Planning, Designing and Analysis of Hostel Building: S.Brahma Naidu, P.Anil, V, Venkatesh, Y.Vinod Kumar, A.Srikanth
Diunggah oleh
sanaDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Planning, Designing and Analysis of Hostel Building: S.Brahma Naidu, P.Anil, V, Venkatesh, Y.Vinod Kumar, A.Srikanth
Diunggah oleh
sanaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
International Journal of Engineering Trends and Applications (IJETA) – Volume 5 Issue 2, Mar-Apr 2018
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS
Planning, Designing And Analysis Of Hostel Building
S.Brahma Naidu [1], P.Anil [2],V,Venkatesh [3],Y.Vinod Kumar [4],A.Srikanth [5]
Assistant professor [1], Students [2], [3], [4], [5]
Department of Civil Engineering
Narayana Engineering College, Gudur
India
ABSTRACT
Planning, scheduling, controlling and measuring design and engineering activities is challenged now a days not only by the
strong competition, but also by the technology and the way projects are organized. The project organization challenges the
planning process through its variety of people, organizations and cultures participating along the whole building project.
Concurrent engineering is a building method dependent on a dynamic planning process that integrates and coordinates all the
entities involved in the project. 3D modeling is a tool that necessitates more specialized engineers and a more collaborative
way of engineering a project. It seems that todays planning systems fail to take into consideration these challenges. This
literature review is an attempt of in dif and how the fields of project management and lean construction deal with planning
and measuring design/engineering activities in a concurrent engineering process that is globally dispersed both on engineering
and on production part of a project.
Keywords:- Structural member, design, Analysis.
for higher education and the high number of form four
I. INTRODUCTION candidates who qualify for university admission.
This has created accommodation shortage such that each year
Nowadays, due to the increase in population leads to the
some students lack accommodation within the school hostel.
availability of horizontal coordination system (due to large
This is a disadvantage to those who cannot afford
area available per person) has been decreasing so that
accommodation outside the university , to those who do not
adoption of vertical co-ordination System (high rise building
hail from Nairobi and probably they have never been to
due to deficiency of area) is needed.
Nairobi before. If a hostel is put up in this land it will reduce
ETABS can also handle the largest and most complex
the problem if not eradicate it The proposed hostel will
building models, including a wide range of nonlinear
provide the following:
behaviours, making it the tool of choice for structural
a) Appropriate environment for living as well as studying
engineers in the building industry. ETABS can be effectively
b) opportunities for informal academic and social interchange
used in the analysis and design of building structures which
c) privacy and quiet place where people are living in close
might consists of structural members like beams, columns,
proximity and are sharing facilities most students will not
slabs, shear walls etc., With ETABS you can easily apply
have the opportunity to choose their neighbours
various construction materials to your structural members like
d) There will be a proportion of foreign students and those
concrete, structural steel, Reinforced Concrete etc. ETABS
attending short courses, who need to be helped to settle in
automatically generates the self-weight and the resultant
quickly
gravity and lateral loads.
Codes recommended are IS 456-2000, SP 16, IS 875-1987 III. DESIGN REQUIREMENTS
(Part I), IS 875-1987 (Part II)
Structural design is an art and science of designing with
II. OBJECTIVES economy and elegance, a safe, serviceable and a durable
1. Provide more accommodation to the university students structure, primarily to meet the functional requirements of the
2. Provide an environment that will ensure social and user or client. The functional requirements and economy of
academic growth the structure for its intended use over the life span of the
3. Reduce the current accommodation crisis at the university. structure are looked by the structural designer.
BACKGROUND AND PROJECT JUSTIFICATION
Currently In most universities, including university of The design of the structure must satisfy three basic
Nairobi, the number of students admitted is not determined by requirements:
the bed spaces available. This is as a result of the high demand
ISSN: 2393-9516 www.ijetajournal.org Page 100
International Journal of Engineering Trends and Applications (IJETA) – Volume 5 Issue 2, Mar-Apr 2018
Stability: To prevent overturning, sliding or buckling of the
structure or parts of it under the action of loads.
Strength: To resist safely the stress induced by the load in the
various structural members.
Serviceability: To ensure satisfactory performance under
service load condition which implies providing adequate
stiffness to contain deflection, crack width, vibrations within
acceptable limits and providing im permeability, durability
etc.,
The process of structural design involves the following
data:
Structural planning
Estimation of loads
Analysis of structural elements
Design of structural elements
The principle elements of an RCC building frame are as
follows:
Slabs to cover large area
Beams to support slabs
Columns to support beams WORKING STRESS METHOD:
Footings to distribute the column loads over large area of soil Working stress method was traditional method of design
basically assumes that the structural material behaves in a
DESIGN PHILOSOPHIES:
linear elastic manner, and that adequate safety can be
RC structures can be designed by using the following design
ensured by restricting the stresses induced in the material
philosophies
by the expected working loads (service loads) on the
Working stress method for serviceability
structure. Permissible stresses are kept well below the
Ultimate load method for safety material strength. The ratio of strength of the material to
the permissible stresses is referred to as the “Factor of
Limit state method safety “. The design usually results in relatively large
section of structural members (comparative U.L.M) there
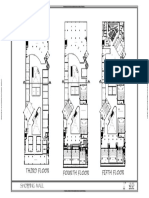
PLANS OF HOSTEL: by resulting in better serviceability, performance under the
usual working loads. This method is notable for its
essential simplicity in concept as well as in application.
ULTIMATE LOAD METHOD (ULM):
The ultimate load method design, the stress condition at the
stage of impending collapse of structure is analysed and
the non - linear stress strain curves of concrete and steel
are made use of, the safety measures in design is
introduced “Load factor “which is the ratio of ultimate load
(design load) to working load. This method generally
ISSN: 2393-9516 www.ijetajournal.org Page 101
International Journal of Engineering Trends and Applications (IJETA) – Volume 5 Issue 2, Mar-Apr 2018
results in more slender sections and often more economical Displacements are extremely small when compared to the
designs when compared to WSM, particularly when high geometry of the structure.
strength steel and concrete are used.
LIMIT STATE METHOD (LSM): LOADS AND CALCULATIONS:
The various loads acting on the structure which need
Limit state method is judicious amalgamation of WSM and
consideration in building design are as follows:
ULM removing all drawbacks of both methods, but
maintaining their good points. LSM aims for a Dead loads.
comprehensive and rational solution to design problems by
considering safety at ultimate loads and serviceability at Live loads.
working loads. The structures shall be designed to carry
Wind loads.
design loads safety throughout its life, and also satisfy the
serviceability requirements such as limitations on Seismic loads.
deflection and cracking. The acceptable limit for safety and
serviceability requirements before failure occurs is called a DEAD LOADS: [IS: 875-1987(Part-I)]
“Limit state “. The aim of design is to achieve acceptable
Dead loads are the loads which do not vary in magnitude and
probabilities so that the structures will not become unfit for
in position. The dead Load of a structure is not known before
the use for which it is intended.
it is not known before it is designed. After designing, the
assumed load is compared with the actual dead load. If the
There are two types of limit states: difference is in significant, the assumed dead load is revised
Limit state of collapse: Deals with strength, overturning, and the structure is redesigned. The dead calculations should
sliding, buckling, fatigue, fracture etc., also include the superimposed loads that are permanently
attached the structure.
Limit state of serviceability: Deals with comfort to
accompany and malfunction, caused by excessive The dead loads include:
deflection, crack width, vibration etc., and loss of durability Self-weight of members.
etc.,
Weight of finishes.
METHOD OF ANALYSIS:
Weight of partitions, walls etc.
Structural analysis involves the determination of internal
forces like axial forces, bending moments, shear forces etc., The unit weights of different materials are as follows:
in the component members for which these members are to Reinforced concrete : 25KN/ m3
designed under the action of given external loads. Hollow Brick masonry: 19KN/ m3
The different approaches to structural analysis are as given Brick masonry: 20KN/ m3
below…
Floor finishes: 1KN/ m2
Elastic analysis based on elastic theory
LIVE LOADS:
Limit analysis based on plastic theory or ultimate load theory
Live loads are the loads which very in
In this project, an elastic analysis has been adopted. Elastic magnitude and in position. Live loads on
analysis deals with the study of strength and behaviour of roofs and floors are as follows:
members and structures at working loads.
Roof slab: 4.0 KN/m2
The elastic analysis is based on the following assumptions:
Other slabs: 4.0 KN/m
Relation between force and displacement is linear.
Balconies : 3.0 KN/m2
ISSN: 2393-9516 www.ijetajournal.org Page 102
International Journal of Engineering Trends and Applications (IJETA) – Volume 5 Issue 2, Mar-Apr 2018
STAAD PRO RESULTS:
WIND LOADS:
Wind loads are not necessary to consider for design of multi-
storeyed building (G+2)
DESIGN OF STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS
DESIGN OF BEAM: Depth =350 mm
DESIGN OF COLOUMN: Size 300*400 mm
DESIGN OF FOOTING:Size 2.8*1.8m
DESIGN OF STAIR CASE: Open newel staircase used
DESIGN OF SLAB: Size =31*14.4m
Literature
literature review was based on internet search and through
Molde University College a number of databases were
searched, such as ProQuest; Science Direct; Planning Planet;
Google Scholars; Project Management Institute, Lean
Advancement Initiative; International Council on Systems
Engineering, and Lean Construction Institute. The
subsequent phase of the research was to find literature
that is specialized in project planning, scheduling,
measuring metrics for engineering activities in order to
find out how this is done in domains like: shipbuilding,
construction, IT, systems engineering, and project management.
One of the most useful documents found is “The Guide to
Lean Enablers for Managing Engineering Programs”
published as a joint collaboration between Massachusetts
Institute of Technology, International Council for
Systems Engineering and Project Management Institute
(Oehmen et al. 2012). The guide actually combines known
best practices from lean literature, project management and
systems engineering with input from an extensive community
of practitioners. The guide identifies and analyse ten major
challenge themes in managing engineering programs and their
possible solutions based on practices from lean thinking,
project management and systems engineering. The references
provided throughout this guide are also useful theoretical
background for this research. Broadly speaking, the most
useful literature is found in Project Management literature
and Lean Construction literature as presented in the next two
sections.
ISSN: 2393-9516 www.ijetajournal.org Page 103
International Journal of Engineering Trends and Applications (IJETA) – Volume 5 Issue 2, Mar-Apr 2018
[6] Mahamad Sabeer, Gouse Peera D, (August 2015)
published as “comparison design result of RCC
building using STAAD and ETAABS software” in
IV. CONCLUSION the journal, International Journal of Innovative
In this present work ETABS is used to analyse the R.C research in aduaval engineering(IJIRAE)
moment resting frame structure of G+2 considering the ISSN:2349=2163;Issue 8; volume 2.
gravity loads. The following conclusion is drawn from [7] Mahesh S, Dr.Panduranga B Rao (2014) published as
present work. “Comparison of analysis and design of regular and
Auto CAD irregular configuration of multi Story building in
software and designed for Beams, Columns, Footings, stairs various seismic zones and various types of soils
and slabs. The dead load, live load are referred using IS using ETABS and STAAD” in the journal, IOSR
875-1987 Journal of mechanical and civil engineering IOSR-
the IS 456- JMCE;ISSN:2278-1684;p-ISSN-2320-334X-volume
2000 and SP16 by considering concrete grade of M25 and 11:Issue-6 ver
steel of HYSD bars Fe500 are used.
building which
meets the requirements of our JIT girls.
calculation
i.e., in MS Excel as well as in software results.
different
dimensions of the beam, column, stairs, footing and slab of
the Hostel building as per the IS 456-2000 and SP16.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
[1] Abhay Gulgeria, (2016) pub1. Abhay Gulgeria,
(2016) published as “structural analysis of a multi
storey building using ETABS for different plan
configurations” in the journal, International Journal
of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT)
ISSN: 2278-0181 IJERTV3 IS051552 Vol. 3 Issue 5.
[2] Anjaneyulu B, Jaya Prakash K, (2016) published as
“Analysis and Design Of Flat Slab By Using Etabs
Software” in the journal, International Journal of
Science Engineering and Advance Technology,
IJSEAT, Vol. 4, Issue 2ISSN 2321-6905.
[3] Chintha Santhosh, Venkatesh Wadki, MadanMohan
S, Sreenatha Reddy S(2016) published as “Analysis
and Design of Multistory Building with Grid Slab
Using ETABS” in the journal, Research paper
volume4; Issue -7; ISSN NO-2277-8179.
[4] Geeta Mehta, Bidhan Sharma and Anuj Kumar(2016)
published as “Optimization of Member Size and
Materials for Multistoried RCC Buildings using
ETABS” in the journal, International Journal of
Science and Technology, vol9(44),
[5] DOI:10.174851/ijst/2016/v9i441105254; ISSN:0974-
6846; ISSN:0974-5645.
ISSN: 2393-9516 www.ijetajournal.org Page 104
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Anchor Bolt ACIDokumen15 halamanAnchor Bolt ACIAnonymous IwqK1Nl67% (3)
- Aws D17.2 - D17.2M-2019Dokumen60 halamanAws D17.2 - D17.2M-2019Rubén Mamani83% (12)
- Reinforced Concrete DesignDokumen993 halamanReinforced Concrete DesignRizal RifdoBelum ada peringkat
- Optimal Stiffness Tall Bldgs PDFDokumen12 halamanOptimal Stiffness Tall Bldgs PDFErik NelsonBelum ada peringkat
- TAMAYAO, John Mophet O. (Steel)Dokumen147 halamanTAMAYAO, John Mophet O. (Steel)Josh EdilreyBelum ada peringkat
- Marine Travelift Mobile Boat Hoist BrochureDokumen8 halamanMarine Travelift Mobile Boat Hoist Brochurebr1404Belum ada peringkat
- Temp Structures - Lesson1 To 7 (Washington University)Dokumen121 halamanTemp Structures - Lesson1 To 7 (Washington University)tony fungBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Design Examples of Seismic Retrofit of StructuresDari EverandAdvanced Design Examples of Seismic Retrofit of StructuresPenilaian: 1 dari 5 bintang1/5 (1)
- Astm C 1609 - 2019Dokumen9 halamanAstm C 1609 - 2019김기준100% (1)
- A 732 - A732M - 02 Equivalencia Ic AstmDokumen8 halamanA 732 - A732M - 02 Equivalencia Ic AstmorivaldopenaBelum ada peringkat
- Sizing Textile LearnerDokumen32 halamanSizing Textile Learnerfazrimajid13100% (1)
- Planning, Designing and Analysis of Hostel BuildingDokumen5 halamanPlanning, Designing and Analysis of Hostel BuildingmadhurjyaarchnehBelum ada peringkat
- Seismic Design With BRBsDokumen15 halamanSeismic Design With BRBsAlex MolinaBelum ada peringkat
- ETABSDokumen6 halamanETABSAbuturab SharikmaslatBelum ada peringkat
- Seismic Performance of Confined Versus Un Reinforced MasonryDokumen32 halamanSeismic Performance of Confined Versus Un Reinforced Masonry2020CEP011 KAUSHIKNANDYBelum ada peringkat
- 9 4 Comparative Study and Decision Making For A FormworkDokumen5 halaman9 4 Comparative Study and Decision Making For A Formworknazi nazBelum ada peringkat
- Steel Concrete Composite Systems For Modular Construction of High-Rise BuildingsDokumen16 halamanSteel Concrete Composite Systems For Modular Construction of High-Rise Buildingsdupe2010Belum ada peringkat
- Group 10 (Repaired)Dokumen13 halamanGroup 10 (Repaired)Sushil GunagaBelum ada peringkat
- Performance-Based Seismic Design Principles and Structural Analysis of Shanghai TowerDokumen18 halamanPerformance-Based Seismic Design Principles and Structural Analysis of Shanghai TowerRichard R. YoroBelum ada peringkat
- Ijet 17730Dokumen5 halamanIjet 17730Angelina AjengBelum ada peringkat
- 152.prefabricated Multistory Structure Exposure To Engineering Seismicity by UsingDokumen6 halaman152.prefabricated Multistory Structure Exposure To Engineering Seismicity by UsingVishvajit KohakadeBelum ada peringkat
- Group 4 Final RevisonDokumen304 halamanGroup 4 Final RevisonGerrard PantopioBelum ada peringkat
- Enabling Adaptable Buildings. Results of A Preliminary Expert SurveyDokumen8 halamanEnabling Adaptable Buildings. Results of A Preliminary Expert Surveycaro.herrera.r88Belum ada peringkat
- Desempeño Sísmico de La Construcción de Acero Modular de Altura Media A AltaDokumen20 halamanDesempeño Sísmico de La Construcción de Acero Modular de Altura Media A AltaDaniel Sunico LewinBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis and Design of Residential Building Using E-TabsDokumen6 halamanAnalysis and Design of Residential Building Using E-TabsSushil GunagaBelum ada peringkat
- 1 s2.0 S0045794924000506 MainDokumen17 halaman1 s2.0 S0045794924000506 MainAntonio CarlosBelum ada peringkat
- 1 s2.0 S235271021630376X MainDokumen17 halaman1 s2.0 S235271021630376X MainParide UboldiBelum ada peringkat
- Design of A Four-Storey Evacuation CenterDokumen69 halamanDesign of A Four-Storey Evacuation CenterRin KutaruBelum ada peringkat
- A Critical Study On Technological Advancements of Formwork in Construction Project ManagementDokumen5 halamanA Critical Study On Technological Advancements of Formwork in Construction Project Managementhrithik agnihotriBelum ada peringkat
- Sarja Extenedlimitstatedesign MS43 2010Dokumen12 halamanSarja Extenedlimitstatedesign MS43 2010Fernando RosalesBelum ada peringkat
- Structural Safety Assessment and ClassifDokumen8 halamanStructural Safety Assessment and ClassifChristian RuizBelum ada peringkat
- Design of Structures An Introduction To Civil EngineeringDokumen7 halamanDesign of Structures An Introduction To Civil Engineeringjulius hot sebeneBelum ada peringkat
- Group 10Dokumen4 halamanGroup 10Sushil GunagaBelum ada peringkat
- Simulation and Analytical Techniques For Construction Resource Planning and SchedulingDokumen15 halamanSimulation and Analytical Techniques For Construction Resource Planning and SchedulingWaheed ErfanyBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Based Design of Buildings & Bridges For Enhanced Seismic ResilienceDokumen8 halamanPerformance Based Design of Buildings & Bridges For Enhanced Seismic ResilienceMohit JainBelum ada peringkat
- Reasearch On Modular / Prefabricated ConstructionDokumen10 halamanReasearch On Modular / Prefabricated ConstructionFuad SaneenBelum ada peringkat
- Topology Design of Optimizing Material Arrangements of Beam-To-Column Connection Frames With Maximal StiffnessDokumen8 halamanTopology Design of Optimizing Material Arrangements of Beam-To-Column Connection Frames With Maximal StiffnessPinank PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Structures: Huu-Tai Thai, Tuan Ngo, Brian UyDokumen26 halamanStructures: Huu-Tai Thai, Tuan Ngo, Brian UyHit PopatBelum ada peringkat
- Announcement - Refresher Course On Performance Based Design For Buildings & Bridges, Sep-Oct 2019Dokumen3 halamanAnnouncement - Refresher Course On Performance Based Design For Buildings & Bridges, Sep-Oct 2019Rameo majumderBelum ada peringkat
- MainDokumen17 halamanMainI Gde Eka WiranathaBelum ada peringkat
- Retrofitting of Reinforced Concrete Structural Elements - Recent Technologies and Future ScopeDokumen15 halamanRetrofitting of Reinforced Concrete Structural Elements - Recent Technologies and Future ScopeSKMBelum ada peringkat
- Performance-Based Seismic Design of Reinforced Concrete Frame Buildings: A Direct Displacement-Based ApproachDokumen12 halamanPerformance-Based Seismic Design of Reinforced Concrete Frame Buildings: A Direct Displacement-Based ApproachSanjeev SahBelum ada peringkat
- 9 III March 2021Dokumen13 halaman9 III March 2021IJRASETPublicationsBelum ada peringkat
- Journal 563Dokumen5 halamanJournal 563MAXSWELL MANGGIE ZAMRYBelum ada peringkat
- Web-Based Knowledge-Based System On Liquid Retaining STR Uctur e Design As Instr Uctional ToolDokumen11 halamanWeb-Based Knowledge-Based System On Liquid Retaining STR Uctur e Design As Instr Uctional ToolAnonymous dK9Qi2XjBelum ada peringkat
- Rubrics RCDDokumen8 halamanRubrics RCDKenneth FungoBelum ada peringkat
- 2022 NB Ndt-Ce EeeDokumen11 halaman2022 NB Ndt-Ce EeeJ. Fernando RodriguesBelum ada peringkat
- BuildingsDokumen33 halamanBuildingsJhony ChoqueBelum ada peringkat
- Steel Concrete Composite Systems For Modular Construction of High-Rise BuildingsDokumen16 halamanSteel Concrete Composite Systems For Modular Construction of High-Rise BuildingsMichael ChewBelum ada peringkat
- Formwork For Concrete: University of WashingtonDokumen36 halamanFormwork For Concrete: University of Washingtonraahul_nBelum ada peringkat
- Structural Design NoteDokumen84 halamanStructural Design NoteSurafelT.100% (1)
- Malzoubi,+1241 Author+Article 572 1 6 20220514Dokumen19 halamanMalzoubi,+1241 Author+Article 572 1 6 20220514Sangsup LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Investigation of Linear Dynamic Analysis and Duc-Tile Design of High Rise Structure As Per Revised Indian CodeDokumen12 halamanInvestigation of Linear Dynamic Analysis and Duc-Tile Design of High Rise Structure As Per Revised Indian CodeIJRASETPublicationsBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Structures: J. Ramon Gaxiola-Camacho, Hamoon Azizsoltani, Francisco J. Villegas-Mercado, Achintya HaldarDokumen11 halamanEngineering Structures: J. Ramon Gaxiola-Camacho, Hamoon Azizsoltani, Francisco J. Villegas-Mercado, Achintya Haldarsriram narendranBelum ada peringkat
- Emerging Trends in Advancement of Formwork: March 2021Dokumen14 halamanEmerging Trends in Advancement of Formwork: March 2021leovinBelum ada peringkat
- SEI May.2012. SIA269StandardsDokumen6 halamanSEI May.2012. SIA269StandardsAntónio Abel HenriquesBelum ada peringkat
- 1 s2.0 S2352012420303040 MainDokumen10 halaman1 s2.0 S2352012420303040 MainkevinBelum ada peringkat
- Optimising Structures Using The Principle of Virtual WorkDokumen10 halamanOptimising Structures Using The Principle of Virtual Workjoaopedro.bragaiaBelum ada peringkat
- Using Pre Fabrication Systems in Building ConstructionDokumen6 halamanUsing Pre Fabrication Systems in Building ConstructionNaveen SBelum ada peringkat
- Roberts Et Al. - 2019 - Post-Occupancy Evaluation A Review of LiteratureDokumen23 halamanRoberts Et Al. - 2019 - Post-Occupancy Evaluation A Review of LiteratureraulBelum ada peringkat
- 31 An Exploratory Model On The Usability of A Prototyping PR 2017 Automation inDokumen12 halaman31 An Exploratory Model On The Usability of A Prototyping PR 2017 Automation inÐânĩĕl JøŚĕ CäŚŧrø ÂrïźăBelum ada peringkat
- A Review On Progressive Collapse of Steel Buildings: Journal of Civil Engineering ResearchersDokumen4 halamanA Review On Progressive Collapse of Steel Buildings: Journal of Civil Engineering ResearchersmdkmlBelum ada peringkat
- Retrofitting of Reinforced Concrete Structural Elements - Recent Technologies and Future ScopeDokumen15 halamanRetrofitting of Reinforced Concrete Structural Elements - Recent Technologies and Future Scope48Tathagata Koley100% (1)
- Analysis and Design of Commercial Building With Different Slab Arrangements Using ETABSDokumen6 halamanAnalysis and Design of Commercial Building With Different Slab Arrangements Using ETABSronald torresBelum ada peringkat
- Comparative Study of Tubular Steel Truss Profiles For Roofing Varying SpanDokumen6 halamanComparative Study of Tubular Steel Truss Profiles For Roofing Varying SpantechbhaskarBelum ada peringkat
- A Project Report On Earthquake Resistant Building Using E Tabs and Manual Designing. PaperDokumen9 halamanA Project Report On Earthquake Resistant Building Using E Tabs and Manual Designing. PaperAbdul RazzakBelum ada peringkat
- 4 CE502 Design ProjectDokumen193 halaman4 CE502 Design ProjectKaty PerryBelum ada peringkat
- Kowloon City Government Hostel 2Dokumen1 halamanKowloon City Government Hostel 2sanaBelum ada peringkat
- Rrcat 1 2019 DTL Eng v2Dokumen4 halamanRrcat 1 2019 DTL Eng v2sanaBelum ada peringkat
- Third Floor Fourth Floor Fifth Floor: Shopping MallDokumen1 halamanThird Floor Fourth Floor Fifth Floor: Shopping MallsanaBelum ada peringkat
- Mall Start Print-Model 5Dokumen1 halamanMall Start Print-Model 5sanaBelum ada peringkat
- Mall Start Print-Model 4Dokumen1 halamanMall Start Print-Model 4sanaBelum ada peringkat
- Building Economics: Assignment ONDokumen5 halamanBuilding Economics: Assignment ONsanaBelum ada peringkat
- Istruct 2019 Bamboo PDFDokumen17 halamanIstruct 2019 Bamboo PDFNiamul IslamBelum ada peringkat
- Materials: Performance Characterization of Semi-Flexible Composite MixtureDokumen13 halamanMaterials: Performance Characterization of Semi-Flexible Composite Mixturethanhnhat5521Belum ada peringkat
- 3 1 at The Proportional Limit A 12 InchDokumen34 halaman3 1 at The Proportional Limit A 12 InchAustin Duke100% (3)
- PS1 Mom IDokumen4 halamanPS1 Mom IMuhammad QasimBelum ada peringkat
- High Entropy Alloys Prepared by Spark Plasma Sintering - Mechanical and Thermal PropertiesDokumen14 halamanHigh Entropy Alloys Prepared by Spark Plasma Sintering - Mechanical and Thermal Propertiesthomasalbatros137Belum ada peringkat
- (3.4) Fundamental Concept of Stress and DeformationDokumen70 halaman(3.4) Fundamental Concept of Stress and DeformationIan Arnold Fami100% (1)
- AS 3600-2009 Ex001Dokumen8 halamanAS 3600-2009 Ex001Antonius AjalahBelum ada peringkat
- Detail Construction Procedure of Atal Tunnel RohtangDokumen23 halamanDetail Construction Procedure of Atal Tunnel RohtangANURAG JAISWALBelum ada peringkat
- Rock Engineering & Ground Control M205Dokumen4 halamanRock Engineering & Ground Control M205Pawan SahuBelum ada peringkat
- Erosion Abrasion and Cavitation of ConcreteDokumen8 halamanErosion Abrasion and Cavitation of ConcreteS Praveenkumar100% (4)
- Material Allowables Material AllowablesDokumen35 halamanMaterial Allowables Material AllowablesElzainie ShehabBelum ada peringkat
- Overhead Transmission Lines - Static Mechanical SupportDokumen7 halamanOverhead Transmission Lines - Static Mechanical SupportbatooganaBelum ada peringkat
- Stroitelni KonstruksiiDokumen40 halamanStroitelni Konstruksiiexcaliber4Belum ada peringkat
- Mec 201 04 Aug 20Dokumen18 halamanMec 201 04 Aug 20hemanth singhBelum ada peringkat
- Prestressed and Precast ConcreteDokumen19 halamanPrestressed and Precast ConcreteKhalilRoumaniBelum ada peringkat
- Lucitone FRS BrochureDokumen2 halamanLucitone FRS BrochureAndi Mauliyani MusdalifahBelum ada peringkat
- Borehole Stability Analysis in Deepwater Shallow Sediments: Yan ChuanliangDokumen7 halamanBorehole Stability Analysis in Deepwater Shallow Sediments: Yan ChuanliangJose Leo MissionBelum ada peringkat
- Relevant Aspects of The Geotechnical Design and Behavior of La Yesca Dam....Dokumen16 halamanRelevant Aspects of The Geotechnical Design and Behavior of La Yesca Dam....jdav1206Belum ada peringkat
- Mechanical, Fracture and Durability Properties of Self-Compacting High Strength Concrete Containing Recycled Polypropylene Particles PDFDokumen12 halamanMechanical, Fracture and Durability Properties of Self-Compacting High Strength Concrete Containing Recycled Polypropylene Particles PDFCristina HleonBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 8Dokumen65 halamanChapter 8DavidBelum ada peringkat
- Eurocode 8 - Part 2. Seismic Design of Bridges: 1. Introduction - SummaryDokumen20 halamanEurocode 8 - Part 2. Seismic Design of Bridges: 1. Introduction - SummarykstayroskBelum ada peringkat
- Embediment LengthDokumen6 halamanEmbediment LengthkelvinBelum ada peringkat
- NCHRP RPT 628Dokumen99 halamanNCHRP RPT 628cags15Belum ada peringkat