Characteristics and Teaching Requirements for Children with Special Needs
Diunggah oleh
Zechrist ZechariahDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Characteristics and Teaching Requirements for Children with Special Needs
Diunggah oleh
Zechrist ZechariahHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
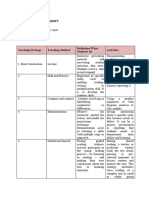
Criteria and Characteristics of Children with Special Needs
Categories of Disability Characteristics Teaching and Learning
Requirements
Attention problem. BBB:
Problems in Utilize Assistive
processing Technology (AT) such
information and lack as large calculators,
of psychological task analysis,
processes. communication cards
Provide appropriate (Augmentative
response Alternative
Difficulty in Communication-
questioning AAC), software to
Speech difficulty check spelling such
Following oral as E-Kamus
instructions Dewan,Ginger
Understanding Software
humour and body Use large “square
Learning disabilities (overall) language line” in Mathematics.
Lack of social skill Help them to organize
Writing problem ideas, take notes,
(written language) write, productivity,
Quantitative disorder. access to references
and modify materials
Reading difficulty
Limited vocabulary
Task/activity/Worksheet:
Grammatical and
Small number of
sentence errors
questions in a single
Excessive repetition page
Understanding Big font size
compound sentences
Classroom setting:
Seating arrangement
- near to the teacher
Include one SWSP in
each group activity
Flexible for individual
and groups
Collaborative learning
(mixed ability groups)
Teaching and learning
management:
Give marks based on
the moral values of
each group activity
Make vow in an
inclusive classroom
so that they help each
other and ensuring
the success of all the
friends in the group.
Encourage pupils to
do reflections at the
end of the class
Repetitions of
teachers’ instructions
with CWD by using
simple sentences
Using “carta
matematik 5 minit”
strategy at the
beginning of the
lesson
Distribute materials
(exercises or notes) to
pupils instead of
letting them to
copying notes from
the white board
Attention Deficits Hyperactive Be careful about using
Hyperactivity Aggressive certain colors that disturb
Disorder(ADHD) students like red
Cerebral Palsy Weak motor capability Seats and tables that
Difficulty in speech are compatible with
their physical
problems.
Use a laptop for
assignment purposes
Autism Spectrum Disorder • Concentration and attention Provide instructions in
• Anxiety disorder simple and printed
• Affective Disorder form
• Learning Difficulties
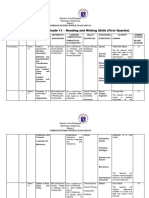
Visual impairment • Having troubles Classroom physical setting:
seeing things on the board • Make sure the
without assistant tools students with visual
(Partially sighted) impairment are seated in
• Hardly see things on front of the classroom or in
the board the middle. This will enable
• Unclear instruction: the students to have the best
have difficulty to follow the view of the black board and
teaching and learning thus they are able to
process if the instructions participate in the T&L
given is too visual-oriented • Make necessary
(here, there) adjustments to the lighting to
• Visual learning aids minimize the negative impact
may pose challenges to of the visual impairment. Put
them. on curtains when necessary.
• Interaction with peers
– pupils have less control on Special equipment:
the social circle • Ensure that the
• Orientation & mobility students with vision
– less control on the physical impairment to get the Optical
environment Aid Tool that suitable for both
• takes longer time to short-sighted and long-
do and complete the sighted.
assignments compared to
their peers Teaching and learning
• requires assistance process:
during co-curricular activities • get help from the
resource teacher to prepare
the diagram, circulars/ notes,
classroom practice,
worksheets, etc., in braille or
big photocopy in advance
• ask the resource
teacher to introduce the
special symbols in braille
(basically in Mathematics:
symbols for logarithms,
angle, etc.) for students with
vision impairment
• Use a specific
language that can be shown
to the blind student.
e.g. For location, we can use
the words “at the upper left”
or “in the middle” or “almost
seven (use the clock
reference system)” to
describe it based on the
diagram given.
Elaborate on the process
specifically to avoid confusion
when there is a
demonstration (especially on
movement and process)
• Time allocation for
task and examination should
be longer because the blind
student may acquire more
time to read, write and
manage his materials.
• Ask someone (who is
responsible) to read out the
notes on the board for the
blind student and to be his
“buddy”.
Collaboration:
• get teacher’s help to
help blind / low vision pupils
during a practical session or
T&L session involving the
use of complicated teaching
aids (eg in Science, Living
Skills, Geography ...)
• get teacher’s
assistance if a new pupil is
placed at the school; if the
activity is outside of the class,
pair the low vision pupils with
the celestial ones
• get resource teacher's
help to prepare large prints /
embossing / distributed
materials in large print or
braille
Co-curricular activities:
• Get a buddy for visual
impairment pupils to carry out
the activities
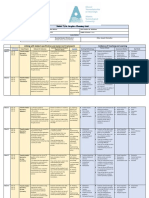
Pupils with hearing Difficult in hearing soft Classroom setting:
impairment sounds Sit at the front row to
Unable to listen to any easily see the teacher
sound Use the mimic method
Facing difficulties in
social interaction/ Teaching aid:
communication Use pictures,
Facing difficulties in multimedia and
expressive and receptive printed materials
communication, reading because they learn
and writing using their vision.
Difficult to involve in Prepare reading
group discussion in class materials/ notes first
Low self-esteem before the teaching
Interpret information and learning (T&L) so
given wrongly that pupils will be
Difficult to comprehend ready.
the text
Difficult to give Support:
respond/feedback of Classmates and
discussion that involves teachers could learn
abstract thinking sign language to help
compared to hands-on the pupils
task.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- CRM 6Dokumen1 halamanCRM 6api-545998611Belum ada peringkat
- Weekly Lesson Plans: Remediation: Objective(s) : Activities / Methods: AssessmentDokumen1 halamanWeekly Lesson Plans: Remediation: Objective(s) : Activities / Methods: Assessmentkosovare3Belum ada peringkat
- Unit Redesign ET 605 Jessica Stith Grade 9 English Language Arts Unit 2: To Kill A MockingbirdDokumen25 halamanUnit Redesign ET 605 Jessica Stith Grade 9 English Language Arts Unit 2: To Kill A Mockingbirdapi-438907642Belum ada peringkat
- English AssignmentDokumen7 halamanEnglish AssignmentKaren VicenteBelum ada peringkat
- The Big Project Christy 1Dokumen15 halamanThe Big Project Christy 1api-547917281Belum ada peringkat
- Classroom Walkthrough (Revised)Dokumen1 halamanClassroom Walkthrough (Revised)Linh HuynhBelum ada peringkat
- Size Patterns IntroDokumen4 halamanSize Patterns Introapi-580849936Belum ada peringkat
- TP5 MarinaGuimaraes LP STDokumen16 halamanTP5 MarinaGuimaraes LP STMarina outlookBelum ada peringkat
- Disabilities MatrixDokumen23 halamanDisabilities Matrixapi-323099162Belum ada peringkat
- HJBBDokumen3 halamanHJBBLeticia GonzálezBelum ada peringkat
- Edma Unit of Work ExtractDokumen9 halamanEdma Unit of Work Extractapi-406612760Belum ada peringkat
- Report on Academic Performance in English 10 at Almeria National High SchoolDokumen2 halamanReport on Academic Performance in English 10 at Almeria National High SchoolRoxy RoxieBelum ada peringkat
- Report On CLLDokumen3 halamanReport On CLLSaluibTanMelBelum ada peringkat
- Report On CLLDokumen3 halamanReport On CLLSaluibTanMelBelum ada peringkat
- Cooperative Language Learning MethodologyDokumen3 halamanCooperative Language Learning MethodologySaluibTanMelBelum ada peringkat
- Maskin - Educ340 - InfographicDokumen4 halamanMaskin - Educ340 - Infographicapi-494885256Belum ada peringkat
- Sample Weekly PlanDokumen2 halamanSample Weekly PlanNeha ShahBelum ada peringkat
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDokumen5 halamanDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningMiras Reah C.Belum ada peringkat
- ELL Strategies WorksheetDokumen7 halamanELL Strategies Worksheetapi-482714429Belum ada peringkat
- Games and SlaDokumen1 halamanGames and SlaDynamic English InstituteBelum ada peringkat
- Philippine Countryville College Teaches PermutationDokumen4 halamanPhilippine Countryville College Teaches Permutationjoeven manzoBelum ada peringkat
- FIDP Correlation AnalysisDokumen2 halamanFIDP Correlation AnalysisMeryll Joy P. MaaliwBelum ada peringkat
- 3:11Dokumen19 halaman3:11Jaysus M. ZainBelum ada peringkat
- ST 3 1 MathsDokumen14 halamanST 3 1 Mathsapi-357648875Belum ada peringkat
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1Dokumen4 halamanGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1api-653779848Belum ada peringkat
- DLP English 8 DemoDokumen2 halamanDLP English 8 DemoAna Mae MaruBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching Inquiry Overview 2017Dokumen2 halamanTeaching Inquiry Overview 2017api-300095367Belum ada peringkat
- Medaille New Lesson Plan 3 Sheila HolmesDokumen10 halamanMedaille New Lesson Plan 3 Sheila Holmesapi-418734224Belum ada peringkat
- UMF Secondary Education Lesson Plan/Learning Event TemplateDokumen5 halamanUMF Secondary Education Lesson Plan/Learning Event Templateapi-509348068Belum ada peringkat
- Compressed Escuela Normal ClassroommanagementDokumen28 halamanCompressed Escuela Normal Classroommanagementjennybacay.12345Belum ada peringkat
- Learning and Fasilitation PlanDokumen4 halamanLearning and Fasilitation PlanTc NorBelum ada peringkat
- PPP TableDokumen6 halamanPPP TableMartha MarthaBelum ada peringkat
- Observation Report 1 - Ariana SzepDokumen3 halamanObservation Report 1 - Ariana Szepapi-666802127Belum ada peringkat
- Reading and Writing BOWDokumen3 halamanReading and Writing BOWRebecca PidlaoanBelum ada peringkat
- Met3 - Course Objectives (Trainee 'S Copy) : Ultimate Goal: To Plan and Teach Lexis EffectivelyDokumen3 halamanMet3 - Course Objectives (Trainee 'S Copy) : Ultimate Goal: To Plan and Teach Lexis Effectivelydiego raulBelum ada peringkat
- ELT201 ActivityDokumen5 halamanELT201 ActivityJoylin BalabboBelum ada peringkat
- Unit Plan 2Dokumen1 halamanUnit Plan 2api-704526922Belum ada peringkat
- Planning Grid Junior Cert Graphics 2nd YearDokumen5 halamanPlanning Grid Junior Cert Graphics 2nd Yearapi-548175102Belum ada peringkat
- MathlessonplanDokumen3 halamanMathlessonplanapi-357473286Belum ada peringkat
- MAP ENGLISH 7 CURRICULUMDokumen28 halamanMAP ENGLISH 7 CURRICULUMMark Cesar VillanuevaBelum ada peringkat
- Foundation University Dumaguete CityDokumen8 halamanFoundation University Dumaguete Citynina amatoBelum ada peringkat
- Classroom Accommodations Students AdhdDokumen1 halamanClassroom Accommodations Students AdhdMeagan JonesBelum ada peringkat
- 12 General - Unit 5 - Lessons 5 - 6 - InnovationDokumen40 halaman12 General - Unit 5 - Lessons 5 - 6 - Innovationshahadjuma801Belum ada peringkat
- LP BT Mar 6-10Dokumen3 halamanLP BT Mar 6-10api-680806307Belum ada peringkat
- WHLP Week 6 - Modal Verbs Nouns AdverbsDokumen3 halamanWHLP Week 6 - Modal Verbs Nouns AdverbsEmerson CalpitoBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching InternshipDokumen7 halamanTeaching InternshipJK De GuzmanBelum ada peringkat
- PBL 2 SchemeDokumen11 halamanPBL 2 Schemeapi-428157976Belum ada peringkat
- Amazing Animals Lesson PlanDokumen7 halamanAmazing Animals Lesson PlannorsenahBelum ada peringkat
- Mathis JDokumen5 halamanMathis Japi-498485128Belum ada peringkat
- Go To PageDokumen4 halamanGo To Pageapi-558436275Belum ada peringkat
- Lesson 5Dokumen3 halamanLesson 5api-381242663Belum ada peringkat
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1Dokumen4 halamanGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1api-595895092Belum ada peringkat
- Lesson Observation Xander Collins BDokumen5 halamanLesson Observation Xander Collins Bapi-601573573Belum ada peringkat
- Individual Learning Plan (Ilp)Dokumen17 halamanIndividual Learning Plan (Ilp)api-358808082Belum ada peringkat
- Beaconhouse School System: Explained The Process of DiffusionDokumen11 halamanBeaconhouse School System: Explained The Process of DiffusionArya StarkBelum ada peringkat
- Reading and Writing Workshop TemplatesDokumen22 halamanReading and Writing Workshop Templatesaleoniem1996Belum ada peringkat
- Assessment, Accoms, Teaching StrategiesDokumen1 halamanAssessment, Accoms, Teaching Strategiesbrianna.korittkoBelum ada peringkat
- Seniors 1 Weekly Plan (13 - 11 - 22)Dokumen3 halamanSeniors 1 Weekly Plan (13 - 11 - 22)Karen CoronelBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 1 Spelling and Sight Words Instructional PlanDokumen6 halamanGrade 1 Spelling and Sight Words Instructional PlanDivine Elcullada Miranda FloresBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan 07.04.2021Dokumen1 halamanLesson Plan 07.04.2021Zechrist ZechariahBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan 08.04.2021Dokumen1 halamanLesson Plan 08.04.2021Zechrist ZechariahBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan 14.04.2021Dokumen1 halamanLesson Plan 14.04.2021Zechrist ZechariahBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan 24.03.2021Dokumen2 halamanLesson Plan 24.03.2021Zechrist ZechariahBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan 15.04.2021Dokumen1 halamanLesson Plan 15.04.2021Zechrist ZechariahBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan 09.04.2021Dokumen1 halamanLesson Plan 09.04.2021Zechrist ZechariahBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan 16.04.2021Dokumen1 halamanLesson Plan 16.04.2021Zechrist ZechariahBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan 24.03.2021Dokumen2 halamanLesson Plan 24.03.2021Zechrist ZechariahBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan 14.04.2021Dokumen1 halamanLesson Plan 14.04.2021Zechrist ZechariahBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan 13.04.2021Dokumen1 halamanLesson Plan 13.04.2021Zechrist ZechariahBelum ada peringkat
- ENGLISH MODUL FrontpageDokumen1 halamanENGLISH MODUL FrontpageZechrist ZechariahBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan 12.04.2021Dokumen1 halamanLesson Plan 12.04.2021Zechrist ZechariahBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan 08.04.2021Dokumen2 halamanLesson Plan 08.04.2021Zechrist ZechariahBelum ada peringkat
- Pupils Refer To Textbook Page 4. CD 1 02 Is Played and Pupils Point To The Character's NamesDokumen2 halamanPupils Refer To Textbook Page 4. CD 1 02 Is Played and Pupils Point To The Character's NamesZechrist ZechariahBelum ada peringkat
- Pupils Are Introduced To The Sounds Y, Z, ZZ, Qu Using A VideoDokumen1 halamanPupils Are Introduced To The Sounds Y, Z, ZZ, Qu Using A VideoZechrist ZechariahBelum ada peringkat
- Pupils Are Introduced To The Sounds J, V, W, X Using A Videos. 2. Pupils Recap On Sounds Introduced in The Previous Lessons (H, B, L, F, SS)Dokumen1 halamanPupils Are Introduced To The Sounds J, V, W, X Using A Videos. 2. Pupils Recap On Sounds Introduced in The Previous Lessons (H, B, L, F, SS)Zechrist ZechariahBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan 15.03.2021Dokumen2 halamanLesson Plan 15.03.2021Zechrist ZechariahBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan 24.03.2021Dokumen2 halamanLesson Plan 24.03.2021Zechrist ZechariahBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan 15.03.2021Dokumen2 halamanLesson Plan 15.03.2021Zechrist ZechariahBelum ada peringkat
- Pupils Are Introduced To The Sounds H, B, L, F, Ss Using A VideosDokumen1 halamanPupils Are Introduced To The Sounds H, B, L, F, Ss Using A VideosZechrist ZechariahBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan 09.03.2021Dokumen1 halamanLesson Plan 09.03.2021Zechrist ZechariahBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan 09.03.2021Dokumen1 halamanLesson Plan 09.03.2021Zechrist ZechariahBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan 09.03.2021Dokumen1 halamanLesson Plan 09.03.2021Zechrist ZechariahBelum ada peringkat
- Pupils Are Introduced To The Sounds CK, E, U, R Using A VideoDokumen1 halamanPupils Are Introduced To The Sounds CK, E, U, R Using A VideoZechrist ZechariahBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan 09.03.2021Dokumen1 halamanLesson Plan 09.03.2021Zechrist ZechariahBelum ada peringkat
- 05 03 2020Dokumen2 halaman05 03 2020Zechrist ZechariahBelum ada peringkat
- Teacher Recap About Colours From Previous Lesson. 2. Pupils Repeat After Teacher The Names of ColoursDokumen2 halamanTeacher Recap About Colours From Previous Lesson. 2. Pupils Repeat After Teacher The Names of ColoursZechrist ZechariahBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan 09.03.2021Dokumen1 halamanLesson Plan 09.03.2021Zechrist ZechariahBelum ada peringkat
- Inclusive Education EssayDokumen4 halamanInclusive Education EssayZechrist Zechariah50% (2)
- Pre TestDokumen1 halamanPre TestZechrist ZechariahBelum ada peringkat
- Teach Kids Advertising LiteracyDokumen8 halamanTeach Kids Advertising LiteracyJohn DoeBelum ada peringkat
- Saya Tahu, Kamu Tahu atau TidakDokumen34 halamanSaya Tahu, Kamu Tahu atau TidakmitchsipBelum ada peringkat
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics V: I - ObjectivesDokumen7 halamanA Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics V: I - ObjectivesMarsha EvangelistaBelum ada peringkat
- Episode 6Dokumen9 halamanEpisode 6Mark Anthony Nieva RafalloBelum ada peringkat
- Math2 - q4 - Mod2 - Comparing Unit of Measures PDFDokumen32 halamanMath2 - q4 - Mod2 - Comparing Unit of Measures PDFVhellyre FerolinoBelum ada peringkat
- Science 8 MDL IDEA L5 PRINTEDDokumen2 halamanScience 8 MDL IDEA L5 PRINTEDClarice Jenn MaltoBelum ada peringkat
- Technology in Teaching and LearningDokumen20 halamanTechnology in Teaching and LearningCris JanBelum ada peringkat
- AF5122Dokumen3 halamanAF5122Chin LBelum ada peringkat
- Educational Research: An IntroductionDokumen36 halamanEducational Research: An IntroductionPaul Aldrin OlaeraBelum ada peringkat
- Philippine & Asian EssaysDokumen6 halamanPhilippine & Asian EssaysKier Martin Patiag EvangelistaBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan Indirect InstructionDokumen4 halamanLesson Plan Indirect InstructionsunshinegrlBelum ada peringkat
- Module 2 Learner Centered ScriptDokumen6 halamanModule 2 Learner Centered ScriptJoey PerezBelum ada peringkat
- Educator Disposition Assessment: © 2017 Almerico, Johnston, Wilson 1Dokumen5 halamanEducator Disposition Assessment: © 2017 Almerico, Johnston, Wilson 1william staffordBelum ada peringkat
- Why Should I Hire YouDokumen6 halamanWhy Should I Hire YouDebasis DuttaBelum ada peringkat
- SQ - Spiritual QuotientDokumen52 halamanSQ - Spiritual Quotientradhekrsna89% (9)
- Soc133 - Martial Law EducationDokumen25 halamanSoc133 - Martial Law EducationKirig_Miming87% (46)
- Educ-30103 (1) (Replica)Dokumen72 halamanEduc-30103 (1) (Replica)Cierly Mae Deguia TantanBelum ada peringkat
- Siop Lesson PlanDokumen3 halamanSiop Lesson Planapi-201990414Belum ada peringkat
- Diversity Lesson PlanDokumen3 halamanDiversity Lesson Planapi-357058154100% (1)
- Weekly Home Learning Plan Grade 10 Week 4 Quarter 1Dokumen1 halamanWeekly Home Learning Plan Grade 10 Week 4 Quarter 1Ramlede BenosaBelum ada peringkat
- Child's Flower Shop Play ObservationDokumen7 halamanChild's Flower Shop Play ObservationQueenieBelum ada peringkat
- TM 1 - Sample Session PlanDokumen5 halamanTM 1 - Sample Session PlanOliver CalledoBelum ada peringkat
- Related Study 2 (Teacher's Preparedness and Professional Learning About Using Education Technology During The Covid 19 PandemicDokumen20 halamanRelated Study 2 (Teacher's Preparedness and Professional Learning About Using Education Technology During The Covid 19 PandemicJayson R. DiazBelum ada peringkat
- Indigenous StudiesDokumen5 halamanIndigenous Studiesapi-291319095Belum ada peringkat
- Student Attendance Punctuality Policy PDFDokumen11 halamanStudent Attendance Punctuality Policy PDFMichael O ConnorBelum ada peringkat
- POWERPOINT PRESENTATION Lesson in English 2Dokumen30 halamanPOWERPOINT PRESENTATION Lesson in English 2Dhel Ramos MalayaoBelum ada peringkat
- Mini Skill Test 5Dokumen2 halamanMini Skill Test 5Nhật Thành ĐỗBelum ada peringkat
- de Thi Hoc Sinh Gioi THPT Cap Quoc Gia (B GD Và ĐT)Dokumen14 halamande Thi Hoc Sinh Gioi THPT Cap Quoc Gia (B GD Và ĐT)Đình KhánhBelum ada peringkat
- Lade Sample ProjectDokumen26 halamanLade Sample ProjectOlumide AdebayoBelum ada peringkat
- Examination Result:: JANUARY 2019Dokumen1 halamanExamination Result:: JANUARY 2019Wong Chui SanBelum ada peringkat