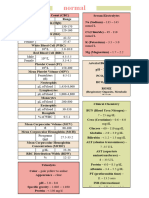
TABLE 2-1. Tests Performed in The Hematology Section: Test Function
Diunggah oleh
Angel Liana Marie Cervantes0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
27 tayangan5 halamanThe document outlines various tests performed in hematology, coagulation, chemistry and blood bank sections of a clinical laboratory. In hematology, tests like complete blood count, differential count and reticulocyte count are used to evaluate numbers and types of blood cells. Coagulation tests include prothrombin time, partial thromboplastin time and D-dimer to assess blood clotting factors. Chemistry tests such as electrolytes, kidney and liver function tests are used to evaluate organ functions. Blood bank tests involve blood typing and screening for antibodies.
Deskripsi Asli:
Tests Performed in the Chemistry Section
Judul Asli
MLS 1204
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniThe document outlines various tests performed in hematology, coagulation, chemistry and blood bank sections of a clinical laboratory. In hematology, tests like complete blood count, differential count and reticulocyte count are used to evaluate numbers and types of blood cells. Coagulation tests include prothrombin time, partial thromboplastin time and D-dimer to assess blood clotting factors. Chemistry tests such as electrolytes, kidney and liver function tests are used to evaluate organ functions. Blood bank tests involve blood typing and screening for antibodies.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
27 tayangan5 halamanTABLE 2-1. Tests Performed in The Hematology Section: Test Function
Diunggah oleh
Angel Liana Marie CervantesThe document outlines various tests performed in hematology, coagulation, chemistry and blood bank sections of a clinical laboratory. In hematology, tests like complete blood count, differential count and reticulocyte count are used to evaluate numbers and types of blood cells. Coagulation tests include prothrombin time, partial thromboplastin time and D-dimer to assess blood clotting factors. Chemistry tests such as electrolytes, kidney and liver function tests are used to evaluate organ functions. Blood bank tests involve blood typing and screening for antibodies.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 5
TABLE 2-1.
Tests Performed in the Hematology Section
TEST FUNCTION
Differential (Diff) Determines the percentage of the
different types of white blood cells and
evaluates red blood cell and platelet
morphology (may be examined
microscopically on a peripheral blood
smear stained with Wright's stain)
Hematocrit (Hct) Determines the volume of red blood
cells packed by centrifugation
(expressed as a percent)
Hemoglobin (Hgb) Determines the oxygen-carrying
capacity of red blood cells
Indices Calculations to determine- the size of
red blood cells and amount of
hemoglobin
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) Determines the amount of hemoglobin
in a red blood cell
Mean Corpuscular hemoglobin Determines the weight of hemoglobin
concentration (MCHC) in a red blood cell and compares it
with the size of the cell (expressed as a
percent)
Mean corpuscular volume (MCV) Determines the size of red blood cells
Platelet (PLT) count Determines the number of platelets in
circulating blood
Red blood cell (RBC) count Determines the number of red blood
cells in circulating blood
Red cell distribution width (RDW) Calculation to determine the
differences in the size of red blood
cells (expressed as a percent)
White blood cell (WBC) count Determines the number of white blood
cells in circulating blood
Body fluid analysis Determines the number and type of
cells in various body fluids
Bone marrow Determines the number and type of
cells in the bone marrow
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) Determines the rate of red blood cell
sedimentation (nonspecific test for
inflammatory disorders)
Sickle Cell Screening test for Hgb S (sickle cell
anemia)
Special Stains Determine the type of leukemia or
other cellular disorders
TABLE 2-2. Tests Performed in the Coagulation Section
TEST FUNCTION
Activated partial thromboplastin time Evaluates the intrinsic system of the
(APTT (PTT)) coagulation cascade and monitors
heparin therapy
Antithrombin III Screening test for increased clotting
tendencies
Anti-Xa heparin assay Monitors unfractionated heparin
therapy
Proteins C and s Evaluate venous thrombosis
Bleeding time (BT) Evaluates the function of platelets
D-dimer Measures abnormal blood clotting and
fibrinolysis
Factor assays Detect factor deficiencies that prolong
coagulation
Fibrin degradation products (FDP) Test for increased fibrinolysis (usually
a STAT test drawn in a special tube)
Fibrinogen Determines the amount of fibrinogen
in plasma
Platelet Aggregation Evaluates the function of platelets
Prothrombin time (PT) and Evaluates the extrinsic system of the
international normalized ratio (INR) coagulation cascade and monitors
Coumadin therapy
Thrombin time (TT) Determines if adequate fibrinogen is
present for normal coagulation
TABLE 2-4. Common Chemistry Organ/Disease Panels
PANEL TESTS
Comprehensive Glucose, BUN, creatinine, sodium (Na),
potassium (K), carbon dioxide (CO2),
chloride (CI), AST, ALT,
total protein, albumin, bilirubin, Ca,
and ALP
Hepatic ALP, ALT, AST, bilirubin total and
direct, total protein, albumin
Lipid Cholesterol, triglycerides, HDL, LDL,
and cholesterol/HDL ratio
Basic metabolic Glucose, BUN, creatinine, Na, CI, K,
CO2, and ionized calcium
Renal Glucose, BUN, creatinine, CO, CI, NA,
K, total protein, albumin, calcium
phosphorous
Table 2-3 Tests performed in the Chemistry Section
TEST FUNCTION
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) Elevated levels indicate liver disorders
Albumin Decreased levels indicate liver or kidney
disorders or malnutrition
Alcohol Elevated levels indicate intoxication
Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) Elevated levels indicate bone or liver
disorders
Ammonia Elevated levels indicate severe liver disorders
Amylase Elevated levels indicate pancreatitis
Arterial Blood Gases (ABGs) Determine the acidity or alkalinity and
oxygen and carbon dioxide levels of blood
Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) Elevated levels indicate myocardial infarction
or liver disorders
Bilirubin Elevated levels indicate liver or hemolytic
disorders
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) Elevated levels indicate kidney disorders
Brain Natriuretic Peptide (BNP) Elevated levels indicate congestive heart
failure
Calcium (Ca) Mineral associated with bone,
musculoskeletal, or endocrine disorders
Cholesterol Elevated levels indicate coronary risk
Creatinine Kinase (CK) Elevated levels indicate myocardial infarction
or other muscle damage
Creatinine Clearance Urine and serum test to measure glomerular
filtration rate
Drug Screening Detects drug abuse and monitors therapeutic
drugs
Electrolytes (CO3, Cl, Na, K) Evaluate body fluid balance
Gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT) Elevated levels indicate early liver disorders
Glucose Elevated levels indicate diabetes mellitus
Glucose tolerance test (GTT) Detects diabetes mellitus or hypoglycemia
Hemoglobin Used to evaluate hemolytic anemia and
certain chronic disease
Hemoglobin AIC Monitors diabetes mellitus
Hemoglobin (Hgb) electrophoresis Detects abnormal hemoglobins
High Density Lipoprotein (HDL) Assesses coronary risk
Iron Decreased levels indicate iron deficiency
anemia
Lactic dehydrogenase (LD [LDH]) Elevated levels indicate myocardial infarction
or lung or liver disorders
Lead Elevated levels indicate poisoning
Lipase Elevated levels indicate pancreatitis
Lithium (Li) Monitors antidepressant drug
Low- density lipoprotein (LDL) Assesses coronary risk
Magnesium Cation involved in neuromuscular excitability
of muscle tissue
Myoglobin Early indicator of myocardial infarction
Phosphorus (P) Mineral associated with skeletal or endocrine
disorders
Prostate-specific Antigen (PSA) Screening for prostatic cancer
Protein Decreased levels associated with liver or
kidney disorders
Total Protein (TP) Decreased levels indicate liver or kidney
disorders
Triglycerides Used to assess coronary risk
Troponin I and T Early indicators of myocardial infarction
Uric Acid Elevated levels indicate kidney disorders or
gout
TABLE 2-5. Tests Performed in the Blood Bank Section
TEST FUNCTION
Antibody (Ab) screen (indirect antiglobulin Detects abnormal antibodies in serum
test)
Direct antihuman globulin test (DAT) or direct Detects abnormal antibodies on red blood
Coombs cells
Group and type ABO and Rh typing
Panel Identifies abnormal antibodies in serum
Type and crossmatch (T&C) ABO, Rh typing, and compatibility test
Type and screen ABO, Rh typing, and antibody screen
TABLE 2-6. Tests Performed in the Serology (Immunology) Section
TEST FUNCTION
Anti-HIV Screening test for human immunodeficiency
virus
Antinuclear antibody (ANA) Detects nuclear autoantibodies
Antistreptolysin O (ASO) screen Detects a previous Streptococcus infection
C-reactive protein (CRP) Elevated levels indicate inflammatory
disorders
Cold agglutinins Elevated levels indicate atypical
(Mycoplasma) pneumonia
Complement levels Evaluate the function of the immune system
Cytomegalovirus antibody (CMV) Detects cytomegalovirus infection
Febrile agglutinins Detect antibodies to microorganisms causing
fever
Fluorescent antinuclear antibody (FANA) Detects and identifies nuclear autoantibodies
Fluorescent treponemal antibody-absorbed Confirmatory test for syphilis
(FTA-ABS)
Hepatitis A antibody Detects hepatitis A current or past infection
Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) Detects hepatitis B infection
Hepatitis C antibody Detects hepatitis C infection
Immunoglobulin (IgG, IgA, IgM) levels Evaluate the function of the immune system
Monospot Screening test for infectious mononucleosis
Rapid plasma reagin (RPR) Screening test for syphilis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) Detects autoantibodies present in
rheumatoid arthritis
Rubella titer Evaluates immunity to German measles
Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL) Screening test for syphilis
Western Blot Confirmatory Test for human
immunodeficiency virus
TABLE 2-7 Tests Performed in the Microbiology Section
TEST FUNCTION
Acid-fast bacillus (AFB) culture Detects acid-fast bacteria, including
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Blood culture Detects bacteria and fungi in the blood
Culture and sensitivity (C&S) Detects microbial infection and determines
antibiotic treatment
Fungal culture Detects the presence of and determines the
type of fungi
Gram stain Detects the presence of and aids in the
identification of bacteria
Occult blood Detects nonvisible blood
Ova and parasites Detects parasitic infection (O&P) (performed
on stool samples)
TABLE 2-8. Routine Urinalysis
TEST FUNCTION
Color Detects blood, bilirubin, and other pigments
Appearance Detects cellular and crystalline elements
Specific gravity (SG) Measures the concentration of urine
pH Determines the acidity of urine
Protein Elevated levels indicate kidney disorders
(proteinuria)
Glucose Elevated levels indicate diabetes mellitus
(glycosuria)
Ketones Elevated levels indicate diabetes mellitus or
starvation (ketonuria)
Blood Detects red blood cells or hemoglobin
(hematuria/hemoglobinuria)
Bilirubin Elevated levels indicate liver disorders
Urobilinogen Elevated levels indicate liver or hemolytic
disorders
Nitrite Detects bacterial infection
Leukocyte esterase Detects white blood cells
Microscopic Determines the number and type of cellular
elements
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Blood Test: For The Novel by Jonathan Kellerman, SeeDokumen7 halamanBlood Test: For The Novel by Jonathan Kellerman, SeeMaharani IndriBelum ada peringkat
- Blood TestDokumen6 halamanBlood TestMaharani Indri100% (1)
- Aarogyam 2Dokumen2 halamanAarogyam 2mechunkBelum ada peringkat
- Blood Studies GuideDokumen21 halamanBlood Studies GuideChigas ManilaBelum ada peringkat
- TERMS and Abbreviation For - Abbrev Meaning NSG Intervention - For - Prep CBCDokumen6 halamanTERMS and Abbreviation For - Abbrev Meaning NSG Intervention - For - Prep CBCMacy DysancoBelum ada peringkat
- Piyas Special Health Package: Complete Haemogram Diabetic Screening TestDokumen1 halamanPiyas Special Health Package: Complete Haemogram Diabetic Screening TestdrmbalarBelum ada peringkat
- Biochemistry Tests 1Dokumen4 halamanBiochemistry Tests 1Lena HasleyBelum ada peringkat
- Common Lab Tests & Their Use in Diagnosis & Treatment PDFDokumen17 halamanCommon Lab Tests & Their Use in Diagnosis & Treatment PDFChAwaisBelum ada peringkat
- CBC Resultsbase Range Normal / Abnormal ExplanationDokumen10 halamanCBC Resultsbase Range Normal / Abnormal Explanationlora_littleBelum ada peringkat
- Venesection: Phlebotomy orDokumen21 halamanVenesection: Phlebotomy orLesly Marie LaxamanaBelum ada peringkat
- Hematological DisorderDokumen87 halamanHematological DisorderAhmed Alaa FareedBelum ada peringkat
- Hematology Overview and RBC AnalysisDokumen9 halamanHematology Overview and RBC AnalysisMonica DomingoBelum ada peringkat
- Abb For Blood TestDokumen10 halamanAbb For Blood Testilma khairaniBelum ada peringkat
- Phlebotomy Procedures and Clinical Analysis TestsDokumen20 halamanPhlebotomy Procedures and Clinical Analysis TestsVera June RañesesBelum ada peringkat
- Normal Laboratory ValuesDokumen40 halamanNormal Laboratory ValuesPrincess Nasima M. Usngan100% (1)
- Clinical ParametersDokumen4 halamanClinical ParametersAditya JayaprakashBelum ada peringkat
- International Clinical LaboratoriesDokumen23 halamanInternational Clinical Laboratoriesmihret geneneBelum ada peringkat
- Blood Routine ExaminationDokumen32 halamanBlood Routine Examinationapi-19641337100% (2)
- PMLS2 - Week 2Dokumen6 halamanPMLS2 - Week 2MA. ANDREA NICOLE DURANBelum ada peringkat
- Biochemical InvestigationsDokumen34 halamanBiochemical InvestigationsPraneethaBelum ada peringkat
- Interpret Your Lab ReportsDokumen30 halamanInterpret Your Lab ReportspeibBelum ada peringkat
- Anaemi A: Joshi Abhishek Ashvinbhai F.Y.P.B.B.Sc - Nursing Govt - College of Nursing JamnagarDokumen82 halamanAnaemi A: Joshi Abhishek Ashvinbhai F.Y.P.B.B.Sc - Nursing Govt - College of Nursing JamnagarReshu ThakuriBelum ada peringkat
- Blood Chemistry Screen: ListenDokumen3 halamanBlood Chemistry Screen: ListenAngie MandeoyaBelum ada peringkat
- How to Understand Lab ResultsDokumen21 halamanHow to Understand Lab ResultsMSKCBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction of Natural ImmunityDokumen4 halamanIntroduction of Natural ImmunitySamanthaBelum ada peringkat
- 060 CLIN+PATH+43s Liver+Function+TestDokumen43 halaman060 CLIN+PATH+43s Liver+Function+TestMSKCBelum ada peringkat
- Normal Lab Values 3 20 16Dokumen2 halamanNormal Lab Values 3 20 16Arraz AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Normal Lab Values 3 20 16 PDFDokumen2 halamanNormal Lab Values 3 20 16 PDFMarian AlixandrescuBelum ada peringkat
- Normal Lab Values 3 20 16 PDFDokumen2 halamanNormal Lab Values 3 20 16 PDFdemi luneBelum ada peringkat
- Normal Lab Values: Complete Blood Count (CBC)Dokumen2 halamanNormal Lab Values: Complete Blood Count (CBC)nabilaBelum ada peringkat
- Normal Lab Values 3 20 16 PDFDokumen2 halamanNormal Lab Values 3 20 16 PDFnabilaBelum ada peringkat
- Laboratory & Diagnostic TerminologyDokumen5 halamanLaboratory & Diagnostic TerminologybashasaruBelum ada peringkat
- Caee Study For Clinical RotationsDokumen8 halamanCaee Study For Clinical RotationseyesontheskyBelum ada peringkat
- 3.5 - 5.5 X 10 Cells/mm 7.4-9.9 Mmol/l HCT: Normal For Female Patients 33% - 45%Dokumen2 halaman3.5 - 5.5 X 10 Cells/mm 7.4-9.9 Mmol/l HCT: Normal For Female Patients 33% - 45%Jeann CaldereroBelum ada peringkat
- Order of DrawDokumen5 halamanOrder of DrawMuhammad AmirBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment No. 11 Laboratory Diagnosis and ProceduresDokumen8 halamanExperiment No. 11 Laboratory Diagnosis and ProceduresBeverly BagayaoBelum ada peringkat
- Complete Blood Count: Performed To Provide An Overview of A Patient's General Health StatusDokumen4 halamanComplete Blood Count: Performed To Provide An Overview of A Patient's General Health StatusRaprnaBelum ada peringkat
- Diagnosing Polycythemia VeraDokumen4 halamanDiagnosing Polycythemia VeraKristine JamilleBelum ada peringkat
- Complete Blood Counts and ExaminationDokumen63 halamanComplete Blood Counts and Examinationzarairahad486Belum ada peringkat
- Slides DR Ashgar Approach To LFTs 12.12.2021Dokumen47 halamanSlides DR Ashgar Approach To LFTs 12.12.2021Maryam OmarBelum ada peringkat
- Case-Based Discussion 20202021 FNLDokumen6 halamanCase-Based Discussion 20202021 FNLThe Mehtab ShowBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Kidney Injury, Anemia, and Recurrent Dark Red Urine: Case PresentationDokumen3 halamanAcute Kidney Injury, Anemia, and Recurrent Dark Red Urine: Case PresentationmonaBelum ada peringkat
- Civd - AjcpDokumen11 halamanCivd - AjcpHenrique MachadoBelum ada peringkat
- Liver Enzymes ExplainedDokumen19 halamanLiver Enzymes ExplainedJosua MakerBelum ada peringkat
- mls2 TransesDokumen13 halamanmls2 TransesHaki TozakiBelum ada peringkat
- Blood TestsDokumen15 halamanBlood Testsclea1100% (2)
- Chapter XI FinalDokumen12 halamanChapter XI FinalFadBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Pathology Panels Guidelines PDFDokumen7 halamanClinical Pathology Panels Guidelines PDFazizBelum ada peringkat
- Interpretation of Urine Testing ResultsDokumen1 halamanInterpretation of Urine Testing ResultsBigPharma HealtcareBelum ada peringkat
- Normal Lab ValuesDokumen2 halamanNormal Lab ValuesGeraldine TeneclanBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Laboratory TestsDokumen90 halamanBasic Laboratory Testsansjoh0217Belum ada peringkat
- Summary of Normal Laboratory ValuesDokumen24 halamanSummary of Normal Laboratory ValuesMissy U. TorrechillaBelum ada peringkat
- Lab ResultsDokumen3 halamanLab ResultsChristina ValeriaBelum ada peringkat
- Overview of AnaemiaDokumen2 halamanOverview of AnaemiaGerardLumBelum ada peringkat
- Diagnostic Tests Reveal Parasitic InfectionDokumen4 halamanDiagnostic Tests Reveal Parasitic InfectionNina MoradaBelum ada peringkat
- Comprehensive health package with 34 tests and profilesDokumen58 halamanComprehensive health package with 34 tests and profilesKhusboo JainBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Laboratory Sections Laboratory Tests Clinical SignificanceDokumen3 halamanClinical Laboratory Sections Laboratory Tests Clinical SignificanceSelrahc AgnilakBelum ada peringkat
- Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation 2016Dokumen11 halamanDisseminated Intravascular Coagulation 2016Cris TobalBelum ada peringkat
- WWW Nhlbi Nih GovDokumen2 halamanWWW Nhlbi Nih GovtahiraimcBelum ada peringkat
- Types of HypersensitivityDokumen10 halamanTypes of HypersensitivitybeeuhBelum ada peringkat
- A Doctor's 4-Step Program To Treat Autoimmune Disease: THE IMMUNE SYSTEM RECOVERY PLAN by Susan BlumDokumen65 halamanA Doctor's 4-Step Program To Treat Autoimmune Disease: THE IMMUNE SYSTEM RECOVERY PLAN by Susan BlumSimon and Schuster85% (26)
- Distemper in Canine, ReviewDokumen13 halamanDistemper in Canine, ReviewLAURA DANIELA VERA BELTRANBelum ada peringkat
- v170 v174 v175 Flockscreen Ai Instruction For Use v1Dokumen7 halamanv170 v174 v175 Flockscreen Ai Instruction For Use v1Nader SedighiBelum ada peringkat
- Guidance Rapid Antibody COVID TestsDokumen2 halamanGuidance Rapid Antibody COVID TestsRaghu NadhBelum ada peringkat
- Anemia HemolitikDokumen20 halamanAnemia HemolitikRandy GipsonBelum ada peringkat
- Immunoglobulins - Structure and FunctionDokumen8 halamanImmunoglobulins - Structure and FunctionNeha KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission Required For ReproductionDokumen33 halamanCopyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission Required For ReproductionKvaleramBelum ada peringkat
- Judge Richard Andrews Decision in Amgen v. SanofiDokumen34 halamanJudge Richard Andrews Decision in Amgen v. SanofiNed PagliaruloBelum ada peringkat
- Immunity: Aman UllahDokumen15 halamanImmunity: Aman UllahSiyar AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- Ouchterlony Double ImmunodiffusionDokumen5 halamanOuchterlony Double ImmunodiffusionKool CherryBelum ada peringkat
- MLT Entry Test PaperDokumen7 halamanMLT Entry Test PaperMuhammad SaeedBelum ada peringkat
- Proteus VulgarisDokumen29 halamanProteus Vulgarisapi-19649313Belum ada peringkat
- Pre-Standardisation: 9700/22 AS & A Level - Mark Scheme March 2023Dokumen11 halamanPre-Standardisation: 9700/22 AS & A Level - Mark Scheme March 2023lailaBelum ada peringkat
- Lec 9 Antihuman Globulin TestingDokumen9 halamanLec 9 Antihuman Globulin TestingMelaine Grace Gemoranion GeopanoBelum ada peringkat
- Poster LESDokumen6 halamanPoster LESAlejandra LuqueBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 34 Guyton and HallDokumen5 halamanChapter 34 Guyton and Hallg_komolafeBelum ada peringkat
- ImmunityDokumen29 halamanImmunitySHREE SWAMINARAYAN NURSING COLLEGE CHIKHLIBelum ada peringkat
- Diagnosis of Typhoid FeverDokumen5 halamanDiagnosis of Typhoid FeverpeterjongBelum ada peringkat
- ALEX PresentationDokumen38 halamanALEX PresentationServis AnalizaBelum ada peringkat
- Monoclonal Antibodies and Engineered AntibodiesDokumen24 halamanMonoclonal Antibodies and Engineered AntibodiesMunawar AliBelum ada peringkat
- 17 Human Health and Disease: SolutionsDokumen14 halaman17 Human Health and Disease: SolutionsEkta ManglaniBelum ada peringkat
- Growth and Development: Toddler: Play Behavior Traits Physical Other Development Developmental Stage TheoriesDokumen6 halamanGrowth and Development: Toddler: Play Behavior Traits Physical Other Development Developmental Stage TheoriesAJ BayBelum ada peringkat
- Jurnal ParuDokumen8 halamanJurnal ParuM Rizal Hermawan PBelum ada peringkat
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Biol4345.001 06s Taught by John Burr (Burr)Dokumen1 halamanUT Dallas Syllabus For Biol4345.001 06s Taught by John Burr (Burr)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupBelum ada peringkat
- US Phadia250 System OverviewDokumen2 halamanUS Phadia250 System OverviewIgnaciaBelum ada peringkat
- Biotechnology PDFDokumen24 halamanBiotechnology PDFShyamlaSobithaBelum ada peringkat
- History of ImmunologyDokumen6 halamanHistory of ImmunologyKitt KittBelum ada peringkat
- Test Bank For Basic Immunology 3rd Edition Abul K AbbasDokumen7 halamanTest Bank For Basic Immunology 3rd Edition Abul K AbbasAdam Seger100% (34)
- Self-Assessment Questions, Group 6Dokumen20 halamanSelf-Assessment Questions, Group 6naveenkovalBelum ada peringkat
- War on Ivermectin: The Medicine that Saved Millions and Could Have Ended the PandemicDari EverandWar on Ivermectin: The Medicine that Saved Millions and Could Have Ended the PandemicPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (7)
- Uncontrolled Spread: Why COVID-19 Crushed Us and How We Can Defeat the Next PandemicDari EverandUncontrolled Spread: Why COVID-19 Crushed Us and How We Can Defeat the Next PandemicBelum ada peringkat
- Summary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDari EverandSummary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (9)
- There Are No Accidents: The Deadly Rise of Injury and Disaster—Who Profits and Who Pays the PriceDari EverandThere Are No Accidents: The Deadly Rise of Injury and Disaster—Who Profits and Who Pays the PricePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (15)
- The Nocebo Effect: When Words Make You SickDari EverandThe Nocebo Effect: When Words Make You SickBelum ada peringkat
- Do You Believe in Magic?: The Sense and Nonsense of Alternative MedicineDari EverandDo You Believe in Magic?: The Sense and Nonsense of Alternative MedicineBelum ada peringkat
- The Wisdom of Plagues: Lessons from 25 Years of Covering PandemicsDari EverandThe Wisdom of Plagues: Lessons from 25 Years of Covering PandemicsPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (5)
- The Atlas of Disease: Mapping Deadly Epidemics and Contagion from the Plague to the CoronavirusDari EverandThe Atlas of Disease: Mapping Deadly Epidemics and Contagion from the Plague to the CoronavirusPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (10)
- Deaths of Despair and the Future of CapitalismDari EverandDeaths of Despair and the Future of CapitalismPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (30)
- The War on Informed Consent: The Persecution of Dr. Paul Thomas by the Oregon Medical BoardDari EverandThe War on Informed Consent: The Persecution of Dr. Paul Thomas by the Oregon Medical BoardPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (2)
- Epic Measures: One Doctor. Seven Billion Patients.Dari EverandEpic Measures: One Doctor. Seven Billion Patients.Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (13)
- Arthritis Diet: Anti-inflammatory Diet for Arthritis Pain ReliefDari EverandArthritis Diet: Anti-inflammatory Diet for Arthritis Pain ReliefBelum ada peringkat
- Epidemics and Society: From the Black Death to the PresentDari EverandEpidemics and Society: From the Black Death to the PresentPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (9)
- The HPV Vaccine On Trial: Seeking Justice For A Generation BetrayedDari EverandThe HPV Vaccine On Trial: Seeking Justice For A Generation BetrayedPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (13)
- Quick Fixes: Drugs in America from Prohibition to the 21st Century BingeDari EverandQuick Fixes: Drugs in America from Prohibition to the 21st Century BingeBelum ada peringkat
- Blood Runs Coal: The Yablonski Murders and the Battle for the United Mine Workers of AmericaDari EverandBlood Runs Coal: The Yablonski Murders and the Battle for the United Mine Workers of AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (2)
- Anti-vaxxers: How to Challenge a Misinformed MovementDari EverandAnti-vaxxers: How to Challenge a Misinformed MovementPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (12)
- The Transformation: Discovering Wholeness and Healing After TraumaDari EverandThe Transformation: Discovering Wholeness and Healing After TraumaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (70)
- The Gut-Immune Connection: How Understanding the Connection Between Food and Immunity Can Help Us Regain Our HealthDari EverandThe Gut-Immune Connection: How Understanding the Connection Between Food and Immunity Can Help Us Regain Our HealthBelum ada peringkat
- The Truth about Wuhan: How I Uncovered the Biggest Lie in HistoryDari EverandThe Truth about Wuhan: How I Uncovered the Biggest Lie in HistoryPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (6)
- Heat Wave: A Social Autopsy of Disaster in ChicagoDari EverandHeat Wave: A Social Autopsy of Disaster in ChicagoPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (40)
- Doctored: The Disillusionment of an American PhysicianDari EverandDoctored: The Disillusionment of an American PhysicianPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (11)
- My House Is Killing Me!: A Complete Guide to a Healthier Indoor Environment (2nd Edition)Dari EverandMy House Is Killing Me!: A Complete Guide to a Healthier Indoor Environment (2nd Edition)Belum ada peringkat
- Clean: Overcoming Addiction and Ending America’s Greatest TragedyDari EverandClean: Overcoming Addiction and Ending America’s Greatest TragedyPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (18)
- AIDS Activist: Michael Lynch and the Politics of CommunityDari EverandAIDS Activist: Michael Lynch and the Politics of CommunityBelum ada peringkat