Worksheet Central Dogma
Diunggah oleh
Rein Jhonnaley DiosoDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Worksheet Central Dogma
Diunggah oleh
Rein Jhonnaley DiosoHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Worksheet: Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
Name: Marcial, Diane Francine Score: ____________ Section: S11-15
Isip, Phloxyn Gyana
Dioso, Rein Jhonnaley
I. Give the meaning/function of the following terms:
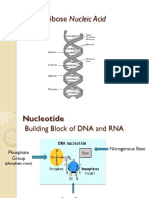
1. Nucleotide – is an organic molecule that is the building block of DNA and RNA. They also have functions
related to cell signaling, metabolism, and enzyme reactions .It consists of a base (one of four chemicals:
adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine) plus a molecule of sugar and one of phosphoric acid.
2. DNA Replication – is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original
DNA molecule occuring in all living organisms acting as the basis for biological inheritance.
3. DNA Transcription – is the process by which the information in DNA is copied (transcribed) into messenger
RNA (mRNA) which carries the information needed for protein synthesis (for protein production).
4. Translation – is the process that takes the information passed from DNA as messenger RNA and turns it into
a series of amino acids bound together with peptide bonds. It is essentially a translation from one code
(nucleotide sequence) to another code (amino acid sequence).
5. Codon – is a specific sequence of three consecutive nucleotides that is part of the genetic code and that
specifies a particular amino acid in a protein or starts or stops protein synthesis.
6. Anti-codons – are sequences of nucleotides that are complementary to codons. They are found in tRNAs,
and allow the tRNAs to bring the correct amino acid in line with an mRNA during protein production.
7. Leading strand of DNA – This is the parent strand of DNA which runs in the 3' to 5' direction toward the
fork, and it's able to be replicated continuously by DNA polymerase.
8. Lagging strand of DNA – is one of two strands of DNA found at the replication fork, or junction, in the
double helix; the other strand is called the leading strand. A lagging strand requires a slight delay before
undergoing replication, and it must undergo replication discontinuously in small fragments.
II. Draw a nucleotide and label its three basic parts:
III. Fill in the tables below:
A. Differentiate DNA from RNA based on the following criteria:
Criteria DNA RNA
Responsible for storing Directly codes for amino acids and
Function and transferring acts as a messenger between DNA
genetic information and ribosomes to make proteins.
Mainly in the Mainly found in cytoplasm
Location in a cell
nucleus of the cell of the cell
Type of sugar Sugar Deoxyribose Molecule Sugar Ribose Molecule
molecule
Adenine(A), Thymine(T), Adenine(A), Uracil(U),
Nitrogen bases present
Cytosine(C), and Guanine(G) Cytosine(C), and Guanine(G).
Number of strands Double-stranded Single Stranded
B. Differentiate the three types of mRNA in terms of function
Criterion mRNA tRNA rRNA
Function transfer the information act as temporary associates with a set of
from DNA to the cell carriers of amino acids proteins to form
machinery that makes to ribosomes and helps ribosomes, complex
proteins. decode a mRNA structures, which
sequence into a protein physically move along
an mRNA molecule,
catalyze the assembly of
amino acids into
protein chains
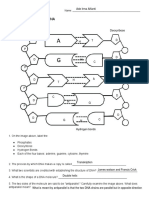
IV. Using the words in the boxes, identify the components of the Replicating DNA strands. Write your
answers on the space provided.
a. Parental DNA
b. DNA
polymerase
c. Leading Strand
d. Lagging Strand
e. DNA ligase
f. Replication fork
V. Give what is asked in each of the following:
A. Write the complementary strand of DNA to the following sequence.
5′ A-C-T-C-G-G-T-A-A-C-A-A-T-A-T-C-A-T-C-G-G 3′
3’ T-G-A-G-C-C-A-T-T-G-T-T-A-T-A-G-T-A-G-C-C 5’
B. Write the complementary mRNA segment of the given DNA sequence in 5’-3’ direction.
5′ A-C-U-C-G-G-U-A-A-C-A-A-U-A-U-C-A-U-C-G-G 3′
C. Using the genetic code below, identify the sequence of amino acids coded by the identified mRNA
segment.
Threonine, Arginine, STOP
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Protein Synthesis: It Is Expected That Students WillDokumen32 halamanProtein Synthesis: It Is Expected That Students WillIMY PAMEROYANBelum ada peringkat
- How Genes Work GENE - Biological Unit of HeredityDokumen5 halamanHow Genes Work GENE - Biological Unit of HeredityAdonis Besa100% (1)
- Central Dogma Review KEYDokumen8 halamanCentral Dogma Review KEYeula faith miracle andam0% (1)
- Mitosi ActivityDokumen3 halamanMitosi ActivityTena, CharleneBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Calculations 2012Dokumen58 halamanPractice Calculations 2012Lia Romain67% (6)
- Phylogenetic Trees Click Learn WorksheetDokumen4 halamanPhylogenetic Trees Click Learn Worksheetfcm31450% (1)
- Transcription Translation ProtocolDokumen10 halamanTranscription Translation ProtocoladindaBelum ada peringkat
- 6 Genetics PDFDokumen97 halaman6 Genetics PDFasaBelum ada peringkat
- Genetics Patterns of Genetic Inheritance Genetic TerminologyDokumen12 halamanGenetics Patterns of Genetic Inheritance Genetic TerminologyJustin CatalanBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Membrane and Transport MechanismsDokumen1 halamanCell Membrane and Transport MechanismsAldemer Laron BoretaBelum ada peringkat
- How Protein Is Made Using Information From DNADokumen30 halamanHow Protein Is Made Using Information From DNADainiel G. PerezBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3: Movement of Substance Across The Plasma MembraneDokumen13 halamanChapter 3: Movement of Substance Across The Plasma MembraneEma FatimahBelum ada peringkat
- MEIOSIS WorksheetDokumen8 halamanMEIOSIS WorksheetEliseo PamandananBelum ada peringkat
- DNA Unit Review WorksheetDokumen2 halamanDNA Unit Review WorksheetAndreaLibonik75% (4)
- Protein Synthesis NotesDokumen6 halamanProtein Synthesis NotesRokunuz Jahan RudroBelum ada peringkat
- 4 Pedigree AnalysisDokumen48 halaman4 Pedigree AnalysisBiologistAhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Dna Replication WorksheetDokumen1 halamanDna Replication WorksheetJohn OsborneBelum ada peringkat
- Biomolecule Worksheet 1 - Fadhlan MusaryDokumen5 halamanBiomolecule Worksheet 1 - Fadhlan MusaryFadhlan MusdaryBelum ada peringkat
- DNA Molecule & Central DogmaDokumen43 halamanDNA Molecule & Central DogmaJoanna Ruth SeproBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Division Mitosis Meiosis Biology LectureDokumen39 halamanCell Division Mitosis Meiosis Biology LectureYonathan Christyanto100% (1)
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet PART A. Read The FollowingDokumen5 halamanProtein Synthesis Worksheet PART A. Read The Followingapi-39708077950% (2)
- GENETICSDokumen45 halamanGENETICSDarlene Joy De LunaBelum ada peringkat
- Cellular Respiration WorksheetDokumen4 halamanCellular Respiration WorksheetGene RoundtreeBelum ada peringkat
- DNA Pairing WSDokumen1 halamanDNA Pairing WSCheska100% (1)
- Biology Lesson 9.1 WorksheetDokumen3 halamanBiology Lesson 9.1 WorksheetAbhay MonBelum ada peringkat
- Cell DivisionDokumen5 halamanCell DivisionJohanna GultianoBelum ada peringkat
- BIO121 Chapter 9 From DNA To ProteinDokumen47 halamanBIO121 Chapter 9 From DNA To ProteinggttettanBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Organelle Review Worksheet Summer ValliniDokumen3 halamanCell Organelle Review Worksheet Summer ValliniSummer ValliniBelum ada peringkat
- Review The Structure of DNA AdeDokumen1 halamanReview The Structure of DNA AdeADE IRMABelum ada peringkat
- Lab #2Dokumen8 halamanLab #2Regina RazoBelum ada peringkat
- North Carolina Biology EOC Study GuideDokumen38 halamanNorth Carolina Biology EOC Study GuideRaquel Galdamez-GaldamezBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Differences Between Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDokumen16 halamanLecture Differences Between Prokaryotes and EukaryotesAyesha MasoodBelum ada peringkat
- Practical Chemistry Voumetric EstimationDokumen9 halamanPractical Chemistry Voumetric EstimationSanjay Shirodkar100% (2)
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet: 1. Filling The BlanksDokumen3 halamanProtein Synthesis Worksheet: 1. Filling The BlanksFelix SimsungBelum ada peringkat
- MeiosisDokumen24 halamanMeiosisMuhammad HamzaBelum ada peringkat
- Transcription and TranslationDokumen9 halamanTranscription and TranslationlinhBelum ada peringkat
- 18 Cell Cycle Regulation-SDokumen6 halaman18 Cell Cycle Regulation-SkriishnaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 8 Cell MembraneDokumen6 halamanChapter 8 Cell MembranerexartoozBelum ada peringkat
- Space WeatherDokumen36 halamanSpace WeatherMat MinBelum ada peringkat
- Evol RelationshipsDokumen15 halamanEvol RelationshipsCarla BanzuelaBelum ada peringkat
- Biology 12 - The Reproductive System!: Name: Block: DateDokumen4 halamanBiology 12 - The Reproductive System!: Name: Block: DateLerr Real Relle100% (1)
- ASTM A674 - Polyethylene Encasement For Ductile Iron Pipe For Water or Other Liquids PDFDokumen7 halamanASTM A674 - Polyethylene Encasement For Ductile Iron Pipe For Water or Other Liquids PDFApolos CastBelum ada peringkat
- Q3 WEEK 4 Protein SynthesisDokumen65 halamanQ3 WEEK 4 Protein SynthesisAdonis SanielBelum ada peringkat
- Clarus500 580UserGuideDokumen442 halamanClarus500 580UserGuideSelvaraj VenkatesanBelum ada peringkat
- Taxonomy - Classification and Hierarchy of OrganismsDokumen16 halamanTaxonomy - Classification and Hierarchy of OrganismsBobbiRedBelum ada peringkat
- 3b.boiler Treatment MethodsDokumen76 halaman3b.boiler Treatment Methodsalokbdas100% (1)
- 13 Cellular Respiration-KEYDokumen6 halaman13 Cellular Respiration-KEYgilBelum ada peringkat
- Activity Sheets For Changes in Chromosome NumberDokumen11 halamanActivity Sheets For Changes in Chromosome NumberGu Jun PyoBelum ada peringkat
- MicrotubulesDokumen39 halamanMicrotubulesAdnan QureshiBelum ada peringkat
- Photosynthesis Study GuideDokumen9 halamanPhotosynthesis Study GuideJunhee KimBelum ada peringkat
- DJ (Microtubules, Microfilaments and Intermediate Filaments) - DJGFDokumen43 halamanDJ (Microtubules, Microfilaments and Intermediate Filaments) - DJGFNick_989893Belum ada peringkat
- Sex-Linked TraitsDokumen36 halamanSex-Linked TraitsRohini GagrooBelum ada peringkat
- BIO 22 MODULE 1 - Chemical Basis of LifeDokumen14 halamanBIO 22 MODULE 1 - Chemical Basis of LifeBryan DGBelum ada peringkat
- MutationsDokumen3 halamanMutationsHanny Pearl S. Camerino100% (2)
- The Electron Transport ChainDokumen15 halamanThe Electron Transport ChainZuhayr Muhammad Chaumun100% (1)
- Sts Quiz Reviewer 1Dokumen11 halamanSts Quiz Reviewer 1理论Belum ada peringkat
- Central Dogma WebquestDokumen4 halamanCentral Dogma Webquestapi-446838554Belum ada peringkat
- Plant CellDokumen112 halamanPlant CellAlfonso PlantillaBelum ada peringkat
- MitosisDokumen15 halamanMitosisJorge MurieteBelum ada peringkat
- Mitosis WorksheetDokumen9 halamanMitosis WorksheetBts/ ArmyBelum ada peringkat
- Quiz Cell MembraneDokumen4 halamanQuiz Cell MembraneDeepan Chakkaravarthi100% (1)
- CH8 DNA Structure and Replication 2021Dokumen4 halamanCH8 DNA Structure and Replication 2021EmileMcBrokeBelum ada peringkat
- Chris Copy of Pretein Synthesis GizmoDokumen6 halamanChris Copy of Pretein Synthesis GizmoChris EffiongBelum ada peringkat
- Non-Mendelian Practice KeyDokumen4 halamanNon-Mendelian Practice KeyJopit O. RiveraBelum ada peringkat
- Science Q3 WK5.Dokumen14 halamanScience Q3 WK5.Hellow FriendzBelum ada peringkat
- Protein Synthesis Transcription and Translation Distance LearningDokumen10 halamanProtein Synthesis Transcription and Translation Distance LearningjaneyzhouBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Paper-01 CHEMISTRY (Theory) Class - XI: Material Downloaded From andDokumen4 halamanSample Paper-01 CHEMISTRY (Theory) Class - XI: Material Downloaded From andSarthakBelum ada peringkat
- DatabaseDokumen112 halamanDatabaseamirulamirBelum ada peringkat
- Copper (II) Sulfate - Reagent - Anhydrous 98 - Acros OrganicsDokumen5 halamanCopper (II) Sulfate - Reagent - Anhydrous 98 - Acros OrganicsGaryoBelum ada peringkat
- CreepDokumen25 halamanCreepORANG BiasaBelum ada peringkat
- Pasteurisation Process Objectives: CFB31103 Food Process Engineering Laboratory 4: Thermal ProcessingDokumen3 halamanPasteurisation Process Objectives: CFB31103 Food Process Engineering Laboratory 4: Thermal Processingnurul nabilah bt khairul anuarBelum ada peringkat
- Specification D6 Virgin: Method Test Result UnitDokumen1 halamanSpecification D6 Virgin: Method Test Result UnitClaudio SantellanesBelum ada peringkat
- Official Draft - 2022-23 Bellevistat-CompressedDokumen72 halamanOfficial Draft - 2022-23 Bellevistat-Compressedtemp accBelum ada peringkat
- Astm B 366Dokumen13 halamanAstm B 366AVINASH CHAVANBelum ada peringkat
- hssc0500t Chaptest ADokumen6 halamanhssc0500t Chaptest AAseel AburajabBelum ada peringkat
- 5982-5753 EUEnglishDokumen6 halaman5982-5753 EUEnglishcungmapBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical EquilibriumDokumen162 halamanChemical EquilibriumAshok PradhanBelum ada peringkat
- Consolidation Theories of Soils: By: Alemayehu Teferra (Prof., Dr.-Ing.)Dokumen33 halamanConsolidation Theories of Soils: By: Alemayehu Teferra (Prof., Dr.-Ing.)ASAMENEWBelum ada peringkat
- Fire Fighting Foam Principles and Ethanol-Blended FuelDokumen38 halamanFire Fighting Foam Principles and Ethanol-Blended FuelFrancois HamiauxBelum ada peringkat
- Comparing Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AISI D2 Steel PDFDokumen7 halamanComparing Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AISI D2 Steel PDFToramaru UtsunomiyaBelum ada peringkat
- STI - SP001-00 - Standard For Inspection of In-Service Shop Fabricated Aboveground Tanks For Storage of Combustible and Flammable LiquidsDokumen20 halamanSTI - SP001-00 - Standard For Inspection of In-Service Shop Fabricated Aboveground Tanks For Storage of Combustible and Flammable LiquidsJoe BetkerBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 - Atoms, Molecules and Stoichiometry PDFDokumen10 halamanChapter 1 - Atoms, Molecules and Stoichiometry PDFRamshaBelum ada peringkat
- Raghavendra Bhat. GPUC High School Section, MegaravalliDokumen8 halamanRaghavendra Bhat. GPUC High School Section, Megaravallisyedyaseen39375Belum ada peringkat
- Digital PH Sensor Orbisint CPS11D: Memosens Glass Electrode For Standard ApplicationsDokumen3 halamanDigital PH Sensor Orbisint CPS11D: Memosens Glass Electrode For Standard ApplicationsAchmad KBelum ada peringkat
- Focuse Ion BeamDokumen34 halamanFocuse Ion BeamAhsan SaleemBelum ada peringkat
- COMEDK Important Topics and Revised SyllabusDokumen49 halamanCOMEDK Important Topics and Revised SyllabusVishal VermaBelum ada peringkat
- 0237e CHBDokumen1 halaman0237e CHBSaif Ahmed SiddiquiBelum ada peringkat
- Polyaluminium Chloride: Product SpecificationsDokumen2 halamanPolyaluminium Chloride: Product SpecificationsMonica Choi SeungjunhyungBelum ada peringkat
- Formulation and Evaluation of Vilazodone Sublingual Tablets by Using Lyophilization TechniqueDokumen9 halamanFormulation and Evaluation of Vilazodone Sublingual Tablets by Using Lyophilization Techniquealamia pharmBelum ada peringkat
- DSR Unit 1Dokumen69 halamanDSR Unit 1hujefaBelum ada peringkat