Walter Podolny, JR., John B. Scalzi) Construction PDFJuan Carlos CastroBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study PrednisoloneDokumen2 halamanDrug Study Prednisoloneunnamed personBelum ada peringkat
- General LPG Installation Guide PDFDokumen60 halamanGeneral LPG Installation Guide PDFgheorghe garduBelum ada peringkat
- 8NCP's For ColostomyDokumen23 halaman8NCP's For ColostomyCzarina Porciuncula79% (14)
- Management of Patients With Immune Deficiency DisordersDokumen11 halamanManagement of Patients With Immune Deficiency DisordersmasheennavirgoBelum ada peringkat
- 8 Drug Study NCM 112Dokumen15 halaman8 Drug Study NCM 112Marie Kelsey Acena MacaraigBelum ada peringkat
- Autoimmune DisordersDokumen88 halamanAutoimmune DisordersJR Rolf NeuqeletBelum ada peringkat
- Med 1.11 - SleDokumen5 halamanMed 1.11 - SleZazaBelum ada peringkat
- Caisip NCM109Dokumen3 halamanCaisip NCM109Vannesa TarifaBelum ada peringkat
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Case: Pathogenisis:: NmcastroDokumen5 halamanSystemic Lupus Erythematosus Case: Pathogenisis:: NmcastroAngelo ErispeBelum ada peringkat
- Brand and Generic Name Action Uses/ Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationDokumen12 halamanBrand and Generic Name Action Uses/ Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationBiggs JuntillaBelum ada peringkat
- Western Mindanao State University College of Nursing: Republic of The PhilippinesDokumen18 halamanWestern Mindanao State University College of Nursing: Republic of The PhilippinesIvy VillalobosBelum ada peringkat
- 2C Franche Pharma1Dokumen10 halaman2C Franche Pharma1Iris FrancheBelum ada peringkat
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: XXX DCEM2 Toulouse Purpan Medical School January 7 2009Dokumen3 halamanSystemic Lupus Erythematosus: XXX DCEM2 Toulouse Purpan Medical School January 7 2009Bren OlivaBelum ada peringkat
- Immunology NotesDokumen14 halamanImmunology NotesJasmine Bernadette CubillaBelum ada peringkat
- Concept Mapping: Hodgskin'S Disease ComplicationDokumen4 halamanConcept Mapping: Hodgskin'S Disease ComplicationAsterlyn ConiendoBelum ada peringkat
- Bulous PEMPHIGOID - SGIMDokumen1 halamanBulous PEMPHIGOID - SGIMAbdul Hamid AlraiyesBelum ada peringkat
- Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDokumen3 halamanSystemic Lupus Erythematosussaranya amuBelum ada peringkat
- SleDokumen33 halamanSleZaira HussainBelum ada peringkat
- DRUG STUDY (Head Injury)Dokumen3 halamanDRUG STUDY (Head Injury)Paula Suplico NiangarBelum ada peringkat
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Authors: Maliha F ShaikhDokumen6 halamanSystemic Lupus Erythematosus: Authors: Maliha F ShaikhAnonymous hF5zAdvwCCBelum ada peringkat
- L7 Is AutoimmunityDokumen3 halamanL7 Is AutoimmunityErickson MoragaBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment of Immune FunctionDokumen175 halamanAssessment of Immune FunctionjeremiahBelum ada peringkat
- Cns - Infections f2022 Slow Virus and Prion DiseasesDokumen14 halamanCns - Infections f2022 Slow Virus and Prion DiseasesMadison MillwoodBelum ada peringkat
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus SLE - A Review of CliDokumen5 halamanSystemic Lupus Erythematosus SLE - A Review of CliJafrinta Irma R.A.Belum ada peringkat
- AutoimmuneDokumen7 halamanAutoimmuneK-idol LiveBelum ada peringkat
- Bibliography: Life Span - Philadelphia, PA 19103: F.A. Davis CompanyDokumen5 halamanBibliography: Life Span - Philadelphia, PA 19103: F.A. Davis CompanyCarlos LleverBelum ada peringkat
- CVS Blood PDFDokumen103 halamanCVS Blood PDF182 ROHIL HBelum ada peringkat
- CCO ICI Based Therapy Slides2Dokumen26 halamanCCO ICI Based Therapy Slides2Yasar HammorBelum ada peringkat
- Artrite ReumatoideDokumen14 halamanArtrite ReumatoideAndreBelum ada peringkat
- Mixed Connective Tissue Disease: NmcastroDokumen7 halamanMixed Connective Tissue Disease: NmcastroAngelo ErispeBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study: 2.5 To 10 Mg/dayDokumen4 halamanDrug Study: 2.5 To 10 Mg/dayJoy SaavedraBelum ada peringkat
- ARTIGO 2 - Immunosenescence As A Convergence Pathway in NeurodegenerationDokumen18 halamanARTIGO 2 - Immunosenescence As A Convergence Pathway in NeurodegenerationthomazdoliveiraBelum ada peringkat
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic Name: Brand Name: Classification: CnsDokumen4 halamanName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic Name: Brand Name: Classification: CnsRoxy TofyBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 29 Child With CancerDokumen9 halamanChapter 29 Child With CancerMARCERA JERALDINE ALESSA P.Belum ada peringkat
- Classification: Indication: CNS: Ototoxicity-: Name: L.Y.C Age/Sex: 59 Y.o/ FDokumen8 halamanClassification: Indication: CNS: Ototoxicity-: Name: L.Y.C Age/Sex: 59 Y.o/ FEden Marie FranciscoBelum ada peringkat
- Kish Drug Study and NCPDokumen5 halamanKish Drug Study and NCPKish Gabriel GanadoBelum ada peringkat
- Eisenberg 2012Dokumen13 halamanEisenberg 2012Juan G. Ovalles B.Belum ada peringkat
- Drug Name Dopamine Indications Contraindications Mechanism of Action Common Side-Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDokumen4 halamanDrug Name Dopamine Indications Contraindications Mechanism of Action Common Side-Effects Nursing ConsiderationsPRINCESS LARA CASILAOBelum ada peringkat
- J Mpmed 2019 11 015Dokumen4 halamanJ Mpmed 2019 11 015egagusmelaBelum ada peringkat
- Baby Kiran Aged 7 Years Brought To The Emergency Opd Accomp: ScenarioDokumen22 halamanBaby Kiran Aged 7 Years Brought To The Emergency Opd Accomp: ScenariobhavanaBelum ada peringkat
- DS - RituximabDokumen3 halamanDS - RituximabKathryne May JinonBelum ada peringkat
- CHAPTER 10 ReviewerDokumen5 halamanCHAPTER 10 ReviewerHannah BuquironBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study: NCM 106 PharmacologyDokumen4 halamanDrug Study: NCM 106 PharmacologyLore Anne Mhae SantosBelum ada peringkat
- DrugStudy - CamaristaColeenMaeC (BSN III-G) (Prednisone)Dokumen2 halamanDrugStudy - CamaristaColeenMaeC (BSN III-G) (Prednisone)Coleen Mae CamaristaBelum ada peringkat
- Myocarditisandpericarditis: Philip Hunter Spotts,, Fan ZhouDokumen14 halamanMyocarditisandpericarditis: Philip Hunter Spotts,, Fan Zhoumiltoncaballero5Belum ada peringkat
- Autoimmune Mash - Up FinalDokumen38 halamanAutoimmune Mash - Up Finalapi-546809761Belum ada peringkat
- Topik 4 PPT Kuliah Gawat Darurat ST Vene Medi Oldr - 092214Dokumen24 halamanTopik 4 PPT Kuliah Gawat Darurat ST Vene Medi Oldr - 092214raisya nabila ayudyaBelum ada peringkat
- Care of Preschoolers With Health ProblemsDokumen5 halamanCare of Preschoolers With Health ProblemsmajoodhBelum ada peringkat
- Diagnosis and Management of Salivar y Gla ND Infec Tions: Eric R. CarlsonDokumen20 halamanDiagnosis and Management of Salivar y Gla ND Infec Tions: Eric R. Carlsonary wisma dewiBelum ada peringkat
- 04 ImmunologyDokumen35 halaman04 ImmunologyKristine Mae ApuradoBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen7 halamanDrug StudyHerwincayeBelum ada peringkat
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: June 1& 8, 2015Dokumen94 halamanSystemic Lupus Erythematosus: June 1& 8, 2015Azizan HannyBelum ada peringkat
- Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy and Its VariantsDokumen19 halamanChronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy and Its VariantsFlea CidBelum ada peringkat
- 2023-Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus-Risks, Mechanism and Therapeutica TargetsDokumen16 halaman2023-Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus-Risks, Mechanism and Therapeutica TargetsCinantya Meyta SariBelum ada peringkat
- Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndromes: Review ArticleDokumen10 halamanAutoimmune Polyendocrine Syndromes: Review Articleinterna MANADOBelum ada peringkat
- PHYSICALm KNDokumen17 halamanPHYSICALm KNMel Izhra N. MargateBelum ada peringkat
- Gender & Human Sexuality: BY: Group IDokumen4 halamanGender & Human Sexuality: BY: Group IMel Izhra N. MargateBelum ada peringkat
- Almon D: AlmondDokumen28 halamanAlmon D: AlmondMel Izhra N. MargateBelum ada peringkat
- Symposium Article: Psychological Aspects of Depression in Cancer Patients: An UpdateDokumen4 halamanSymposium Article: Psychological Aspects of Depression in Cancer Patients: An UpdateMel Izhra N. MargateBelum ada peringkat
- A Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in Disaster Readiness and Risk ReductionDokumen4 halamanA Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in Disaster Readiness and Risk ReductionMel Izhra N. MargateBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study CHFDokumen16 halamanDrug Study CHFIzhra MargateBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDokumen3 halamanAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationMel Izhra N. MargateBelum ada peringkat
- Epi PptyyyDokumen18 halamanEpi PptyyyMel Izhra N. MargateBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care PlanDokumen4 halamanNursing Care PlanMel Izhra N. MargateBelum ada peringkat
- DM Drug StudyDokumen17 halamanDM Drug StudyMel Izhra N. MargateBelum ada peringkat
- 3ros & PeDokumen4 halaman3ros & PeMel Izhra N. MargateBelum ada peringkat
- Significant: BullousDokumen6 halamanSignificant: BullousMel Izhra N. MargateBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of Pathophysiology - Bullock, ShaneDokumen2 halamanPrinciples of Pathophysiology - Bullock, ShaneMel Izhra N. MargateBelum ada peringkat
- Malaria: Control ProgramDokumen40 halamanMalaria: Control ProgramMel Izhra N. MargateBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Goal Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Impaired Physical Mobility Related ToDokumen3 halamanAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Goal Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Impaired Physical Mobility Related ToMel Izhra N. MargateBelum ada peringkat
- Objectives Content Outline Methods of Instruction Time Alloted Resources Plan For Evaluation General Objective: Human Material FinancialDokumen2 halamanObjectives Content Outline Methods of Instruction Time Alloted Resources Plan For Evaluation General Objective: Human Material FinancialMel Izhra N. MargateBelum ada peringkat
- Women and ChildDokumen10 halamanWomen and ChildMel Izhra N. MargateBelum ada peringkat
- Health and Wellnes ProgramsDokumen12 halamanHealth and Wellnes ProgramsIzhra Margate100% (1)
- Philippine Reproductive HealthDokumen14 halamanPhilippine Reproductive HealthMel Izhra N. MargateBelum ada peringkat
- Excreta and Sewage DisposalDokumen51 halamanExcreta and Sewage DisposalMel Izhra N. MargateBelum ada peringkat
- Causes of Morbidity in Barangay 98 Camansihay, Tacloban CityDokumen6 halamanCauses of Morbidity in Barangay 98 Camansihay, Tacloban CityMel Izhra N. MargateBelum ada peringkat
- BALANITISDokumen2 halamanBALANITISMel Izhra N. MargateBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study: Classification Contraindication Classification ContraindicationDokumen6 halamanDrug Study: Classification Contraindication Classification ContraindicationMel Izhra N. MargateBelum ada peringkat
- Air PollutionDokumen14 halamanAir PollutionIzhra MargateBelum ada peringkat
- Buddhism Banned in CHINADokumen17 halamanBuddhism Banned in CHINAMel Izhra N. MargateBelum ada peringkat
- OsteoarthritisDokumen1 halamanOsteoarthritisMel Izhra N. MargateBelum ada peringkat
- DMNCP AnxietyDokumen3 halamanDMNCP AnxietyMel Izhra N. MargateBelum ada peringkat
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity DisorderDokumen4 halamanAttention Deficit Hyperactivity DisorderMel Izhra N. MargateBelum ada peringkat
- Red Hat Ceph Storage-1.2.3-Ceph Configuration Guide-en-US PDFDokumen127 halamanRed Hat Ceph Storage-1.2.3-Ceph Configuration Guide-en-US PDFJony NguyễnBelum ada peringkat
- Balkhu Squatter SettlementDokumen10 halamanBalkhu Squatter SettlementShramina ShresthaBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 3 Module 2 Simple Annuity (Savings Annuity and Payout Annuity)Dokumen8 halamanTopic 3 Module 2 Simple Annuity (Savings Annuity and Payout Annuity)millerBelum ada peringkat
- LLB IV Sem GST Unit I Levy and Collection Tax by DR Nisha SharmaDokumen7 halamanLLB IV Sem GST Unit I Levy and Collection Tax by DR Nisha Sharmad. CBelum ada peringkat
- Almutairy / Musa MR: Boarding PassDokumen1 halamanAlmutairy / Musa MR: Boarding PassMusaBelum ada peringkat
- BERKLYNInformation SheetDokumen6 halamanBERKLYNInformation SheetvillatoreubenBelum ada peringkat
- Put Them Into A Big Bowl. Serve The Salad in Small Bowls. Squeeze Some Lemon Juice. Cut The Fruits Into Small Pieces. Wash The Fruits. Mix The FruitsDokumen2 halamanPut Them Into A Big Bowl. Serve The Salad in Small Bowls. Squeeze Some Lemon Juice. Cut The Fruits Into Small Pieces. Wash The Fruits. Mix The FruitsNithya SweetieBelum ada peringkat
- Oracle® Secure Backup: Installation and Configuration Guide Release 10.4Dokumen178 halamanOracle® Secure Backup: Installation and Configuration Guide Release 10.4andrelmacedoBelum ada peringkat
- Consumer Price SummaryDokumen5 halamanConsumer Price SummaryKJ HiramotoBelum ada peringkat
- Aruba 8325 Switch SeriesDokumen51 halamanAruba 8325 Switch SeriesgmtrlzBelum ada peringkat
- CP AssignmentDokumen5 halamanCP AssignmentMSSM EngineeringBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 3 - Analyzing The Marketing EnvironmentDokumen28 halamanTopic 3 - Analyzing The Marketing Environmentmelissa chlBelum ada peringkat
- Cs09 404 Programming Paradigm (Module 1 Notes)Dokumen24 halamanCs09 404 Programming Paradigm (Module 1 Notes)Rohith BhaskaranBelum ada peringkat
- Available Online Through: International Journal of Mathematical Archive-4 (12), 2013Dokumen4 halamanAvailable Online Through: International Journal of Mathematical Archive-4 (12), 2013Gwen WalkerBelum ada peringkat
- InfltiDokumen13 halamanInfltiLEKH021Belum ada peringkat
- Nationalisation of Insurance BusinessDokumen12 halamanNationalisation of Insurance BusinessSanjay Ram Diwakar50% (2)
- Steinecker Boreas: Wort Stripping of The New GenerationDokumen16 halamanSteinecker Boreas: Wort Stripping of The New GenerationAlejandro Javier Delgado AraujoBelum ada peringkat
- 20131022-Additive Manufacturing & Allied Technologies, PuneDokumen56 halaman20131022-Additive Manufacturing & Allied Technologies, Puneprakush_prakushBelum ada peringkat
- Provable Security - 8th International Conference, ProvSec 2014Dokumen364 halamanProvable Security - 8th International Conference, ProvSec 2014alahbarBelum ada peringkat
- Luigi Cherubini Requiem in C MinorDokumen8 halamanLuigi Cherubini Requiem in C MinorBen RutjesBelum ada peringkat
- Urban LifestyleDokumen27 halamanUrban LifestyleNindy AslindaBelum ada peringkat
- D-Dimer DZ179A Parameters On The Beckman AU680 Rev. ADokumen1 halamanD-Dimer DZ179A Parameters On The Beckman AU680 Rev. AAlberto MarcosBelum ada peringkat
- Calculating Measures of Position Quartiles Deciles and Percentiles of Ungrouped DataDokumen43 halamanCalculating Measures of Position Quartiles Deciles and Percentiles of Ungrouped DataRea Ann ManaloBelum ada peringkat
- Acm Queue PDFDokumen12 halamanAcm Queue PDFShubham Anil ShahareBelum ada peringkat
- Atmosphere Study Guide 2013Dokumen4 halamanAtmosphere Study Guide 2013api-205313794Belum ada peringkat
- Upend RA Kumar: Master List of Approved Vendors For Manufacture and Supply of Electrical ItemsDokumen42 halamanUpend RA Kumar: Master List of Approved Vendors For Manufacture and Supply of Electrical Itemssantosh iyerBelum ada peringkat