Blood Culture
Diunggah oleh
Janine San Pedro0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
4 tayangan2 halamanNotes and lessons
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniNotes and lessons
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
4 tayangan2 halamanBlood Culture
Diunggah oleh
Janine San PedroNotes and lessons
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
Blood Culture
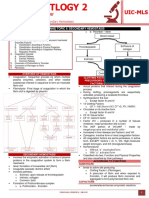
• Major difficulty in the interpretation of blood
cultures is contamination by microbial flora on
Blood Cultures – help determine the presence and
the skin
extent of infection as well as indicating the type of
• Skin antisepsis – the destruction of
organism responsible and the antibiotic to which it is
microorganisms on the skin (critical part of the
most susceptible
blood culture collection procedure)
• Blood cultures should be ordered on the basis • Failure to do so, can introduce skin-surface
of whether the patient has a condition in which bacteria into the blood culture bottles and
bloodstream invasion is possible and not only interfere with the interpretation of the results
when a patient experiences a fever of unknown • The collection sites require a 30-60 second
(FUO) friction scrub
o Bacteremia – bacteria in the blood ➢ Tincture of iodine, chlorhexidine
o Septicemia – microorganisms or their gluconate, and povidone/70% ethyl
toxins in the blood alcohol combination
Specimen requirements:
• Two to four blood cultures are necessary to BACTEC Blood
Culture Bottles
optimize the detection of bacteremia and
fungemia
• For optimum results, such specimens should be
drawn 30-60 mins apart. If the patient is in
critical condition or an antibiotic must be given Blood Culture Specimen Collection
right away, cultures should be drawn 1. Follow normal identification protocol, explain
consecutively and immediately from different collection procedure
sites. 2. Identify venipuncture site and release
• Second set of blood culture should be obtained tourniquet
from a separately prepared site on the opposite 3. Aseptically select and assemble equipment
arm if possible 4. Perform friction scrub – 30 to 60 seconds
• “Second site” blood cultures are more useful 5. Allow the site to dry – 30 second wait allows
when drawn 30 mins apart time for the antiseptic to be effective against
Key point → The volume of blood drawn for infants and skin-surface bacteria
younger children should be from 1-4% of the patient’s 6. Remove the flip-off cap of the culture bottles
total blood volume. For adults or people weighing more and inspect the bottle for visible defects
than 80 pounds, 20-30 mL per culture with a minimum 7. Cleanse the culture bottle stopes while the site
of 10 mL per draw is recommended. is drying – culture bottles with plastic caps can
be cleaned with 70% isopropyl alcohol
• Blood culture specimens are collected in special 8. Mark the minimum and maximum fill on the
bottles containing nutrient broth (referred to as culture bottles – 10-20 ml for adults; 1-2 mL for
medium) the encourages the growth of children
microorganisms 9. Reapply the tourniquet and perform the
o Aerobic – with air; filled first when venipuncture without touching or repalpating
butterfly is used the site
o Anaerobic – without air; filled first 10. Inoculate the medium as required – can occur
when syringe system is used directly into the bottle during specimen
collection or after collection when a syringe is
Skin Antisepsis
used
11. Invert the bottle several times
Blood Culture
12. Clean the patient’s skin if applicable – if an
iodine preparation was used to clean the arm,
Antimicrobial neutralization products
the iodine should be removed with alcohol or
suitable cleanser • Presence of the antimicrobial agent (antibiotic
13. Label the specimen containers with required therapy) in the patient’s blood can inhibit the
identification information, including the site of growth of the microorganisms in the blood
blood collection – noting the collection site or culture bottle.
source such as a port-a-cath is necessary in case • Physicians may order blood cultures to be
there is a localized infection collected in fastidious antimicrobial
14. Dispose of used and contaminated materials neutralization (FAN) or Antimicrobial removal
15. Thank the patient, remove gloves and sanitize device (ARD)
hands • ARD - contains a resin that removes
16. Transport specimens to the lab as quickly as antimicrobials from the blood
possible • FAN – bottles contain activated charcoal which
Key point → blood cultures should not be drawn neutralizes the antibiotic
through an indwelling IV or arterial catheter unless o Should be delivered to the lab for
absolutely necessary processing as soon as possible
Media Inoculation methods
• Can occur several different ways: directly
into the bottle during specimen collection
or after collection as when blood has been
FAN and ARD blood culture
collected in a syringe bottles
• Third way is to use an intermediate
collection tube to collect the sample for
inoculation in the lab
o Direct inoculation – using a butterly
and specially designed holder
o Syringe inoculation – the blood
must be transferred to the bottles
after the draw is completed; usually
require the use of safety transfer
device
Media inoculation methods
*never hold the culture bottle in your hand during the
inoculation process. Place it on a surface or in a rack.
Intermediate collection tube
• Blood is sometimes collected in an intermediate
collection tube rather than blood culture bottles
o Yellow-top Sodium polyanethol
sulfonate (SPS) tube
o It is discouraged
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- MCB502 2020 Exam #1Dokumen9 halamanMCB502 2020 Exam #1Cameron KeetonBelum ada peringkat
- Mid Module 3rd Year MBBSDokumen8 halamanMid Module 3rd Year MBBSShahzaib Ullah ChatthaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 8Dokumen53 halamanChapter 8contactrafiakhuramBelum ada peringkat
- HemophiliaDokumen60 halamanHemophiliavibhurocksBelum ada peringkat
- NucleusDokumen10 halamanNucleusPinak ChowdhuryBelum ada peringkat
- Blood and Its DisordersDokumen55 halamanBlood and Its DisordersPaapa MorrisBelum ada peringkat
- TGA Letter of Demand - 4 July 2023Dokumen30 halamanTGA Letter of Demand - 4 July 2023Tim BrownBelum ada peringkat
- Cytological and Mathematical Basis of InheritanceDokumen6 halamanCytological and Mathematical Basis of InheritanceJobelle CajipoBelum ada peringkat
- Hema 2 - Prelim Topic 4 - Secondary HemostasisDokumen8 halamanHema 2 - Prelim Topic 4 - Secondary HemostasisLowenstein JenzenBelum ada peringkat
- Covid TestingDokumen4 halamanCovid TestingIlham MenorBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 The Sexual SelfDokumen13 halamanChapter 4 The Sexual SelfSherilyn Picarra100% (1)
- CoVid-19: The Coronavirus Disease 2019Dokumen23 halamanCoVid-19: The Coronavirus Disease 2019M.J CapbooksBelum ada peringkat
- Bacte ReviewerDokumen124 halamanBacte ReviewerMarie LlanesBelum ada peringkat
- HBII Lab Manual 14-1-2019Dokumen50 halamanHBII Lab Manual 14-1-2019Ahmed Khaled Abo EldahabBelum ada peringkat
- Thrombocytopenia in PregnancyDokumen31 halamanThrombocytopenia in Pregnancyari naBelum ada peringkat
- 3 PracticalDokumen47 halaman3 PracticalT NBelum ada peringkat
- Molecular Basis of InheritanceDokumen8 halamanMolecular Basis of InheritancePriyanshu ShivamBelum ada peringkat
- 10 All GrantsDokumen277 halaman10 All GrantsRyan SloanBelum ada peringkat
- Lymphoma and HIVDokumen20 halamanLymphoma and HIVALEX NAPOLEON CASTA�EDA SABOGAL100% (1)
- Vere Chip TMDokumen12 halamanVere Chip TMRubi RubiandaniBelum ada peringkat
- Ch05 Lecture-Cell Membranes and SignalingDokumen95 halamanCh05 Lecture-Cell Membranes and SignalingbearreBelum ada peringkat
- Magnetic Pulse Therapy and Rife HealingDokumen9 halamanMagnetic Pulse Therapy and Rife HealingHaSophim88% (8)
- Practice Exam - Qats PDFDokumen53 halamanPractice Exam - Qats PDFsdfbgshfgBelum ada peringkat
- Bacterial Culture Media: Types and Applications: Mlt422: Clinical Microbiology IDokumen13 halamanBacterial Culture Media: Types and Applications: Mlt422: Clinical Microbiology Inuraini sofeaBelum ada peringkat
- Scdal 1Dokumen23 halamanScdal 1Cwali MohamedBelum ada peringkat
- Gastroenterología y Hepatología: Scientific LettersDokumen2 halamanGastroenterología y Hepatología: Scientific LettersAswin ArinataBelum ada peringkat
- CELL-PPT-DR.-LINAO, Updated Aug.2,2020Dokumen103 halamanCELL-PPT-DR.-LINAO, Updated Aug.2,2020Allan Q VenusBelum ada peringkat
- Ap Bio Unit 6 Quick Study CardDokumen1 halamanAp Bio Unit 6 Quick Study CardAbhi ShahBelum ada peringkat
- Sylvia Mader BiotechnologyDokumen55 halamanSylvia Mader Biotechnologykevin_ramos007Belum ada peringkat
- Pre Malignant and Malignant Lesions of Cervix: Gynaec Unit 5Dokumen147 halamanPre Malignant and Malignant Lesions of Cervix: Gynaec Unit 5FarazBelum ada peringkat