Action Potential Propagation of Action Potential: Central Nervous System
Diunggah oleh
lez20 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
11 tayangan2 halaman1. Action potentials propagate along nerve fibers through electrical and chemical gradients, transmitting signals between neurons.
2. At synapses, neurotransmitters are released from presynaptic terminals and received by postsynaptic cells, allowing either excitatory or inhibitory transmission across the synaptic gap.
3. Neuroglia including astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia and others nourish and protect neurons in the central nervous system.
Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
3.docx
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Ini1. Action potentials propagate along nerve fibers through electrical and chemical gradients, transmitting signals between neurons.
2. At synapses, neurotransmitters are released from presynaptic terminals and received by postsynaptic cells, allowing either excitatory or inhibitory transmission across the synaptic gap.
3. Neuroglia including astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia and others nourish and protect neurons in the central nervous system.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
11 tayangan2 halamanAction Potential Propagation of Action Potential: Central Nervous System
Diunggah oleh
lez21. Action potentials propagate along nerve fibers through electrical and chemical gradients, transmitting signals between neurons.
2. At synapses, neurotransmitters are released from presynaptic terminals and received by postsynaptic cells, allowing either excitatory or inhibitory transmission across the synaptic gap.
3. Neuroglia including astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia and others nourish and protect neurons in the central nervous system.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
I.
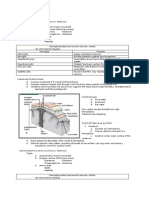
Transmission within the Nerve fiber
Action potential
Chemical gradient
Electrical gradient
Propagation of Action Potential
1. Resting stage (positive outside, negative inside)
2. Depolarization phase (negative outside, positive inside)
II. Transmission across Synapse
Synapses-small gaps between neurons
Chemical or electrical
One-way junction
1. Impulses reaches the presynaptic terminal
2. Vesicles release neurotransmitters
3. Neurotransmitters inactivated to prevent sustained response
Neurotransmitters-can be excitatory or inhibitory)
Types:
1. Acetylcholine-muscle movement
2. Biogenic amines (thinking process)
-Dopamine -Serotonin
-Norepinephrine -Histamine
3. Amino acids
-GABA
-Peptides
Neuroglia-protect and nourish neurons; mitotic
- do not transmit impulses
Neuroglia Function
Astrocytes Supply nutrients to neurons
Microglia Provide protection against microorganisms
Oligodendrocytes Wrap tightly around nerve fibers to form myelin
sheath
Ependymal cells Ciliated; line brain cavities; forms CSF
Schwann cells Phagocytic cells that form myelin sheath around
nerve fibers
Satellite cells Found in the PNS; may maintain chemical balance of
neurons
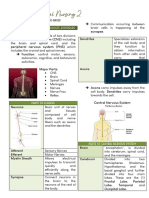
Cranium and Cerebral column
Cranium-composed of 8 cranial and facial bones
Foramen magnum-largest hole through which the brain stem extends to the spinal cord
Vertebral column-protects the spinal cord, supports the head and provides flexibility; strengthened by
ligaments and fibrocartilage disc
Cranial meninges
Dura mater
Arachnoid
Pia mater
Falx cerebri-divides the left from right
hemispheres
Subdural-more bleeding
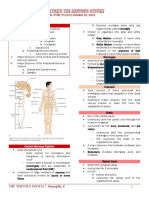
Central Nervous system:
I. Cerebrum
a. Consists of 2 hemisphere
b. Corpus callosum-connects two
hemisphere
c. Cerebral cortex-outer surface of the
cerebrum
d. Basal ganglia-located deep within cerebral hemisphere
e. Internal capsule-white matter consisting of bundle of nerve fibers carrying motor and sensory
impulses to and from cerebral cortex
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Nervous System: The Dog Stole the Professor's NotesDari EverandNervous System: The Dog Stole the Professor's NotesBelum ada peringkat
- Central Nervous SystemDokumen1 halamanCentral Nervous Systemlez2Belum ada peringkat
- Central Nervous SystemDokumen2 halamanCentral Nervous Systemlez2Belum ada peringkat
- Neurophysiology: Action Potential Propagation of Action PotentialDokumen2 halamanNeurophysiology: Action Potential Propagation of Action Potentiallez2Belum ada peringkat
- Neuro 1Dokumen5 halamanNeuro 1Treng EstradaBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous SystemDokumen5 halamanNervous SystemJake SimBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous System - HistologyDokumen8 halamanNervous System - HistologyambercrisologoBelum ada peringkat
- W1 - MEDSURG Introduction On Neurologic DisordersDokumen24 halamanW1 - MEDSURG Introduction On Neurologic DisordersKyla L. MadjadBelum ada peringkat
- The Nervous System First PartDokumen15 halamanThe Nervous System First PartNicole NipasBelum ada peringkat
- Neurology Week 1 Trans 01 31 23Dokumen3 halamanNeurology Week 1 Trans 01 31 23anime listBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous TissueDokumen10 halamanNervous TissueWrigley PatioBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous Tissue: Nervous System Neuron - The Only Cell Type Capable of Generating and PropagatingDokumen5 halamanNervous Tissue: Nervous System Neuron - The Only Cell Type Capable of Generating and PropagatingAlyssa AlferezBelum ada peringkat
- Sistem NervosumDokumen35 halamanSistem NervosumRaniyah Az-zahraBelum ada peringkat
- Transes Nervous SystemDokumen13 halamanTranses Nervous SystemAlther LorenBelum ada peringkat
- Neuroanatomy L1 (Intro Nervous System)Dokumen4 halamanNeuroanatomy L1 (Intro Nervous System)Charlize MarthaBelum ada peringkat
- BioPsychology Chapter 34Dokumen10 halamanBioPsychology Chapter 34Johnreih BanggaBelum ada peringkat
- Organization of Nervous System - MBBS NewDokumen53 halamanOrganization of Nervous System - MBBS NewDorin PathakBelum ada peringkat
- Human Anatomy TerminologiesDokumen26 halamanHuman Anatomy TerminologiesKrisha Mabel TabijeBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous SystemDokumen11 halamanNervous SystemYUAN FRANCIS SINGCULANBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy No.2Dokumen71 halamanAnatomy No.2hendalzeer02Belum ada peringkat
- Human Regulatory SystemDokumen37 halamanHuman Regulatory SystemRudolfBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous SystemDokumen5 halamanNervous SystemArantxa HilarioBelum ada peringkat
- Points To Remember: Neural Control and CoordinationDokumen107 halamanPoints To Remember: Neural Control and CoordinationRagheBelum ada peringkat
- Biology F4 Review Summary NoteDokumen117 halamanBiology F4 Review Summary NoteSocdal AbdiBelum ada peringkat
- 8 Nervous System MergedDokumen25 halaman8 Nervous System MergedCherry Ann Cagayat MadrigalBelum ada peringkat
- 8 Nervous SystemDokumen8 halaman8 Nervous SystemjurieBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous System CNS 1481841Dokumen5 halamanNervous System CNS 1481841Jglacier godBelum ada peringkat
- Failure of Neuropores To Close Can Cause Neural Tube DefectsDokumen6 halamanFailure of Neuropores To Close Can Cause Neural Tube DefectsMargo Roth SpiegelmanBelum ada peringkat
- CNS NotesDokumen9 halamanCNS NotesAysha AishaBelum ada peringkat
- Medical SurgicalDokumen119 halamanMedical SurgicalNursyNurseBelum ada peringkat
- Nervoussystem: Functions (Crime)Dokumen13 halamanNervoussystem: Functions (Crime)Dave ChenBelum ada peringkat
- Neuro 0411-1323Dokumen21 halamanNeuro 0411-1323Lea Jane ArmeñaBelum ada peringkat
- PRACTICEDokumen1 halamanPRACTICEPurple Ivy GuarraBelum ada peringkat
- Sheniblog-10 Biology (Eng Med) Revision Notes by Rasheed OdakkalDokumen14 halamanSheniblog-10 Biology (Eng Med) Revision Notes by Rasheed OdakkalhadiyxxBelum ada peringkat
- Nervou S Syste M: Types of NeuronsDokumen8 halamanNervou S Syste M: Types of NeuronsMayet BautistaBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous System ReviewerDokumen9 halamanNervous System ReviewerPlacido Edgar MagaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 22 Points To RememberDokumen6 halamanChapter 22 Points To RememberSaksham YadavBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous System ANAPHY NotesDokumen10 halamanNervous System ANAPHY NotesAlloiza CaguiclaBelum ada peringkat
- Medical Surgical Nursing 64 PagsDokumen64 halamanMedical Surgical Nursing 64 Pagstanya nBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous SystemDokumen6 halamanNervous SystemCellina De LeonBelum ada peringkat
- MC1 REVIEWER (Nervous System) - MIDTERMSDokumen7 halamanMC1 REVIEWER (Nervous System) - MIDTERMSFrancine Dominique CollantesBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous + Animal DiversityDokumen7 halamanNervous + Animal DiversityMaisonette MichBelum ada peringkat
- Neuro NursingDokumen22 halamanNeuro Nursingheiyu100% (6)
- Chapter 2 - Structure and Functions For The Cells of The Nervous SystemDokumen14 halamanChapter 2 - Structure and Functions For The Cells of The Nervous SystemLANCE GILL Tolentino100% (1)
- B373 Unit 2 CNS W22Dokumen60 halamanB373 Unit 2 CNS W22tamaraamhaBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Nervous System OutlinesDokumen45 halaman1 Nervous System OutlinesTestingAccBelum ada peringkat
- Anaphy Nervous - SystemDokumen8 halamanAnaphy Nervous - SystemArcher RiegoBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous System PDFDokumen9 halamanNervous System PDFJomeena MaeBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous System Session 1Dokumen104 halamanNervous System Session 1Jojo LouBelum ada peringkat
- Ncm116 CDN Nervous LecDokumen11 halamanNcm116 CDN Nervous LecMilcah NuylesBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous SystemDokumen9 halamanNervous SystemMuhamad Hafiz Bin Mohd BakriBelum ada peringkat
- Cva MedbackDokumen15 halamanCva MedbackDavid TiongsonBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 8: Nervous SystemDokumen15 halamanChapter 8: Nervous SystemAndrea BoocBelum ada peringkat
- Anaphy Nervous SystemDokumen7 halamanAnaphy Nervous SystemFraiza BirowaBelum ada peringkat
- #4 Nervous-SystemDokumen19 halaman#4 Nervous-SystemLapitan Jared Anne S.Belum ada peringkat
- Functional Classification of The Peripheral Nervous SystemDokumen20 halamanFunctional Classification of The Peripheral Nervous SystemLapitan Jared Anne S.Belum ada peringkat
- Neuro IDokumen6 halamanNeuro IElenaBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous TissueDokumen49 halamanNervous TissueDAVE CANALETABelum ada peringkat
- Nervous System: Nissl Bodies-Sites of Protein Synthesis in NeuronsDokumen16 halamanNervous System: Nissl Bodies-Sites of Protein Synthesis in NeuronsZella ViaBelum ada peringkat
- HANDOUTSDokumen3 halamanHANDOUTSElaiza Eline LaguaBelum ada peringkat
- What Is A Course Outline and Where Do I Find It?: Approximately Two Weeks Prior To The Commencement of The SemesterDokumen16 halamanWhat Is A Course Outline and Where Do I Find It?: Approximately Two Weeks Prior To The Commencement of The Semesterlez2Belum ada peringkat
- AvenDokumen23 halamanAvenlez2Belum ada peringkat
- What Is A Course Outline and Where Do I Find It?: Approximately Two Weeks Prior To The Commencement of The SemesterDokumen16 halamanWhat Is A Course Outline and Where Do I Find It?: Approximately Two Weeks Prior To The Commencement of The Semesterlez2Belum ada peringkat
- AvenDokumen23 halamanAvenlez2Belum ada peringkat
- What Is A Course Outline and Where Do I Find It?: Approximately Two Weeks Prior To The Commencement of The SemesterDokumen16 halamanWhat Is A Course Outline and Where Do I Find It?: Approximately Two Weeks Prior To The Commencement of The Semesterlez2Belum ada peringkat
- AvenDokumen23 halamanAvenlez2Belum ada peringkat
- Description of The Nervous SystemDokumen8 halamanDescription of The Nervous Systemlez2Belum ada peringkat
- CCCCDokumen3 halamanCCCClez2Belum ada peringkat
- What Is A Course Outline and Where Do I Find It?: Approximately Two Weeks Prior To The Commencement of The SemesterDokumen16 halamanWhat Is A Course Outline and Where Do I Find It?: Approximately Two Weeks Prior To The Commencement of The Semesterlez2Belum ada peringkat
- Writing: Alice in Wonderland Oz The Great and PowerfulDokumen10 halamanWriting: Alice in Wonderland Oz The Great and Powerfullez2Belum ada peringkat
- BBBDokumen1 halamanBBBlez2Belum ada peringkat
- 1Dokumen2 halaman1lez2Belum ada peringkat
- Need Quotation To VerifyDokumen2 halamanNeed Quotation To Verifylez2Belum ada peringkat
- Last Published: 7/18/2019: Information Technology (IT)Dokumen3 halamanLast Published: 7/18/2019: Information Technology (IT)lez2Belum ada peringkat
- The Alchemist (Coelho) SummaryDokumen5 halamanThe Alchemist (Coelho) Summarylez2Belum ada peringkat
- National Institutes of Health The BrainDokumen9 halamanNational Institutes of Health The Brainlez2Belum ada peringkat
- Description of The Nervous SystemDokumen8 halamanDescription of The Nervous Systemlez2Belum ada peringkat
- Test Instructions: Group, 74 Brick BLVD., Bldg. 4, Suite 206, Brick, NJ 08723. We Will Mail YourDokumen6 halamanTest Instructions: Group, 74 Brick BLVD., Bldg. 4, Suite 206, Brick, NJ 08723. We Will Mail Yourlez2Belum ada peringkat
- Description of The Nervous SystemDokumen8 halamanDescription of The Nervous Systemlez2Belum ada peringkat
- Description of The Nervous SystemDokumen8 halamanDescription of The Nervous Systemlez2Belum ada peringkat
- The Alchemist (Coelho) SummaryDokumen5 halamanThe Alchemist (Coelho) Summarylez2Belum ada peringkat
- The Alchemist (Coelho) SummaryDokumen5 halamanThe Alchemist (Coelho) Summarylez2Belum ada peringkat
- The Alchemist (Coelho) SummaryDokumen5 halamanThe Alchemist (Coelho) Summarylez2Belum ada peringkat
- Description of The Nervous SystemDokumen8 halamanDescription of The Nervous Systemlez2Belum ada peringkat
- Test Instructions: Group, 74 Brick BLVD., Bldg. 4, Suite 206, Brick, NJ 08723. We Will Mail YourDokumen6 halamanTest Instructions: Group, 74 Brick BLVD., Bldg. 4, Suite 206, Brick, NJ 08723. We Will Mail Yourlez2Belum ada peringkat
- 1Dokumen2 halaman1lez2Belum ada peringkat
- 1Dokumen2 halaman1lez2Belum ada peringkat
- Specific Objectives Content Time Allotment Teaching Strategies Evaluative MeasuresDokumen5 halamanSpecific Objectives Content Time Allotment Teaching Strategies Evaluative Measureslez2Belum ada peringkat
- Vein Vs ArteryDokumen4 halamanVein Vs ArterySaarwin MuruganBelum ada peringkat
- Heat-Related IllnessDokumen1 halamanHeat-Related IllnessEdie OwensBelum ada peringkat
- Energy Expenditure and FatigueDokumen49 halamanEnergy Expenditure and FatigueAh Zhang100% (1)
- Photosynthesis 9700 CieDokumen8 halamanPhotosynthesis 9700 CietrinhcloverBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiac EnzymesDokumen25 halamanCardiac EnzymesMonette Abalos MendovaBelum ada peringkat
- ML009 - RevJ - NCP Operator Training (NCP-5) - Jun2018Dokumen84 halamanML009 - RevJ - NCP Operator Training (NCP-5) - Jun2018alvin susetyoBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Disease Flashcards PDFDokumen52 halamanPathophysiology of Disease Flashcards PDFFlowerBelum ada peringkat
- Rhythm Summary Review Packet EKG CLassDokumen12 halamanRhythm Summary Review Packet EKG CLassmisslhen.rn04Belum ada peringkat
- Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (Psqi) : InstructionsDokumen7 halamanPittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (Psqi) : InstructionsmacmohitBelum ada peringkat
- Antihypertensive DrugsDokumen29 halamanAntihypertensive Drugsmailforrandomuse100% (1)
- Journal of Ayurveda and Integrative Medicine: Apar Avinash Saoji, B.R. Raghavendra, N.K. ManjunathDokumen9 halamanJournal of Ayurveda and Integrative Medicine: Apar Avinash Saoji, B.R. Raghavendra, N.K. ManjunathALiint Nissa NisaniestBelum ada peringkat
- Penetrating Abdominal Trauma (Stab Wound)Dokumen1 halamanPenetrating Abdominal Trauma (Stab Wound)P BBelum ada peringkat
- Faculties of Arts Science 21 22 Without LocationsDokumen22 halamanFaculties of Arts Science 21 22 Without LocationsHenrixy BellBelum ada peringkat
- The Respiratory Structure and Breathing Mechanism in AnimalsDokumen6 halamanThe Respiratory Structure and Breathing Mechanism in AnimalsNur Busyra100% (1)
- Homeostasis and The Excretory SystemDokumen21 halamanHomeostasis and The Excretory Systemmark smithBelum ada peringkat
- MC Chapter 10 TestDokumen12 halamanMC Chapter 10 TestdanaBelum ada peringkat
- Laporan Pendahuluan DM RsumDokumen17 halamanLaporan Pendahuluan DM RsumMelinia AnggitaBelum ada peringkat
- PhysioEX Exercise 3 Activity 1Dokumen8 halamanPhysioEX Exercise 3 Activity 1patricia ankarBelum ada peringkat
- Rinehart, and Winston Modern Biology (2002) - Research Will Focus On The Structure and FunctionDokumen7 halamanRinehart, and Winston Modern Biology (2002) - Research Will Focus On The Structure and FunctionSiegrid Anne TamayoBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiovascular DiseasesDokumen67 halamanCardiovascular DiseasesokaciaBelum ada peringkat
- Nurses Notes: Student Nurse: Casas, Jannen A. Patient's Name: - N.T.M - Doctor: Bed No.Dokumen2 halamanNurses Notes: Student Nurse: Casas, Jannen A. Patient's Name: - N.T.M - Doctor: Bed No.Jannen CasasBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology OF HEART FAILUREDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology OF HEART FAILUREJessa AdenigBelum ada peringkat
- Sensation: by Dr. Mufeed Akram TahaDokumen38 halamanSensation: by Dr. Mufeed Akram TahaAhmed JawdetBelum ada peringkat
- Heart FailureDokumen41 halamanHeart FailureMatthew Jerome van HuizenBelum ada peringkat
- FEU Review Pre Board Exam 2016 PathophysioDokumen8 halamanFEU Review Pre Board Exam 2016 PathophysioDharlyn MungcalBelum ada peringkat
- PP - Week 5 - Premature Newborn - Concept MapDokumen2 halamanPP - Week 5 - Premature Newborn - Concept MapSarah CollinsBelum ada peringkat
- Psy Chapter 2Dokumen146 halamanPsy Chapter 2OceanBelum ada peringkat
- Chloroplasts and MitochondriaDokumen6 halamanChloroplasts and Mitochondriaapi-3277246050% (2)
- UWorld Step 2 CK Notes - 2015Dokumen4 halamanUWorld Step 2 CK Notes - 2015Ernesto Prado67% (3)
- NSTP NotesDokumen14 halamanNSTP NotesA 3Belum ada peringkat