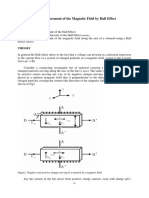
EP15 Measurement of The Acceleration Gravity
Diunggah oleh
Kw ChanJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniEP15 Measurement of The Acceleration Gravity
Diunggah oleh
Kw ChanEP15 Measurement of the Acceleration Gravity,
Using a Simple Pendulum
OBJECTIVE
To measure the acceleration gravity using a simple pendulum
THEORY
The periodic time T in seconds of a simple pendulum doing small vibrations can be
shown to be given by
L
T = 2π
g
where l is the length in m, and g is the acceleration gravity in m ⋅ s −2
This equation transforms to
g
L = ( 2 )T 2
4π
Thus a graph of L against T 2 will be a straight line and its gradient will
g
be K = , then g can be obtained.
4π 2
PROCEDURE
(1) Rotate the screw at the top of the device to make the length of the string about
60cm.
(2)Adjust the screws under the base of the device to make the frame vertical, and then
the string is parallel to the frame.
(3)Measure the diameter of the bob (denoted as d) five times along different direction
using vernier caliper, and then calculate its average.
d
(4)Measure the length of the string, denoted as l. So L = l + .
2
(5)Let the simple pendulum swing with a small angle. Record the time swinging 20
periods from the time tester. Repeat this 3 times.
(6)Change the length of the string to make it respective about 70cm, 80cm, 90cm,
100cm, 110cm.Repeat procedure (5) for various lengths, obtaining six sets of data.
DATA RECORDING AND PROCESSING
Zero reading of the vernier caliper d0=
Table1 diameter of bob
n 1 2 3 4 5 average
d(m)
Table2
Length in m Time of 20 periods in s
n Period T2 in
String Radius of Total T in s s2
1 2 3 mean
l bob d/2 L
1
2
3
4
5
6
g
Plot L against T 2 ,and then calculate the gradient of the straight line. Since K = ,
4π 2
use it calculate a value for g.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Chapter 9Dokumen155 halamanChapter 9Kw ChanBelum ada peringkat
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Diseases of Digestive SystemDokumen126 halamanDiseases of Digestive SystemKw ChanBelum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Teaching Calendar (2020-2021) .Docteaching Calendar (2020-2021)Dokumen7 halamanTeaching Calendar (2020-2021) .Docteaching Calendar (2020-2021)Kw ChanBelum ada peringkat
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- 11 GMppt-chapter9-2020 (Ok)Dokumen37 halaman11 GMppt-chapter9-2020 (Ok)Kw ChanBelum ada peringkat
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Liver and The Biliary TractDokumen109 halamanThe Liver and The Biliary TractKw ChanBelum ada peringkat
- 15 GMppt-chapter18-2020 (Ok)Dokumen19 halaman15 GMppt-chapter18-2020 (Ok)Kw ChanBelum ada peringkat
- 16 GMppt-chapter20-2020 (Ok)Dokumen9 halaman16 GMppt-chapter20-2020 (Ok)Kw ChanBelum ada peringkat
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- 13 GMppt-chapter16-2019 (Ok)Dokumen17 halaman13 GMppt-chapter16-2019 (Ok)Kw ChanBelum ada peringkat
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- 8.2 GMppt-chapter5-2-2020 (Ok and Important)Dokumen41 halaman8.2 GMppt-chapter5-2-2020 (Ok and Important)Kw ChanBelum ada peringkat
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Huang Z-GM Review-2020Dokumen202 halamanHuang Z-GM Review-2020Kw ChanBelum ada peringkat
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- 10 GMppt-chapter8-2020 (Ok)Dokumen30 halaman10 GMppt-chapter8-2020 (Ok)Kw ChanBelum ada peringkat
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- 14 GMppt-chapter17-2020 (Ok)Dokumen16 halaman14 GMppt-chapter17-2020 (Ok)Kw ChanBelum ada peringkat
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- EP09 Measuring The Curvature Radius of Lens Using NewtonDokumen2 halamanEP09 Measuring The Curvature Radius of Lens Using NewtonKw ChanBelum ada peringkat
- EP05 Tuning Fork Frequency Measurement With Stand MethodDokumen4 halamanEP05 Tuning Fork Frequency Measurement With Stand MethodKw ChanBelum ada peringkat
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- 12 GMppt-chapter12-2020 (Ok)Dokumen19 halaman12 GMppt-chapter12-2020 (Ok)Kw ChanBelum ada peringkat
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- 13 GMppt-chapter16-2019 (Ok)Dokumen17 halaman13 GMppt-chapter16-2019 (Ok)Kw ChanBelum ada peringkat
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- 9 GMppt-chapter7-2020 (Ok)Dokumen83 halaman9 GMppt-chapter7-2020 (Ok)Kw ChanBelum ada peringkat
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- EP13 Measurement of Angle of Prism - Use of SpectrometerDokumen5 halamanEP13 Measurement of Angle of Prism - Use of SpectrometerKw ChanBelum ada peringkat
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- 8.1 GMppt-chapter5-1-2020 (Ok and Important)Dokumen37 halaman8.1 GMppt-chapter5-1-2020 (Ok and Important)Kw ChanBelum ada peringkat
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- EP12 The Wheatstone Bridge and Specific ResistanceDokumen4 halamanEP12 The Wheatstone Bridge and Specific ResistanceKw ChanBelum ada peringkat
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- EP14 Index Refraction With The Prism SpectrometerDokumen5 halamanEP14 Index Refraction With The Prism SpectrometerKw ChanBelum ada peringkat
- EP10 Operation of A Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CRO)Dokumen4 halamanEP10 Operation of A Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CRO)Kw ChanBelum ada peringkat
- EP11 Measuring The Magnitude of The Magnetic Field Using Hall EffectDokumen5 halamanEP11 Measuring The Magnitude of The Magnetic Field Using Hall EffectKw ChanBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 3 - Chapter 8-Cytoskeleton ADokumen75 halamanLecture 3 - Chapter 8-Cytoskeleton AKw Chan33% (3)
- EP07 Measuring Coefficient of Viscosity of Castor OilDokumen2 halamanEP07 Measuring Coefficient of Viscosity of Castor OilKw ChanBelum ada peringkat
- Ep08 Measuring The Concentration of Sugar Solutions With Optical ActivityDokumen2 halamanEp08 Measuring The Concentration of Sugar Solutions With Optical ActivityKw ChanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1b - CellDokumen49 halamanChapter 1b - CellKw ChanBelum ada peringkat
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)