US3393046 Chlorine Removal
Diunggah oleh
kaushik0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
14 tayangan2 halamanchlorine remove from zinc sulphate
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Inichlorine remove from zinc sulphate
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
14 tayangan2 halamanUS3393046 Chlorine Removal
Diunggah oleh
kaushikchlorine remove from zinc sulphate
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
3,393,046
United States Patent Office Patented July 16, 1968
1. 2
extraction stages, the time of phase mixing at each stage
3,393,046 being one minute.
METHOD FOR PURIFICATION OF ZINC It is advantageous to carry out the process of purifi
SULPHATESOLUTIONS cation in the presence of a saturated monohydric alcohol
Georgy Petrovich Giganov, Ulitsa Metallurgov 33, kv.19; 5 added to the solution of the amine in kerosene, the volume
Gennady Leonidovich Pashkov, Ulitsa Proletarskaya ratio of the amine, kerosene and alcohol being 1-3:8-6:1,
124, kv. 73; Mikhail Ivanovich Batjukov, Prospekt respectively.
Lenina 18, kv. 52; Akhat Salemkhatovich Kulenov, Extraction yields an organic phase consisting of the
Prospekt Lenina 36, kv. 50; Taimurz Khadzhiomaro
vich Tserekov, Prospekt Lenina 16/a, kv. 31; Georgy extract of amine hydrochloride in kerosene or in kerosene
Arkadievich Pelymsky, Ulitsa Kosmicheskaya 3, kv. 21; 0 and alcohol, and an aqueous phase consisting of the zinc
Alexandr Efimovich Porkhunov, Ulitsa Promyshlennaya sulfate solution freed of chlorine. The organic phase is
5, kv. 1; and Jury Ivanovich Pavlov, Ulitsa Kosmiche Separated from the aqueous phase by a known technique
skaya 3, kv. 23, all of Ustkamenogorsk, U.S.S.R. and thereafter washed with water to extract zinc admix
No Drawing. Filed Feb. 21, 1967, Ser. No. 617,493 tures present. Washing is effected countercurrently, the
Claims priority, application Union of Soviet Socialist number of washing stages being from 2 to 4, provided the
Republics, Feb. 21, 1966, 1,056,728 5
2 Claims. (CI. 23-125) organic and the aqueous phase are taken in a ratio of
5-10:1 by volume and the washing time at each stage
equals one minute.
ABSTRACT OF THE DISCLOSURE Aqueous solutions, obtained as a result of washing the
Chlorine is removed from zinc sulfate solution by 20 organic phase, are combined with the starting zinc sulfate
treatment with a solution of an aliphatic amine contain solution to be purified of chlorine.
ing 7-10 carbon atoms in kerosene in proportions of Chlorine recovery from the organic phase is carried out
by 4-to-6-stage extraction with 10% aqueous ammonia,
1-3:9-7 by volume. the volume ratio of the organic and the aqueous phase
25 being 15-20:1, and re-extraction time at each stage being
This invention relates to methods for the purification of equal to one minute.
Upon chlorine removal the organic phase is recycled
Zinc sulfate solutions obtained in the course of zinc pro to the extraction step.
duction. The process of purification of zinc sulfate solutions is
It is known to purify zinc sulfate solutions from chlo 30 carried in Pachuca-type apparatus.
rine by treatment with a chlorine-combining reagent, e.g. Ammonium chloride solutions obtained in the process
copper cake, followed by separating the chloride obtained, of chlorine re-extraction are evaporated to recover am
the usual separation techniques being settling or filtration. monium chloride in the solid form.
The known methods have a disadvantage in that the For a better understanding of the present invention, the
extent to which chlorine is removed from zinc sulfate so 35 following example is presented by way of illustration.
lutions is low, so that the electrolytic production of zinc Example
from said solutions involves the consumption of exces Chlorine is removed from the zinc sulfate solution
sively high amounts of non-ferrous metals.
A further disadvantage of the known methods is that (pH =5), containing 143 g/l. Zn, 2.1 g/l. Cd, and 0.55
the purification process is time consuming and requires 40 g./l. Cl, by the countercurrent 4-stage extraction proced
the employment of a considerable body of process equip lure. The extracting solution consists of a mixture of
ment. amines (65% of trioctylamine and 35% of primary and
It is an object of the present invention to provide a secondary amines having from 7 to 12 carbon atoms) dis
method for the purification of zinc sulfate solutions that solved in kerosene and isooctyl alcohol, the volume ratio
will make it possible to obtain a higher degree of chlorine 45 of amines, kerosene and alcohol being 1:8:1, respectively.
removal from the solutions with the resultant reduction At the extraction step, the volume ratio of the organic
of non-ferrous metal consumption in the course of the and the aqueous phase equals 1:4.
electrolytic production of zinc from said solutions. The purified zinc sulfate solution contains 141 g/l. Zn,
It is another object of the present invention to shorten 2.1 g/l. Cd, and 0.03 g/l. Cl.
the purification process time, as well as to reduce the 50 The degree of chlorine extraction from the zinc sulfate
amount of the process equipment used. solution to the organic phase amounts to 94.6%.
These and other objects of the present invention are Although the present invention has been described with
accomplished by using a chlorine-combining reagent reference to a preferred embodiment thereof, it will be
consisting of an aliphatic amine, containing 7 to 10 carbon readily understood by those skilled in the art that various
atoms, dissolved in kerosene, the amine and kerosene be 55 changes and modifications can be resorted to without de
ing taken in a volume of 1-3:9-7. parting from the spirit and scope of the present inven
In order to prevent the extract, obtained in the course tion.
of purification, from separation into layers, it is expedient These changes and modifications are to be considered
to add to the solution of amine in kerosene a saturated as falling within the spirit and scope of the present inven
monohydric alcohol, the volume ratio of the amine, kero 60 tion as defined in the appended claims.
sene and alcohol being 1-3:8-6:1, respectively. We claim:
The method of the present invention is realized in the 1. A process for the removal of chlorine from zinc
following manner. sulfate solutions comprising extracting the chlorine by
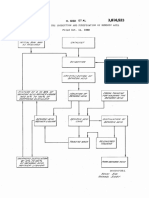
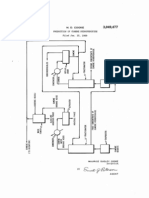
Chlorine-containing zinc sulfate solutions are subjected treating said solution with an aliphatic amine containing
to countercurrent extraction, wherein extracting solution 65 7 to 10 carbon atoms, said amine being dissolved in
consists of an aliphatic amine, having 7 to 10 carbon kerosene in the ratio amine to kerosene: 1-3 to 9-7 by
atoms, such as trioctylamine, trinonylamine, or tridecyl volume, and separating the chlorine from the amine.
amine, dissolved in kerosene, the amine-to-kerosene ratio 2. The process of claim 1 wherein a saturated mono
being 1-3:9-7 by volume. hydric alcohol is added to the solution of amine in kero
The volume ratio of the organic and aqueous phase 70 sene, whereby the ratio of amine:Kerosene:alcohol is
equals 1:1-4. 1-3:8-6:1 by volume respectively.
The process of extractive purification involves 4 to 6 (References on following page)
3,393,046
3. 4.
References Cited OTHER REFERENCES
UNITED STATES PATENTS Bray J. L. and Morral, F. R.: “Journal of The Electro
1901,925 3/1933 O'Brien et al. -------- 23-125 chemical Society, volume 78; pp. 309-316; 1940.
2,245,086 6/1941 Bray et al. ---------- 204-55
2,393,741 1/1946 Bray et al. ---------- 204-55 5 OSCAR R. VERTIZ, Primary Examiner.
3,317,412 5/1967 Dahlmann ----------- 204-55 G. PETERS, Assistant Examiner.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Hydrometallurgy: Cao Zhan-Fang, Zhong Hong, Qiu Zhao-HuiDokumen5 halamanHydrometallurgy: Cao Zhan-Fang, Zhong Hong, Qiu Zhao-HuiPablo C. VicencioBelum ada peringkat
- Anaerobic Biochemical Treatment of Wastewater Containing Highly Concentrated Organic CyanogenDokumen7 halamanAnaerobic Biochemical Treatment of Wastewater Containing Highly Concentrated Organic CyanogenStone BrickWallBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment # 8 Six-Step Synthesis Aniline To 1-Bromo-3cholor-5iodobenzeneDokumen10 halamanExperiment # 8 Six-Step Synthesis Aniline To 1-Bromo-3cholor-5iodobenzeneColin CheBelum ada peringkat
- UV Spectrophotometric Determination of Theobromine and Caffeine in Cocoa BeansDokumen4 halamanUV Spectrophotometric Determination of Theobromine and Caffeine in Cocoa BeansIwanOne'ajjBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment # 2 (ChE 501 SP)Dokumen1 halamanAssignment # 2 (ChE 501 SP)Shawala AzharBelum ada peringkat
- US3816523Dokumen5 halamanUS3816523Argo Rizky Kusuma 2007110716Belum ada peringkat
- Limnology Oceanography - September 1969 - Sol Rzano - Determination of Ammonia in Natural Waters by TheDokumen3 halamanLimnology Oceanography - September 1969 - Sol Rzano - Determination of Ammonia in Natural Waters by TheOmar Miguel Peña SánchezBelum ada peringkat
- Urea ProjectDokumen17 halamanUrea ProjectAbdo Shaaban100% (2)
- Acetone ProductionDokumen2 halamanAcetone ProductionpehweihaoBelum ada peringkat
- Anone PlantDokumen2 halamanAnone PlantAbijith100% (1)
- Checal ReviewerDokumen8 halamanChecal ReviewerChristian Dela CruzBelum ada peringkat
- In Situ Hypochlorous Acid Generation For The Treatment of Distillery SpentwashDokumen4 halamanIn Situ Hypochlorous Acid Generation For The Treatment of Distillery SpentwashGregorio ValeroBelum ada peringkat
- Patent US3801634Dokumen5 halamanPatent US3801634Santiago BorgesBelum ada peringkat
- Bergman N SanikDokumen3 halamanBergman N SanikShanmugaprakasham ShanBelum ada peringkat
- Uslu 2007Dokumen6 halamanUslu 2007raquelBelum ada peringkat
- Separation ProcessesDokumen3 halamanSeparation ProcessesJoshua SolomonBelum ada peringkat
- Us Patent Process For Production of Urea, 1970Dokumen4 halamanUs Patent Process For Production of Urea, 197025A Syifa Salsabila AlfianiBelum ada peringkat
- JChemEdu (56) 270Dokumen3 halamanJChemEdu (56) 270Filipe César100% (1)
- Phenol PlantDokumen33 halamanPhenol PlantrakeshBelum ada peringkat
- European Patent Application C01C 1/248, C01C 1/24,: Method For The Preparation of Granular Ammonium SulphateDokumen20 halamanEuropean Patent Application C01C 1/248, C01C 1/24,: Method For The Preparation of Granular Ammonium SulphateiruqiBelum ada peringkat
- NitrogenDokumen51 halamanNitrogenGeoo Geoo GeorgeBelum ada peringkat
- Us 4378342Dokumen9 halamanUs 4378342هیمن مBelum ada peringkat
- Proposal ChlorobenzeneDokumen12 halamanProposal ChlorobenzeneDavid Akomolafe100% (1)
- Acid Soluble Nucleotides of Ripening Rice GrainsDokumen6 halamanAcid Soluble Nucleotides of Ripening Rice GrainsSHASHANK SINGHBelum ada peringkat
- Mixc?gg 33:3: Mexzmeqze EgesDokumen3 halamanMixc?gg 33:3: Mexzmeqze EgesSiswand BIn Mohd AliBelum ada peringkat
- Caprolactam Process DescriptionDokumen8 halamanCaprolactam Process DescriptionJohannah Jane Abuel100% (2)
- Note: 1. Answer All Questions 2.any Missing Data May Be Suitably Assumed 3. Solve Problems AnalyticallyDokumen2 halamanNote: 1. Answer All Questions 2.any Missing Data May Be Suitably Assumed 3. Solve Problems AnalyticallyNishanth ChandranBelum ada peringkat
- AlkylationDokumen9 halamanAlkylationabhishek sharma100% (1)
- Copolymerization of Styrene and Acrylonitrile in Aqueous DispersionDokumen15 halamanCopolymerization of Styrene and Acrylonitrile in Aqueous DispersionPhilip ShihBelum ada peringkat
- SLE Experiment (REPORT)Dokumen8 halamanSLE Experiment (REPORT)Kuknesvary PuniamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- Santa Monica College Chem 22 Lab ManualDokumen59 halamanSanta Monica College Chem 22 Lab ManualMide Ogundipe100% (1)
- Solvent Extraction Process and ApplicationsDokumen4 halamanSolvent Extraction Process and ApplicationsSyedMeherAliBelum ada peringkat
- Ekstraksi Asam Sitrat Dan Asam Oksalat: Pengaruh Konsentrasi Solut Terhadap Koefisien DistribusiDokumen7 halamanEkstraksi Asam Sitrat Dan Asam Oksalat: Pengaruh Konsentrasi Solut Terhadap Koefisien DistribusiIto PurnomoBelum ada peringkat
- Although This Process Is No Longer in Common UseDokumen15 halamanAlthough This Process Is No Longer in Common Usedia_aldy100% (1)
- Tratamiento AguaDokumen5 halamanTratamiento AguaCarlos Manuel RamosBelum ada peringkat
- LAB QO 4 - Nitration of ChlorobenzeneDokumen9 halamanLAB QO 4 - Nitration of Chlorobenzenemario100% (1)
- Bioresources: Estimation of Hardwood Lignin Concentrations by Uv Spectroscopy and Chlorine DemethylationDokumen13 halamanBioresources: Estimation of Hardwood Lignin Concentrations by Uv Spectroscopy and Chlorine DemethylationThiago SantosBelum ada peringkat
- Activated Carbon From Corn Cobs and Coconut Shell For Heavy Metal Ions AdsorptionDokumen8 halamanActivated Carbon From Corn Cobs and Coconut Shell For Heavy Metal Ions AdsorptionS Bharadwaj Reddy100% (1)
- SepaDokumen2 halamanSepaRobert DelfinBelum ada peringkat
- Synthesis of Camphor by The Oxidation of BorneolDokumen6 halamanSynthesis of Camphor by The Oxidation of BorneolCyrene MBolañosBelum ada peringkat
- Precipitation Titrimetry-221Dokumen11 halamanPrecipitation Titrimetry-221HudzaifiBelum ada peringkat
- 1324-Article Text-2490-1-10-20210315Dokumen6 halaman1324-Article Text-2490-1-10-20210315vivek_negiBelum ada peringkat
- Probset3. MaterialbalancesDokumen8 halamanProbset3. MaterialbalancesAbi MukundBelum ada peringkat
- Recovery of Copper From Alkaline Glycine Leach Solution Using SolventDokumen8 halamanRecovery of Copper From Alkaline Glycine Leach Solution Using SolventmtanaydinBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Manual Yr 3 InorganicDokumen33 halamanLab Manual Yr 3 InorganicOmSilence2651Belum ada peringkat
- United States Patent (15) 3,697,598: Leif Urban Folke Thorsen, Örn Primary Examiner-Retiri RaymondDokumen7 halamanUnited States Patent (15) 3,697,598: Leif Urban Folke Thorsen, Örn Primary Examiner-Retiri RaymondSalsabila CacaBelum ada peringkat
- Spectrophotometric Determination of Acrylonitrile: A Fumigant in AirDokumen7 halamanSpectrophotometric Determination of Acrylonitrile: A Fumigant in Airdavid steven olaya montoyaBelum ada peringkat
- Exercise - ChE CalculationsDokumen8 halamanExercise - ChE Calculationsma.elizabeth.sulitBelum ada peringkat
- Styrene Methods 2520of ProductionDokumen9 halamanStyrene Methods 2520of ProductionMohd Zulazreen50% (2)
- New Treatment of The Black Liquor Produced From Pulping of Rice StrawDokumen8 halamanNew Treatment of The Black Liquor Produced From Pulping of Rice StrawDrWael ElheleceBelum ada peringkat
- EOR With Penn State Surfactants: T.G. ArfDokumen11 halamanEOR With Penn State Surfactants: T.G. ArfSajad FalahBelum ada peringkat
- CN116803492A Description 20240409 1450Dokumen9 halamanCN116803492A Description 20240409 1450Simona GhimisBelum ada peringkat
- The Mcardle School, University of Wisconsin, Madison, Wisconsin)Dokumen11 halamanThe Mcardle School, University of Wisconsin, Madison, Wisconsin)Denise RoblesBelum ada peringkat
- Determinacion de Cromo M1Dokumen6 halamanDeterminacion de Cromo M1aramis21trisha23Belum ada peringkat
- The Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresDari EverandThe Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Application of IC-MS and IC-ICP-MS in Environmental ResearchDari EverandApplication of IC-MS and IC-ICP-MS in Environmental ResearchRajmund MichalskiBelum ada peringkat
- Adsorption Processes for Water TreatmentDari EverandAdsorption Processes for Water TreatmentPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Topics in Heterocyclic Chemistry Vol 2 Heterocyclic Antitumor Antibiotics - Grupta - 2006Dokumen252 halamanTopics in Heterocyclic Chemistry Vol 2 Heterocyclic Antitumor Antibiotics - Grupta - 2006Luis AlpizarBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry 213Dokumen7 halamanChemistry 213KoladeBelum ada peringkat
- Form 4: Important Units For 2020 SPMDokumen2 halamanForm 4: Important Units For 2020 SPMmuhammad4fadzelyBelum ada peringkat
- InorganicDokumen105 halamanInorganicKishan Gupta100% (6)
- Rare Earth Elements (Metals) - ListDokumen3 halamanRare Earth Elements (Metals) - Listasset68Belum ada peringkat
- 02-Chemistry EDokumen25 halaman02-Chemistry Ewissam riyasBelum ada peringkat
- Learning Task 1. Identify The Reactant Needed in The Following Chemical Equation, Choose Your AnswerDokumen15 halamanLearning Task 1. Identify The Reactant Needed in The Following Chemical Equation, Choose Your AnswerPearl Irene Joy NiLoBelum ada peringkat
- 6CH05 01 Que 20170621 PDFDokumen28 halaman6CH05 01 Que 20170621 PDFAhmad MohdBelum ada peringkat
- G12 - Classification of MatterDokumen32 halamanG12 - Classification of MatterChristian CatacutanBelum ada peringkat
- CHEM 2015 (Spectroscopy) CHEM 2015 (Spectroscopy)Dokumen10 halamanCHEM 2015 (Spectroscopy) CHEM 2015 (Spectroscopy)Michaela Maria GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- DLL - Science 9 - 2nd Quarter - Week 3Dokumen6 halamanDLL - Science 9 - 2nd Quarter - Week 3Rodney BarbaBelum ada peringkat
- Biomimetic Materials: A ReviewDokumen11 halamanBiomimetic Materials: A ReviewRiya KvBelum ada peringkat
- Reviewer For Physical ScienceDokumen13 halamanReviewer For Physical ScienceTimothy James Tolentino BruceBelum ada peringkat
- Mirasilcm 5Dokumen2 halamanMirasilcm 5icraoBelum ada peringkat
- Cbse QP - XI - CHEMISTRYDokumen12 halamanCbse QP - XI - CHEMISTRYRamana PadalaBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Bonding 01Dokumen151 halamanChemical Bonding 01Rao GootleyBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry SSC-I SolutionDokumen6 halamanChemistry SSC-I SolutionJavaidBelum ada peringkat
- Expertiment2 - TheoryDokumen12 halamanExpertiment2 - Theorydhruveshbhure9999Belum ada peringkat
- Earth Science Module 1Dokumen37 halamanEarth Science Module 1Joksian TrapelaBelum ada peringkat
- Science Notes IGCSE Grade 7Dokumen57 halamanScience Notes IGCSE Grade 7callista.d.fBelum ada peringkat
- Solids Conveying Edu Ctors Data SheetDokumen11 halamanSolids Conveying Edu Ctors Data SheetBenny GomezBelum ada peringkat
- Why Use Silicones in Personal Care Part 1Dokumen8 halamanWhy Use Silicones in Personal Care Part 1JulioBelum ada peringkat
- Manufacturing of Fly Ash Brick and Finding The Optimal Mix of Materials With Replacement of Cement by Lime Sludge and GypsumDokumen4 halamanManufacturing of Fly Ash Brick and Finding The Optimal Mix of Materials With Replacement of Cement by Lime Sludge and GypsumshivaBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Organic ChemistryDokumen15 halamanAdvanced Organic ChemistryJamaica FielBelum ada peringkat
- Subsea: Fluids Pte LTDDokumen7 halamanSubsea: Fluids Pte LTDcacalot93Belum ada peringkat
- UntitledDokumen31 halamanUntitledKenneth NicolasBelum ada peringkat
- Biology XII (12th Grade/Class) MCQs KEYDokumen268 halamanBiology XII (12th Grade/Class) MCQs KEYInni CallmeinniBelum ada peringkat
- Final Report Envoy LastDokumen88 halamanFinal Report Envoy LastMehzabeen ShahidyBelum ada peringkat
- Organic-Synthesis & ChiralityDokumen34 halamanOrganic-Synthesis & ChiralityAlaa Al HamedBelum ada peringkat
- Rep Microcrete 4Dokumen3 halamanRep Microcrete 4Paresh AhirBelum ada peringkat