Analog
Diunggah oleh
Maurice Ghanem0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
23 tayangan1 halamanJudul Asli
Analog.docx
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
23 tayangan1 halamanAnalog
Diunggah oleh
Maurice GhanemHak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 1
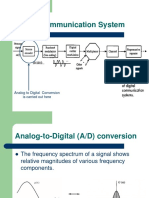
Analog – digital conversion
Analog-to-digital conversion is an electronic process in which a
continuously variable (analog) signal is changed, without altering its
essential content, into a multi-level (digital) signal. The input to an analog-
to-digital converter (ADC) consists of a voltage that varies among a
theoretically infinite number of values. The output of the digital sign is
represented as binary form(0 and 1).
An ADC is defined by its bandwidth and its signal-to-noise ratio. The
bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate. The
analog signal is continuous in time and it is necessary to convert this to a
flow of digital values. It is therefore required to define the rate at which new
digital values are sampled from the analog signal.
The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective
number of bits (ENOB).
Types of ADC: Digital Ramp ADC, Successive Approximation ADC, Flash
ADC, Wilkinson, Integrating, Delta-encoded, Pipeline, Sigma-delta, Time-
interleaved, Intermediate FM stage.
The use of ADC:
Music recording: producing music on computers
Digital signal processing
Scientific instruments
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Analog To Digital ConvertersDokumen11 halamanAnalog To Digital ConvertersAshutosh YadavBelum ada peringkat
- Nama: Refin Ananda NIM: 3.32.17.0.20 Kelas: EK-3A Individual Presentation 2 Analog To Digital Converter 1. The Meaning of ADCDokumen4 halamanNama: Refin Ananda NIM: 3.32.17.0.20 Kelas: EK-3A Individual Presentation 2 Analog To Digital Converter 1. The Meaning of ADCRifky Yoga PratamaBelum ada peringkat
- Wireless AssignmentDokumen7 halamanWireless AssignmentJawad SandhuBelum ada peringkat
- Multimedia PresentationDokumen16 halamanMultimedia PresentationHusain PoonawalaBelum ada peringkat
- Analog To Digital Converter - Block Diagram, Types Its ApplicationsDokumen10 halamanAnalog To Digital Converter - Block Diagram, Types Its ApplicationsNikka Hernandez FloresBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation Sensor and TransducerDokumen8 halamanPresentation Sensor and TransducerRam Vijay YadavBelum ada peringkat
- Acknowledgement: Term Paper of Analog Communication System (ECE 302')Dokumen13 halamanAcknowledgement: Term Paper of Analog Communication System (ECE 302')ishan65Belum ada peringkat
- Experiment No. 6: Objective: ApparatusDokumen4 halamanExperiment No. 6: Objective: ApparatusNioBelum ada peringkat
- Analog To Digital IO: Group MembersDokumen7 halamanAnalog To Digital IO: Group MembersRam Vijay YadavBelum ada peringkat
- Analog To Digital ConverterDokumen14 halamanAnalog To Digital Converterparth bhardwajBelum ada peringkat
- Adc DacDokumen16 halamanAdc DacchillnessBelum ada peringkat
- Analog-To-Digital Conversion Btech IIIDokumen50 halamanAnalog-To-Digital Conversion Btech IIILisa BhagatBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 10 (Part Ni Solo)Dokumen10 halamanChapter 10 (Part Ni Solo)edward solomonBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Measurement and Instrumentation: Digital Signal ProcessingDokumen17 halamanElectrical Measurement and Instrumentation: Digital Signal ProcessingSamuel AdamuBelum ada peringkat
- Analog To Digital ConverterDokumen4 halamanAnalog To Digital Convertermuzamiru Kahise sayumweBelum ada peringkat
- Basics of Analog-To-digital ConvertionDokumen9 halamanBasics of Analog-To-digital ConvertionThanh Nhan LeBelum ada peringkat
- ADC FinalDokumen35 halamanADC FinalAmit BarBelum ada peringkat
- Analog To Digital ConverterDokumen57 halamanAnalog To Digital ConverterAnurag Chauhan100% (1)
- Digital Control SystemDokumen23 halamanDigital Control SystemBHAVNA AGARWALBelum ada peringkat
- Mbed Course Notes - Analog Input and OutputDokumen24 halamanMbed Course Notes - Analog Input and OutputBelkhiri MohammedBelum ada peringkat
- Unit II DAS & Signal CommunicationDokumen65 halamanUnit II DAS & Signal CommunicationHOD MechanicalBelum ada peringkat
- Medical Signal Processing (BM321) Report 1: Configuration of A DSP System Homework 1Dokumen15 halamanMedical Signal Processing (BM321) Report 1: Configuration of A DSP System Homework 1Batool HerzallahBelum ada peringkat
- Analog To Digital ConvertersDokumen15 halamanAnalog To Digital ConvertersJuan Angel AlvaradoBelum ada peringkat
- Using A BJT As A Switch: An Example: BelowDokumen10 halamanUsing A BJT As A Switch: An Example: BelowPrakhar BhatnagarBelum ada peringkat
- Jadavpur University: PptonDokumen39 halamanJadavpur University: PptonAmit BarBelum ada peringkat
- Analog-to-Digital-Convesion v2 - StudentDokumen43 halamanAnalog-to-Digital-Convesion v2 - StudentJysh MamusogBelum ada peringkat
- ADCDokumen5 halamanADCnazmulBelum ada peringkat
- Digital To Analogue ConvertersDokumen6 halamanDigital To Analogue ConvertersAbhinav SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Analog To Digital Converters PresentationDokumen15 halamanAnalog To Digital Converters Presentationnguyenphuonghuy1979100% (1)
- ADCsDokumen12 halamanADCswalidBelum ada peringkat
- Unit - 1 - Introduction To Digital ElectronicsDokumen25 halamanUnit - 1 - Introduction To Digital ElectronicsAvinash SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Communication System: Analog To Digital Conversion Is Carried Out HereDokumen37 halamanDigital Communication System: Analog To Digital Conversion Is Carried Out Hereahmed yuosifBelum ada peringkat
- Bel - 16 - ADC and DACDokumen26 halamanBel - 16 - ADC and DACBharavi K SBelum ada peringkat
- Sistem Tertanam: Analog and Digital SignalDokumen19 halamanSistem Tertanam: Analog and Digital SignaldsadasdasBelum ada peringkat
- I. Analog To Digital ConversionDokumen1 halamanI. Analog To Digital ConversionMariel Mae A. MaculbeBelum ada peringkat
- Mechatronics Adc DacDokumen24 halamanMechatronics Adc DacPrasanth NavaBelum ada peringkat
- Analog and Digital SignalsDokumen2 halamanAnalog and Digital SignalsMark ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- DSP PartADokumen106 halamanDSP PartAchanduBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Communication IntroductionDokumen69 halamanDigital Communication IntroductionlokeshwarrvrjcBelum ada peringkat
- What Is The Use of PCM When There Are ADokumen2 halamanWhat Is The Use of PCM When There Are Asamiksha choudharyBelum ada peringkat
- ADCDokumen2 halamanADCMayilsamy MayilBelum ada peringkat
- Lec 4Dokumen24 halamanLec 4بشير عماد كاظمBelum ada peringkat
- Analog To Digital ConvertersDokumen21 halamanAnalog To Digital ConvertersMazhar AliBelum ada peringkat
- Analog To Digital ConvertorDokumen77 halamanAnalog To Digital ConvertorDarshan ValaBelum ada peringkat
- A Level PracticeDokumen2 halamanA Level PracticeRakotoarison Louis FrederickBelum ada peringkat
- D/A Conversion and A/D ConversionDokumen6 halamanD/A Conversion and A/D Conversionvishwanath cBelum ada peringkat
- CH 08Dokumen42 halamanCH 08engaydiBelum ada peringkat
- Course Topic 2. Discrete-Time Signals and Systems (16x9)Dokumen28 halamanCourse Topic 2. Discrete-Time Signals and Systems (16x9)Gennelyn IsraelBelum ada peringkat
- 1.1 - Introduction To DSP - 20F-ELEG631-610 - Digital Signal ProcessingDokumen2 halaman1.1 - Introduction To DSP - 20F-ELEG631-610 - Digital Signal Processingalexsg5Belum ada peringkat
- Adcs Wikipedia BookmarkedDokumen30 halamanAdcs Wikipedia BookmarkedBenedict JoBelum ada peringkat
- Analog To DigitalDokumen46 halamanAnalog To DigitalSaleem HaddadBelum ada peringkat
- CB and Delta ModulationDokumen58 halamanCB and Delta ModulationPraghadeeshBelum ada peringkat
- Inverters SpecsDokumen11 halamanInverters SpecsbhuwaneshtakBelum ada peringkat
- Class Notes - ADC For Numerical RelayDokumen5 halamanClass Notes - ADC For Numerical RelaybiswajitsahooBelum ada peringkat
- Analog-To-Digital Converter - WikipediaDokumen16 halamanAnalog-To-Digital Converter - WikipediaMina zhouBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4Dokumen23 halamanChapter 4Tejan Kumar SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Intro To Digital CommunicationDokumen29 halamanIntro To Digital CommunicationRyan OlaybalBelum ada peringkat
- A D ConverterDokumen20 halamanA D ConverterRenu TyagiBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Signal Processing: Instant AccessDari EverandDigital Signal Processing: Instant AccessPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2)
- Meet The Awesome Orchestra! Instrument Families: ObjectiveDokumen9 halamanMeet The Awesome Orchestra! Instrument Families: ObjectiveMaurice GhanemBelum ada peringkat
- Food Combination LessonsDokumen26 halamanFood Combination LessonsMaurice GhanemBelum ada peringkat
- Food Combining Chart Arise and ShineDokumen1 halamanFood Combining Chart Arise and ShineMaurice GhanemBelum ada peringkat
- Food Combining ChartDokumen1 halamanFood Combining Chart57starsBelum ada peringkat
- Food Combining ChartDokumen2 halamanFood Combining Chartmixy92mixyBelum ada peringkat
- Holst JupiterDokumen1 halamanHolst JupiterMaurice GhanemBelum ada peringkat
- William Wallace: About The ArtistDokumen3 halamanWilliam Wallace: About The ArtistMaurice GhanemBelum ada peringkat
- Music Fun Free Printables by Leslie DiederichDokumen5 halamanMusic Fun Free Printables by Leslie DiederichMaurice GhanemBelum ada peringkat
- 10 Little Indians PDFDokumen1 halaman10 Little Indians PDFMaurice Ghanem0% (1)
- FormDokumen20 halamanFormMaurice Ghanem0% (1)
- FreeBoomwhackersStaffNoteChart PDFDokumen2 halamanFreeBoomwhackersStaffNoteChart PDFMaurice GhanemBelum ada peringkat
- When This Boy Meets WorldDokumen1 halamanWhen This Boy Meets WorldMaurice GhanemBelum ada peringkat
- 20th Century Form by James Tenney PDFDokumen21 halaman20th Century Form by James Tenney PDFPaul ChauncyBelum ada peringkat
- MaterialsDokumen1 halamanMaterialsMaurice GhanemBelum ada peringkat
- EqualizersDokumen2 halamanEqualizersMaurice GhanemBelum ada peringkat
- GamesDokumen1 halamanGamesMaurice GhanemBelum ada peringkat
- Got Those BluesDokumen1 halamanGot Those BluesMaurice GhanemBelum ada peringkat
- Analog - Digital ConversionDokumen1 halamanAnalog - Digital ConversionMaurice GhanemBelum ada peringkat
- DYCONEX Materials en 2020 ScreenDokumen2 halamanDYCONEX Materials en 2020 ScreenhhaiddaoBelum ada peringkat
- ANSI AAMI ST63 2002 - Sterilization of Healthcare Products - Dry HeatDokumen54 halamanANSI AAMI ST63 2002 - Sterilization of Healthcare Products - Dry HeatGraciane TagliettiBelum ada peringkat
- Thesis StoryboardDokumen5 halamanThesis StoryboardJill Brown100% (2)
- Technical Test 03Dokumen13 halamanTechnical Test 03KartikBelum ada peringkat
- Excavation Trench Permit Ex 1 F0206Dokumen5 halamanExcavation Trench Permit Ex 1 F0206emeka2012Belum ada peringkat
- Assignment 5 WarehousingDokumen4 halamanAssignment 5 WarehousingabbasBelum ada peringkat
- Quemador BrahmaDokumen4 halamanQuemador BrahmaClaudio VerdeBelum ada peringkat
- Machine Design REE 302: CH 1: Introduction To Mechanical Engineering DesignDokumen26 halamanMachine Design REE 302: CH 1: Introduction To Mechanical Engineering DesignDull PersonBelum ada peringkat
- Pedagogical Leadership. Baird - CoughlinDokumen5 halamanPedagogical Leadership. Baird - CoughlinChyta AnindhytaBelum ada peringkat
- Bug Life Cycle in Software TestingDokumen2 halamanBug Life Cycle in Software TestingDhirajBelum ada peringkat
- Creative LibrarianDokumen13 halamanCreative LibrarianulorBelum ada peringkat
- Aquinas Five Ways To Prove That God Exists - The ArgumentsDokumen2 halamanAquinas Five Ways To Prove That God Exists - The ArgumentsAbhinav AnandBelum ada peringkat
- Report Painter GR55Dokumen17 halamanReport Painter GR55Islam EldeebBelum ada peringkat
- Fcu Valve Honeywel PDFDokumen6 halamanFcu Valve Honeywel PDFRyn YahuFBelum ada peringkat
- APPSC GROUP 4 RESULTS 2012 - Khammam District Group 4 Merit ListDokumen824 halamanAPPSC GROUP 4 RESULTS 2012 - Khammam District Group 4 Merit ListReviewKeys.comBelum ada peringkat
- Power-Miser 12 Water Heater ManualDokumen32 halamanPower-Miser 12 Water Heater ManualClaudeVanDammBelum ada peringkat
- ITP - Plaster WorkDokumen1 halamanITP - Plaster Workmahmoud ghanemBelum ada peringkat
- Bio 104 Lab Manual 2010Dokumen236 halamanBio 104 Lab Manual 2010Querrynithen100% (1)
- 09-11-2016 University Exam PaperDokumen34 halaman09-11-2016 University Exam PaperSirisha AsadiBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To SCRDokumen19 halamanIntroduction To SCRAlbin RobinBelum ada peringkat
- ZH210LC 5BDokumen24 halamanZH210LC 5BPHÁT NGUYỄN THẾ0% (1)
- RV900S - IB - Series 3Dokumen28 halamanRV900S - IB - Series 3GA LewisBelum ada peringkat
- Catalog NeosetDokumen173 halamanCatalog NeosetCarmen Draghia100% (1)
- IDL6543 ModuleRubricDokumen2 halamanIDL6543 ModuleRubricSteiner MarisBelum ada peringkat
- Research Paper On N Queen ProblemDokumen7 halamanResearch Paper On N Queen Problemxvrdskrif100% (1)
- Content Analysis of Studies On Cpec Coverage: A Comparative Study of Pakistani and Chinese NewspapersDokumen18 halamanContent Analysis of Studies On Cpec Coverage: A Comparative Study of Pakistani and Chinese NewspapersfarhanBelum ada peringkat
- Sim Educ101Dokumen101 halamanSim Educ101Rolando AmadBelum ada peringkat
- Yz125 2005Dokumen58 halamanYz125 2005Ignacio Sanchez100% (1)
- Motive 27Tmx: Data SheetDokumen2 halamanMotive 27Tmx: Data SheetUlisesGómezBelum ada peringkat
- SKF CMSS2200 PDFDokumen2 halamanSKF CMSS2200 PDFSANTIAGOBelum ada peringkat