Nlreader - dll@BookID 114778&FileName Page 3
Diunggah oleh
minh thếDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Nlreader - dll@BookID 114778&FileName Page 3
Diunggah oleh
minh thếHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
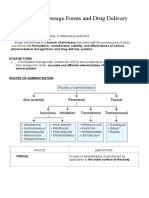
THE DESIGN OF DOSAGE FORMS
general ways, by passive diffusion and by specialized The physical form of the oral dosage form will also
transport mechanisms. In passive diffusion, which is influence absorption rate and onset of action, with
thought to control the absorption of most drugs, the solutions acting faster than suspensions, which in turn
process is driven by the concentration gradient that generally act faster than capsules and tablets. Dosage
exists across the cellular barrier, with drug molecules forms can thus be listed in order of time of onset of
passing from regions of high to those of low concen- therapeutic effect (Table 1.2). However, all drugs, irre-
tration. Lipid solubility and the degree of ionization of
the drug at the absorbing site influence the rate of dif- Table 1 .2 Variation in time of onset of action for
fusion. Several specialized transport mechanisms are different dosage forms
postulated, including active and facilitated transport.
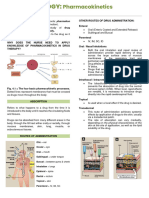
Once absorbed, the drug can exert a therapeutic effect Time of onset of action Dosage forms
either locally or at a site of action remote from that of Seconds i.v. injections
administration. In the latter case the drug has to be
Minutes i.m. and s.c. injections,
transported in body fluids (Fig. 1.1). buccal tablets, aerosols, gases
When the drug is administered from dosage forms
designed to deliver via the buccal, respiratory, rectal, Minutes to hours Short-term depot injections,
solutions, suspensions,
intramuscular or subcutaneous routes, it passes powders, granules, capsules,
directly into the blood-stream from absorbing tissues, tablets, modified-release
but the intravenous route is the most direct of all. tablets
When delivered by the oral route the onset of drug Several hours Enteric-coated formulations
action will be delayed because of the required transit Days Depot injections, implants
time in the gastrointestinal tract, the absorption
Varies Topical preparations
process and hepatoenteric blood circulation features.
Fig. 1.1 Pathways a drug may take following the administration of a dosage form by different route.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Handbook of Drug Interaction and the Mechanism of InteractionDari EverandHandbook of Drug Interaction and the Mechanism of InteractionPenilaian: 1 dari 5 bintang1/5 (1)
- Pharmacology- The Molecular Dance: Understanding Drug Interactions: Harmony and Chaos: The Symphony of Drug InteractionsDari EverandPharmacology- The Molecular Dance: Understanding Drug Interactions: Harmony and Chaos: The Symphony of Drug InteractionsBelum ada peringkat
- Respon Obat: Faktor Fisiologis Dan PatologisDokumen27 halamanRespon Obat: Faktor Fisiologis Dan Patologisfauziah qurrota a'yuniBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacokinetics and PharmacodynamicsDokumen8 halamanPharmacokinetics and PharmacodynamicsAnonymous vKjGGgBelum ada peringkat
- Week 4 - Pharma LecDokumen11 halamanWeek 4 - Pharma LecJayla MarieBelum ada peringkat
- 2 Drug AdministrationDokumen93 halaman2 Drug AdministrationNajib HPBelum ada peringkat
- TMDR PharmaChapter3Dokumen8 halamanTMDR PharmaChapter3JkimBelum ada peringkat
- BIOPHARMACEUTICS Part1aDokumen225 halamanBIOPHARMACEUTICS Part1aAmirabbas SaffariBelum ada peringkat
- Week 2 - Drugs and The BodyDokumen18 halamanWeek 2 - Drugs and The BodyDino MicaBelum ada peringkat
- What Is PharmacologyDokumen5 halamanWhat Is PharmacologyShardendu MishraBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Absorption-DistributionDokumen60 halamanDrug Absorption-DistributionRuqayya AdamuBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction and Routes of Drug ADM: Terminologi PenjelasanDokumen6 halamanIntroduction and Routes of Drug ADM: Terminologi PenjelasanAmirah AnfBelum ada peringkat
- Routes of Drug Administration and Dosage FormsDokumen39 halamanRoutes of Drug Administration and Dosage FormsAditya RathoreBelum ada peringkat
- Pharma NotesDokumen6 halamanPharma NotesKatrina MercadoBelum ada peringkat
- Module 4. NotesDokumen40 halamanModule 4. NotesEdrese AguirreBelum ada peringkat
- Route of Drug AdministrationDokumen4 halamanRoute of Drug AdministrationMr. PREMNATH D. 930Belum ada peringkat
- In This ExperimentDokumen4 halamanIn This ExperimentIzzati FazeliBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacokinetics and Drug MetabolismDokumen54 halamanPharmacokinetics and Drug MetabolismDeirdreBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Pharmacology, 10 R's To Drugs, Nursing ProcessDokumen16 halamanIntroduction To Pharmacology, 10 R's To Drugs, Nursing ProcessJasmin AdoraBelum ada peringkat
- Oral (PO) - Per Os Latin Phrase Meaning by Way of Mouth: HarmacokineticsDokumen10 halamanOral (PO) - Per Os Latin Phrase Meaning by Way of Mouth: Harmacokineticsdlneisha61Belum ada peringkat
- PHBP Prelims - ReviewerDokumen39 halamanPHBP Prelims - ReviewerAia RohaBelum ada peringkat
- Essay: Oral RouteDokumen2 halamanEssay: Oral RouteSHEENA JOY HABITANBelum ada peringkat
- Intramuscular InjectionDokumen2 halamanIntramuscular InjectionBlazy InhumangBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacology Transes - Unit 1Dokumen13 halamanPharmacology Transes - Unit 1venturaphoenixBelum ada peringkat
- Nasib Obat Dalam Tubuh (Farmakokinetika) : Apa Yang Terjadi Pada Obat Setelah Masuk Ke Tubuh Kita ?Dokumen30 halamanNasib Obat Dalam Tubuh (Farmakokinetika) : Apa Yang Terjadi Pada Obat Setelah Masuk Ke Tubuh Kita ?Charisatun NawafilaBelum ada peringkat
- Share Pharmacology Book 1Dokumen101 halamanShare Pharmacology Book 1Jmcle AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To PharmacologyDokumen136 halamanIntroduction To Pharmacologycathlynjoy.marsamoloBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacokinetics and PharmacodynamicsDokumen113 halamanPharmacokinetics and PharmacodynamicsEvelyn MedinaBelum ada peringkat
- 1 - C PharmacokineticDokumen14 halaman1 - C PharmacokineticMaoth AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 - PsychopharmacologyDokumen11 halamanChapter 4 - Psychopharmacologymanilyn dacoBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacology: Alo AquinoDokumen54 halamanPharmacology: Alo AquinotychynBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacology HandoutDokumen84 halamanPharmacology Handoutnanashimii100% (4)
- Document 2Dokumen9 halamanDocument 2zoha fatimaBelum ada peringkat
- Pharma - 2020 General Principles of Drug ActionDokumen163 halamanPharma - 2020 General Principles of Drug Actiongelean payodBelum ada peringkat
- Lectura FX Cinética1Dokumen7 halamanLectura FX Cinética1Jeraldiin BeltranBelum ada peringkat
- Pharma 1,2Dokumen10 halamanPharma 1,2Ahmed KafajiBelum ada peringkat
- General Pharmacology Nina 2017-2018newDokumen33 halamanGeneral Pharmacology Nina 2017-2018newSheba RoymonBelum ada peringkat
- Morgan 140 149Dokumen10 halamanMorgan 140 149Marta DumitracheBelum ada peringkat
- Pharma Lesson 2Dokumen5 halamanPharma Lesson 2BabyJane GRomeroBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Pharmacology: Dr. Zaid Al-AttarDokumen29 halamanIntroduction To Pharmacology: Dr. Zaid Al-Attarعلي حميد فريحBelum ada peringkat
- Pilapil PharmacologyDokumen6 halamanPilapil PharmacologyIza FaboresBelum ada peringkat
- Route of AdministrationDokumen10 halamanRoute of Administration言爱邦Belum ada peringkat
- المحاضرة ٥٥٦الاولى سيوتيكس 1-1Dokumen5 halamanالمحاضرة ٥٥٦الاولى سيوتيكس 1-1Kareem FayedBelum ada peringkat
- Factors Affecting Drug AbsorptionDokumen11 halamanFactors Affecting Drug AbsorptionClarilaine JavierBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacokinetics Lecture NotesDokumen22 halamanPharmacokinetics Lecture Notesbmhsh100% (2)
- Pharmacology Lab (1) : Routes of Drug AdministrationDokumen14 halamanPharmacology Lab (1) : Routes of Drug AdministrationBotan AbdullahBelum ada peringkat
- Adventist Medical Center College School of Nursing: Daverly M. Cañeda, R.N., M.NDokumen174 halamanAdventist Medical Center College School of Nursing: Daverly M. Cañeda, R.N., M.NEvelyn MedinaBelum ada peringkat
- 12 Chapter 1Dokumen67 halaman12 Chapter 1Michael Ballacky100% (1)
- Pharma CompilationDokumen113 halamanPharma CompilationGulayan, Renz Bryelle T.Belum ada peringkat
- NCM 106 Drugs and The BodyDokumen46 halamanNCM 106 Drugs and The BodyYra JhaneBelum ada peringkat
- Winona'SDokumen4 halamanWinona'SWinona Louise Anne CarpioBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacology LectureDokumen27 halamanPharmacology LectureCurtney PedriaBelum ada peringkat
- PHARMACOKINETICSDokumen4 halamanPHARMACOKINETICSMichiko CiriacoBelum ada peringkat
- 1introDokumen158 halaman1introDea MaharanisBelum ada peringkat
- NCM 106-CompDokumen26 halamanNCM 106-Compprincess pantinopleBelum ada peringkat
- Routes of Administration of DrugDokumen40 halamanRoutes of Administration of DrugNova AzzuEra Sweetygirl100% (1)
- Introduction To Dosage Forms and Drug Delivery Systems: PharmaceuticsDokumen20 halamanIntroduction To Dosage Forms and Drug Delivery Systems: PharmaceuticsJelight Faith Salero GachoBelum ada peringkat
- Biopharmaceutics and Drug Delivery SystemsDokumen15 halamanBiopharmaceutics and Drug Delivery SystemsSabiruddin Mirza DipuBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacology LecturesDokumen7 halamanPharmacology LecturesMutya XDBelum ada peringkat
- EVALUATION OF THE INFLUENCE OF TWO DIFFERENT SYSTEMS OF ANALGESIA AND THE NASOGASTRIC TUBE ON THE INCIDENCE OF POSTOPERATIVE NAUSEA AND VOMITING IN CARDIAC SURGERYDari EverandEVALUATION OF THE INFLUENCE OF TWO DIFFERENT SYSTEMS OF ANALGESIA AND THE NASOGASTRIC TUBE ON THE INCIDENCE OF POSTOPERATIVE NAUSEA AND VOMITING IN CARDIAC SURGERYBelum ada peringkat
- Emergency Drug Doses - PBS Doctor's Bag Items - Australian PrescriberDokumen4 halamanEmergency Drug Doses - PBS Doctor's Bag Items - Australian PrescriberChhabilal BastolaBelum ada peringkat
- CDC Infection Prevention Practices 2016Dokumen44 halamanCDC Infection Prevention Practices 2016Hayes MaineBelum ada peringkat
- Myomodulation With Facial Fillers A ComprehensiveDokumen13 halamanMyomodulation With Facial Fillers A ComprehensiveThiago MouraBelum ada peringkat
- Greater Palatine Nerve BlockDokumen3 halamanGreater Palatine Nerve BlockEcho WhyBelum ada peringkat
- Rusan Pharma Product ListDokumen4 halamanRusan Pharma Product ListSanjay SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Nasopalatine Nerve BlockDokumen29 halamanNasopalatine Nerve Blockoutright RohitBelum ada peringkat
- The Administration of Medications I. Speaking 'Administering Medications'Dokumen5 halamanThe Administration of Medications I. Speaking 'Administering Medications'Meri AndaniBelum ada peringkat
- Green Book Chapter 4Dokumen10 halamanGreen Book Chapter 4ChamCham AquinoBelum ada peringkat
- 5.00 Safe Injection Practices Point of Care DevicesDokumen40 halaman5.00 Safe Injection Practices Point of Care DevicesDrVishal BhattBelum ada peringkat
- NMC Radiation Shielding Catalog 01Dokumen22 halamanNMC Radiation Shielding Catalog 01Moisés GuevaraBelum ada peringkat
- Popular Perceptions of MedicineDokumen28 halamanPopular Perceptions of Medicineallure_chBelum ada peringkat
- MECA HandoutsDokumen118 halamanMECA HandoutsJun JavierBelum ada peringkat
- Short Lecture On Drugs Education and RA 9165: First Aid and Water SafetyDokumen48 halamanShort Lecture On Drugs Education and RA 9165: First Aid and Water SafetyEarl Jann LaurencioBelum ada peringkat
- Med Admin Practice QuestionsDokumen5 halamanMed Admin Practice QuestionsArmelle DelvaBelum ada peringkat
- Ats SorowakoDokumen12 halamanAts SorowakoFirmanBelum ada peringkat
- 1527Dokumen5 halaman1527Ajay KaundalBelum ada peringkat
- Penicillin G BenzathineDokumen1 halamanPenicillin G BenzathineIvanne Hisoler100% (7)
- Nur 1208 2021 Prep of MedsDokumen38 halamanNur 1208 2021 Prep of MedsDannielle EvangelistaBelum ada peringkat
- Safe Practice in Syringe Pump Management PDFDokumen3 halamanSafe Practice in Syringe Pump Management PDFDian NoveraBelum ada peringkat
- Injection & Infusion: Chirathawornkhun, Parinda Meimban, Giuzeppe Edrel VeniegasDokumen42 halamanInjection & Infusion: Chirathawornkhun, Parinda Meimban, Giuzeppe Edrel VeniegasNdor Baribolo100% (4)
- Humulin R: Regular U-500 (Concentrated) Insulin Human Injection, Usp (Rdna Origin)Dokumen7 halamanHumulin R: Regular U-500 (Concentrated) Insulin Human Injection, Usp (Rdna Origin)Rebecca BlackburnBelum ada peringkat
- Dicynone InjectionDokumen3 halamanDicynone InjectionAhmed Ebid100% (2)
- A Simple Practice Guide For Dose Conversion Between Animals and HumanDokumen6 halamanA Simple Practice Guide For Dose Conversion Between Animals and Humannisa yulianti suprahmanBelum ada peringkat
- New Jersey Takes Action Against Unlicensed Medical Spas Practicing Botox and Vampire FacialsDokumen2 halamanNew Jersey Takes Action Against Unlicensed Medical Spas Practicing Botox and Vampire FacialsranggaBelum ada peringkat
- Exam For NursesDokumen15 halamanExam For Nursesaringkinking100% (2)
- Magic Molecules - How Drugs WorkDokumen288 halamanMagic Molecules - How Drugs WorkJack BBelum ada peringkat
- Parental Routes of AdministrationDokumen2 halamanParental Routes of AdministrationdrugdrugBelum ada peringkat
- s6 Pharma AnesDokumen14 halamans6 Pharma AnesTara Lingating0% (1)
- PrometricDokumen68 halamanPrometricAjurs UrsabiaBelum ada peringkat
- Refinement of Technique in Injection Lipolysis Based On Scientific Studies and Clinical EvaluationDokumen15 halamanRefinement of Technique in Injection Lipolysis Based On Scientific Studies and Clinical EvaluationtassianaBelum ada peringkat