Guided Notes - The Carrying Capacity of Ecosystems 1
Diunggah oleh
Yassine KootHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Guided Notes - The Carrying Capacity of Ecosystems 1
Diunggah oleh
Yassine KootHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
The Carrying Capacity of
Ecosystems
Glossary
TERM DEFINITION
population a group of the same species that inhabits a geographical area
carrying capacity
invasive species
a direct or indirect interaction between organisms that harms each other's chances of
competition
securing vital resources
Objective
In this lesson, you will _______________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________.
Measuring Populations
When scientists use the term population, they are usually referring to the _____________ of individuals of the
same _____________ that live in an area.
Population Size and Distribution
Population size: the __________________ of individuals in a population
Population density: the _____________ number of individuals per unit area
For example, 12,600 spiders are in
a region of 525 square meters.
Population
= Population
density =
population area density
= spiders per square meter
Copyright © 2019 Edmentum Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Population distribution (or dispersion): the _____________ in which individuals space themselves within
the region.
Distribution Types
Uniform • Individuals can live anywhere in their habitat and ____________
______ to use the available resources.
• Individuals form ___________ in their habitat. Few or none are
found between the clusters.
• Common in __________ organisms and when resources are few
and _____________ distributed.
• Individuals are dispersed ______________ and capable of living
anywhere in the habitat.
• Found among many _____________ species.
Population Growth and Limits
Three factors influence the growth or number of individuals in a population:
1. __________________: the number of individuals born over a given time period
2. ____________ ________: the number of individuals that die over a given time period
3. Migration: the movement of individuals
• __________________: individuals moving out of the population
• __________________: individuals moving into the population
Birth and immigration increase population size, while death and emigration reduce population size.
Limiting Factors on Population Growth
Factors that prevent populations from growing indefinitely are called limiting factors.
Resource availability
___________________ _______________ ___________________
the amount of resources an increase in the number of the frequency of reproductive
available regulates a predators can ______________ ___________ in a species’
population’s growth the population size lifetime and the ___________
e.g. __________, water, and of ______________ produced in
________ a single reproductive event
Copyright © 2019 Edmentum Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Minimal Viable Population
The minimal viable population (MVP) is a measurement that biologists use to determine the ______________
number of individuals a species needs to reproduce successfully and remain _________ without facing
________________. Biologists estimate the MVP of a population for a particular time period.
Survivorship Curves
Survivorship curves are graphs that show the ________________________ of a species, an important factor in
calculating a species’ minimal viable population. It helps scientists predict how an environmental change may
affect a population.
Type I
▪ indicates a _______ death rate and a
_______ survival rate for most of an
organism’s lifetime
▪ _______ individuals reach
_______________, but the number of
those who survive into old age then
rapidly declines
Type III Type II
▪ found in species that have a _______ death rate at an ▪ ______________ death rate
__________ age ▪ individuals die ________________ the
▪ only a _____ individuals reach _______________, and live ____________ of the species
to old age
Carrying Capacity
Carrying capacity (K) is the _________________ _________________ _______ that a particular habitat can
________________ indefinitely.
• Environmental conditions and resources affect a habitat’s carrying capacity. The __________
__________________ resource determines the carrying capacity.
• Carrying capacity isn’t a __________ number. A change in resource availability could change it.
Copyright © 2019 Edmentum Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Population Growth Models Exponential growth model describes populations
with a constant birthrate and ______________
any ______________ ____________.
▪ The population grows slowly, then the growth
rate _______________ ____________.
▪ All populations show this pattern until a
limiting factor affects them.
Logistic growth model describes populations that
experience a _____________ factor.
▪ The growth slows as resources become scarce
and population numbers reach the habitat’s
_____________ _____________.
Monitoring Beetle Population Trends: A population of beetles currently has 11,500 individuals on a
wildlife preserve of 115 hectares, with a carrying capacity at 14,600 individuals.
Part A: The population increases 5% Part B: What will likely happen to the beetle population during the
each year. The population will reach next year if the resource level stays the same?
or exceeded the carrying capacity
during year _______.
Part C: Given uniform distribution, in year 1, how Part D: At carrying capacity, a flood decreased the
many beetles are there per hectare? How many population to 77 beetles per hectare. What is the
beetles per hectare were there at carrying capacity? total estimated beetle population after the flood?
Part E: After reaching carrying capacity, pollution made 55 hectares of the land uninhabitable for the
beetles. How will the estimated carrying capacity change due to a decrease of 55 hectares of habitat?
Copyright © 2019 Edmentum Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Changes That Affect Populations
Environmental changes may affect a population’s ability to access resources and be beneficial or harmful.
The Effect of Environmental Changes
Environmental Change Effect on Populations
Natural Disasters are geological or • can reduce a population directly through ____________
_______________ events that devastate • can have the indirect effect of destroying sources of food and
an area, such as hurricanes, __________
_________________, wildfires, floods, and • may limit access to resources
_______ _______. • can ___________ populations, preventing separated groups
from intermingling
• can ___________ populations if done without limits
Human Exploitation by
• change the way the ecosystem functions, directly impacting
• removing organisms for _________, to
population numbers
keep as ________, or for other products
• altering the natural landscape for
_______________, logging, construction
Habitat Loss due to natural disasters and • causes ______________ ______________ for available
human alteration can make the habitat resources which lowers the habitat’s ____________
_________________ or inaccessible. ____________, and the population decreases
Disease • can cause population numbers to ________ drastically
• if a species develops resistance to a particular disease, its
population will increase
Climate Change is causing an increase in • some species may suffer, while others might benefit as
average ____________ _______________, previously inhospitable areas now become suitable
which affect a species’ ability to survive in • changes an area’s ____________ ________________, as
an area and disrupts ecosystems. some species die or emigrate while others immigrate
• affects the ecosystem balance
Copyright © 2019 Edmentum Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Invasive Species
Invasive species are organisms that are _____ __________ to the location where they live. They often have
few ____________ ____________, allowing them to quickly spread. Invasive species can affect populations of
native species in several ways, including:
• ________________: The invasive species can feed on a native species and ____________ its
population or even drive it to ______________.
• ________________ for resources: Invasive species may be ___________ ____________ to use the
resources, leaving few for the native species.
Invasive species can enter a habitat in several ways. Most involve humans:
Intentional introduction Unintentional human-caused Loss or changes to habitat
introduction
Species can stow away in cars,
boats, trains, and planes and be
brought to new places. Pet trade
and horticulture introduce foreign
species into a new area, and can
become invasive when pets or
seeds escape into the wild.
Careers in Science: Systems Ecologist
Systems ecologists study the entire ecosystem and how the system as a whole reacts to change. System
ecologists evaluate the _____________ and determine how they affect the ecosystem. The ecologists then
theorize how changes will affect the ________________ of ecosystems as a whole. System ecologists are
especially concerned with how ___________ ____________ affects ecosystems.
Summary
Think of a change that can occur to an ecosystem and the populations that live in that area. In what ways can
the different populations be affected? How does the change affect the carrying capacity of the populations?
Copyright © 2019 Edmentum Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Kira Bush - Env. Notes 8-1 (Fill In)Dokumen3 halamanKira Bush - Env. Notes 8-1 (Fill In)Kira BushBelum ada peringkat
- Edited - Biodiversity CMDokumen8 halamanEdited - Biodiversity CMjenniferBelum ada peringkat
- كيف تختار المضاد الحيوي المناسب برعاية مدونة الصيادلة PDFDokumen5 halamanكيف تختار المضاد الحيوي المناسب برعاية مدونة الصيادلة PDFAnonymous rFtiDaRuBelum ada peringkat
- Opc Ecology A3 HL Revision-SheetmodelansDokumen1 halamanOpc Ecology A3 HL Revision-SheetmodelansFrancisBelum ada peringkat
- Wellbeing Indicators Dominoes 2023Dokumen2 halamanWellbeing Indicators Dominoes 2023NoBelum ada peringkat
- Population Ecology WorksheetDokumen7 halamanPopulation Ecology WorksheetrkvBelum ada peringkat
- EcologyguidednotesDokumen6 halamanEcologyguidednotesapi-251568608Belum ada peringkat
- Population Evolution, Genetic Drift, Hardy-Weinberg WebquestDokumen8 halamanPopulation Evolution, Genetic Drift, Hardy-Weinberg WebquestLucas NavarroBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 3 NotetakingDokumen22 halamanUnit 3 NotetakingAllan YUBelum ada peringkat
- Ap Hug Unit 2 Reading Guide1Dokumen3 halamanAp Hug Unit 2 Reading Guide1api-94057686Belum ada peringkat
- Social Interactions & Population DynamicsDokumen5 halamanSocial Interactions & Population DynamicsDustin N. PeckhamBelum ada peringkat
- UNIT 3 CHANGING POPULATIONS - 2d CGC 1D1-REVIEW FILL IN THE BLANKSDokumen2 halamanUNIT 3 CHANGING POPULATIONS - 2d CGC 1D1-REVIEW FILL IN THE BLANKSReyan MahmoudBelum ada peringkat
- TRENDS and FADSDokumen3 halamanTRENDS and FADSMarchee AlolodBelum ada peringkat
- Edited - Human Pop QuizDokumen1 halamanEdited - Human Pop QuizjenniferBelum ada peringkat
- Human Rights, Citizenship, Human Dignity, Common Good Human Rights, Citizenship, Human Dignity, Common GoodDokumen1 halamanHuman Rights, Citizenship, Human Dignity, Common Good Human Rights, Citizenship, Human Dignity, Common GoodEditha BalolongBelum ada peringkat
- Predator-Prey Relationships Graphs ExplainedDokumen4 halamanPredator-Prey Relationships Graphs ExplainedCatherine ChildBelum ada peringkat
- Population Growth WorksheetDokumen5 halamanPopulation Growth WorksheetRuby SamarBelum ada peringkat
- Study GuidesDokumen13 halamanStudy Guidesmanar.artanBelum ada peringkat
- 21697a1ef05dab2cf2d7cd0d12ce8710Dokumen15 halaman21697a1ef05dab2cf2d7cd0d12ce8710Adrian DelatadoBelum ada peringkat
- Interactions NotesDokumen14 halamanInteractions NotessmedificationBelum ada peringkat
- Study Guide AnswersDokumen4 halamanStudy Guide AnswersKymberBelum ada peringkat
- 2021 Demographics Demographic VocabularyDokumen2 halaman2021 Demographics Demographic VocabularyJonathan PinheiroBelum ada peringkat
- Further Practice - Bài 1 - Unit 6Dokumen3 halamanFurther Practice - Bài 1 - Unit 6Đăng ĐặngBelum ada peringkat
- 1.4.9 Conservation WorksheetDokumen11 halaman1.4.9 Conservation WorksheetRomlah RomlahBelum ada peringkat
- Location, Location, Location: Cross-Curricular Focus: History/Social SciencesDokumen2 halamanLocation, Location, Location: Cross-Curricular Focus: History/Social SciencesVinieysha LoganathanBelum ada peringkat
- Atividade - Livro 3 - Unidade 7Dokumen5 halamanAtividade - Livro 3 - Unidade 7daniel.english.spanish.frenchBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter2 For StudentsDokumen1 halamanChapter2 For StudentscocoBelum ada peringkat
- Stimuli & Responses 1.3 & 1.4Dokumen5 halamanStimuli & Responses 1.3 & 1.4Yusrahanis NadilahBelum ada peringkat
- 1Dokumen7 halaman1api-372548146Belum ada peringkat
- U4c1 VocabDokumen3 halamanU4c1 Vocabapi-308919474Belum ada peringkat
- Chap 1Dokumen29 halamanChap 1Linh NguyễnBelum ada peringkat
- Agriculture HandoutDokumen6 halamanAgriculture Handoutcdavis339Belum ada peringkat
- Core Concepts On Therapeutic CommunicationDokumen6 halamanCore Concepts On Therapeutic CommunicationDiane AbanillaBelum ada peringkat
- Active Reading Chapter 10 Section 2Dokumen2 halamanActive Reading Chapter 10 Section 2zoe drullardBelum ada peringkat
- VariationDokumen30 halamanVariationFarhan RosleeBelum ada peringkat
- Population-Ecology-Graph-Worksheet KeyDokumen4 halamanPopulation-Ecology-Graph-Worksheet Keyamari roachBelum ada peringkat
- Canada's Changing PopulationDokumen5 halamanCanada's Changing PopulationRania IhsanBelum ada peringkat
- 3.3 Threats To BiodiversityDokumen10 halaman3.3 Threats To BiodiversitysnehaBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet Community InteractionsDokumen12 halamanWorksheet Community InteractionsrkvBelum ada peringkat
- Stimuli & Responses 1.3 & 1.4Dokumen5 halamanStimuli & Responses 1.3 & 1.4Yusrahanis NadilahBelum ada peringkat
- When People Have to Leave Home Due to Violence and PovertyDokumen2 halamanWhen People Have to Leave Home Due to Violence and Povertylucia xdBelum ada peringkat
- Natural Selection Notes Sheet (Recovered)Dokumen3 halamanNatural Selection Notes Sheet (Recovered)Sandra WheelerBelum ada peringkat
- Earth and Life Sci q2 w7 RTPDokumen8 halamanEarth and Life Sci q2 w7 RTPjuu yoonBelum ada peringkat
- Trends and Issues PrelimDokumen4 halamanTrends and Issues PrelimJunriv RiveraBelum ada peringkat
- 1.1-Environmental-Value-Systems B5Dokumen3 halaman1.1-Environmental-Value-Systems B5Nexon 303Belum ada peringkat
- Guided Notes - Relationships in Ecosystems 1Dokumen6 halamanGuided Notes - Relationships in Ecosystems 1Yassine KootBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 10 - Unit 6 HSDokumen23 halamanGrade 10 - Unit 6 HSGiang NguyễnBelum ada peringkat
- Biodiversity Notes From WWFDokumen6 halamanBiodiversity Notes From WWFGian BanaresBelum ada peringkat
- January-February 2007 Coulee Birder Newsletter Coulee Region Audubon SocietyDokumen4 halamanJanuary-February 2007 Coulee Birder Newsletter Coulee Region Audubon SocietyCoulee Region Audubon SocietyBelum ada peringkat
- 1.4.1 Ecology WorksheetDokumen5 halaman1.4.1 Ecology WorksheetMaria Jazzle ArboBelum ada peringkat
- Dustin N. Peckham - Ch. 16Dokumen5 halamanDustin N. Peckham - Ch. 16Dustin N. PeckhamBelum ada peringkat
- Yr 8 HPE - Closing the Gap in Indigenous HealthDokumen13 halamanYr 8 HPE - Closing the Gap in Indigenous HealthRyan SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet 1: College of Liberal ArtsDokumen1 halamanWorksheet 1: College of Liberal ArtsJohn Felix PalenciaBelum ada peringkat
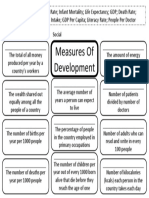
- Measure of DevelopmentDokumen1 halamanMeasure of DevelopmentLost UchihaBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding State and Non-State InstitutionsDokumen8 halamanUnderstanding State and Non-State InstitutionsCHRISTIAN DAVED BARROZOBelum ada peringkat
- Nominalization (Exercise)Dokumen2 halamanNominalization (Exercise)KryzQuinonesBelum ada peringkat
- HDI WorksheetDokumen1 halamanHDI Worksheetfeliciatqs100% (1)
- Contempo Final ExamDokumen3 halamanContempo Final ExamDianne Medel GumawidBelum ada peringkat
- Hand Out EcosystemDokumen6 halamanHand Out EcosystemEvan GamingBelum ada peringkat
- Guided Notes - Relationships in Ecosystems 1Dokumen6 halamanGuided Notes - Relationships in Ecosystems 1Yassine KootBelum ada peringkat
- Radiation Safety For Site RadiographyDokumen64 halamanRadiation Safety For Site RadiographyMohammad Aamir PerwaizBelum ada peringkat
- Guided Notes - Cycles in Ecosystems 1Dokumen6 halamanGuided Notes - Cycles in Ecosystems 1Yassine Koot33% (3)
- Paut NDT InternationalDokumen151 halamanPaut NDT InternationalMurugananthamParamasivamBelum ada peringkat
- 654 Wcndtfinal00655Dokumen9 halaman654 Wcndtfinal00655Yassine KootBelum ada peringkat
- 25 BradyDokumen53 halaman25 BradyYassine KootBelum ada peringkat
- PAUT Course Material PDFDokumen189 halamanPAUT Course Material PDFYassine Koot100% (3)
- HARDNESS TEST METHODSDokumen13 halamanHARDNESS TEST METHODShaizum_adamBelum ada peringkat
- Xray ProdDokumen25 halamanXray ProdSrikanthBatnaBelum ada peringkat
- Manual Ultrasonic Inspection of Thin Metal WeldsDokumen16 halamanManual Ultrasonic Inspection of Thin Metal WeldsSimon LeeBelum ada peringkat
- Boiler & Pressure Vessel Inspection Report PDFDokumen1 halamanBoiler & Pressure Vessel Inspection Report PDFEslam KhamisBelum ada peringkat
- Hased Array Ultrasonic Testing, Sectorial ScanDokumen7 halamanHased Array Ultrasonic Testing, Sectorial Scanநந்த குமார் சம்பத் நாகராஜன்100% (1)
- Basic Principles of Ultrasonic Testing. Theory and Practice.Dokumen42 halamanBasic Principles of Ultrasonic Testing. Theory and Practice.Teckelino89% (9)
- Basic Principles of Ultrasonic TestingDokumen42 halamanBasic Principles of Ultrasonic TestingyoungfpBelum ada peringkat
- Visual Inspection Procedure 0222 160 P PT PTJ 0008Dokumen7 halamanVisual Inspection Procedure 0222 160 P PT PTJ 0008Yassine Koot100% (1)
- ASME Code CalculationsDokumen45 halamanASME Code CalculationsPunith Rangegowda100% (12)
- Welding ProcessesDokumen1 halamanWelding ProcessesYassine KootBelum ada peringkat
- 12 - RadiosensitivityDokumen2 halaman12 - RadiosensitivityYassine KootBelum ada peringkat
- Handout 4Dokumen5 halamanHandout 4bakhtawar soniaBelum ada peringkat
- Gene FlowDokumen7 halamanGene FlowManikantan KBelum ada peringkat
- Demographic TheoryDokumen21 halamanDemographic TheoryRyan BowenBelum ada peringkat
- Comparative Study of Housing Amenities in Slums in Kerala Using 2011 Census Data.-By Reena .SDokumen73 halamanComparative Study of Housing Amenities in Slums in Kerala Using 2011 Census Data.-By Reena .SAnonymous 0lgF204rue100% (1)
- (Springer Transactions in Civil and Environmental Engineering) Fumihiko Seta, Joy Sen, Arindam Biswas, Ajay Khare (eds.)-From Poverty, Inequality to Smart City_ Proceedings of the National Conference.pdfDokumen184 halaman(Springer Transactions in Civil and Environmental Engineering) Fumihiko Seta, Joy Sen, Arindam Biswas, Ajay Khare (eds.)-From Poverty, Inequality to Smart City_ Proceedings of the National Conference.pdfCivil structureBelum ada peringkat
- Census of India 2011 - MCQ Questions On Current Affairs For Various ExaminationsDokumen10 halamanCensus of India 2011 - MCQ Questions On Current Affairs For Various ExaminationsSudipta RoyBelum ada peringkat
- 2002-03 Uganda Population Census ReportDokumen13 halaman2002-03 Uganda Population Census ReportThe New Vision100% (1)
- Eugenics Racism Population ControlDokumen5 halamanEugenics Racism Population Controlx321d0% (1)
- Celso Furtado-Economic Development of Latin America - Historical Background and Contemporary Problems (Cambridge Latin American Studies) (1977)Dokumen334 halamanCelso Furtado-Economic Development of Latin America - Historical Background and Contemporary Problems (Cambridge Latin American Studies) (1977)ManuelEfYiBelum ada peringkat
- 4b BIOL 1001 W2023 How Does Natural Selection Affect VariationDokumen5 halaman4b BIOL 1001 W2023 How Does Natural Selection Affect Variations3ippnpBelum ada peringkat
- w7b Seven Billion and CountingDokumen4 halamanw7b Seven Billion and Countingapi-253479558Belum ada peringkat
- Region XII's diverse landscape and culturesDokumen3 halamanRegion XII's diverse landscape and culturesKrisha VittoBelum ada peringkat
- UrbanizationDokumen16 halamanUrbanizationHari Srinivas100% (1)
- ICSE Solutions For Class 8 Geography Voyage - Population - A Plus TopperDokumen16 halamanICSE Solutions For Class 8 Geography Voyage - Population - A Plus TopperBinu Kumar SBelum ada peringkat
- Powerpoint Template UTHM 2022 16x9 Design 1Dokumen20 halamanPowerpoint Template UTHM 2022 16x9 Design 1nightbytheBelum ada peringkat
- Assam General InformationDokumen19 halamanAssam General InformationDonbor Shisha PohsngapBelum ada peringkat
- Biological Conservation: Ryo Sakurai, Hiromi Kobori, Masako Nakamura, Takahiro KikuchiDokumen7 halamanBiological Conservation: Ryo Sakurai, Hiromi Kobori, Masako Nakamura, Takahiro Kikuchihalim danangBelum ada peringkat
- 8BillionAndCounting 1-28Dokumen28 halaman8BillionAndCounting 1-28OnPointRadioBelum ada peringkat
- Tangshan Earthquake, ChinaDokumen2 halamanTangshan Earthquake, ChinaSurbhi ModiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 WcuDokumen19 halamanChapter 2 WcuKubaBelum ada peringkat
- 11.4 Hardy-Weinberg EquilibriumDokumen4 halaman11.4 Hardy-Weinberg EquilibriumOmar AlwaerBelum ada peringkat
- Line GraphDokumen13 halamanLine GraphMikelAgberoBelum ada peringkat
- 10global Demography (58 69)Dokumen12 halaman10global Demography (58 69)Tam Gerald CalzadoBelum ada peringkat
- Slums Case StudyDokumen20 halamanSlums Case StudyKoushali BanerjeeBelum ada peringkat
- Historical Glimpse of Dalongue Elementary SchoolDokumen4 halamanHistorical Glimpse of Dalongue Elementary SchoolDaisy De VeraBelum ada peringkat
- Learnenglish Podcasts Themes Overpopulation Support PackDokumen3 halamanLearnenglish Podcasts Themes Overpopulation Support PackrosrajenBelum ada peringkat
- The Evolution of Populations: Powerpoint Lectures ForDokumen56 halamanThe Evolution of Populations: Powerpoint Lectures ForLaura EspinolaBelum ada peringkat
- Environment The Science Behind The Stories Second Canadian Edition With Myenvironmentplace Canadian 2nd Edition Withgott Solutions ManualDokumen26 halamanEnvironment The Science Behind The Stories Second Canadian Edition With Myenvironmentplace Canadian 2nd Edition Withgott Solutions ManualKevinBensongjykx100% (55)
- Biodiversity, Population Growth and Carrying CapacityDokumen10 halamanBiodiversity, Population Growth and Carrying CapacityMARITESS COLLADOBelum ada peringkat
- Review On Triumph of The City PDFDokumen3 halamanReview On Triumph of The City PDFAnuj ManeBelum ada peringkat