Tutorial Problems
Diunggah oleh
Joel CurryHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Tutorial Problems
Diunggah oleh
Joel CurryHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Preparation for quiz
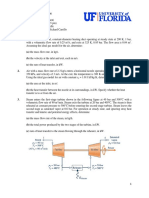
5–40 Air at 80 kPa, 27°C, and 220 m/s enters a diffuser at a
rate of 2.5 kg/s and leaves at 42°C. The exit area of the diffuser
is 400 cm2. The air is estimated to lose heat at a rate of 18 kJ/s
during this process. Determine (a) the exit velocity and (b) the
exit pressure of the air. Answers: (a) 62.0 m/s, (b) 91.1 kPa
5–120 Steam enters an insulated pipe at 200 kPa and 200°C
and leaves at 150 kPa and 150°C. The inlet-to-outlet diameter
ratio for the pipe is D1/D2_1.80. Determine the inlet and exit
velocities of the steam.
5–127 A 2-m3 rigid tank initially contains air at 100 kPa and
22°C. The tank is connected to a supply line through a valve.
Air is flowing in the supply line at 600 kPa and 22°C. The
valve is opened, and air is allowed to enter the tank until the
pressure in the tank reaches the line pressure, at which point
the valve is closed. A thermometer placed in the tank indicates
that the air temperature at the final state is 77°C. Determine
(a) the mass of air that has entered the tank and (b) the amount
of heat transfe
6–150 A heat pump receives heat from a lake that has an
average winter time temperature of 6°C and supplies heat
into a house having an average temperature of 27°C.
(a) If the house loses heat to the atmosphere at the rate
of 64,000 kJ/h, determine the minimum power supplied to the
heat pump, in kW.
(b) A heat exchanger is used to transfer the energy from
the lake water to the heat pump. If the lake water temperature
decreases by 5°C as it flows through the lake water-to-heat
pump heat exchanger, determine the minimum mass flow rate
of lake water, in kg/s. Neglect the effect of the lake water
pump.
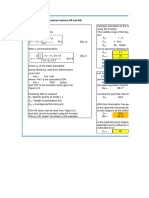
E X A M P L E 4 . 1 Feedwater Heater at Steady State
1. A feedwater heater operating at steady state has two inlets and one exit. At inlet 1, water
vapor enters at p1 _ 7 bar, T1 _
200_C with a mass flow rate of 40 kg/s. At inlet 2, liquid water at p2 _ 7 bar, T2 _ 40_C enters through
an area A2 _ 25 cm2.
Saturated liquid at 7 bar exits at 3 with a volumetric flow rate of 0.06 m 3/s. Determine the mass flow
rates at inlet 2 and at
the exit, in kg/s, and the velocity at inlet 2, in m/s.
2. Steam enters a converging–diverging nozzle operating at steady state with p1 _ 40 bar, T1 _
400_C, and a velocity of 10 m/s.
The steam flows through the nozzle with negligible heat transfer and no significant change in potential
energy. At the exit,
p2 _ 15 bar, and the velocity is 665 m/s. The mass flow rate is 2 kg/s. Determine the exit area of the
nozzle, in m2.
3. Steam enters a turbine operating at steady state with a mass flow rate of 4600 kg/h. The
turbine develops a power output of 1000 kW. At the inlet, the pressure is 60 bar, the
temperature is 400_C, and the velocity is 10 m/s. At the exit, the pressure
is 0.1 bar, the quality is 0.9 (90%), and the velocity is 50 m/s. Calculate the rate of heat transfer
between the turbine and surroundings,in kW.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- A Feedwater Heater Operating at Steady State Has Two Inlets and One ExitDokumen1 halamanA Feedwater Heater Operating at Steady State Has Two Inlets and One ExitAhmed MasoudBelum ada peringkat
- A Feedwater Heater Operating at Steady State Has Two Inlets and One ExitDokumen1 halamanA Feedwater Heater Operating at Steady State Has Two Inlets and One ExitMuthiah Chidambaram Muthiah0% (2)
- Tutorial 5Dokumen4 halamanTutorial 5Jamilah MrafiBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 6 ExamplesDokumen29 halamanLecture 6 ExamplesMohamed ZahranBelum ada peringkat
- T 5Dokumen2 halamanT 5jfl2096Belum ada peringkat
- Tutorial Sheet 4Dokumen2 halamanTutorial Sheet 4Syed YousufuddinBelum ada peringkat
- Set 6Dokumen3 halamanSet 6Jose FBelum ada peringkat
- Energy Analysis of Control VolumesDokumen5 halamanEnergy Analysis of Control VolumesSam FraserBelum ada peringkat
- Set 5Dokumen2 halamanSet 5Olliver Ceni de OliveiraBelum ada peringkat
- Tarea 1Dokumen2 halamanTarea 1Aangel Tello PechBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5, 6, and 7Dokumen6 halamanChapter 5, 6, and 7nageshBelum ada peringkat
- ME 201 AssignmentDokumen3 halamanME 201 Assignmentmz_haqBelum ada peringkat
- Answers: (A) 0.796 KG/S, (B) 58 CMDokumen2 halamanAnswers: (A) 0.796 KG/S, (B) 58 CMArnold Thamrin van LutteranBelum ada peringkat
- Sheet 5 SolutionDokumen36 halamanSheet 5 SolutionJoseph CorderoBelum ada peringkat
- Ned University of Engineering & Technology Department of Food Engineering Thermodynamics - Assignment SPRING SEMESTER 2020-2021Dokumen4 halamanNed University of Engineering & Technology Department of Food Engineering Thermodynamics - Assignment SPRING SEMESTER 2020-2021Sahar Batool QaziBelum ada peringkat
- In A Gas TurbineDokumen7 halamanIn A Gas TurbineANBU RAJ ABelum ada peringkat
- Assignment ProblemsDokumen2 halamanAssignment ProblemsRam SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- ME 211 Chapter - 4 - Examples SolutionsDokumen21 halamanME 211 Chapter - 4 - Examples SolutionsCarlosCD17Belum ada peringkat
- TD TutorialDokumen2 halamanTD TutorialloopycrowBelum ada peringkat
- M 3.2 M, in KG/HDokumen3 halamanM 3.2 M, in KG/HGabriel FerreiraBelum ada peringkat
- ThermoDokumen4 halamanThermowong zhi chengBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment EntropyDokumen2 halamanAssignment Entropyme22b009Belum ada peringkat
- Homework #7Dokumen3 halamanHomework #7Sebastián SantarrosaBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment2 Btech Sem3 TD Mu207Dokumen3 halamanAssignment2 Btech Sem3 TD Mu207nageshBelum ada peringkat
- Ch04b 1st Law Os-ExamplesDokumen23 halamanCh04b 1st Law Os-ExamplesBereketBelum ada peringkat
- Termodinamik 1 - Uygulama 2Dokumen38 halamanTermodinamik 1 - Uygulama 2david tennantBelum ada peringkat
- 3 PPDokumen1 halaman3 PPMuhammad UsamaBelum ada peringkat
- Availability Analysis: Tutorial QuestionsDokumen2 halamanAvailability Analysis: Tutorial QuestionsJackson TeohBelum ada peringkat
- Thermodynamics Review ProblemsDokumen3 halamanThermodynamics Review ProblemssayanBelum ada peringkat
- Ex - C2 - First Law of Thermo Open SystemsDokumen3 halamanEx - C2 - First Law of Thermo Open SystemsmehdihorwBelum ada peringkat
- QuestionsDokumen3 halamanQuestionsmonalBelum ada peringkat
- ME215 CH6 Example Solutions1Dokumen5 halamanME215 CH6 Example Solutions1Jordan SolisBelum ada peringkat
- Chapt 4 Problem SetDokumen2 halamanChapt 4 Problem SetLORD BOY SILONGBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial Sheet 6Dokumen2 halamanTutorial Sheet 6Syed YousufuddinBelum ada peringkat
- Sheet #1-ADokumen2 halamanSheet #1-Aفضائح لا تصدقBelum ada peringkat
- Thermo Finals - Questionnaire Quizzes and Sample Probs With AnswersDokumen21 halamanThermo Finals - Questionnaire Quizzes and Sample Probs With Answersmarc rodriguezBelum ada peringkat
- Ch04b 1st Law OS-EXAMPLESDokumen9 halamanCh04b 1st Law OS-EXAMPLESTSEGAAB NIGUSSEBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Thermodynamics ProblemsDokumen3 halamanEngineering Thermodynamics Problemsdhruv0010% (1)
- Basic Engineering Practice Problem 1Dokumen2 halamanBasic Engineering Practice Problem 1neva000Belum ada peringkat
- AssignDokumen2 halamanAssignHabtamu Tkubet EbuyBelum ada peringkat
- Problemas Sugeridos EntropíaDokumen1 halamanProblemas Sugeridos EntropíaMercedes VidalBelum ada peringkat
- EML3100 Exam2ReviewDokumen3 halamanEML3100 Exam2ReviewMax MichaudBelum ada peringkat
- THERMO1 - 4 Control Volume PDFDokumen11 halamanTHERMO1 - 4 Control Volume PDFEdmark AldeaBelum ada peringkat
- Thermodynamics QuestionsDokumen4 halamanThermodynamics Questionsprateek vyasBelum ada peringkat
- Sheet 1 (Thermo) - ProblemsDokumen9 halamanSheet 1 (Thermo) - ProblemsKarim MetwallyBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 0 Revision ThermoIDokumen1 halamanAssignment 0 Revision ThermoIMaria SarwatBelum ada peringkat
- Taller 2 2023-1Dokumen8 halamanTaller 2 2023-1anderson ortizBelum ada peringkat
- Iitbombay: Me209 Thermodynamics: 2014 Jul-Dec Exercises Set FDokumen5 halamanIitbombay: Me209 Thermodynamics: 2014 Jul-Dec Exercises Set FSunil SainiBelum ada peringkat
- Taller Termo FinalDokumen5 halamanTaller Termo FinalYordany Alexander Ruano OrtegaBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial ThermodynamicsDokumen2 halamanTutorial Thermodynamics23f3001728Belum ada peringkat
- Question Based On SFEE of ME2010DDokumen1 halamanQuestion Based On SFEE of ME2010DMohamed ZaheenBelum ada peringkat
- Problem Set 1 For All The Problems State The Assumptions You Consider ClearlyDokumen2 halamanProblem Set 1 For All The Problems State The Assumptions You Consider ClearlychandrahasBelum ada peringkat
- Thermo I Set of Questions 2022Dokumen6 halamanThermo I Set of Questions 2022Paa Kwesi ArhinfulBelum ada peringkat
- 11me201 Thermodynamics QuestionsDokumen12 halaman11me201 Thermodynamics QuestionsramsastryBelum ada peringkat
- SAQ 6-ThermodynamicsDokumen1 halamanSAQ 6-Thermodynamicsjhigs amfufuBelum ada peringkat
- ECON 101 - Systematisation (Quizzes, Midterm Samples (2015) )Dokumen5 halamanECON 101 - Systematisation (Quizzes, Midterm Samples (2015) )Joel CurryBelum ada peringkat
- Programming For EngineersDokumen2 halamanProgramming For EngineersJoel CurryBelum ada peringkat
- ProogrammingDokumen1 halamanProogrammingJoel CurryBelum ada peringkat
- Asteroid ImpactDokumen1 halamanAsteroid ImpactJoel CurryBelum ada peringkat
- Asteroid ImpactDokumen1 halamanAsteroid ImpactJoel CurryBelum ada peringkat
- Eschatology Is A Part of Theology Concerned With What Are BelievedDokumen2 halamanEschatology Is A Part of Theology Concerned With What Are BelievedJoel CurryBelum ada peringkat
- Asteroid ImpactDokumen1 halamanAsteroid ImpactJoel CurryBelum ada peringkat
- Asteroid ImpactDokumen1 halamanAsteroid ImpactJoel CurryBelum ada peringkat
- KoioDokumen1 halamanKoioJoel CurryBelum ada peringkat
- Curriculum Vitae: Personal InformationDokumen1 halamanCurriculum Vitae: Personal InformationJoel CurryBelum ada peringkat
- Agriculture Water Usage Poster ProjectDokumen1 halamanAgriculture Water Usage Poster Projectapi-339004071Belum ada peringkat
- Department of Agrarian Reform Adjudication Board (Darab) : PetitionDokumen3 halamanDepartment of Agrarian Reform Adjudication Board (Darab) : PetitionDe Dios JVBelum ada peringkat
- Royal Classic e BrochureDokumen14 halamanRoyal Classic e Brochureidreesali8654Belum ada peringkat
- TIAPortalOpennessenUS en-USDokumen656 halamanTIAPortalOpennessenUS en-USskyttt135Belum ada peringkat
- 14.quality of Life in Patients With Recurrent AphthousDokumen7 halaman14.quality of Life in Patients With Recurrent AphthousCoste Iulia RoxanaBelum ada peringkat
- 2023 - Kadam - Review On Nanoparticles - SocioeconomicalDokumen9 halaman2023 - Kadam - Review On Nanoparticles - Socioeconomicaldba1992Belum ada peringkat
- Abstract 2 TonesDokumen8 halamanAbstract 2 TonesFilip FilipovicBelum ada peringkat
- Test Your Skills For Computer Basics: November 2013Dokumen24 halamanTest Your Skills For Computer Basics: November 2013Charie C. OrbocBelum ada peringkat
- Corporation Law Syllabus With Assignment of CasesDokumen4 halamanCorporation Law Syllabus With Assignment of CasesMarilou AgustinBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study: PointDokumen1 halamanCase Study: PointprasadzinjurdeBelum ada peringkat
- Murugan Temple of North America: Ahkpuf F Gankd - FZGJP JizDokumen8 halamanMurugan Temple of North America: Ahkpuf F Gankd - FZGJP JizOurMuruganTempleBelum ada peringkat
- JKBMS Tutorial SetupDokumen7 halamanJKBMS Tutorial SetupFabricio Varovsky Muñiz ArteagaBelum ada peringkat
- F110 Payment Run - CheckDokumen29 halamanF110 Payment Run - Checktawfikmohamed213Belum ada peringkat
- Teaching Strategies, Styles and Qualities of ADokumen6 halamanTeaching Strategies, Styles and Qualities of AjixBelum ada peringkat
- From 1-73Dokumen95 halamanFrom 1-73Shrijan ChapagainBelum ada peringkat
- Penn State: The Dickinson School of LawDokumen88 halamanPenn State: The Dickinson School of LawHafiz UmmarBelum ada peringkat
- Lapid V CADokumen11 halamanLapid V CAChami YashaBelum ada peringkat
- S No Name of The Company Regional OfficeDokumen39 halamanS No Name of The Company Regional OfficeNo nameBelum ada peringkat
- Workflows in RUP PDFDokumen9 halamanWorkflows in RUP PDFDurval NetoBelum ada peringkat
- 04 HSE Inspection ChecklistDokumen2 halaman04 HSE Inspection ChecklistAjay Hazarika100% (2)
- Plewa2016 - Reputation in Higher Education: A Fuzzy Set Analysis of Resource ConfigurationsDokumen9 halamanPlewa2016 - Reputation in Higher Education: A Fuzzy Set Analysis of Resource ConfigurationsAlice ChenBelum ada peringkat
- Warman Slurry Correction Factors HR and ER Pump Power: MPC H S S L Q PDokumen2 halamanWarman Slurry Correction Factors HR and ER Pump Power: MPC H S S L Q Pyoel cueva arquinigoBelum ada peringkat
- Application Form ICDFDokumen2 halamanApplication Form ICDFmelanie100% (1)
- Utah State Hospital Policies and Procedures RadiologyDokumen9 halamanUtah State Hospital Policies and Procedures RadiologysultanarahmanBelum ada peringkat
- 201805graphene PDFDokumen204 halaman201805graphene PDFMohammad RezkyBelum ada peringkat
- RRLDokumen4 halamanRRLWen Jin ChoiBelum ada peringkat
- Synchronization Checklist PDFDokumen8 halamanSynchronization Checklist PDFAdhyartha KerafBelum ada peringkat
- k90mcc6 PDFDokumen381 halamank90mcc6 PDFTammy JohnsonBelum ada peringkat
- Profile 5930 Series Dispersoil. Viscosity Reducer RSKDokumen1 halamanProfile 5930 Series Dispersoil. Viscosity Reducer RSKIwan SetiawanBelum ada peringkat
- Scope: Manufacture of High Precision and CloseDokumen1 halamanScope: Manufacture of High Precision and CloseAnuranjanBelum ada peringkat
- Fire on the Horizon: The Untold Story of the Gulf Oil DisasterDari EverandFire on the Horizon: The Untold Story of the Gulf Oil DisasterBelum ada peringkat
- Power of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesDari EverandPower of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (21)
- The Permaculture City: Regenerative Design for Urban, Suburban, and Town ResilienceDari EverandThe Permaculture City: Regenerative Design for Urban, Suburban, and Town ResilienceBelum ada peringkat
- Guidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisDari EverandGuidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Solar Power Demystified: The Beginners Guide To Solar Power, Energy Independence And Lower BillsDari EverandSolar Power Demystified: The Beginners Guide To Solar Power, Energy Independence And Lower BillsPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (2)
- Shorting the Grid: The Hidden Fragility of Our Electric GridDari EverandShorting the Grid: The Hidden Fragility of Our Electric GridPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (2)
- A Pathway to Decarbonise the Shipping Sector by 2050Dari EverandA Pathway to Decarbonise the Shipping Sector by 2050Belum ada peringkat
- Nuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressDari EverandNuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionDari EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- The Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialDari EverandThe Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialBelum ada peringkat
- Offshore Wind Energy Generation: Control, Protection, and Integration to Electrical SystemsDari EverandOffshore Wind Energy Generation: Control, Protection, and Integration to Electrical SystemsBelum ada peringkat
- A Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersDari EverandA Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- Renewable Energy: A Very Short IntroductionDari EverandRenewable Energy: A Very Short IntroductionPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (12)
- Practical Power Distribution for IndustryDari EverandPractical Power Distribution for IndustryPenilaian: 2.5 dari 5 bintang2.5/5 (2)
- Heat Transfer Engineering: Fundamentals and TechniquesDari EverandHeat Transfer Engineering: Fundamentals and TechniquesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- Workbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesDari EverandWorkbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (3)
- Guidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsDari EverandGuidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsBelum ada peringkat
- Handbook on Battery Energy Storage SystemDari EverandHandbook on Battery Energy Storage SystemPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (2)
- Live Off Grid: Escape The City, Learn How To Travel Intelligently Using Solar PowerDari EverandLive Off Grid: Escape The City, Learn How To Travel Intelligently Using Solar PowerBelum ada peringkat
- Practical Reservoir Engineering and CharacterizationDari EverandPractical Reservoir Engineering and CharacterizationPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)
- Photovoltaic Solar Energy: From Fundamentals to ApplicationsDari EverandPhotovoltaic Solar Energy: From Fundamentals to ApplicationsBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Hydrogen Production and Utilization in Fuel Cell SystemsDari EverandFundamentals of Hydrogen Production and Utilization in Fuel Cell SystemsBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Load-Curve Coverage: Proceedings of the Symposium on Load-Curve Coverage in Future Electric Power Generating Systems, Organized by the Committee on Electric Power, United Nations Economic Commission for Europe, Rome, Italy, 24 – 28 October 1977Dari EverandElectrical Load-Curve Coverage: Proceedings of the Symposium on Load-Curve Coverage in Future Electric Power Generating Systems, Organized by the Committee on Electric Power, United Nations Economic Commission for Europe, Rome, Italy, 24 – 28 October 1977Belum ada peringkat
- Rules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersDari EverandRules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (12)
- Idaho Falls: The Untold Story of America's First Nuclear AccidentDari EverandIdaho Falls: The Untold Story of America's First Nuclear AccidentPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (21)
- Renewable Energy Sources - Wind, Solar and Hydro Energy Revised Edition : Environment Books for Kids | Children's Environment BooksDari EverandRenewable Energy Sources - Wind, Solar and Hydro Energy Revised Edition : Environment Books for Kids | Children's Environment BooksBelum ada peringkat