Paediatric ECG Interpretation Guide
Diunggah oleh
ChrisJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Paediatric ECG Interpretation Guide
Diunggah oleh
ChrisHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
PAEDIATRIC ECG INTERPRETATION
Routine interpretation: Suggested sequence
1. Rhythm (sinus or non sinus) by considering the P axis
2. Heart rate (atrial and ventricular rates, if different)
3. The QRS axis
4. Intervals: PR, QRS and QT
5. The P wave amplitude and duration
6. The QRS amplitude and R/S ratio, also abnormal Q waves
7. ST segment and T wave abnormalities
Rhythm:
Sinus rhythm is characterized by
• P waves preceding each QRS complex
• Normal P axis (0 to +90 degrees) i.e. upright P in I and aVF
Heart rate:
At usual paper speed of 25mm/sec, 1mm = 0.04s, 5mm = 0.2s
Methods used to calculate HR include
• Count the R-R cycle in 6 large divisions (1/50 min) and multiply by 50
• Count the number of large divisions between the two R waves and divide that into
300
When the ventricular and atrial rates are different, the atrial rate can be calculated using the
P-P interval
QRS Axis:
RV dominance in infants gradually changes to LV dominance in adults
Hence, there is right axis deviation of QRS till 1 month, adult axis by 3 yr
Mean and ranges of Normal QRS Axes
Age Range
1 wk-1mo +110° (+30 to +180)
1-3mo +70° (+10 to +125)
3mo-3yr +60° (+10 to +110)
Older than 3yr +60° (+20 to +120)
Adults +50° (-30 to +105)
Intervals:
• PR interval varies with age and heart rate
Age Lower limit Upper limit of norm
< 3 yr. 0.08sec 0.15 (HR < 100)
3 - 16 yr. 0.10sec 0.16 (HR < 100)
> 16 yr. 0.12sec 0.18 (HR < 100)
QRS duration QT interval
Prem infants 0.04sec QT measured (sec)
Full term 0.05sec QTc =
1 - 3 yr. 0.06sec
RR interval (sec)
Child > 3 yr. 0.07sec
Adult 0.08sec
According to Bazett’s formula, the
QTc interval should not exceed
0.44 sec
P wave amplitude and duration:
• Mean P amplitude 1.5mm, max. 3mm.
• Normal P wave duration 0.06±0.02s.
• Max. P wave duration <12mo 0.08sec
Child 0.10sec
• Right atrial enlargement - P > 3 mm peaked (P pulmonale)
• Left atrial enlargement - Bifid P > 0.10s (0.08s in infants) (P mitrale)
P inversion >1mm in V1
Abnormal Q waves:
• Q wave commonly present in I, aVL and/or V5 and V6. May also be present in II,
III and aVF.
• Presence of Q in V1 = RVH
• Deep Q waves suggest LVH
• Average Q wave duration is 0.02s and does not exceed 0.03s
ST segment and T waves
• ST segment horizontal, isoelectric shifts may be normal up to
1mm in limb leads
2mm in praecordial leads
• T wave amplitude usually less than the following :
in V5: < 1yr 11mm > 1yr 14mm
V6: < 1yr 7mm > 1yr 9mm
• Tall and peaked in hyperkalaemia
Criteria for RVH
• RV1 > 20mm at all ages
• SV6 > 14mm (0-7days); > 10mm (1wk-6mth); > 7mm (6mth-1yr); > 5mm (>
1yr)
• R/S V1 6.5 (0-3mth); 4.0 (3-6mth); 2.4 (6mth-3yr); 1.6 (3-5yr); 0.8 (6-15yr)
• T wave upright in V4R or V1 after 72 hrs.
• Presence of Q wave in V1.
RVH in the newborn
• S waves in lead I, ≥ 12mm
• R waves in aVR, ≥ 8mm
• Important abnormalities in V1 such as:
o Pure R waves (without S) in V1, ≥ 10mm
o R waves in V1, ≥ 25mm
o QR pattern in V1 (also seen in 10% of normal newborns)
o Upright T waves in V1 in newborns > 3days old
• QRS axis greater than +180°
Criteria for LVH
• SV1 > 20mm
• RV6 > 20mm > 26mm in older child
• SV1 + RV6 > 40mm over 1yr of age; > 30mm if < 1yr
• Q wave of 4mm or more in V 5-6
• T wave inversion in V 5-6
Combined biventricular hypertrophy
• Direct evidence of RVH or LVH
• R + S in V4 > 70mm
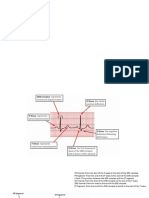
Diagram illustrating important intervals (or
durations) and segments of an ECG cycle
Electrolyte changes affecting ECG
Hypokalaemia < 2.5 mmol/l Hyperkalaemia > 6 mmol/l
T Waves low, flat or inverted Tall peaked T
ST Segment depressed Widening QRS
QT interval increased Prolonged PR, Lengthening QT
U Waves prominent Diminishing size of P & R waves
Depressed ST Segment
Hypocalcaemia Hypercalcaemia
QT prolonged. QT shortened
ST Segment unchanged Cardiac arrhythmias
Enhances effect of hypokalaemia
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- ECG%20 ReviewDokumen103 halamanECG%20 ReviewJenna NiemiecBelum ada peringkat
- Electrocardiogram BY Dr. Ayesha ARDokumen19 halamanElectrocardiogram BY Dr. Ayesha ARMobin Ur Rehman KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Ecg, CXRDokumen62 halamanEcg, CXRBrave LionBelum ada peringkat
- Paeds ECG InterpretationDokumen28 halamanPaeds ECG InterpretationMuhammad Moazzam GulzarBelum ada peringkat
- ECGDokumen33 halamanECGTamia PutriBelum ada peringkat
- Basic ECG ReadingDokumen41 halamanBasic ECG ReadingBenj100% (3)
- Peadiatric ECGDokumen54 halamanPeadiatric ECGshalini0580% (5)
- ECGDokumen115 halamanECGBhakti WashilkarBelum ada peringkat
- Lab NameDokumen4 halamanLab NameShamsuzzaman SharifBelum ada peringkat
- ECG Lecture 20141007Dokumen21 halamanECG Lecture 20141007Anne Lorraine BringasBelum ada peringkat
- EKG Interpretation Guide: The 10 Key Steps for Reading EKGsDokumen66 halamanEKG Interpretation Guide: The 10 Key Steps for Reading EKGsAltama L. SidartaBelum ada peringkat
- EKG Calibration and Interval GuideDokumen19 halamanEKG Calibration and Interval Guidechat5619Belum ada peringkat
- Basic ECG Interpretation GuideDokumen60 halamanBasic ECG Interpretation GuideLexadkBelum ada peringkat
- Presentasi Ws Ekg SakinahDokumen40 halamanPresentasi Ws Ekg SakinahsiskaBelum ada peringkat
- ECG InterpretationDokumen95 halamanECG InterpretationNur Rahmat Wibowo100% (8)
- Ecg CookbookDokumen2 halamanEcg CookbookCalin Popa100% (1)
- Joseph Brian L. Costiniano, MD, DPCPDokumen70 halamanJoseph Brian L. Costiniano, MD, DPCPcarmsBelum ada peringkat
- EKG Interpretation: Amir Aziz AlkatiriDokumen51 halamanEKG Interpretation: Amir Aziz AlkatiriShabrina Sari MedinaBelum ada peringkat
- Basic ECG Reading GuideDokumen63 halamanBasic ECG Reading GuideJofandAndrea MendozaBelum ada peringkat
- Step-by-step ECG interpretation guideDokumen3 halamanStep-by-step ECG interpretation guideVergiling SheebaBelum ada peringkat
- Leads II, III, and aVF During NSR. If The P Waves Are Negative in Leads II, III, andDokumen1 halamanLeads II, III, and aVF During NSR. If The P Waves Are Negative in Leads II, III, andRudy PCBelum ada peringkat
- EKG Characteristics of a Normal ECGDokumen45 halamanEKG Characteristics of a Normal ECGCasiana GuiBelum ada peringkat
- Basic ECG Workshop For ParamedicsDokumen75 halamanBasic ECG Workshop For ParamedicsRobyn FormosoBelum ada peringkat
- ElectrocardiogramDokumen169 halamanElectrocardiogramjitendra magarBelum ada peringkat
- BASIC ECG READING For Nle NOVEMBER 2018Dokumen63 halamanBASIC ECG READING For Nle NOVEMBER 2018Sharmaine KimmayongBelum ada peringkat
- A Simple Guide to ECG InterpretationDokumen53 halamanA Simple Guide to ECG Interpretationedy suyantoBelum ada peringkat
- Approach To Pediatric ECGDokumen5 halamanApproach To Pediatric ECGMateen ShukriBelum ada peringkat
- EKG Interpretation: DR K P Tripathy Kims, BhubaneswarDokumen58 halamanEKG Interpretation: DR K P Tripathy Kims, BhubaneswarAbhilash MohantyBelum ada peringkat
- Ecg Interpretation New TemplateDokumen88 halamanEcg Interpretation New TemplateJonathan NgBelum ada peringkat
- EcgDokumen6 halamanEcgMohamed IbrahimBelum ada peringkat
- EKG Interpretation 1Dokumen56 halamanEKG Interpretation 1usmleusmle86Belum ada peringkat
- Ecg For InternsDokumen31 halamanEcg For InternsAggamemnon populosBelum ada peringkat
- 2019.02.04 - Dr. Alius - Basic ElectrocardiographyDokumen104 halaman2019.02.04 - Dr. Alius - Basic Electrocardiographyyohanes gabriel dwirianto w.aBelum ada peringkat
- Ekg Panum or OsceDokumen69 halamanEkg Panum or OsceGladish RindraBelum ada peringkat
- 10 Warning Signs of ImmunodeficiencyDokumen23 halaman10 Warning Signs of ImmunodeficiencyChin ChanBelum ada peringkat
- Final Practical Revision Physiology 2 Prof - Dr.heba Shawky-1Dokumen74 halamanFinal Practical Revision Physiology 2 Prof - Dr.heba Shawky-1Mariam RaoufBelum ada peringkat
- EKG Interpretation: UNC Emergency Medicine Medical Student Lecture SeriesDokumen58 halamanEKG Interpretation: UNC Emergency Medicine Medical Student Lecture SeriesrsadellaBelum ada peringkat
- Readecg2010 PDFDokumen63 halamanReadecg2010 PDFShiju P SBelum ada peringkat
- Abnormal ECGDokumen55 halamanAbnormal ECGdevilbata50% (2)
- ECG For InternsDokumen31 halamanECG For InternsAgus SyaifudinBelum ada peringkat
- Interpretasi EKGDokumen81 halamanInterpretasi EKGGyna MarsianaBelum ada peringkat
- Basics of Ecg: DR Shyama Assistant Professor General Medicine Aiims, PatnaDokumen117 halamanBasics of Ecg: DR Shyama Assistant Professor General Medicine Aiims, PatnaSimran KothariBelum ada peringkat
- EKG Interpretation Guide for Medical StudentsDokumen58 halamanEKG Interpretation Guide for Medical StudentsHasnahdurrBelum ada peringkat
- EKG Interpretation Guide for Medical StudentsDokumen58 halamanEKG Interpretation Guide for Medical StudentsHasnahdurrBelum ada peringkat
- EKG Interpretation: UNC Emergency Medicine Medical Student Lecture SeriesDokumen58 halamanEKG Interpretation: UNC Emergency Medicine Medical Student Lecture SeriesanisaBelum ada peringkat
- EKG InterpretationDokumen58 halamanEKG InterpretationIman Sama-aliBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Abnormal ECG FadhlyDokumen55 halamanBasic Abnormal ECG FadhlyFadhly SharimanBelum ada peringkat
- Ecg Basics - NAVEENDokumen65 halamanEcg Basics - NAVEENNaveen MathieuBelum ada peringkat
- Pediatric ElectrocardiographyDokumen7 halamanPediatric ElectrocardiographyTri NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- ECG for Interns: Establish a Consistent Approach to Interpreting ECGsDokumen25 halamanECG for Interns: Establish a Consistent Approach to Interpreting ECGsusmleusmle86Belum ada peringkat
- ECG Interpretation Guide: Learn How to Read and Analyze an ElectrocardiogramDokumen40 halamanECG Interpretation Guide: Learn How to Read and Analyze an ElectrocardiogramAnonymous HAbhRTs2TfBelum ada peringkat
- ECG Made Easy by DR Bashir Ahmed Dar Associate Professor Medicine Chinkipora Sopore KashmirDokumen320 halamanECG Made Easy by DR Bashir Ahmed Dar Associate Professor Medicine Chinkipora Sopore KashmirProf Dr Bashir Ahmed Dar Chinki Pora Sopore Kashmir100% (2)
- ECG tutorial covers basics, axis, waves, intervals, hypertrophy and moreDokumen56 halamanECG tutorial covers basics, axis, waves, intervals, hypertrophy and morefeby_valBelum ada peringkat
- TH4-127 KreuzDokumen113 halamanTH4-127 Kreuzakp892818Belum ada peringkat
- ECG Findings in AthletesDokumen1 halamanECG Findings in AthletesHershel LaytonBelum ada peringkat
- 02 - ECG - General Approach and Normal Aspects 2Dokumen18 halaman02 - ECG - General Approach and Normal Aspects 2hussain alkhrsanyBelum ada peringkat
- EKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookDari EverandEKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookBelum ada peringkat
- Torsade De Pointes, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDari EverandTorsade De Pointes, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsBelum ada peringkat
- HE Catalogue Jul15 FinalDokumen42 halamanHE Catalogue Jul15 FinalChrisBelum ada peringkat
- Sinopsis PsikiatriDokumen5 halamanSinopsis PsikiatriChrisBelum ada peringkat
- Fear of EyesDokumen16 halamanFear of EyesChrisBelum ada peringkat
- MR IcuDokumen42 halamanMR IcuChrisBelum ada peringkat
- 10 PDFDokumen1 halaman10 PDFChrisBelum ada peringkat
- Week 1 SundayDokumen1 halamanWeek 1 SundaydsadasdsakdjsakljBelum ada peringkat
- Paranoma ExcisionDokumen1 halamanParanoma ExcisionChrisBelum ada peringkat
- FEAR OF HOLE Ade WibowoArif PDFDokumen19 halamanFEAR OF HOLE Ade WibowoArif PDFChrisBelum ada peringkat
- 1diphtheria Spain Rapid Risk Assessment June 2015Dokumen8 halaman1diphtheria Spain Rapid Risk Assessment June 2015Francisca BallesterosBelum ada peringkat
- Why So Many Scoliosis Patients Are Using The Spinecor Brace and The Schroth Method of Exercises Together (PDF Reference)Dokumen3 halamanWhy So Many Scoliosis Patients Are Using The Spinecor Brace and The Schroth Method of Exercises Together (PDF Reference)ChrisBelum ada peringkat
- Week 1 Tuesday Thursday SaturdayDokumen1 halamanWeek 1 Tuesday Thursday SaturdaydsadasdsakdjsakljBelum ada peringkat
- Week 1 Monday Wednesday FridayDokumen1 halamanWeek 1 Monday Wednesday FridaydsadasdsakdjsakljBelum ada peringkat
- Melloni's Pocket Medical DictionaryDokumen2.992 halamanMelloni's Pocket Medical DictionaryChrisBelum ada peringkat
- Result of Hyperthyroidism: Sumber: Mayo ClinicDokumen9 halamanResult of Hyperthyroidism: Sumber: Mayo ClinicChrisBelum ada peringkat
- Scoliosis Exercises: Physical Therapy DepartmentDokumen4 halamanScoliosis Exercises: Physical Therapy DepartmentIfa10371% (7)
- Exercises For Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis (Protocol) (PDF Reference)Dokumen16 halamanExercises For Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis (Protocol) (PDF Reference)ChrisBelum ada peringkat
- Exercises For Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis (Protocol) (PDF Reference)Dokumen16 halamanExercises For Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis (Protocol) (PDF Reference)ChrisBelum ada peringkat
- Anti ArrhythmicdrugsDokumen52 halamanAnti ArrhythmicdrugsChrisBelum ada peringkat
- Exercises For Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis (Protocol) (PDF Reference)Dokumen16 halamanExercises For Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis (Protocol) (PDF Reference)ChrisBelum ada peringkat
- Scoliosis Exercises: Physical Therapy DepartmentDokumen4 halamanScoliosis Exercises: Physical Therapy DepartmentIfa10371% (7)
- Heart Sounds and MurmursDokumen38 halamanHeart Sounds and MurmursLaura Moise100% (5)
- Exercises For Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis (Protocol) (PDF Reference)Dokumen16 halamanExercises For Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis (Protocol) (PDF Reference)ChrisBelum ada peringkat
- The Way People Dress Reveals Their Personality and Taste.: GoldDokumen3 halamanThe Way People Dress Reveals Their Personality and Taste.: GoldChrisBelum ada peringkat
- Pentalaksanaan RBDokumen84 halamanPentalaksanaan RBFara Sakina RahmaBelum ada peringkat
- ItilDokumen11 halamanItilNarendar P100% (2)
- Hotel Housekeeping EQUIPMENTDokumen3 halamanHotel Housekeeping EQUIPMENTsamahjaafBelum ada peringkat
- GSIS vs. de LeonDokumen9 halamanGSIS vs. de Leonalwayskeepthefaith8Belum ada peringkat
- of Types of Nuclear ReactorDokumen33 halamanof Types of Nuclear Reactormandhir67% (3)
- Lesson Plan 7 Tabata TrainingDokumen4 halamanLesson Plan 7 Tabata Trainingapi-392909015100% (1)
- LabyrinthDokumen4 halamanLabyrinthAyezaZuberyBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas B InggrisDokumen9 halamanTugas B InggrisDellyna AlmaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4Dokumen26 halamanChapter 4Lana AlakhrasBelum ada peringkat
- Family MedicineDokumen156 halamanFamily MedicinedtriggBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5Dokumen16 halamanChapter 5Ankit GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Abstract - Tropen Tag 2011 PDFDokumen634 halamanAbstract - Tropen Tag 2011 PDFzmoghesBelum ada peringkat
- Soal UTS Bahasa Inggris SMP Semester Genap Tahun Ajaran 2020Dokumen5 halamanSoal UTS Bahasa Inggris SMP Semester Genap Tahun Ajaran 2020awan MustofaBelum ada peringkat
- Indonesia Organic Farming 2011 - IndonesiaDOCDokumen18 halamanIndonesia Organic Farming 2011 - IndonesiaDOCJamal BakarBelum ada peringkat
- Sigma monitor relayDokumen32 halamanSigma monitor relayEdwin Oria EspinozaBelum ada peringkat
- TDS Versimax HD4 15W40Dokumen1 halamanTDS Versimax HD4 15W40Amaraa DBelum ada peringkat
- The Secret of The House WTDokumen22 halamanThe Secret of The House WTPetr -50% (2)
- DR - Hawary Revision TableDokumen3 halamanDR - Hawary Revision TableAseel ALshareefBelum ada peringkat
- Aging and Elderly IQDokumen2 halamanAging and Elderly IQ317537891Belum ada peringkat
- Gate Installation ReportDokumen3 halamanGate Installation ReportKumar AbhishekBelum ada peringkat
- G10 Bio CellsDokumen6 halamanG10 Bio CellsswacaneBelum ada peringkat
- B.Sc. (AGRICULTURE) HORTICULTURE SYLLABUSDokumen31 halamanB.Sc. (AGRICULTURE) HORTICULTURE SYLLABUSgur jazzBelum ada peringkat
- Mabuhay Wedding Package2006Dokumen3 halamanMabuhay Wedding Package2006Darwin Dionisio ClementeBelum ada peringkat
- Laboratorio 1Dokumen6 halamanLaboratorio 1Marlon DiazBelum ada peringkat
- Test Report OD63mm PN12.5 PE100Dokumen6 halamanTest Report OD63mm PN12.5 PE100Im ChinithBelum ada peringkat
- Benefits at Cognizant Technology SolutionsDokumen5 halamanBenefits at Cognizant Technology Solutions8130089011Belum ada peringkat
- Sub Erna RekhaDokumen2 halamanSub Erna Rekhasurabhi mandalBelum ada peringkat
- Growing Turmeric: Keys To SuccessDokumen4 halamanGrowing Turmeric: Keys To SuccessAnkit ShahBelum ada peringkat
- Dimensional Data: For Valves and ActuatorsDokumen52 halamanDimensional Data: For Valves and ActuatorsPaulBelum ada peringkat
- EEDMATH1 - Teaching Mathematics in The Primary Grades Beed 2E Learning Activity PlanDokumen3 halamanEEDMATH1 - Teaching Mathematics in The Primary Grades Beed 2E Learning Activity PlanBELJUNE MARK GALANANBelum ada peringkat
- Practice of Epidemiology Performance of Floating Absolute RisksDokumen4 halamanPractice of Epidemiology Performance of Floating Absolute RisksShreyaswi M KarthikBelum ada peringkat