Content: Experiment No. Name of The Experiment No
Diunggah oleh
P SankarJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Content: Experiment No. Name of The Experiment No
Diunggah oleh
P SankarHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Department Of CSE & IT
CONTENT
Experiment Page
Name of the Experiment
No. No.
1
1 To recognize various component of PC.
Dismantling and assembling of PC. 6
2
3
Use of h/w trainer kit.
12
Simulation of simple fundamental units like
4 half adder full adder etc. 25
Page | 1 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE REQUIREMENTS :-
1.PC components.
2. Hardware trainer kit for
Printer ,SMPS, Motherboard, Real time clock, CPU, Hard disk.
3. Simulation software(XLINIX).
Page | 2 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Lab Experiment No. :- 1
Objective :-
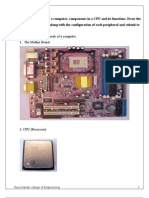
To Recognize the various components of a Personal Computer.
Theory:-
The basic components of a PC are
1. Input Unit
2. Output unit
3. Memory unit
4. Control unit
5. Arithmetic logic unit
Input Unit :-
It is the unit through which data/instructions can be entered into the
computers .
e.g. Keyboard , Mouse etc.
Output Unit :-
It is the unit by which we can get output from the entered input from the
computer.
e.g. Monitors ,Printer, Speaker etc.
Page | 3 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Memory Unit :-
It stores the information by providing facility to the CPU actively by
providing necessary data to CPU.
Memory units are of two types
1.Primary memory
2. Secondary memory.
Primary Memory:- It is also of two types:
i) RAM
ii) ROM
RAM:- It can be randomly accessed.
Memory is temporarily used because when the power goes off ,all
the data stored in it are erased.So it is volatile in nature.It can be read and
the data can be written into it.
ROM:- It is also randomly accessed. It is only readmemory unit.It is non-
volatile in nature.
It can be read only but datas can’t be written into it.
ALU:- It performs arithmetic operation like addition,subtraction etc and
logical operation loke AND,OR,NAND etc. It works in electronic speed but
the device attached to it works in low speed.That’s why processor can
handle all the peripheral devices at a time.
IT establishes well coordination between other four functional unit.
Page | 4 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
CU:- It is the unit which controls the flow of information through the
processor and coordinate the activities the activities of other unit which are
within it.
So it is the brain within the brain as it controls what happens inside the
processor.
It generate timing signal and control signal for well coordination.
Configurtion of a PC.
SI Name of Name of Capacity/frequency interface
NO component Manufacturer
1. Processor
2. MotherBoard
3. RAM
4. HDD
5. FDD
6. DVD
7. TFT/CRT
8. Keyboard
9. Mouse
10. UPS
11. Cabinet
12. Speaker
Page | 5 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Processor:- The microprocessor accepts inputs from the user in the
form of data and instruction. It process the information and instruction and
then send the processed information to the output device.
Motherboard:- It is the main circuit of PC.It conatains the interface for
the microprocessor,BIOS,Memory and storage device neeed to control
peripheral devices such as monitor,keyboard,mouse etc.
RAM:- It stores data temporarily.So it is called volatile.
HDD:- IT is a secondary storage device for permanent data storage
device i.e. placed in the system.It is similar to human brain where all the
past to present events are stored.
DVD RAM: The Digital versatile disc stored digitally.
A DVD writer is a DVD player as well as a writer.
FDD: It is a n external storage device. It is magnetic round disc enclosed
in a plastic jacket.
Today we have double size high quality to density disk with 1.44 MB of
size.
Page | 6 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Keyboard:- It is a primary input device of the PC similar to type writer.
Mouse:- It is used to point to the desired position in the computer. It is
also an input device.
UPS:- It is the device that produce supply to the PC.
It provides all the time of power cut.So we can save the current data and
shut down properly.
Speaker: It is an output device through which CPU can produce sound
for the user.
TFT monitor:- It is an output device through wich we can read data.
Cabinet:- outer covering of CPU.
Conclusion:-
Page | 7 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
EXPERIMENT NO:-02
OBJECTIVES:- To understand how the different components of PC
are connected to work properly.
Components required:-
1.cabinet
2.SMPS.
3.HDD
4.processor
5.Motherboard
6.Ram
7.IDE cable.
8.ROM
9.System fan and CPU fan.
10.Tool kit
Description:
The required components are taken and checked whether the
components are good condition or not.
At first clean the required components and it should be done with
paint brush.
All the components handled with care.
The step by step procedure should be followed for dismantling and
assembling of the PC.
The procedure dismantling and assembling are as follows :
Page | 8 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Building TheComputer
Step 1: Prepare the case
Remove the empty computer case from its packing and remove both side panels and
takeout any items that may be inside the case .Place it on the work space so that the
motherboard facing up.
Step 2: Installing the Mother Board rises
Inspect whether the motherboard risers are installed properly, if not then install it
properly so that the motherboard will not be in direct contact with the metal case.
Step 3: Installing the Dives and mother board in the case
1: Remove side panel
Remove the side panel from the case in order to gain access to the cabinet as well as
the motherboard properly.
2: Remove front external drive panel
Remove the drive bay blanking the spaces.. So that we can install the required drives
properly and freely.
3: Installing external drives
With the blanking places removed slide the drives into their corresponding bays.
4: Case screws
Fix the drives using the case screw provided .The screw should not be so tightly placed,
otherwise it may harm the respective components of the PC.
5: Fixing the drives
Fix the optical and floppy drives into its places with screwed properly.
6: Drives installed
The optical and floppy drives located in the correct
bays in the pc case.
Page | 9 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
7: motherboard mask
8: Discard unwanted parts
After everything is in its place just discard the unwanted parts that were present initially
in the case.
Page | 10 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Step 4 :Installing mother board in the case
1: Installing the Processor
Place the CPU into its slot properly seeing the cut marks
present in the processor for identification. Care must be
given while installing the CPU, if any Pin breaks then the
Processor will become useless. Then place the sink and
CPU fan properly and lock it with the lock provided.
Page | 11 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
2: CPU and Fan
The CPU fan should be placed over the CPU to
keep the processor cool .
Place the RAM into its slots. Press it to
3: Installing the RAM
get the RAM Locked. If the RAM is not
placed properly then the PC will not
start. And will give a beep sound.
4: Installing the power supply
Use the SMPS(Switch Mode Power Supply) cables to give power supply to the
individual components of the PC.
5: Installing The HDD
The HDD should be Placed in its
proper place and should be
connected with the ATA cable or The
SATA cable as the port may be. And
power supply should be given to it.
Page | 12 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
6: Connecting the case cable
Connect the below cables properly as per instruction. And connect the same cable to
the motherboard also.
Step 5: Closing The system case by cover
Once all the parts of the PC are connected to its slots properly and firmly just close the
system case and screw it properly.
Conclusion :-
Page | 13 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Experiment No. 3
Objective :
i)Study of Fault analysis point of the CPU trainer kit.
ii) Study of Dot Matrix Printer.
iii) To study the Fault analysis points of Dot Matrix printer
iv) Study of VBMB 40 HD Trainer kit.
v) Study of real time clock using 465 hard disk driver.
EQUIPMENTS REQUIRED:
1. CPU Trainer kit
2. Monitor
3. Keyboard
4. Mouse
THEORY :
The CPU Trainer kit has 8 different fault analysis point. To estimate the various
fault covering the individual sections of personal computers
T1: For Keyboard logic
T2 : For BIOS logic
T3: For Hard Disk logic
T4 : For Mouse logic
T5: For Video logic(for synchronization horizontally)
T6: For Video logic(for Vertical synchronization)
T7: For Serial Communication logic
T8: For Parallel Communication logic
Page | 14 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
PROCEDURE :
T1:
Fault Analysis: Switch off the system, Put T1 in open mode and switch ON the
system.
Symptom: Any character that is to be given through the keyboard can not be
displayed or the keyboard can not work properly.
T2:
Fault Analysis: Switch off the system, Put T2 in open mode and switch ON the
system.
Symptom: Without processing any key the control will automatically flow to the
BIOS
T3:
Fault Analysis: Switch off the system, Put T3 in open mode and switch ON the
system.
Symptom: The OS will not be properly loaded, HDD will not be initialized
T4:
Fault Analysis: Switch off the system, Put T4 in open mode and switch ON the
system.
Symptoms: The mouse will not work properly.
T5:
Fault Analysis: Switch off the system, Put T5 in open mode and switch ON the
system.
Symptoms:Display scroll horizontally
Page | 15 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
T6
Fault Analysis: Switch off the system, Put T6 in open mode and switch ON the
system.
Symptom:Display scroll vertically
T7:
Fault Analysis: Switch off the system, Put T7 in open mode and switch ON the
system.
Symptoms: Serial Port does not receive or transmit information to or from its sub
system or interface unit.
T8:
Fault Analysis: Switch off the system, Put T8 in open mode and switch ON the
system.
Symptom:It prints junk character
CPU TRAINER KIT
CONCLUSION 1:
Page | 16 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Objective 2:- Study of Dot Matrix Printer.
EQUIPMENTS REQUIRED:
1.DOT Matrix Printer
2.Power supply unit
3.Power cord
DESCRIPTION:
1.Thisthe first type of printer to be used in home and school but they are not used
now-a-days.
2.A Dot Matrix Printer or impact matrix printer is a type of computer printer with a
print head that run back and forth or up and down motion, in the phase and print
by impact , striking an ink soaked cloth ribbon against the paper, much like the
print mechanism on a type writer.
3. Each dot is produced by a tiny metal rod also called a wire or pin which is
driven forward by the power of tiny electromagnet or solenoid either directly or
through small parts.
Page | 17 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
ADVANTAGES:
1.Relatively cheap to buy
2.Low operating cost
3.Create carbon copy using carbonated papers.
DISADVANTAGES:
1.Print quality is poor and important documents are not suitable to give managers
or customers.
2.Very Slow
3.Noisy
4.Can not produce colour copies.
CONCLUSION 2:
Page | 18 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
OBJECTIVE 3: To study the Fault analysis points of Dot Matrix printer
EQUIPMENTS REQUIRED:
1.Dot matrix printer Trainer kit.
2.Power supply
PROCEDURE:
Dot matrix printer Trainer kit has 8 Fault analysis point to identify 8 different fault
generated in DMP Trainer kit.
The fault analysis points are
T1:Power logic
T2.Wrong Character printing
T3.Paper sensor without paper
T4.Print in the same line
T5.Home position
T6.Line space incorrect
T7.Paper out
T8.Single dot or collection of dots are missing
Page | 19 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
DESCRIPTION:
T1:
Fault Analysis:T1 is normally in closed position, to introduce the problem switch
off the printer . T1 is open and switch on the printer to identify the problem.
Symptom:No printer operation can be performed
T2:
Fault Analysis:T2 is normally in closed position, to introduce the problem switch
off the printer . T2 is open and switch on the printer to identify the problem.
Symptom:Printer prints wrong character.
T3:
Fault Analysis:T3 is normally in closed position, to introduce the problem switch
off the printer . T3 is open and switch on the printer to identify the problem.
Symptoms:The printer will sense the paper even when the paper is not available for
printing.
T4:
Fault Analysis:T4 is normally in closed position, to introduce the problem switch
off the printer . T4 is open and switch on the printer to identify the problem.
Symptom:Overlapping of characters will be identified.
T5:
Fault Analysis:T5 is normally in closed position, to introduce the problem switch
off the printer . T5 is open and switch on the printer to identify the problem.
Symptom:Home position sensor may be defective. The sensor will not at the initial
position by pressing initialization button. It will move to the end.
T6:
Fault Analysis:T6 is normally in closed position, to introduce the problem switch
off the printer . T6 is open and switch on the printer to identify the problem.
Page | 20 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Symptoms:Line feeding is not proper.
T7:
Fault Analysis:T7 is normally in closed position, to introduce the problem switch
off the printer . T7 is open and switch on the printer to identify the problem.
Symptom:Carriage motor struck while initializing the printer. The sensor can not
be initialized by pressing the initialization button.
T8:
Fault Analysis:T8 is normally in closed position, to introduce the problem switch
off the printer . T8 is open and switch on the printer to identify the problem.
Symptom:While printing single dot or line of dots are missing consistently.
CONCLUSION 3:
Page | 21 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
OBJECTIVE 4 : Study of VBMB 40 HD Trainer kit.
EQUIPMENTS REQUIRED:
1.Micro controller 51EB
2.One Hard Disk
3.VBMB 40 Card
4.One 40 core cable, one 50 core cable and one serial cable
5.Multi output power supply unit
6.one VBMB 40 installer CD
7.One keyboard
PROCEDURE:
1.Go to WINXTALK program
2.Choose open point (the communication setting are already set, do not change).
3.Choose communication window (from the WINXTALK menu or F2 shortcut)
4.From Micro controller type the command “ SM” and press enter
5. You will find # prompt on the monitor and serial mode on the micro 51 LED
display
6.Type command “pi 4100” on the 3 prompt of WINXTALK communication
windows and press enter
Page | 22 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
7.From the text file option of WINX communication window choose download
push button(note the number of characters transmitted appear on the status bar of
WINX communication window)
8.Click on # type the command “go 4100” and press enter, the message appears ,
the information about HD that is cylinder, comma, sector etc and the next
command prompt is LBA= 0x00000000,(R)ead , (W)rite,(L)BA , (U)p , (D)own ,
(h)ex dump, (q)uit
9.Press 'L' from key board to select the hexa decimal address , then provide the
address value suppose “55”
10.Once again the previous command prompt LBA= 0x00000000,(R)ead ,
(W)rite,(L)BA , (U)p , (D)own , (h)ex dump, (q)uit will appear.
11.Choose 'R' and ' H' to see the information stored in the address of the HD.
12.Press “INT” key from the micro 51EB then # prompt will appear on the WINX
communication window.
13.Type the command “FP 600061ff 77” (here 77 is data) then press enter.
14.At the # prompt once again type the command “go 4100” and press enter.
15.Press “L” key from the key board and provide LBA address “55” then press
enter.
16.At the command prompt LBA= 0x00000000,(R)ead , (W)rite,(L)BA , (U)p ,
(D)own , (h)ex dump, (q)uit will appear. Then press “W” key when warning
message will appear then press “Y” “sector write OK” .
17.At LBA prompt press 'R' and 'H' , you can see the written in the HD
Page | 23 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
MICRO 51 EB 50 and
40 CORE CABLE
VBMB 40 CARD
CONCLUSION 4:
Page | 24 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
OBJECTIVE 5 : Study of real time clock using 465 hard disk driver.
EQUIPMENTS REQUIRED:
1.VBMB 15 card
2.PCI driver
3.50 core cable
PROCEDURE:
1.Open PLXP on the desktop, go to command click on it.
2.Reset COP then open my computer.
3.Go to CD-drive click on VPCI-107 then click on program.
4.Then double click on VBMB 15 exe file.
5.One black screen will come and it will ask for confirmation. Enter 'y' then give
value for hour,minute and second.
6.The given time will be displayed in real-time clock kit.
Page | 25 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
PCI DRIVER REAL TIME CLOCK
VBMB 15 CARD
CONCLUSION 5:
Page | 26 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
EXPERIMENT NO.4
OBJECTIVE:-
Simulation of fundamental unit like
1. Half adder
2. Full adder and
3. Multiplexer
Software required:-
XILINX ISE 9.1i
Theory:-
Halfadder:-
Procedure:-
Step1:
To simulate the functional working of Halfadder we need XILINX 9.1i to
run in Admin mode as shown below.
Page | 27 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Step2:
Go to file menu and chose new project.
Step3:
Type the project name and then choose the top level source type as
HDL.
Page | 28 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Stpe4:
Set the parameter in the window as
Family- Spantan3
Device-XC3S200
Package-FT256
Speed- 4
Preferred Language-VHDL
And press next
Page | 29 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Step5:
Choose the new source and press next and whenever the new window
open,Put the same file name and choose VHDL module
.
Page | 30 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Step6:
In the next window input two port name as input1 and input2 and direction as
in.Then input two port name as sum and carry and set direction as out.
Step7: And press next.
Page | 31 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Step8: Press next
Step9: Press next
Page | 32 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Step10: Press next
Step11:Press finish
Page | 33 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Step12: Write the HDL code for half adder followed by begin.
Step13:
Double click on the Synthesize.xst and go to check syntax and if error not
found the following screen appear.
Page | 34 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Step14:
Then click on the view RTL schme
Page | 35 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Step15:Then following output screen output screen appear.
Page | 36 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Conclusion:-
Page | 37 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
FULL ADDER
Theory:
Procedure
Step1:
To simulate the functional working of full adder we need XILINX 9.1i to run in
Admin mode as shown below.
Page | 38 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Step2:
Go to file menu and chose new project.
Step3:
Type the project name and then choose the top level source type as HDL.
Page | 39 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Stpe4:
Set the parameter in the window as
Family- Spantan3
Device-XC3S200
Package-FT256
Speed- 4
Preferred Language-VHDL
And press next
Page | 40 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Step5:
Choose the new source and press next and whenever the new window open, Put the
same file name and choose VHDL module
Page | 41 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Step6:
In the next window input two port name as input1 and input2 and direction as
in.Then input two port name as sum and carry and set direction as out.
Step7: And press next.
Page | 42 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Step8: Press next
Step9: Press next
Page | 43 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Step10: Press next
Step11:Press finish
Page | 44 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Step12: Write the HDL code for half adder followed by begin.
Page | 45 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Step13:
Double click on the Synthesize.xst and go to check syntax and if
error not found the following screen appear.
Page | 46 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Step14:
Then click on the view RTL schme
Step15:Then following output screen output screen appear.
Page | 47 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Conclusion:-
Page | 48 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
MULTIPLEXER
Step1:
To simulate the functional working of full adder we need XILINX 9.1i to run in
Admin mode as shown below.
Step2:
Go to file menu and chose new project.
Page | 49 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Step3
Type the project name and then choose the top level source type as HDL.
Stpe4:
Set the parameter in the window as
Family- Spantan3
Device-XC3S200
Package-FT256
Speed- 4
Preferred Language-VHDL
And press next
Page | 50 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Step5:
Choose the new source and press next and whenever the new
window open, Put the same file name and choose VHDL module
Page | 51 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Page | 52 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Step6:
In the next window input two port name as input1 and input2
and direction as in.Then input two port name as sum and carry
and set direction as out.
Step7: And press next.
Page | 53 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Step8: And press next
Step9: And press next
Page | 54 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Step10: And press finish
Step12: Write the HDL code for half adder followed by begin
Page | 55 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Step13:
Double click on the Synthesize.xst and go to check syntax and
if error not found the following screen appear.
Page | 56 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Step14:Then following output screen output screen appear
Page | 57 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Department Of CSE & IT
Conclusion:-
Page | 58 Prepared By Mr.Neelamani Samal
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Installation of Operating SystemDokumen56 halamanInstallation of Operating SystemRandy RgtBelum ada peringkat
- 2G CMDDokumen3 halaman2G CMDأبوعمر الفاروق عبدالرحمنBelum ada peringkat
- Install Computer Systems and NetworkDokumen61 halamanInstall Computer Systems and NetworkRhenmar Morales GalvezBelum ada peringkat
- Thermal Methods of AnalysisDokumen76 halamanThermal Methods of AnalysisAzuriak1100% (2)
- TCD 114 RPD ON trouble detection and countermeasuresDokumen7 halamanTCD 114 RPD ON trouble detection and countermeasuresFERNSBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7 Additional Problems SolutionsDokumen9 halamanChapter 7 Additional Problems SolutionsypobuleshBelum ada peringkat
- 3264 - 01 - 02 - FU Steering Control Unit Handwheel, Type 105-106Dokumen20 halaman3264 - 01 - 02 - FU Steering Control Unit Handwheel, Type 105-106MariosBelum ada peringkat
- Introducing Unisab II Version 2.05.1 and 2.05.2Dokumen4 halamanIntroducing Unisab II Version 2.05.1 and 2.05.2Mahmoud Mohamed100% (1)
- Wifi Offload CiscoDokumen70 halamanWifi Offload Ciscorachid190274Belum ada peringkat
- SSC - Ict10 - Q1 - W8 - Installing and Configuring Computer System 8Dokumen8 halamanSSC - Ict10 - Q1 - W8 - Installing and Configuring Computer System 8Cielo Marie CastroBelum ada peringkat
- COA - Lab ManualDokumen48 halamanCOA - Lab ManualKarthiBelum ada peringkat
- IT WorkShop Lab ManualDokumen74 halamanIT WorkShop Lab ManualcomputerstudentBelum ada peringkat
- Itwork ShopDokumen63 halamanItwork ShopSai KumarBelum ada peringkat
- CSS11 SSLM Week 7-1Dokumen8 halamanCSS11 SSLM Week 7-1Axel RamirezBelum ada peringkat
- PSP (20AES0503) AK20 Record Programs OnlyDokumen87 halamanPSP (20AES0503) AK20 Record Programs Onlyckissyou04Belum ada peringkat
- PC Assembly & Troubleshooting Lab ReportDokumen37 halamanPC Assembly & Troubleshooting Lab ReportjakasBelum ada peringkat
- Quarter-1 FilipinoDokumen14 halamanQuarter-1 FilipinoLeonesa De Gracia DalisayBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Assembly and DisassemblyDokumen9 halamanComputer Assembly and DisassemblyAllel CensoBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter Four 4. Computer Assembly and Disassembly: Dmiot School of Computing Info. Tech. Ac/ProgramDokumen9 halamanChapter Four 4. Computer Assembly and Disassembly: Dmiot School of Computing Info. Tech. Ac/Programbelete tilahunBelum ada peringkat
- Installing Computer Components Cumulative AssessmentDokumen6 halamanInstalling Computer Components Cumulative AssessmentMuhd AriffBelum ada peringkat
- ICT-40Dokumen8 halamanICT-40Allel CensoBelum ada peringkat
- Tle-Css Grade9 q1 Las8Dokumen16 halamanTle-Css Grade9 q1 Las8Van ImperialBelum ada peringkat
- Assemble a Computer from PartsDokumen16 halamanAssemble a Computer from PartsJessie MangaboBelum ada peringkat
- TLE ICT 7 Module 4Dokumen6 halamanTLE ICT 7 Module 4cid ladjamatliBelum ada peringkat
- CSS Grade 12 - Module 1Dokumen10 halamanCSS Grade 12 - Module 1allencalamba100% (1)
- Tle 9 CSS Q4 Week 1 2Dokumen10 halamanTle 9 CSS Q4 Week 1 2ArciBelum ada peringkat
- COALab ManualDokumen62 halamanCOALab ManualKarthick PalaniBelum ada peringkat
- ITWS - Manual - Version1.0Dokumen65 halamanITWS - Manual - Version1.0Ananya ChowdharyBelum ada peringkat
- CSS ICT Reviewer NCIIDokumen117 halamanCSS ICT Reviewer NCIICHRISTIAN ELEAZAR LAZANASBelum ada peringkat
- CSS3 M6Dokumen5 halamanCSS3 M6Lielanie NavarroBelum ada peringkat
- Field Report For Cs StudentsDokumen61 halamanField Report For Cs StudentsAdam NjameBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 11 Computer System Assembly GuideDokumen17 halamanGrade 11 Computer System Assembly GuideAC BalioBelum ada peringkat
- Monaco Institute of Business & Computer Science Diploma in Software EngineeringDokumen5 halamanMonaco Institute of Business & Computer Science Diploma in Software EngineeringKwizera AndrewBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Maintenance Establishment PDFDokumen7 halamanComputer Maintenance Establishment PDFNaol SintayehuBelum ada peringkat
- Q2 - MODULE6-7 - G7 - G8 - CSS - San Nicolas NHSDokumen13 halamanQ2 - MODULE6-7 - G7 - G8 - CSS - San Nicolas NHSDirty Sam LicudoBelum ada peringkat
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan FinalDokumen4 halamanSemi Detailed Lesson Plan FinalJunnil SulampidBelum ada peringkat
- Learning Objectives: 1. Open The CaseDokumen27 halamanLearning Objectives: 1. Open The CaseJhay Dee XhiaoBelum ada peringkat
- Manual Cws 1Dokumen34 halamanManual Cws 1raramit2Belum ada peringkat
- Types and Parts of Computer: Reviewer For Quarterly AssessmentDokumen18 halamanTypes and Parts of Computer: Reviewer For Quarterly Assessmentsamson benielBelum ada peringkat
- Assembling The Computer SystemDokumen22 halamanAssembling The Computer SystemvivekkumarsBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 6 Disassemble and Assemble of ComputerDokumen25 halamanLesson 6 Disassemble and Assemble of ComputerMELCHOR CASTROBelum ada peringkat
- CpE001L Lab Exercise # 2 - Personal Computer (PC) AssemblyDokumen5 halamanCpE001L Lab Exercise # 2 - Personal Computer (PC) AssemblyLouieMurioBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Hardware and MaintananceDokumen17 halamanComputer Hardware and MaintananceFIONA CHATOLABelum ada peringkat
- Lab ManualDokumen37 halamanLab Manualvidhya seemanBelum ada peringkat
- Day-1-2-Week-2-Q4-ICT-CSS-10Dokumen10 halamanDay-1-2-Week-2-Q4-ICT-CSS-10cardenoharrajane78Belum ada peringkat
- Computer disassembly and assembly guideDokumen21 halamanComputer disassembly and assembly guideJulie Ann Gonzales ChentesBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment No - 01: AIM: Assembling of Personal ComputerDokumen29 halamanExperiment No - 01: AIM: Assembling of Personal ComputerMukesh Sahu100% (1)
- Catolico Abegail 075135Dokumen38 halamanCatolico Abegail 075135amethyst BoholBelum ada peringkat
- Module For CSSDokumen18 halamanModule For CSSrecquelle danoBelum ada peringkat
- Diada Kimberly NDokumen25 halamanDiada Kimberly Namethyst BoholBelum ada peringkat
- Philip Ict Final Form Ultra EgoDokumen16 halamanPhilip Ict Final Form Ultra EgoZarii AltBelum ada peringkat
- Q2 CHS 9 MODULE 2 Week 23Dokumen9 halamanQ2 CHS 9 MODULE 2 Week 23Chris John Dave RosarioBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Peripherals and CPU Block DiagramDokumen9 halamanComputer Peripherals and CPU Block DiagramKiran KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Weblect ItworkDokumen12 halamanWeblect ItworkYuri CortezBelum ada peringkat
- CH&NW LabDokumen18 halamanCH&NW LabNavaRatnamBelum ada peringkat
- Mentenance Chapter 3Dokumen10 halamanMentenance Chapter 3primhaile assefaBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson7 How To Upgrade A Slow ComputerDokumen3 halamanLesson7 How To Upgrade A Slow Computerleonard thuoBelum ada peringkat
- Differences Related To Computer MaintenanceDokumen5 halamanDifferences Related To Computer MaintenanceAlpesh ThesiyaBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 1 UNPACKING AND PREPARING COMPUTER HARDWAREDokumen16 halamanLesson 1 UNPACKING AND PREPARING COMPUTER HARDWAREShane GabadBelum ada peringkat
- How To Assemble and Disassemble A Computer IT Assingment 1Dokumen15 halamanHow To Assemble and Disassemble A Computer IT Assingment 1HARSHITA AKANKSHABelum ada peringkat
- How To Assemble (15 Steps) and Disassemble (9 Steps) A ComputerDokumen14 halamanHow To Assemble (15 Steps) and Disassemble (9 Steps) A ComputerYenewligne AyenewBelum ada peringkat
- PC Assembly and Disassembly Guide in 40 StepsDokumen61 halamanPC Assembly and Disassembly Guide in 40 StepsStephanie S. Afable-Reyes100% (1)
- Topic 3a Computer Disassembly and Reassembly Upgrading A Computer PDFDokumen42 halamanTopic 3a Computer Disassembly and Reassembly Upgrading A Computer PDFTheo NdedaBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Assembly Procedures: Background Information For LearnersDokumen9 halamanComputer Assembly Procedures: Background Information For Learnersjojo podesBelum ada peringkat
- 2nd-Grading 2Dokumen57 halaman2nd-Grading 2justinejamesimportanteBelum ada peringkat
- Q2 W1 L1 G10 - Assembly and Disassembly Computer HardwareDokumen6 halamanQ2 W1 L1 G10 - Assembly and Disassembly Computer HardwareAnuar AliBelum ada peringkat
- Intelligent Power Supply Design and Its DescriptionDokumen45 halamanIntelligent Power Supply Design and Its Descriptionmilind kailaBelum ada peringkat
- Reece 32Dokumen190 halamanReece 32Danh NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- 0-IBM - Brocade Product Quick Ref Guide (Matrix Mapping) - 23290543Dokumen3 halaman0-IBM - Brocade Product Quick Ref Guide (Matrix Mapping) - 23290543Nguyen Van HaiBelum ada peringkat
- Monbat 12V200AhDokumen1 halamanMonbat 12V200AhMaria MuresanBelum ada peringkat
- Electro-Pneumatic Lift and Carry Conveying SystemDokumen4 halamanElectro-Pneumatic Lift and Carry Conveying SystemIJSTEBelum ada peringkat
- Uc 3525 ADokumen17 halamanUc 3525 AespaguetesBelum ada peringkat
- SPWM Full Bridge Transformerless PV Grid Connected InverterDokumen9 halamanSPWM Full Bridge Transformerless PV Grid Connected InverterOdnamra AlvarezBelum ada peringkat
- 24 Ficha Tecnica Desktop Handset 7265-202 Partida 29Dokumen8 halaman24 Ficha Tecnica Desktop Handset 7265-202 Partida 29Carlos LopezBelum ada peringkat
- 36.331 RRCDokumen217 halaman36.331 RRCBilal AwanBelum ada peringkat
- Broch Specs EnglDokumen12 halamanBroch Specs EnglSteve WanBelum ada peringkat
- Exploded View & Part ListDokumen44 halamanExploded View & Part ListGardufBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To UT Flaw DetectorDokumen26 halamanIntroduction To UT Flaw DetectorNail Widya Satya100% (1)
- RF Card Access Control SystemDokumen8 halamanRF Card Access Control SystemJosé Daniel Hernández SánchezBelum ada peringkat
- Manual de Servicio de Equipo de Sonido de Radio mp3Dokumen46 halamanManual de Servicio de Equipo de Sonido de Radio mp3daniel perezBelum ada peringkat
- 2Dokumen28 halaman2Srikanth Mudiraj100% (1)
- Scribner Product Catalog 2016Dokumen24 halamanScribner Product Catalog 2016dtsiplakBelum ada peringkat
- Velocity of Longitudinal WaveDokumen12 halamanVelocity of Longitudinal WaverenzoBelum ada peringkat
- Value1200ELCD/Value1500ELCD/Value2200ELCD User 'S Manual: Important Safety Instructions Basic OperationDokumen2 halamanValue1200ELCD/Value1500ELCD/Value2200ELCD User 'S Manual: Important Safety Instructions Basic OperationDigimonBelum ada peringkat
- Advance Electrical MachinesDokumen14 halamanAdvance Electrical MachinesSammar AbbasBelum ada peringkat
- ATOP Pick To Light Systems - Boreal Technologies PDFDokumen2 halamanATOP Pick To Light Systems - Boreal Technologies PDFWagner MontielBelum ada peringkat
- Honeywell Rondostat Hr20 SpesificationDokumen2 halamanHoneywell Rondostat Hr20 Spesificationfrox123Belum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Paper 2 End-of-Year Test Cemerlang Studi Secondary School MalaysiaDokumen20 halamanChemistry Paper 2 End-of-Year Test Cemerlang Studi Secondary School MalaysiaCemerlang StudiBelum ada peringkat