Kidney Stones: What Is A Kidney Stone?
Diunggah oleh
sajidJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Kidney Stones: What Is A Kidney Stone?
Diunggah oleh
sajidHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Kidney stones
Emergency department factsheets General
What is a kidney stone? An attack may last many hours. This often settles when the
stone has passed into your bladder, which may take some time.
Kidney stones (the medical term is renal calculi) are small hard
Most stones are not painful to pass (once past the bladder) and
stones that form in the kidney when the salts in the urine
some people don’t even know when this happens.
become solid. They can vary in size and location.
Most stones are small and are flushed out in the urine. Treatment
Some grow over many years to become quite large. Stones While in the emergency department, you may be given:
can lodge anywhere in the urinary tract and cause severe pain.
• a strong painkiller to ease your pain (such as Panadeine
There can be one or more stones present at any one time.
Forte or morphine through a drip) – do not drive home
Anyone can get a kidney stone. One in 10 men and one in if you feel drowsy or have had morphine
35 women develop a kidney stone in their lifetime. Most occur • medication for nausea
between the ages of 20 and 60. Some people keep getting
• fluids into the vein (intravenous) to help flush out the stone
kidney stones throughout their lives.
• a urine test to look for infection, blood and crystals
• a blood test to look at the salts in your blood and how well
your kidneys are working
• an X-ray or CT scan to see whether there is a stone and
check the state of the urinary tract (this may be done as an
outpatient).
A doctor may prescribe pain relief such as Panadeine Forte
(paracetamol and codeine) for you to take home. Some people
need anti-inflammatory medications such as ibuprofen or
Voltaren. Indomethacin suppositories may be helpful. These
What causes a kidney stone? are not suitable for everyone. Ask your doctor or health care
Stones can be made of different matter. The most common professional for advice.
ones are made of calcium. They form because there is the
wrong mix of chemicals in the urine, which allows salts to turn Home care
into crystals. • Drink at least eight glasses of water a day to help flush out
For most people with stones, the exact cause is not found. the kidney stone.
• If you have pain, take painkillers such as paracetamol
You are more likely to have a stone if you drink only small
or the medication the doctor has prescribed.
amounts of fluids. This makes the urine more concentrated.
Check the packet for the correct dose and take only
If you have a urinary tract infection (UTI) this can also lead
as directed.
to a stone forming.
• Be guided by your doctor.
You may be unaware that you have a kidney stone. It is only
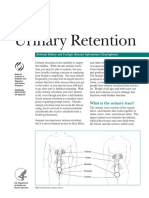
if the stone blocks the ureter (the tube that runs from the
What to expect
kidney to the bladder) that you have problems. When this Most people will pass the kidney stone without any trouble in
happens it causes severe pain and is called renal colic. the next few days to weeks. The time it takes to pass a stone
varies from person to person.
What are the symptoms?
A large stone may cause a blockage and you may be referred
You may feel a strong gripping pain in the back below the ribs, to an urologist (a doctor who specialises in kidney stones) for
and you may also have pain in your side, groin and thigh. treatment. A treatment called lithotripsy may be used to break
Other symptoms may include: the stone up into smaller pieces. Some people need surgery
to remove the stone.
• blood in your urine
• nausea and vomiting If a stone blocks the natural flow of urine this can cause an
infection in the urinary tract and antibiotics will be needed.
• sweating, fever and shivers.
Kidney stones
Emergency department factsheets General
Prevention Seeking help
If you have had a kidney stone, there is a higher chance
you will have another kidney stone in the future. In a medical emergency go to the nearest
• Studies suggest that you can halve your risk of forming hospital emergency department or call an
another stone by drinking two litres of water a day. ambulance (dial 000).
If your urine is dark yellow you are not drinking enough. See your local doctor or health care professional
• You can help prevent a kidney stone by getting prompt if you have:
treatment for a urinary tract infection (UTI). See your doctor.
• pain that is getting worse despite taking
• If you have had more than one attack your doctor may painkillers
arrange tests to check for troublesome acids and minerals
• fever, sweats or shivers
in your blood.
• repeated vomiting
• Changes in your diet are only advised for some causes
• urine that is cloudy or has blood in it
of kidney stones. Please check with your doctor before
• pain on passing urine
changing your diet.
• any other concerns.
Notes: For health advice from a Registered Nurse you
can call NURSE-ON-CALL 24 hours a
day on 1300 60 60 24 for the cost of a local
call from anywhere in Victoria.*
NURSE-ON-CALL provides access to
interpreting services for callers not confident
with English. Call 1300 60 60 24.
*Calls from mobile calls may be charged at a higher rate
Want to know more?
• Ask your local doctor or health care professional.
• Visit the Better Health Channel
www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au
• Visit Kidney Health Australia
www.kidney.org.au
If you would like to receive this publication in an accessible format,
please phone 9096 0578 or email edfactsheets@health.vic.gov.au
December 2010. Also available online at www.health.vic.gov.au/edfactsheets
Authorised by the
Disclaimer: This health information is for general education purposes only. Please consult Victorian Government
with your doctor or other health professional to make sure this information is right for you. Melbourne (1009025)
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Ed-Kidney StonesDokumen2 halamanEd-Kidney StonesPearl NardoBelum ada peringkat
- KIDNEY STONES - LetterDokumen6 halamanKIDNEY STONES - LetterFloreleneBelum ada peringkat
- 51 Tips For Dealing With Kidney StonesDokumen16 halaman51 Tips For Dealing With Kidney StonesFeenyxBelum ada peringkat
- Types, Symptoms, and Treatment of Kidney StonesDokumen6 halamanTypes, Symptoms, and Treatment of Kidney StonesKatte VillenasBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 9Dokumen5 halamanTopic 989qqzp4yhkBelum ada peringkat
- All About Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) : Fact SheetDokumen4 halamanAll About Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) : Fact SheetJar JarBelum ada peringkat
- Renal Calculi (NS Presentation)Dokumen24 halamanRenal Calculi (NS Presentation)Norsyakira NawirBelum ada peringkat
- Symptoms: Kidney StonesDokumen5 halamanSymptoms: Kidney StonesLucía Flores FaríasBelum ada peringkat
- Colic RenalDokumen21 halamanColic RenalJoyaa ShaloomBelum ada peringkat
- Bladder Stones and Kidney Stones: Common ConditionsDokumen2 halamanBladder Stones and Kidney Stones: Common ConditionsDella FerginaBelum ada peringkat
- UrolithiasisDokumen1 halamanUrolithiasisNovitaBelum ada peringkat
- Kidney StonesDokumen11 halamanKidney StonesNader Smadi100% (1)
- Adult Nursing 1 Renal Calculi 1Dokumen25 halamanAdult Nursing 1 Renal Calculi 1ChonnetteAshlynKingBelum ada peringkat
- Renal Colic RCHT0793Dokumen6 halamanRenal Colic RCHT0793Angga PermanaBelum ada peringkat
- Kidney Stones: Jenny ZhaDokumen16 halamanKidney Stones: Jenny ZhaJenny ZhaBelum ada peringkat
- UrolithiasisDokumen7 halamanUrolithiasismariaBelum ada peringkat
- Renal StonesDokumen12 halamanRenal StonesDamandeep KaurBelum ada peringkat
- Kidney Stone Owner's Manual v2Dokumen12 halamanKidney Stone Owner's Manual v2Martin HaynesBelum ada peringkat
- Kidney Stones: Causes and TreatmentDokumen4 halamanKidney Stones: Causes and TreatmentVanessa ArellanoBelum ada peringkat
- Some Disorders of Excretory SystemDokumen5 halamanSome Disorders of Excretory SystemANUBHAB SAHABelum ada peringkat
- Kidney Stones AdultsDokumen12 halamanKidney Stones AdultsMahesh Babu.KBelum ada peringkat
- Kidney Stone Patient Education GuideDokumen2 halamanKidney Stone Patient Education GuideJamesBelum ada peringkat
- Kidney StonesDokumen2 halamanKidney StonesnacklessBelum ada peringkat
- How necessary is Kidney Stone treatmentDokumen2 halamanHow necessary is Kidney Stone treatmentnacklessBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary Lithiasis 161269200418Dokumen14 halamanUrinary Lithiasis 161269200418ተሣለነ ወልድBelum ada peringkat
- What Causes Kidney Stones? News Yale MedicineDokumen10 halamanWhat Causes Kidney Stones? News Yale Medicinemarwa humairaBelum ada peringkat
- Diagnosis: Small Stones With Minimal SymptomsDokumen5 halamanDiagnosis: Small Stones With Minimal SymptomsKatte VillenasBelum ada peringkat
- Urolithiasis: Getaneh T. (MD, Urologist)Dokumen28 halamanUrolithiasis: Getaneh T. (MD, Urologist)Bersisa chalchisaBelum ada peringkat
- Kidney Stones - Symptoms, Causes, Types, and Treatment - National Kidney FoundationDokumen11 halamanKidney Stones - Symptoms, Causes, Types, and Treatment - National Kidney FoundationamanuelBelum ada peringkat
- Kidney Stones: Causes, Symptoms & TreatmentDokumen3 halamanKidney Stones: Causes, Symptoms & TreatmentsssmouBelum ada peringkat
- High Protein, Calcium or Oxalate Intake in Diet Low Water Intake Urinary Tract Infections Obesity Family History of Kidney Stones CystinuriaDokumen5 halamanHigh Protein, Calcium or Oxalate Intake in Diet Low Water Intake Urinary Tract Infections Obesity Family History of Kidney Stones Cystinuriasharma_761816814Belum ada peringkat
- The Perfect Kidney Stone Diet Cookbook:The Complete Nutrition Guide To Treating And Managing Kidney Problem With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesDari EverandThe Perfect Kidney Stone Diet Cookbook:The Complete Nutrition Guide To Treating And Managing Kidney Problem With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesBelum ada peringkat
- Managing Urolithiasis: Treatment and Nursing Care for Kidney StonesDokumen34 halamanManaging Urolithiasis: Treatment and Nursing Care for Kidney StonesChandrashekar N.k.Belum ada peringkat
- Kidney StonesDokumen17 halamanKidney Stonessv swamy100% (1)
- Types of Kidney StonesDokumen9 halamanTypes of Kidney StonesAngelina100% (1)
- Renal CalculiDokumen30 halamanRenal CalculiAnaiah Jaaziel KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Disorders of the Excretory System ExplainedDokumen9 halamanDisorders of the Excretory System ExplainedArpita SinghBelum ada peringkat
- A Power Point Show: Er - SulthanDokumen38 halamanA Power Point Show: Er - Sulthanராஜா MVSBelum ada peringkat
- Renal Stones: Causes, Symptoms & TreatmentDokumen15 halamanRenal Stones: Causes, Symptoms & TreatmentGabrielle Frances FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Draft Kidney StonesDokumen6 halamanDraft Kidney StonesMercy Anne EcatBelum ada peringkat
- Kidney FailureDokumen4 halamanKidney FailureAslimah RakimBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary DisordersDokumen77 halamanUrinary DisordersjohnaaaBelum ada peringkat
- KB 10Dokumen5 halamanKB 10Reband AzadBelum ada peringkat
- Kidney stones: causes, symptoms and treatmentDokumen3 halamanKidney stones: causes, symptoms and treatmentSisti AninditaBelum ada peringkat
- Urolithiasis SeminarDokumen50 halamanUrolithiasis SeminarSiddharth GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- NephrolithiasisDokumen3 halamanNephrolithiasisVince GagarBelum ada peringkat
- Female Urinary System: Open Pop-Up Dialog BoxDokumen7 halamanFemale Urinary System: Open Pop-Up Dialog BoxAziil LiizaBelum ada peringkat
- URETEROLITHIASISDokumen21 halamanURETEROLITHIASISDhea Faizia TasyaBelum ada peringkat
- UrinaryRetention_508(1)Dokumen8 halamanUrinaryRetention_508(1)earldioborrinagaBelum ada peringkat
- Benigna Hiperplasia ProstatDokumen23 halamanBenigna Hiperplasia ProstatShanti ArianiBelum ada peringkat
- NRSE 3540 Exam 2 Study GuideDokumen12 halamanNRSE 3540 Exam 2 Study GuideNelson MandelaBelum ada peringkat
- Renal Stone and Renal FailureDokumen14 halamanRenal Stone and Renal FailurereboBelum ada peringkat
- Vishnu Dental CollegeDokumen6 halamanVishnu Dental CollegeudayBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Kidney StonesDokumen4 halamanTypes of Kidney StoneskapczukBelum ada peringkat
- Gagal GinjalDokumen5 halamanGagal GinjaljayaBelum ada peringkat
- 333-Article Text-563-1-10-20180226Dokumen9 halaman333-Article Text-563-1-10-20180226No NameBelum ada peringkat
- Nephrolithiasis XXDokumen37 halamanNephrolithiasis XXzebzeb STEMABelum ada peringkat
- Bladder StoneDokumen3 halamanBladder StonePutriCaesarriniBelum ada peringkat
- One kidney can still provide up to 75 percent of normal kidney functionDokumen3 halamanOne kidney can still provide up to 75 percent of normal kidney functionDaveBelum ada peringkat
- Elphos Erald: Second Shot: Hillary Clinton Running Again For PresidentDokumen10 halamanElphos Erald: Second Shot: Hillary Clinton Running Again For PresidentThe Delphos HeraldBelum ada peringkat
- Pathology - List - 89.8.20Dokumen25 halamanPathology - List - 89.8.20Mamula RiazBelum ada peringkat
- Dental Anomalies II New PDFDokumen34 halamanDental Anomalies II New PDFFranco Coco SartoriBelum ada peringkat
- ADS ADEA ANZCA NZSSD - DKA - SGLT2i - Alert - Ver July 2022Dokumen3 halamanADS ADEA ANZCA NZSSD - DKA - SGLT2i - Alert - Ver July 2022tom.condon.02Belum ada peringkat
- Kriya For Balancing The ChakrasDokumen5 halamanKriya For Balancing The ChakrasFedra Fox Cubeddu100% (2)
- Integrating Modern Dermatology and AyurvedaDokumen25 halamanIntegrating Modern Dermatology and AyurvedachandusgBelum ada peringkat
- Oral Hygiene in VentilatorDokumen136 halamanOral Hygiene in VentilatorFelicia Risca RyandiniBelum ada peringkat
- Republic of The PhilippinesDokumen95 halamanRepublic of The Philippineshitler dangatanBelum ada peringkat
- Academica Science Journal PSYCHOLOGICA - No 2Dokumen3 halamanAcademica Science Journal PSYCHOLOGICA - No 2Ciotea ValentinBelum ada peringkat
- Journal Hydrodynamic Theory by Brnnstrm1986Dokumen5 halamanJournal Hydrodynamic Theory by Brnnstrm1986Fifth TsuchikageBelum ada peringkat
- Archives of Gerontology and GeriatricsDokumen7 halamanArchives of Gerontology and GeriatricsAna ArhipBelum ada peringkat
- Obesity Exercise PrescriptionDokumen34 halamanObesity Exercise Prescriptionkhushbu88% (8)
- Keeler Ophthalmoscope Bulb and Retinoscope Bulb ModelsDokumen1 halamanKeeler Ophthalmoscope Bulb and Retinoscope Bulb ModelsEDRAES17Belum ada peringkat
- Giant Skin TagDokumen2 halamanGiant Skin Tagshf.mxlikBelum ada peringkat
- DR Wong Teck WeeipadDokumen2 halamanDR Wong Teck Weeipadtwwong68Belum ada peringkat
- Mental Illness Attitude Scale (Modified OMICC QuestionnaireDokumen6 halamanMental Illness Attitude Scale (Modified OMICC QuestionnaireSyed Faizan100% (7)
- Resume 2019Dokumen1 halamanResume 2019api-316723361Belum ada peringkat
- FISIOGRAFT ENG Set 17 PDFDokumen28 halamanFISIOGRAFT ENG Set 17 PDFmaxBelum ada peringkat
- Management of Perioperative ArrhythmiasDokumen51 halamanManagement of Perioperative ArrhythmiasAbhishek LonikarBelum ada peringkat
- Medicine in Situ Panchen TraditionDokumen28 halamanMedicine in Situ Panchen TraditionJigdrel77Belum ada peringkat
- Science Blood TransfusionsDokumen10 halamanScience Blood Transfusionsapi-237866019Belum ada peringkat
- Documentation: Siji M. SunnyDokumen5 halamanDocumentation: Siji M. SunnySUNNY__SIJIBelum ada peringkat
- Pre Employment Occupational Health FormDokumen7 halamanPre Employment Occupational Health Formlinks2309Belum ada peringkat
- YOU IN SURGICAL - Product CatalogDokumen222 halamanYOU IN SURGICAL - Product CatalogfarazBelum ada peringkat
- PRC FormDokumen5 halamanPRC FormPamela DomingoBelum ada peringkat
- Spring 2011 21st AnniversaryDokumen56 halamanSpring 2011 21st AnniversaryRajesh SekhriBelum ada peringkat
- Audit of Barangay Health Centers in PhilippinesDokumen26 halamanAudit of Barangay Health Centers in PhilippineskenvysBelum ada peringkat
- Hydralazine For Severe PIHDokumen4 halamanHydralazine For Severe PIHYwagar YwagarBelum ada peringkat
- Novo NordiskDokumen2 halamanNovo NordiskSpotlightBelum ada peringkat
- Pre Conference Final ProgDokumen2 halamanPre Conference Final ProgkeithlyndBelum ada peringkat