3rd-Trial 14-15
Diunggah oleh
api-2536790340 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
194 tayangan2 halaman1) The document is a math exam for the third trial of 2015 containing 4 exercises.
2) The first exercise contains 5 multiple choice questions about trigonometry, coordinate geometry, and inequalities.
3) The second exercise involves plotting points, lines, calculating slopes, and using vectors to find a value of n.
4) The third exercise analyzes data from a study on students' weekly extra math exercises through a frequency table.
5) The fourth exercise uses properties of circles, triangles, perpendiculars, and similarity to solve geometric problems.
Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
3rd-trial 14-15
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Ini1) The document is a math exam for the third trial of 2015 containing 4 exercises.
2) The first exercise contains 5 multiple choice questions about trigonometry, coordinate geometry, and inequalities.
3) The second exercise involves plotting points, lines, calculating slopes, and using vectors to find a value of n.
4) The third exercise analyzes data from a study on students' weekly extra math exercises through a frequency table.
5) The fourth exercise uses properties of circles, triangles, perpendiculars, and similarity to solve geometric problems.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
194 tayangan2 halaman3rd-Trial 14-15
Diunggah oleh
api-2536790341) The document is a math exam for the third trial of 2015 containing 4 exercises.
2) The first exercise contains 5 multiple choice questions about trigonometry, coordinate geometry, and inequalities.
3) The second exercise involves plotting points, lines, calculating slopes, and using vectors to find a value of n.
4) The third exercise analyzes data from a study on students' weekly extra math exercises through a frequency table.
5) The fourth exercise uses properties of circles, triangles, perpendiculars, and similarity to solve geometric problems.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
2015 - 4102 التجربة الثالثة لعام الشهادة المتوسطة ليسه دي زار
: الرقم : اإلسم ساعتان: المدة
ّ مسابقة في الرياضيات االنكليزي
:إ رشادات عامة
. يسمح بإستعمال آلة حاسبة غير قابلة للبرمجة-
. يمكن اإلجابة على المسائل بالترتيب االذي تريد-
. يرجى اإلجابة بخط واضح ومرتب-
30 العالمة القصوى من-
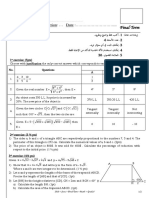
1st exercise: (5¼ pts)
In the following table, only one of the proposed answers to each question is correct. Write the number of each
question and the corresponding answer, and justify.
Answers
No. Questions
A B C
2 3 24 3
1. If α is an acute angle such that sin , 24 3 2 2
3 3
then cos …….. (1 pt) 3 3
If in an orthonormal system of axes the point M m 1, n 2 m 1 m 5 m5
belongs to the straight line ( D ) : y 3 x 11 , which makes an acute
2. & & &
angle with the positive x axis such that tan m 2n ,
then……. (1 pt) n 5 n 1 n 1
In triangle ABC , consider the points M and N such that M is the C is the N is the
3.
midpoint of midpoint of midpoint of
AM BC and AN AB AC , then………… (1¼ pts) [BC ] [MN ] [BC ]
x 2 x2 x 2
If M x, y belongs to ( D) : 2 y 3x 4 0 where x & y are
4. and and and
proportional to 2 & 5 respectively, then …………(1 pt)
y -5 y 5 y5
5. The inequality: x 2
1 x 3 0 is satisfied for x … (1 pt) ] ,3[ ]3, [ ] ,3]
2nd exercise: (13¾ pts)
In the orthonormal system of axes x' Ox & y' Oy where the unit of length is cm, consider the points
A(3;0), C (3;8), E ( 1;0), B( 3;2 n 5) and the straight lines (d ) : y 2 x 2 and ( ) : 4 y x 29
(n is a real parameter)
Part A:
1) Prove that C is the point of intersection of the two straight-lines ( d ) and ( ) . (1 pt)
2) Plot the points A, E and C then draw ( d ) and ( ) . (1½ pts)
3) a. Using the properties of the coordinates, prove that triangle ACE is right. (1 pt)
b. Using the slope of the straight-line (CE ) calculate the angles of triangle ACE . (1¼ pts)
,
4) a. Determine graphically the coordinates of CE . (Leave the traces on the figure) (¾pt)
b. The straight line ( ' ) is the image of ( ) by the translation of vector CE . Draw ( ' ) . (¾pt)
c. Determine the equation of ( ' ) . (1pt)
5) a. On which straight line does the point B vary? Justify. (¾pt)
b. Calculate the coordinates of each of the vectors: CE and CB . (1pt)
c. Using the coordinates of vectors CE and CB , calculate the numerical value of n , so that the points C , E and B
are collinear.
Part B:
In this part, you are given the orthonormal system that you have drawn in part A (you can solve this part without
depending on part A). Consider the point D, intersection point of (d) with the ordinate axis and let P be a variable
point on (d) such that C is between P and D.
The perpendicular drawn from P to (d) cuts ( ) at Q.
(PH) is the height relative to [DQ] in the right triangle PDQ such that
PD = 4x - 16 and PQ = 3x – 12, where x > 4.
1) Place the points D, Q and H on your own figure. (½ pt)
2) Prove that the area of triangle PDQ is A( x) 6( x 4) 2 . (1 pt)
Prove that DQ 5 x 4 , then deduce that PH
12
3) x 4 . (1¼ pts)
5
4) If A( x ) 54 , then calculate the length of [PD ] . (1 pt)
3rd exercise: (4 pts)
The following study is made to record the number of supplementary exercises performed by each 9th grade student in math
per week. The results are organized in the table below:
Number of supplementary exercises per week 1 2 3 4 6
Number of students 5 y 7 x 3
Increasing cumulative frequency (I.C.F) 5 25
1) Determine the population and the character under study then precise its nature. (¾pt)
2) Determine the number of students in this class. Justify. (½ pt)
3) Interpret the meaning of x in the above table. (½ pt)
4) a) Find a relation between x and y. (½ pt)
b) Show that if the average number of extra exercises done by the students is 3.2, then x = 8 and y =2. (1 pt)
5) Set up the table of increasing cumulative frequency in percentage and interpret any value. (¾ pt)
4th exercise: (7 pts)
(C) is a semi-circle of center O, radius R=3 cm and of diameter [AB].
C is a point on the semi straight-line [Ox) passing through B exterior to the semi-circle (C) such
that BC = 2cm.
The tangent to the semi- circle (C) through the point C cuts (C) in D.
The perpendicular through A to [AB] cuts (CD) in E.
1) Draw a figure. (½ pt)
2) Show that the triangles BCD and ACD are similar. (1 pt)
3) The perpendicular to [AB] through O, cuts (CE) in F.
a. Use cos(OCˆ D) in 2 convenient right triangles to calculate FD. (1½ pts)
15
b. If OF cm , then use Thales’ property to calculate EF. (¾ pt)
4
c. Deduce that [EO) is the bisector of the angle AEˆ C . (¾ pt)
4) a. Prove that the triangles OFD & ACE are similar, and deduce the ratio of similitude. (1 pt)
DF 3
b. Prove that the ratio of similitude: k . (½ pt)
AE 8
5) Determine the locus of the point M, the midpoint of [OE], as C varies on [Bx). (1 pt)
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- MS0105 2122S2 ExamDokumen8 halamanMS0105 2122S2 ExammudamudaBelum ada peringkat
- Cat4 Test Practice For Year 11 Level GDokumen6 halamanCat4 Test Practice For Year 11 Level GJoel OkohBelum ada peringkat
- AASW Code of Ethics-2004Dokumen36 halamanAASW Code of Ethics-2004Steven TanBelum ada peringkat
- Kormos - Csizer Language Learning 2008Dokumen29 halamanKormos - Csizer Language Learning 2008Anonymous rDHWR8eBBelum ada peringkat
- 3rd-Trial 10-11Dokumen2 halaman3rd-Trial 10-11api-253679034Belum ada peringkat
- 3rd-Trial 16-17Dokumen2 halaman3rd-Trial 16-17api-253679034Belum ada peringkat
- 3rd-Trial 12-13Dokumen3 halaman3rd-Trial 12-13api-253679034Belum ada peringkat
- 3rd-Trial 13-14Dokumen2 halaman3rd-Trial 13-14api-253679034Belum ada peringkat
- 3rd-Trial 17-18Dokumen2 halaman3rd-Trial 17-18api-253679034Belum ada peringkat
- 3rd-Trial 15-16Dokumen3 halaman3rd-Trial 15-16api-253679034Belum ada peringkat
- 3rd-Trial 11-12Dokumen2 halaman3rd-Trial 11-12api-253679034Belum ada peringkat
- 1st-Trial 21-22Dokumen2 halaman1st-Trial 21-22api-253679034Belum ada peringkat
- 1st-Trial 11-12Dokumen2 halaman1st-Trial 11-12api-253679034Belum ada peringkat
- Midyear 07-08Dokumen2 halamanMidyear 07-08api-253679034100% (1)
- Maths - Race#057Dokumen2 halamanMaths - Race#057PkrBelum ada peringkat
- IX NSTSE Level-1 Mock Test-2-5Dokumen15 halamanIX NSTSE Level-1 Mock Test-2-5puneet manglaBelum ada peringkat
- 137 Class Test (E-TOAS, TNAS, TEAS) - StudentDokumen4 halaman137 Class Test (E-TOAS, TNAS, TEAS) - Studentpranay100% (1)
- January 2008 QP - c1 AqaDokumen4 halamanJanuary 2008 QP - c1 AqaTamannaBhatiaBelum ada peringkat
- 8th Final 2010Dokumen2 halaman8th Final 2010api-253679034Belum ada peringkat
- Mathematics Mpc1 Unit Pure Core 1Dokumen4 halamanMathematics Mpc1 Unit Pure Core 1Equitable BrownBelum ada peringkat
- 1 (Ls 2013 Questions)Dokumen4 halaman1 (Ls 2013 Questions)jassem danafBelum ada peringkat
- Science Sample Paper - 2 (Standard)Dokumen20 halamanScience Sample Paper - 2 (Standard)lendiman00abcdBelum ada peringkat
- 81E Maths Model - QP - 23 24Dokumen16 halaman81E Maths Model - QP - 23 24ianaarondosuza1230% (1)
- Z' 1iziwithz 1 Z ' 1 1 I Z 1 .: AM AM2Dokumen4 halamanZ' 1iziwithz 1 Z ' 1 1 I Z 1 .: AM AM2Ysf HrbBelum ada peringkat
- 09march MainsDokumen38 halaman09march Mainsprakash karnaBelum ada peringkat
- S6.2016 Maths P2Dokumen5 halamanS6.2016 Maths P2Eremu Thomas100% (1)
- Geometry - Set I QP (23-24)Dokumen5 halamanGeometry - Set I QP (23-24)aryannagdev8Belum ada peringkat
- 8th Final 2011Dokumen3 halaman8th Final 2011api-253679034Belum ada peringkat
- (O I, J, K )Dokumen4 halaman(O I, J, K )Hayam ItaniBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematics Mpc1 Unit Pure Core 1Dokumen4 halamanMathematics Mpc1 Unit Pure Core 1Equitable BrownBelum ada peringkat
- 1st-Trial 12-13Dokumen2 halaman1st-Trial 12-13api-253679034Belum ada peringkat
- X 2t1 y T Z 1: Page 1 of 2Dokumen4 halamanX 2t1 y T Z 1: Page 1 of 2Ysf HrbBelum ada peringkat
- مراجعة ماث - 2 ع - مارس - ذاكروليDokumen82 halamanمراجعة ماث - 2 ع - مارس - ذاكروليm73419886Belum ada peringkat
- Question I (2 Points) ::) 12 Sin (2) 12 Cos (2) 12 Sin 12 Cos (Dokumen4 halamanQuestion I (2 Points) ::) 12 Sin (2) 12 Cos (2) 12 Sin 12 Cos (Ali RammalBelum ada peringkat
- Midterm 07-08Dokumen2 halamanMidterm 07-08api-253679034Belum ada peringkat
- X NSTSE Level-1 Mock Test-2-5Dokumen15 halamanX NSTSE Level-1 Mock Test-2-5puneet manglaBelum ada peringkat
- For More Study Material & Test Papers: Manoj Chauhan Sir (Iit-Delhi) Ex. Sr. Faculty (Bansal Classes)Dokumen5 halamanFor More Study Material & Test Papers: Manoj Chauhan Sir (Iit-Delhi) Ex. Sr. Faculty (Bansal Classes)jaspreet singhBelum ada peringkat
- For More Study Material & Test Papers: Manoj Chauhan Sir (Iit-Delhi) Ex. Sr. Faculty (Bansal Classes)Dokumen5 halamanFor More Study Material & Test Papers: Manoj Chauhan Sir (Iit-Delhi) Ex. Sr. Faculty (Bansal Classes)jaspreet singhBelum ada peringkat
- Core 1 MPC1-June13 (Condensed)Dokumen4 halamanCore 1 MPC1-June13 (Condensed)Stuart GregoryBelum ada peringkat
- THE SPARK t2 2023 pp2-2Dokumen17 halamanTHE SPARK t2 2023 pp2-2exan14431Belum ada peringkat
- First Semester Examination Mathematics Paper 2 2 Hours 30 MinutesDokumen13 halamanFirst Semester Examination Mathematics Paper 2 2 Hours 30 MinutesNajla SueBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematics PP2Dokumen15 halamanMathematics PP2Rainbow ICTBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Paper 13Dokumen19 halamanSample Paper 13twisha.guptaBelum ada peringkat
- Circle 2311A - QPDokumen4 halamanCircle 2311A - QP78bynzhbpvBelum ada peringkat
- Part (C) : Mathematics: x6 Y10 z14 5 3 8 x7 Y2 z4 3 6 2 x7 Y2 z4 3 5 1Dokumen13 halamanPart (C) : Mathematics: x6 Y10 z14 5 3 8 x7 Y2 z4 3 6 2 x7 Y2 z4 3 5 1JainBelum ada peringkat
- AQA-MPC1-QP-Jun11 (Condensed)Dokumen5 halamanAQA-MPC1-QP-Jun11 (Condensed)Stuart GregoryBelum ada peringkat
- Topper 144 2 3 Maths Question Up202212261542 1672049540 4596Dokumen7 halamanTopper 144 2 3 Maths Question Up202212261542 1672049540 4596Rahul ChardeBelum ada peringkat
- Ncert Exemplar Jan2021 Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 3Dokumen11 halamanNcert Exemplar Jan2021 Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 3jaya s singhBelum ada peringkat
- Final Al-Mahdi11thg 13-14Dokumen3 halamanFinal Al-Mahdi11thg 13-14api-253679034Belum ada peringkat
- 1st-Trial 14-15Dokumen2 halaman1st-Trial 14-15api-253679034Belum ada peringkat
- Term-1 Paper 2023-24 StandardDokumen5 halamanTerm-1 Paper 2023-24 Standardradhicadurgesh2015Belum ada peringkat
- In These ExerciseDokumen4 halamanIn These ExerciseHayam ItaniBelum ada peringkat
- 8 THDokumen3 halaman8 THapi-253679034Belum ada peringkat
- CLASS TEST-1 (Straight Line) Maths RC SirDokumen2 halamanCLASS TEST-1 (Straight Line) Maths RC Sircaptainprice351100Belum ada peringkat
- Class-X - Preparatory Test I 2023-24 1.0Dokumen7 halamanClass-X - Preparatory Test I 2023-24 1.0Nirmala DeviBelum ada peringkat
- General Instructions:: (Space For Rough Work)Dokumen31 halamanGeneral Instructions:: (Space For Rough Work)gpkr373Belum ada peringkat
- 10 Mathematics StandardDokumen54 halaman10 Mathematics StandardYesha Shah CherubsBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Paper 10-CroppedDokumen15 halamanSample Paper 10-CroppedCBSE MaterialBelum ada peringkat
- Sample MTD203Dokumen9 halamanSample MTD203IIan StefanoBelum ada peringkat
- 2011 Mock Paper BythemathscafeDokumen6 halaman2011 Mock Paper BythemathscafefardeenBelum ada peringkat
- Drill PMRDokumen15 halamanDrill PMRHanafizar Hanafi Napi AtanBelum ada peringkat
- Total Marks: 80 Marks Time: 2.5 Hours: Rahul Tuition ClassesDokumen4 halamanTotal Marks: 80 Marks Time: 2.5 Hours: Rahul Tuition Classesdfgffhg7530Belum ada peringkat
- Lycée Des Arts: Areas & Perimeters of Plane FiguresDokumen2 halamanLycée Des Arts: Areas & Perimeters of Plane Figuresapi-253679034Belum ada peringkat
- 1st-Trial 21-22Dokumen2 halaman1st-Trial 21-22api-253679034Belum ada peringkat
- Lycée Des Arts: Mathematics 9 - Grade Name: - . - . - . - . - . "Overview About Special Quadrilaterals"Dokumen4 halamanLycée Des Arts: Mathematics 9 - Grade Name: - . - . - . - . - . "Overview About Special Quadrilaterals"api-253679034Belum ada peringkat
- 8 THDokumen3 halaman8 THapi-253679034Belum ada peringkat
- Mathematics - Grade Name: - . - . - . - . " Statistics" W.S-14Dokumen2 halamanMathematics - Grade Name: - . - . - . - . " Statistics" W.S-14api-253679034Belum ada peringkat
- 3rd-Trial 15-16Dokumen3 halaman3rd-Trial 15-16api-253679034Belum ada peringkat
- Midterm 17-18Dokumen2 halamanMidterm 17-18api-253679034Belum ada peringkat
- 3rd-Trial 11-12Dokumen2 halaman3rd-Trial 11-12api-253679034Belum ada peringkat
- 3rd-Trial 08-09Dokumen2 halaman3rd-Trial 08-09api-253679034Belum ada peringkat
- 3rd-Trial 07-08Dokumen2 halaman3rd-Trial 07-08api-253679034Belum ada peringkat
- Al-Mahdi High Mathematics 11 - Grade Name: - . - . - . - . - Orthogonality in Space W.S-7Dokumen1 halamanAl-Mahdi High Mathematics 11 - Grade Name: - . - . - . - . - Orthogonality in Space W.S-7api-253679034Belum ada peringkat
- GRADE 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LOG: TLE6AG-Oc-3-1.3.3Dokumen7 halamanGRADE 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LOG: TLE6AG-Oc-3-1.3.3Roxanne Pia FlorentinoBelum ada peringkat
- Reported Speech StatementsDokumen1 halamanReported Speech StatementsEmilijus Bartasevic100% (1)
- An Introduction To Kriging Using SASDokumen21 halamanAn Introduction To Kriging Using SASbilisolyBelum ada peringkat
- Lorraln - Corson, Solutions Manual For Electromagnetism - Principles and Applications PDFDokumen93 halamanLorraln - Corson, Solutions Manual For Electromagnetism - Principles and Applications PDFc. sorasBelum ada peringkat
- 576 1 1179 1 10 20181220Dokumen15 halaman576 1 1179 1 10 20181220Sana MuzaffarBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 6Dokumen15 halamanMathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 6Ray Phillip G. Jorduela0% (1)
- Springfield College Lesson Plan Template PHED 237: The Learning and Performance of Physical ActivitiesDokumen5 halamanSpringfield College Lesson Plan Template PHED 237: The Learning and Performance of Physical Activitiesapi-285421100Belum ada peringkat
- Old San Agustin NHS MSISAR Sept 2021Dokumen2 halamanOld San Agustin NHS MSISAR Sept 2021ERICSON SABANGANBelum ada peringkat
- Butterfly Valve Info PDFDokumen14 halamanButterfly Valve Info PDFCS100% (1)
- Long 1988Dokumen4 halamanLong 1988Ovirus OviBelum ada peringkat
- Quarter: FIRST Week: 2: Ballecer ST., Central Signal, Taguig CityDokumen2 halamanQuarter: FIRST Week: 2: Ballecer ST., Central Signal, Taguig CityIRIS JEAN BRIAGASBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Midterm ExamDokumen6 halamanSample Midterm ExamRenel AluciljaBelum ada peringkat
- Calendar of Cases (May 3, 2018)Dokumen4 halamanCalendar of Cases (May 3, 2018)Roy BacaniBelum ada peringkat
- Joshua 24 15Dokumen1 halamanJoshua 24 15api-313783690Belum ada peringkat
- A Terrifying ExperienceDokumen1 halamanA Terrifying ExperienceHamshavathini YohoratnamBelum ada peringkat
- Batch 4 PPTDokumen20 halamanBatch 4 PPTAbhi ShekBelum ada peringkat
- Producto Académico #2: Inglés Profesional 2Dokumen2 halamanProducto Académico #2: Inglés Profesional 2fredy carpioBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan: Pt.'s Data Nursing Diagnosis GoalsDokumen1 halamanNursing Care Plan: Pt.'s Data Nursing Diagnosis GoalsKiran Ali100% (3)
- Name Numerology Calculator - Chaldean Name Number PredictionsDokumen2 halamanName Numerology Calculator - Chaldean Name Number Predictionsarunamurugesan7Belum ada peringkat
- Thermal Systems: Introduction To Heat TransferDokumen33 halamanThermal Systems: Introduction To Heat TransferParas SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Biology - Solved ExamDokumen27 halamanBiology - Solved ExamlyliasahiliBelum ada peringkat
- List of Saturday Opened Branches and Sub BranchesDokumen12 halamanList of Saturday Opened Branches and Sub BranchesSarmad SonyalBelum ada peringkat
- Mezbah Uddin Ahmed (173-017-054) Chapter 11Dokumen12 halamanMezbah Uddin Ahmed (173-017-054) Chapter 11riftBelum ada peringkat
- Yukot,+houkelin 2505 11892735 Final+Paper+Group+41Dokumen17 halamanYukot,+houkelin 2505 11892735 Final+Paper+Group+410191720003 ELIAS ANTONIO BELLO LEON ESTUDIANTE ACTIVOBelum ada peringkat
- The Importance of Logo DesignDokumen1 halamanThe Importance of Logo DesignDanielBelum ada peringkat
- AdverbsDokumen10 halamanAdverbsKarina Ponce RiosBelum ada peringkat
- Rem - Manila Bankers Vs NG Kok Wei - Noel DomingoDokumen3 halamanRem - Manila Bankers Vs NG Kok Wei - Noel DomingoNoel DomingoBelum ada peringkat