Posterun PDF
Diunggah oleh
Albert Leonardo Aguilar SuarezJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Posterun PDF
Diunggah oleh
Albert Leonardo Aguilar SuarezHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
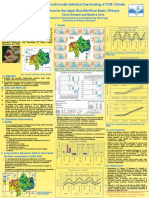
Spatiotemporal Evolution of Source Properties in the
Colombia-Huila Seismic Sequence
Albert Aguilar * & Germán Prieto
*alaguilars@unal.edu.co
30 seconds abstract: Three earthquakes Ml > 5 have occurred near Colombia – Huila in less than two years. The
earthquake catalog from 2012 to 2018 in a big area around Colombia – Huila was relocated and analyzed . The new
locations show that the Altamira Fault and Nazareth dipping to the NW and seismicity is clustered towards their
intersection. A systematic search for more earthquakes was performed using template matching. More than 2500
new events were detected including some repeating families.
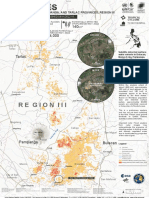
Of special interest in our catalog are the events that occurred near Colombia,
Huila where 3 events Ml > 5 have occurred on October 2016, February 2017
Figure1 .
(a) (b) Inset in (a):
and July 2018. In order to gain resolution in the earthquake catalog and the
A effects of this larger events on nearby faults, we focus on the catalog confined
NP by the dashed lines in 1(b) and occurring since 2016, we refer to this catalog
Nazca Plate hereafter.
CP Events Ml > 5
Caribean Plate
NAB
North Andean Template matching starts
Nazareth Fault Block
Algeciras Fault
System
SAP
South
Figure 2. (Top) Starting earthquake
Altamira Fault American Plate catalog shown as a histogram. Note
the bursts of activity accompanying
A
Ml 5.3 Ml 4.8
Ml 5.4
(a) & (b) the larger events (stars).
Cumulative number of events
(a) (Right) The template matching
A Inverted triangles
are seismological search was performed from
January 1st, 2016 until October g s
Ml 5.4
stations, earthquakes
10th, 2018, scanning a total of 822 lo
are color coded by a ta
depth and size is templates. 2526 new events were c
proportional to local detected(blue line), compared to ned
b i
1830 of the starting catalog (green
magnitude. m ing
line). Aftershock Sequences (AS): Co a tc h
Oct 2016 events have a short and e M
The recent seismicity near Colombia-Huila has been widely felt in big cities such as Bogotá and Neiva. All detections reported by Red Sismológica Nacional de la t
small AS, whereas the Feb 2017 p
m
Colombia (RSNC) from January 2012 until October 2018, a total of 4690 events are shown in 1(a). The inset shows the location of the study area in Colombia event has a much larger one. What Te l og
at a
indicating its tectonic setting . Also, the slip direction of The Algeciras Fault System (AFS) is indicated with green arrows. appears to be a foreshock sequence c
The 4690 were relocated using catalog and cross correlation differential travel times using HypoDD (Waldhauser & Elsworth, 2001). The results are shown in for the Jul 2018 is in fact i n ary
contamination of the catalog due to re lim
1(b), where the seismicity along the three major faults involved, the AFS, the Altamira and Nazareth Faults are projected to cross section A. The location and P
relocation show NW, dipping structures (extended with dotted lines), being the Altamira the one that reaches a higher depth. This structural parameter is in a burst of activity in the Nevado
del Huila Volcano. In fact, it had a
opposition to that proposed by Dimaté et al., 2003 and Velandia et al., 2005. Also, the larger events have occurred close to the contact Altamira-Nazareth.
small and short lived AS.
Template Matching calculates the normalized cross correlation (CC) Daily Stacked Cross Correlation Function Figure 4. (Top) All detections for the same day as Figure 3, events in the starting catalog
between templates and continuous data(Peng & Zhao,2009, are indicated with green vertical lines, those from which templates were built are
Chamberlain et al.,2018), as detailed by equation (1). Where CC(y) is indicated with the red triangle. This particular day is a sequence of events near Nevado
the CC at time y, t is the template, n is the number of points of the Bottom detection del Huila Volcano, following a Ml 4.5. Notice that there are many detections for the same
template, "̅ is the mean of the template, c is the continuous data and #̅ event. The detection with the highest SCC value in a 5 seconds window was kept as the
is its local mean. official detection. The number 3 corresponds to the detection shown in Figure 3. (Bottom)
Hour of day Seismogram and envelope (clipped at small amplitudes) for a few hours at station PRA
are shown to validate the new detections (see Figure 1 b for station location location).
(1)
3
Equation 1 accounts for just one channel, then the cross correlation is
calculated for each channel at each station i (of a total S) and shifted to Repeaters
account for arrival time delays d and summed over the network
(Equation 2) to produce the stacked cross correlation function (SCC):
(2)
SCC detection value = 0.73 Hour of day
Bandpassed seismograms 2 –7 Hz
Figure 3 shows the SCC for the correlation of a template with one day
of continuous data. Once the SCC is calculated, all samples above ?
certain threshold are considered as detections. In our case our
threshold is 10 times the median absolute deviation (MAD) defined as:
(3) Bandpassed seismogram 2 –7 Hz PRA.HHZ
Templates were built from the events in the confined catalog keeping Envelope of seismogram
?
for templates those channels with a signal to noise ratio (SNR) higher
than 3 comparing 4 s before and 4 s after the P or S arrival. and with Figure 3. (Top) Daily cross correlation function for template 20180707005735, a
at least nine channels. Templates are 6 seconds long, with 1 s before Ml 1.3 at ~ 3.0 N, -75.9 during July 7th, 2018. Threshold and number of
the P or S arrival. All waveforms were bandpassed filtered between 2- detections are indicated. (Bottom) Waveforms showing the detection indicated
7 Hz as this is the bandwidth that maximizes the SNR for our events. with in the top plot. Continuous waveforms are in gray and template channels
All the waveforms presented herein are bandpassed filtered 2-7 Hz. in blue, channel code is indicated to the right of each seismogram. Hour of day
Miscellanea Discussion
The contrast in dip and the offset between the Altamira and Nazareth faults may be acting as a barrier
that builds up stress and thus causes the elevated seismicity, but also this disconnection works as a
Earthquake Directivity Repeating Seismicity barrier that prevents the nucleation of even larger events.
Repeating earthquakes, (i.e. events with high CC) are a mystery. As pointed out The amount of new detections of nearly 130 % more events than in the starting catalog is a low
As of June 2018 we searched for suitable Empirical Green’s
compared to other studies involving similarity searches, as the quantity of newly detected earthquakes
Functions to constrain relative source time function, but found no in Figure 4 (top) repeating events can be spotted after scanning the templates,
is usually around 10 times as many as in starting catalogs. But, this numbers are appropriate given the
appropriate pairs of events. The search will soon be extended. these events can be associated in repeating families. A couple of examples are wide aperture of the network. The causes for difference in aftershock behavior remain unknown.
Instead, Aguilar & Prieto, 2018 calculated the radiated energies from shown below. The first is a repeating triplet whose magnitude and time The ? In Figure 4 points to what probably is volcanic tremor, there was a Ml 4.5 earlier that day that
body wave spectra for three major events in 2016 and 2017 at evolution are indicated. Waveforms are shown after CC pick realignment and caused the burst of activity mentioned in Figure 2. But by observing long day seismograms on the
broadband stations following the procedure presented by Ide et al., amplitude normalization. days and days after the big events there are many signals that are promising candidates to be tectonic
2003, using the equation: GARC.HHZ tremor very likely to occur in the Algeciras Fault System.
2016-06-01 Ml 1.3 We found repeating events along the AFS, but the search for those must be extended aiming to
47 days understand its relation to what seems to be earthquake triggering.
2016-07-18 Ml 1.9
1 second 60 days
2016-09-26 Ml 2.7 Selected References
F. Waldhauser, W L. Ellsworth; A Double-Difference Earthquake Location Algorithm: Method and Application to the Northern Hayward Fault,
California. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America ; 90 (6): 1353–1368. doi: https://doi.org/10.1785/0120000006.
Repeating pair in the AFS (see Figure 1 for station location) at 4.48 , -73.46. F Velandia, J Acosta, R Terraza, H VillegasThe current tectonic motion of the Northern Andes along the Algeciras Fault System in SW Colombia
Where R is the focal mechanism correction, rho is density, v is Tectonophysics 399 (1-4), 313-329.
seismic velocity, r is source-receiver distance, f is frequency, f0 the CHI.HHZ CC=0.982 ORTC.HHZ CC = 0.899 C Dimaté et al., Seismotectonique des Cordilleres Centrale et Orientale Colombiennes. PhD Thesis. Université Louis Pasteur – Strasbourg. 2003.
C J. Chamberlain, C J. Hopp, C M. Boese, E Warren-Smith, D Chambers, S X. Chu, K Michailos, J Townend; EQcorrscan: Repeating and
corner frequency, t is the travel time and Q to quality factors. All the Near-Repeating Earthquake Detection and Analysis in Python. Seismological Research Letters ; 89 (1): 173–181.
doi: https://doi.org/10.1785/0220170151.
variables for P or S waves. The calculations showed the highest
energies to the SW for the three largest events of 2016-2017
regardless of their focal mechanisms. It suggests rupture Top 2017-08-31 Ml 2.0 Acknowledgements
propagation to the SW. Bottom 2017-09-04 Ml 1.3 The computations in this work were run on the Odyssey cluster supported by the
FAS Division of Science, Research Computing Group at Harvard University.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Rough Guide to Belize (Travel Guide eBook): with Tikal and FloresDari EverandThe Rough Guide to Belize (Travel Guide eBook): with Tikal and FloresBelum ada peringkat
- 0014 Railroad Prediction FinalDokumen3 halaman0014 Railroad Prediction FinalChus MourazosBelum ada peringkat
- Application of Geostatistics in Facies Modeling of Reservoir E, "Hatch Field" Offshore Niger Delta Basin, NigeriaDokumen13 halamanApplication of Geostatistics in Facies Modeling of Reservoir E, "Hatch Field" Offshore Niger Delta Basin, Nigeriaعلي سعيد سعودBelum ada peringkat
- Gutscher 2000Dokumen20 halamanGutscher 2000Stalin Paúl SolanoBelum ada peringkat
- Precambrian Crustal Provinces of Eastern Colombia PDFDokumen4 halamanPrecambrian Crustal Provinces of Eastern Colombia PDFEsteban Giraldo ZuluagaBelum ada peringkat
- SIO 210: Dynamics VII: Sverdrup Balance and Western Boundary CurrentsDokumen26 halamanSIO 210: Dynamics VII: Sverdrup Balance and Western Boundary CurrentstropantumanqueBelum ada peringkat
- Sanguinetti Etal PaperDokumen19 halamanSanguinetti Etal PaperJesus Ponce GBelum ada peringkat
- STD Drainage Drawings Page 2 PDFDokumen1 halamanSTD Drainage Drawings Page 2 PDFcherielyn.riveraBelum ada peringkat
- Desk No. 1 Rendered Image: Office of The Municipal EngineerDokumen1 halamanDesk No. 1 Rendered Image: Office of The Municipal EngineerRaymundo GirayBelum ada peringkat
- Document BSFBSFBDokumen34 halamanDocument BSFBSFBMiler Fernandezgmail.comBelum ada peringkat
- Extension VS Compression Miocene Betic.. - Crespo Blanc Et Al 1994Dokumen11 halamanExtension VS Compression Miocene Betic.. - Crespo Blanc Et Al 1994Miguel gonzálezBelum ada peringkat
- Segment 1 (Existing Parking) Segment 2 (New Parking) : Office of The Municipal EngineerDokumen1 halamanSegment 1 (Existing Parking) Segment 2 (New Parking) : Office of The Municipal EngineerRaymundo GirayBelum ada peringkat
- 2021-07-02 CORDILLERA ANH Ronda Colombia 2021Dokumen56 halaman2021-07-02 CORDILLERA ANH Ronda Colombia 2021Julian OrtizBelum ada peringkat
- Poster Agu ZZ ESDokumen1 halamanPoster Agu ZZ ESAlfanBelum ada peringkat
- Climate Modelling Poster by Netsanet ZelalemDokumen1 halamanClimate Modelling Poster by Netsanet ZelalemNetsanetBelum ada peringkat
- Lec5 Exploration-Geology-Overview Delr 20221022Dokumen40 halamanLec5 Exploration-Geology-Overview Delr 20221022crystal deligeroBelum ada peringkat
- ArcGIS Imagery Platform For Fellowship Class - Yabdilah PDFDokumen85 halamanArcGIS Imagery Platform For Fellowship Class - Yabdilah PDFDataby 2018Belum ada peringkat
- Interplate Coupling Along The Nazca Subduction Zone On The Pacific Coast of Colombia Deduced From GeoRED GPS Observation DataDokumen16 halamanInterplate Coupling Along The Nazca Subduction Zone On The Pacific Coast of Colombia Deduced From GeoRED GPS Observation Datalorenatb674Belum ada peringkat
- Site AnalysisDokumen6 halamanSite Analysisjames arajaBelum ada peringkat
- Lomas de Omedo SismicaDokumen12 halamanLomas de Omedo SismicaClaudia Prezzi PrezziBelum ada peringkat
- Aug05 PDFDokumen24 halamanAug05 PDFKishor DeshmukhBelum ada peringkat
- Final Residential Effect PDFDokumen1 halamanFinal Residential Effect PDFNicholas SpaltBelum ada peringkat
- Bayona Et Al., 2011Dokumen20 halamanBayona Et Al., 2011Estefania AnguloBelum ada peringkat
- Mapa Geotectonico2018Dokumen1 halamanMapa Geotectonico2018Francisco Pérez QuesadaBelum ada peringkat
- Desk No. 2 (Front View) Desk No. 2 (Top View) : Office of The Municipal EngineerDokumen1 halamanDesk No. 2 (Front View) Desk No. 2 (Top View) : Office of The Municipal EngineerRaymundo GirayBelum ada peringkat
- Linares Americas Consulting S.a.CDokumen3 halamanLinares Americas Consulting S.a.CCarlos Eduardo Meneses AvilesBelum ada peringkat
- 0680 - 21 ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT - Question Paper June 2020Dokumen3 halaman0680 - 21 ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT - Question Paper June 2020robinsonBelum ada peringkat
- Our Alberta Activity Booklet Chapter 2 The Rocky Mountain RegionDokumen3 halamanOur Alberta Activity Booklet Chapter 2 The Rocky Mountain Regions.farah1999Belum ada peringkat
- The Himalayan: Looms, Nepal Grapples With Indecision, Bureaucratic InertiaDokumen8 halamanThe Himalayan: Looms, Nepal Grapples With Indecision, Bureaucratic InertiaKhuBelum ada peringkat
- 2010 PifDokumen1.241 halaman2010 PifJosselle Sempio Calienta100% (1)
- Safety Net From Centuries Past: The Quest For Progress Drowns A Turkish Gem A New Love For Merkel in GermanyDokumen16 halamanSafety Net From Centuries Past: The Quest For Progress Drowns A Turkish Gem A New Love For Merkel in Germanyenock-readersBelum ada peringkat
- Decluster Reasenberg1985Dokumen17 halamanDecluster Reasenberg1985Francisco Javier Acuña OlateBelum ada peringkat
- Arturo S. Daag, Margarita P. Dizon, Kimberley M. Vitto, Hannah Melissa M. Baltazar, and Ron Stephen D. PitapitDokumen1 halamanArturo S. Daag, Margarita P. Dizon, Kimberley M. Vitto, Hannah Melissa M. Baltazar, and Ron Stephen D. PitapitRJay JacabanBelum ada peringkat
- 3D Avo Workflow Deva June2002Dokumen31 halaman3D Avo Workflow Deva June2002eesBelum ada peringkat
- Perspective Drawing: The SiteDokumen4 halamanPerspective Drawing: The SiteDominic DatuinBelum ada peringkat
- 2021 - Arteta Et Al - Ground-Motion Model For Subduction Earthquakes in Northern South AmericaDokumen34 halaman2021 - Arteta Et Al - Ground-Motion Model For Subduction Earthquakes in Northern South AmericaJhoana GaviriaBelum ada peringkat
- UNOSAT A3 Natural Portrait TC20221028PHL BulacanNuevaEcijaPampangaTarlac 03nov2022Dokumen1 halamanUNOSAT A3 Natural Portrait TC20221028PHL BulacanNuevaEcijaPampangaTarlac 03nov2022Ayessa MendozaBelum ada peringkat
- EEDM Rubinos ADokumen1 halamanEEDM Rubinos AMarvvvBelum ada peringkat
- Inundaciones ProvocadasDokumen15 halamanInundaciones ProvocadasCesar Canul-MacarioBelum ada peringkat
- Pagegen NM PDFDokumen1 halamanPagegen NM PDFAmeer AlabriBelum ada peringkat
- La Faja Plegada y Corrida Subandina DelDokumen24 halamanLa Faja Plegada y Corrida Subandina DelRMBelum ada peringkat
- Operation Listo Report-Ppt2Dokumen39 halamanOperation Listo Report-Ppt2carlos armonesBelum ada peringkat
- 02 Section ADokumen34 halaman02 Section AJose Antonio ATBelum ada peringkat
- Ssue 5 2014 (Doi 10.1139 - Cjes-2013-0148) Quartero, E.M. Bechtel, D. Leier, A.L. Bentley, L.R. Rivard, - Gamma-Ray Normalization of Shallow Well-LogDokumen15 halamanSsue 5 2014 (Doi 10.1139 - Cjes-2013-0148) Quartero, E.M. Bechtel, D. Leier, A.L. Bentley, L.R. Rivard, - Gamma-Ray Normalization of Shallow Well-LogMujtabaBelum ada peringkat
- 4th ISSMGE McClelland Lecture - Presentation Reduced PDFDokumen63 halaman4th ISSMGE McClelland Lecture - Presentation Reduced PDFCescyle CostaBelum ada peringkat
- Emergence and Evolution of The South Atlantic Anomaly Revealed by The New Paleomagnetic Reconstruction SHAWQ2kDokumen10 halamanEmergence and Evolution of The South Atlantic Anomaly Revealed by The New Paleomagnetic Reconstruction SHAWQ2kCristiana StefanBelum ada peringkat
- Paper de Lessons Learned El Teniente 1997-2007Dokumen10 halamanPaper de Lessons Learned El Teniente 1997-2007pelaojavierBelum ada peringkat
- An Aborted Rift Process of Aptian-Albian Age in Central Peru, and Its Significance For The Margin GeodynamicsDokumen4 halamanAn Aborted Rift Process of Aptian-Albian Age in Central Peru, and Its Significance For The Margin GeodynamicsMateo Cornejo ZezenarroBelum ada peringkat
- Proposal of Characterization of Hydraulic Fractures and Their Correlation To 3D Seismic Data in The Granite WashDokumen1 halamanProposal of Characterization of Hydraulic Fractures and Their Correlation To 3D Seismic Data in The Granite WashianstarkmsBelum ada peringkat
- Our Town December 6, 1919Dokumen4 halamanOur Town December 6, 1919narberthcivicBelum ada peringkat
- Super Final File CMPMDokumen15 halamanSuper Final File CMPMFOEBE MARREY MANUELBelum ada peringkat
- Global Boundary Stratotype Section and Point (GSSP) of The International Commission On StratigraphyDokumen17 halamanGlobal Boundary Stratotype Section and Point (GSSP) of The International Commission On StratigraphyIryan AnugrahBelum ada peringkat
- El-Nino-Briefer Update05022023 ElNinoAlertDokumen3 halamanEl-Nino-Briefer Update05022023 ElNinoAlertCar DilgopcenBelum ada peringkat
- OCHA PHL TyphoonVamco Snapshot 201116Dokumen1 halamanOCHA PHL TyphoonVamco Snapshot 201116Cindy Tulinao GamaoBelum ada peringkat
- Ground Shaking Hazard Map West Valley FaultDokumen1 halamanGround Shaking Hazard Map West Valley FaultfrancoisesdimaanoBelum ada peringkat
- Hell's Vengeance - Poster Map FolioDokumen4 halamanHell's Vengeance - Poster Map FolioRoberto100% (3)
- Pages From P24019-30-99-63-1601 - 1-2ggDokumen1 halamanPages From P24019-30-99-63-1601 - 1-2ggRaeesBelum ada peringkat
- Rev - Plans 17FC0077 Labo SciTech MPBDokumen7 halamanRev - Plans 17FC0077 Labo SciTech MPBBoy Bangus100% (1)
- Plabasan ST Rev01 S06Dokumen1 halamanPlabasan ST Rev01 S06Sherwin DominguezBelum ada peringkat
- Seconds Before The Big One (Sci Am 2011)Dokumen6 halamanSeconds Before The Big One (Sci Am 2011)Francisco Javier Estrada OrdónñezBelum ada peringkat
- Ursa Major Elementary School Collapse Prevention Findings ReportDokumen33 halamanUrsa Major Elementary School Collapse Prevention Findings ReportAlaska's News SourceBelum ada peringkat
- Seismological and Geological Investigation For Earthquake Hazard in The Greater Accra Metropolitan AreaDokumen132 halamanSeismological and Geological Investigation For Earthquake Hazard in The Greater Accra Metropolitan Areacaleb mensahBelum ada peringkat
- Ai-Lrrts Proposal Wiguna Et Al - IndonesiaDokumen34 halamanAi-Lrrts Proposal Wiguna Et Al - IndonesiaPutu PerdanaBelum ada peringkat
- Empirical Global Relations Converting MS and MB To Moment MagnitudeDokumen12 halamanEmpirical Global Relations Converting MS and MB To Moment MagnitudeMileyvi Selene Quispe Gamero100% (1)
- 9 Patna Seismic StudyDokumen33 halaman9 Patna Seismic StudyAnis ShatnawiBelum ada peringkat
- Margaret Gooding Masters Thesis, 2007, Fontana FaultDokumen50 halamanMargaret Gooding Masters Thesis, 2007, Fontana FaultvolcanoclasticBelum ada peringkat
- Seismic Performance of Shallow Underground Subway Stations in Soft SoilDokumen20 halamanSeismic Performance of Shallow Underground Subway Stations in Soft SoilRoozbeh OwjiBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Strong Motion (EMS)Dokumen22 halamanEngineering Strong Motion (EMS)DonatoBelum ada peringkat
- Weichert MethodDokumen44 halamanWeichert MethodwahyuaryokBelum ada peringkat
- Ce-6411 Class Lecture - Ansari SirDokumen117 halamanCe-6411 Class Lecture - Ansari SirMOZAHER UL KABIR MAHADIBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Seismology: Seismic Hazard Analysis 1Dokumen23 halamanIntroduction To Seismology: Seismic Hazard Analysis 1Asad ALiBelum ada peringkat
- Diagnostic Test g8 ScienceDokumen8 halamanDiagnostic Test g8 Sciencemharlit cagaananBelum ada peringkat
- Earthquake QuizDokumen5 halamanEarthquake QuizDaven ClaveriaBelum ada peringkat
- KTM Eq en Rep PDFDokumen36 halamanKTM Eq en Rep PDFSasin PrajapatiBelum ada peringkat
- Biot Response SpectrumDokumen10 halamanBiot Response SpectrumMacBelum ada peringkat
- Finding Epicenters and Measuring Magnitudes WorksheetDokumen5 halamanFinding Epicenters and Measuring Magnitudes WorksheetAlyssa YutigaBelum ada peringkat
- The Kumamoto EarthquakeDokumen106 halamanThe Kumamoto EarthquakeRomanbabu OinamBelum ada peringkat
- Geophysical Maps of Spain PDFDokumen8 halamanGeophysical Maps of Spain PDFamol goleBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Geography Form 3&4Dokumen263 halamanUnderstanding Geography Form 3&4JOHN100% (2)
- 2004 Idriss & Boulanger - Semi-Empirical Method For Evaluating LiquefactionDokumen26 halaman2004 Idriss & Boulanger - Semi-Empirical Method For Evaluating LiquefactionJuan Pablo PradaBelum ada peringkat
- rr166 PDFDokumen115 halamanrr166 PDFArianta RianBelum ada peringkat
- Bssa 2019Dokumen15 halamanBssa 2019RenzoBelum ada peringkat
- IS 1893 Part 1 - 2016-UnlockedDokumen49 halamanIS 1893 Part 1 - 2016-Unlockeddhamodharan24100% (2)
- Tilenga ESIA Volume VI (B) - 28/02/19 - p1 To 300Dokumen300 halamanTilenga ESIA Volume VI (B) - 28/02/19 - p1 To 300Total EP UgandaBelum ada peringkat
- CEE1Dokumen10 halamanCEE1Reina BenguaBelum ada peringkat
- Science 8 9.2 EarthquakesDokumen24 halamanScience 8 9.2 EarthquakesDoreen Fatima Bisin Tirado-BarteBelum ada peringkat
- Earthquakes and Faults: ScienceDokumen34 halamanEarthquakes and Faults: ScienceMary Grace Lemon100% (1)
- Module 1 Earthquake EngineeringDokumen7 halamanModule 1 Earthquake EngineeringJUSTIN TOMAGUIBelum ada peringkat
- The Mexican National Seismological Service An OverviewDokumen6 halamanThe Mexican National Seismological Service An OverviewRizkia NugrahaniBelum ada peringkat