Organelles
Diunggah oleh
IceLand0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
11 tayangan3 halamanOrganelles
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniOrganelles
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
11 tayangan3 halamanOrganelles
Diunggah oleh
IceLandOrganelles
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 3
Organelles
Organelle Functions Structure
Nucleus Controls the cell and It is surrounded by two
contains genetic membranes known as the
material nuclear envelope. There are
chromosomes in a loosely
coiled state known as
chromatin.
Nucleolus Produces ribosomes It is small and found inside the
nucleus.
Endoplasmic Produces and A network of flattened sacs
Reticulum modifies proteins, running through the cytoplasm
lipids and of eukaryotic cells. It can be
carbohydrates smooth (no ribosomes) and
rough (with ribosomes)
Ribosome Produces proteins A tiny organelle found in
eukaryotic cell. They are made
up by proteins and ribosomal
RNA and have two subunits.
Golgi Body Sorts, modifies and Found in eukaryotic cells.
packages the Consists of a stack of flattened
material with vesicles sacs.
Lysosome Digest food or Found in eukaryotic cells.
harmful materials Contain digestive enzymes.
inside the cell
Mitochondria Produces energy The place where aerobical
needed for cell respiration takes place. It has a
activity double membrane and is filled
with a substance called matrix.
Roles of the components of cell membrane
Phospholipids They form the phospholipid bilayer and act as a
barrier to water-soluble substances. They can be
signalling molecules.
Choleresterol They maintain the mechanical stability of the
membrane and prevent ions or polar molecules
from passing through the membrane.
Glycolipids They act as receptor molecules or cell markers,
called antigens. They are involved in endocytosis,
too.
Glycoproteins Similar to glycolipids, they act as receptor
molecules or cell markers, called antigens. They are
involved in endocytosis, too.
Proteins They make possible the active transport. They can
be antibodies, which attack and destroy invading
microorganisms. They can be hormones, such as
insuline or glycagone and can be signalling
molecules or receptors.
They can also act as enzymes.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- CellDokumen17 halamanCellAaliyah Quesha LadjamatliBelum ada peringkat
- Introductiontophysiologylecture 101020230212 Phpapp02Dokumen34 halamanIntroductiontophysiologylecture 101020230212 Phpapp02DR KARSHAN NANDANIYABelum ada peringkat
- Cell OrganellesDokumen2 halamanCell OrganellesSurminie MuksinBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Organelles: Structures and FunctionsDokumen6 halamanCell Organelles: Structures and FunctionsSai Deekshita VijayakumarBelum ada peringkat
- Cell (Biochemical Aspects) : Dr. Abid AliDokumen49 halamanCell (Biochemical Aspects) : Dr. Abid AliShahzad MazharBelum ada peringkat
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells (Contrast)Dokumen2 halamanProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells (Contrast)Joyce DegomaBelum ada peringkat
- Biochemistry ReviewerDokumen5 halamanBiochemistry Reviewer202370092Belum ada peringkat
- Cell Organelles and Their FunctionsDokumen3 halamanCell Organelles and Their FunctionsAly FayeBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 Summary and Model Answers:: 3.2.1 Cell StructureDokumen22 halamanChapter 2 Summary and Model Answers:: 3.2.1 Cell StructureteeeBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Organelles GuideDokumen43 halamanCell Organelles GuideMariam Qais100% (1)
- What Are Cell OrganellesDokumen19 halamanWhat Are Cell OrganellesMaraon CharitaBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Structures & Organelles FunctionsDokumen9 halamanCell Structures & Organelles Functionsnasimzand78Belum ada peringkat
- Kingdom: Animal CellDokumen8 halamanKingdom: Animal CellShaila IvoryBelum ada peringkat
- Carbohydrates: Organic Vs Inorganic CompoundsDokumen16 halamanCarbohydrates: Organic Vs Inorganic CompoundsTsu Wei Chua100% (5)
- g11 Els OrganellesDokumen3 halamang11 Els OrganellesJarod PeñaflorBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Te Unit of Life Revision NotesDokumen8 halamanCell Te Unit of Life Revision NotesHarismita AlagurajBelum ada peringkat
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDokumen19 halamanProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsjhabBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamental Unit of LifeDokumen5 halamanFundamental Unit of Lifechabalalalulama5Belum ada peringkat
- Cell Structure2Dokumen6 halamanCell Structure2CRYSTAL A. ARIETABelum ada peringkat
- Topic 2-Parts and Functions of The CellDokumen45 halamanTopic 2-Parts and Functions of The CellDe Guia, Yuan Loriene NinaBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 1: Overview of the Cellular Basis of LifeDokumen3 halamanLesson 1: Overview of the Cellular Basis of LifeYLADE, ERICCA ANDREABelum ada peringkat
- General Biology ReviewerDokumen6 halamanGeneral Biology ReviewerBaby AleiraBelum ada peringkat
- Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDokumen70 halamanFunctional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsTrixie De GuzmanBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment in General Biology 1Dokumen3 halamanAssignment in General Biology 1neil aldwin garciaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 The CellDokumen2 halamanChapter 2 The CellGela ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- Act 2CDokumen3 halamanAct 2CCHARLIENE FAYE ASPRERBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Structure OrganellesDokumen89 halamanCell Structure OrganellesNo NameBelum ada peringkat
- Plant Cell and Animal CellDokumen8 halamanPlant Cell and Animal CelltipsyleopardBelum ada peringkat
- Dokumen - Tips - Cell Structure Functions Introduction Eucaryotic Cell StructureDokumen31 halamanDokumen - Tips - Cell Structure Functions Introduction Eucaryotic Cell StructureJairra Jae LunaBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Organelles - Structure and FunctionDokumen6 halamanCell Organelles - Structure and FunctionKaryl Marie Rodas JaminBelum ada peringkat
- BiochemistryDokumen4 halamanBiochemistryAaliyah Ashley CerboBelum ada peringkat
- ER and Golgi Apparatus: Structure and Functions of Key Cell OrganellesDokumen5 halamanER and Golgi Apparatus: Structure and Functions of Key Cell OrganellesJohn Rey BandongBelum ada peringkat
- Parts of A Cell 1. NucleusDokumen2 halamanParts of A Cell 1. NucleusVon Lester SanchezBelum ada peringkat
- Activity No.1 Cell and Molecular BiologyDokumen4 halamanActivity No.1 Cell and Molecular Biologyjocelynmillano115Belum ada peringkat
- The Basic Unit of LifeDokumen18 halamanThe Basic Unit of LifeKenneth Myro GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDokumen16 halamanCell Structure and Cell OrganisationanippoBelum ada peringkat
- Cellular Biology: Cell Structure and TaxonomyDokumen7 halamanCellular Biology: Cell Structure and TaxonomyFelyn Roseann AretaBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Vocabulary: NameDokumen3 halamanCell Vocabulary: NameStephanie BannickBelum ada peringkat
- L 2 Cell Structure and FunctionDokumen25 halamanL 2 Cell Structure and Functionkaukab azimBelum ada peringkat
- Cell The Basic Unit of Life 1Dokumen22 halamanCell The Basic Unit of Life 1Matt Andrei AmorosoBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 2 notesDokumen53 halamanTopic 2 notessuperhigh06Belum ada peringkat
- Cells to OrganismsDokumen15 halamanCells to OrganismsElleBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Biology BasicsDokumen23 halamanCell Biology BasicsAbume DougyBelum ada peringkat
- Acp1 ActDokumen6 halamanAcp1 ActAldrin VillanuevaBelum ada peringkat
- Reviewer in BiologyDokumen16 halamanReviewer in BiologyAngel CastilloBelum ada peringkat
- بايو م 2Dokumen7 halamanبايو م 2alidoctor678Belum ada peringkat
- Cell VocabularyDokumen3 halamanCell Vocabularyapi-537617514Belum ada peringkat
- Chap 5 FullDokumen130 halamanChap 5 Fullgaelle tannousBelum ada peringkat
- Ch. 3 Cell ReviewDokumen5 halamanCh. 3 Cell ReviewDivine GelasiusBelum ada peringkat
- Premidterms NotesDokumen4 halamanPremidterms NotesRenee Andrei Concepcion MozarBelum ada peringkat
- Cell theory in 40 charactersDokumen22 halamanCell theory in 40 charactersKent TediosBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Structure Function and PropertiesDokumen10 halamanCell Structure Function and PropertiesWanda JohnBelum ada peringkat
- Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDokumen6 halamanComparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsRishabh JainBelum ada peringkat
- Enzymes and Cell Membrane SystemsDokumen10 halamanEnzymes and Cell Membrane SystemsMuhammad LawalBelum ada peringkat
- Animal Cell: Prokaryotes Are Unicellular Organisms That Lack Organelles or Other InternalDokumen6 halamanAnimal Cell: Prokaryotes Are Unicellular Organisms That Lack Organelles or Other InternalJohnson Macayan FernándezBelum ada peringkat
- Intro, Cell, TissueDokumen29 halamanIntro, Cell, Tissueanisa930804Belum ada peringkat
- Group 5-4Dokumen84 halamanGroup 5-4googlegirl18Belum ada peringkat
- Module 2 LectureDokumen13 halamanModule 2 LectureJeal NochefrancaBelum ada peringkat
- OrganellesDokumen13 halamanOrganellesjanaBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksDari EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- Linked ListsDokumen21 halamanLinked ListsIceLandBelum ada peringkat
- This Is Tricky: Only Advance If No DeletionDokumen24 halamanThis Is Tricky: Only Advance If No DeletionIceLandBelum ada peringkat
- Using Namespace: Isdudeney MainDokumen2 halamanUsing Namespace: Isdudeney MainIceLandBelum ada peringkat
- Double Int Int Int Int Int Int Int Int Int: Average Count MainDokumen2 halamanDouble Int Int Int Int Int Int Int Int Int: Average Count MainIceLandBelum ada peringkat
- Muscular System: Structure and Function: 1. Types of MusclesDokumen3 halamanMuscular System: Structure and Function: 1. Types of MusclesIceLandBelum ada peringkat
- Untitled 3Dokumen1 halamanUntitled 3IceLandBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 12 - EL Book PDFDokumen169 halamanGrade 12 - EL Book PDFIceLandBelum ada peringkat
- Using Namespace Using Namespace: #Include #Include #Include #IncludeDokumen3 halamanUsing Namespace Using Namespace: #Include #Include #Include #IncludeIceLandBelum ada peringkat
- Math PDFDokumen1 halamanMath PDFIceLandBelum ada peringkat
- Omar Khayyam PDFDokumen1 halamanOmar Khayyam PDFIceLandBelum ada peringkat
- Male Reproductive SystemDokumen19 halamanMale Reproductive SystemAli JafriBelum ada peringkat
- What Does The Endocrine System Do?Dokumen10 halamanWhat Does The Endocrine System Do?hadiqa azizBelum ada peringkat
- Surgical Anatomy of Mandible DeptDokumen92 halamanSurgical Anatomy of Mandible Deptbhavaaishu100% (1)
- Pharynx: Dr. U OfforDokumen29 halamanPharynx: Dr. U OfforugochukwuBelum ada peringkat
- The Respiratory System Grade 7Dokumen44 halamanThe Respiratory System Grade 7VANSHIKA AGARWALBelum ada peringkat
- Blood Grouping Catalog 2022Dokumen8 halamanBlood Grouping Catalog 2022Nas simaBelum ada peringkat
- Anaphy - Lesson 4 - Topic 4 and 5Dokumen21 halamanAnaphy - Lesson 4 - Topic 4 and 5Rica Abigail DagosBelum ada peringkat
- Hematology AtlasDokumen733 halamanHematology Atlasrakshit09100% (10)
- Anatomy of PharynxDokumen27 halamanAnatomy of PharynxParul Gupta100% (2)
- Ai Chi - Meridians2Dokumen4 halamanAi Chi - Meridians2sale18100% (1)
- EsophagusDokumen41 halamanEsophagusrayBelum ada peringkat
- CanineDokumen144 halamanCanineJAZON MENDOZABelum ada peringkat
- Morphology and Function of Malpighian Tubules and Associated Structures in The Cockroach, Periplaneta AmericanaDokumen42 halamanMorphology and Function of Malpighian Tubules and Associated Structures in The Cockroach, Periplaneta AmericanaManojit ChatterjeeBelum ada peringkat
- Chang Sepsis and Septic ShockDokumen19 halamanChang Sepsis and Septic ShockPediatria UDec 2020Belum ada peringkat
- Ectopic Pregnancy Case StudyDokumen54 halamanEctopic Pregnancy Case StudyLawrence CapuchinoBelum ada peringkat
- 2021 - Evaluation of Liver Histopathological Findings of COVID-19 by Minimally Invasive AutopsiesDokumen24 halaman2021 - Evaluation of Liver Histopathological Findings of COVID-19 by Minimally Invasive AutopsiesMario Martínez TorijaBelum ada peringkat
- Lampiran Bongros 5ccDokumen7 halamanLampiran Bongros 5ccNgurah AndhikaBelum ada peringkat
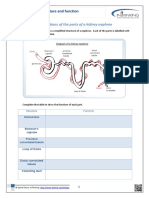
- Activity 1-The Functions of The Parts of A Kidney NephronDokumen3 halamanActivity 1-The Functions of The Parts of A Kidney NephronLynn SleimanBelum ada peringkat
- Modern Blood Banking and Transfusion Practices 6th Edition Harmening Test BankDokumen9 halamanModern Blood Banking and Transfusion Practices 6th Edition Harmening Test Bankxaviaalexandrawp86i100% (26)
- Difference Between Primary and Permanent TeethDokumen15 halamanDifference Between Primary and Permanent TeetharthisaBelum ada peringkat
- Weekly AssignmentDokumen7 halamanWeekly AssignmentBajwa AyeshaBelum ada peringkat
- Inflammatory Mechanisms: The Molecular Basis of Inflammation and DiseaseDokumen7 halamanInflammatory Mechanisms: The Molecular Basis of Inflammation and DiseaseMaximeBelum ada peringkat
- HBII Lab Manual 14-1-2019Dokumen50 halamanHBII Lab Manual 14-1-2019Ahmed Khaled Abo EldahabBelum ada peringkat
- Edema ParuDokumen4 halamanEdema ParuSri BayaniBelum ada peringkat
- Defining Physiology: Principles, Themes, Concepts.: Hwee Ming Cheng Kin Kheong Mah Kumar SeluakumaranDokumen104 halamanDefining Physiology: Principles, Themes, Concepts.: Hwee Ming Cheng Kin Kheong Mah Kumar SeluakumaranGiovanni HenryBelum ada peringkat
- Capitulo 56 SBEDokumen9 halamanCapitulo 56 SBEMayraPesantezCBelum ada peringkat
- The Musculoskeletal System: Structure and Movement in 38 CharactersDokumen30 halamanThe Musculoskeletal System: Structure and Movement in 38 CharactersJosee50% (2)
- (HST) Lab Le 2 SamplexDokumen12 halaman(HST) Lab Le 2 SamplexFrances Dei100% (1)
- Typhoid Fever Case Study in a ChildDokumen43 halamanTyphoid Fever Case Study in a ChildJef Sembrano DiplomaBelum ada peringkat
- Rispiratory System & Circulatory SystemDokumen23 halamanRispiratory System & Circulatory Systemapi-19753215Belum ada peringkat