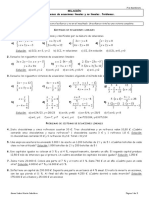
Ejercicios de Calculo Diferencial
Diunggah oleh
Adriana Luna AldacoHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Ejercicios de Calculo Diferencial
Diunggah oleh
Adriana Luna AldacoHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
CENTRO DE BACHILLERATO TECNOLÓGICO agropecuario No.
28
CURSO INTERSEMESTRAL _CÁLCULO DIFERENCIAL _
I. CONTESTA LAS SIGUIENTES PREGUNTAS:
1) ¿Cuándo se remontan los orígenes del cálculo?
2) ¿A quiénes se les atribuye el descubrimiento del cálculo como tal?
3) ¿En qué siglo se dice que inicio el estudio del cálculo como lo conocemos hoy en día?
4) Menciona los 4 problemas principales que estudia el cálculo
5) ¿Cuáles son los números naturales?
6) ¿Cuáles son los números enteros?
7) ¿Cómo se definen los números racionales?
8) ¿Cómo se definen los números irracionales?
9) Define los números reales
10) De qué trata la propiedad de transitividad
11) ¿Qué dice la Ley de tricotomía?
12) ¿Cuáles son los nombres de los ejes X y Y respectivamente?
13) ¿Qué es y cuál otro nombre recibe un sistema de coordenadas rectangulares?
14) Define lo que es un intervalo
15) ¿A qué se le llama un intervalo abierto?
16) ¿A qué se le llama un intervalo cerrado?
17) ¿Cómo se define una desigualdad?
18) ¿Cuáles son las tres formas de expresar el resultado de una desigualdad?
19) ¿Qué les pasa a las desigualdades cuando se multiplican o dividen por un número negativo?
20) ¿Cuál es la condición al despejar una desigualdad que la hace diferente a una igualdad?
21) ¿Cuál es la diferencia entre una relación y una función?
22) ¿Cuáles son los tres tipos de clasificaciones de una función?
23) ¿Cómo se define una función?
24) ¿Qué es el dominio de una función?
25) ¿Qué es el contradominio o rango de una función?
26) ¿Cuál es la clasificación general de las funciones?
27) ¿Cómo se definen las funciones polinómicas?
28) ¿Cómo se definen las funciones racionales?
29) ¿Cómo es una función exponencial?
30) ¿Cómo es una función logarítmica?
31) ¿Qué es una función inyectiva?
32) ¿Qué es una función biyectiva?
33) Define una función continua
34) Define una función discontinua
35) ¿Qué es una constante?
36) ¿Qué es una variable?
37) ¿Qué es una variable independiente?
38) Escribe la definición común de límite
39) ¿Qué es un límite en matemáticas?
40) ¿Cómo es la forma abreviada (notación) para escribir la definición de límite?
41) Escribe y define al menos cuatro de los teoremas sobre límites
42) ¿Qué entiendes y cómo se denotan los límites laterales?
43) ¿Cuál es la definición de límite lateral por la izquierda?
44) ¿Cuál es la definición de límite lateral por la derecha?
45) ¿Qué significa cuando los dos límites laterales son iguales, y que significa cuando son diferentes?
46) ¿Qué significan (o representan) los símbolos x ó y?
y
47) ¿Cómo se llama y que representa el símbolo ?
x
48) ¿Cuál es la definición de derivada de una manera general?
49) ¿Cuáles son las cuatro notaciones para las derivadas?
¡SIEMPRE ES MUY PRONTO PARA RENDIRSE!
50) ¿Cuál es la definición de derivada (cómo límite o por incrementos)?
II. CLASIFICA ADECUADAMENTE EL SIGUIENTE CONJUNTO DE NÚMEROS SEGÚN LAS
ESPECIFICACIONES ESTABLECIDAS EN LA TABLA:
Número real Positivo/ Racional/ Entero/ Natural
Negativo Irracional Fracción (si es el caso)
5.25
–3
11
e
4.47213595499958…
36
– 8.333333…
17
0.345 x 103
– 3/7
2e
71
0.9876 x 104
6.525
–2/9
49
– 7.4343434343…
–7
10
7.47213595499958…
3.2121212121…
– 4/7
0.34685 x 105
121
75.225
π
– 9.3678976332783…
15
22
– 11
III. RESUELVE LAS SIGUIENTES DESIGUALDADES Y EXPRESA SUS RESULTADOS DE LAS TRES
FORMAS POSIBLES:
¡SIEMPRE ES MUY PRONTO PARA RENDIRSE!
1) 2 x 5 4 19) 4 x 12 0
2) 7 x 28 0 2 x 1 5x
20) 2
3) 10 7 x 3 4 9 9 9
4) 21 6 6 x 20 2 x 1 3x
21) 3
5) 25 4 x 5 7 7 7
6) 17 3 x 10 4 22) 7 x 5 3x 13
7) 4 x 3 8 5 x 23) 2 x 5 4
8) 100 0.1x 10 24) 13 2 x 1
9) 9 x 4 2 x 10 25) 6 3 x 15 15
2( x 5) 26) 5 3 x 4
10) 4 0
3 27) 3 5 2 x 7
11) 2 10 x 9 x 6 28) 2x 5 x 9
12) 7 x 28 0 29) 8 3 x 1 2
13) 8 3 x 11 30) 5 10 x 8 x 15
14) 17 3 2 x 7 8 2x
31) 2 4
15) 3 x 6 0 9
16) 10 2 x 4 2 5y 5
32) 5
17) 19 6 x 7 22 8 8
1 x 1 1 2 x 1 3x
18) 33) 2
3 5 9 3 2 4
¡SIEMPRE ES MUY PRONTO PARA RENDIRSE!
II. INDICA SI LAS SIGUIENTRES GRÁFICAS SON O NO SON FUNCIONES Y EXPLICA POR QUÉ
a) b) c)
__________________________ _______________________ ______________________
d) e) f)
__________________________ ________________________ ____________________
g) h)
__________________________ _______________________
III. CLASIFICA DE MANERA GENERAL Y LUEGO DE MANERA PARTICULAR LAS SIGUIENTES
FUNCIONES:
¡SIEMPRE ES MUY PRONTO PARA RENDIRSE!
1) y sen 2 cos 2 x 5) y 2 x 4
2x
1 2 yx
3) xy
2) y 2 x 4
2x
yx x 1
6) f x
4) f x 3 x 1
3
x
IV. REALIZA LAS OPERACIONES INDICADAS PARA LOS SIGUENTES PARES DE FUNCIONES:
3
a) f x , g x x 2 4
x
b) f x x 2 3 x 28 , g x x 4
1
c) f x x 3 1, g x
x
d) f x x 2 x 24 , g x x 4
2
1) f x g x
2) f x g x
f x
3)
g x
4) f x g x
5) g x f x
II. CALCULA LA DERIVADA DE LAS SIGUIENTES FUNCIONES UTILIZANDO LA DEFINICIÓN DE DERIVADA
(POR INCREMENTOS):
1) f x x 2 4) y 5x 2 8 7) y 3x 2 5
1 5) y(x) = 3x2 + 5x 8) f(x) = x – 9
2) y
x2 6) f x x 2x 4
3
9) f(x) = 5x2
3) y(x) = 2x +1
III. RESUELVE LOS SIGUIENTES LÍMITES
x2 x 2 1
1) lim f ( x) 7) lim 3 x
x 2 2
x 2 x 2 2x
2) lim
1 x 2 1 8) lim
2y 2 3y 5
y y 2 5 y 2
x 0 x
3) lim
3n 5n 62
9)
x 1
lim 4 x 3 2 x 2 3 5 x 6
n 4n 2 2
x2 9
5 x 2x 2 10) lim
4) lim 3 x 3 x3
x 5 x 3 x 6
11) lim tan x csc x
x4 5 x
5) lim
x 1 x 2 x3 3x 2 5
12) lim
3 x 4
x 2 5x 6 x
6) lim
x 1 x 1 13) lim ( x 2 x 1)
x 3
¡SIEMPRE ES MUY PRONTO PARA RENDIRSE!
14) lim
x2 6x 8 25) lim ( x14 125x10 18 x 6 12)
x 0
x 4 x4
x2 x
x2 2 26) lim f ( x)
15) lim x 1 2x 2
x 2 x2
x 10
6 x3 5 x 2 3 27) lim
16) lim x x
x 2 x 3 4 x 7
x3 2
4t 2 3t 2 28) lim
17) lim 3 x 2 5 x 24
t 0 t 2t 6
x2 9
7x 8 29) lim
18) lim x 3 x 3
x 4 x 3
30) lim ( 2 x 2 3 x 1 )
x 2 2x x 5
19) lim
x2 4 x 2 x 2 5x 4
31) lim
20) lim 7 x x 1 x 1
xa
1 32) lim(2 x 2 3 x 1)
x5
21) lim
x 4 2 x 3 x 5
2
3x 2 5
33) lim
5 2x2 x 3 x 4
22) lim
x x3 ax 4 bx 2 c
34) lim
x 25
2
x cx 5 dx 3 ex
lim
23) x 5 x5 2 x 2 8x
35) lim
24) lim tan x cos x x 4 x4
lim tan x sen x
x
36) x
¡SIEMPRE ES MUY PRONTO PARA RENDIRSE!
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Integrales Impropias Con Limites InfinitosDokumen3 halamanIntegrales Impropias Con Limites InfinitosJavier Guerrero100% (1)
- Taller Operaciones Básicas y EcuacionesDokumen4 halamanTaller Operaciones Básicas y EcuacionesAndres FelipeBelum ada peringkat
- Teoría clásica del crecimiento económico: Modelos de crecimiento exógenoDari EverandTeoría clásica del crecimiento económico: Modelos de crecimiento exógenoBelum ada peringkat
- Razonamiento cuantitativo: Notas de claseDari EverandRazonamiento cuantitativo: Notas de clasePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Actividad 5 CalculoDokumen9 halamanActividad 5 CalculoDaniel RebillasBelum ada peringkat
- Ecuaciones de Primer GradoDokumen5 halamanEcuaciones de Primer Gradodanny roldanBelum ada peringkat
- Ecuaciones ExponencialesDokumen1 halamanEcuaciones ExponencialesArley Chuquin100% (1)
- Fracciones Algebraicas IiDokumen3 halamanFracciones Algebraicas IimatesdemanuBelum ada peringkat
- GUIA 5. Integracion de Conceptos de MatematicaDokumen4 halamanGUIA 5. Integracion de Conceptos de MatematicaSandra RedaelliBelum ada peringkat
- Relación Tema 3. Inecuaciones y Sistemas. Problemas. SolucionesDokumen4 halamanRelación Tema 3. Inecuaciones y Sistemas. Problemas. SolucionesE&GBelum ada peringkat
- Relación Tema 5. Polinomios. ProblemasDokumen8 halamanRelación Tema 5. Polinomios. ProblemasE&GBelum ada peringkat
- NOVENODokumen8 halamanNOVENOliceth rayana dayanaBelum ada peringkat
- Actividad de Aplicación Conceptos Básicos Propiedades y Reglas de Derivación. (Individual) 4.5 PDFDokumen9 halamanActividad de Aplicación Conceptos Básicos Propiedades y Reglas de Derivación. (Individual) 4.5 PDFAngElica CoNtrerasBelum ada peringkat
- Práctica Sobre Las Expresiones AlgebraicasDokumen1 halamanPráctica Sobre Las Expresiones AlgebraicasDarlin Alejandro ValdezBelum ada peringkat
- Actividades Inecuaciones NUEVASDokumen2 halamanActividades Inecuaciones NUEVASNatalia PerelloBelum ada peringkat
- Trabajo de Nivelación Clei V Primer PeriodoDokumen1 halamanTrabajo de Nivelación Clei V Primer PeriodoangeldemadridBelum ada peringkat
- Taller 7 Matemática BásicaDokumen2 halamanTaller 7 Matemática BásicaValeria RodriguezBelum ada peringkat
- Práctica Nivelación IDokumen2 halamanPráctica Nivelación IEliezer Moreta GonzálezBelum ada peringkat
- TP Diag. 2024Dokumen2 halamanTP Diag. 2024Florencia SardoBelum ada peringkat
- Guia de Ejercicios de Limites de Funciones y ContinuidadDokumen4 halamanGuia de Ejercicios de Limites de Funciones y ContinuidadIgnacio AbarcaBelum ada peringkat
- Taller 1Dokumen9 halamanTaller 1Aaron H 指 HerreraBelum ada peringkat
- UN - 05 Ecuaciones 2Dokumen2 halamanUN - 05 Ecuaciones 2lalalalashhlivingmylifeBelum ada peringkat
- Recuperacion FinalDokumen24 halamanRecuperacion FinalCarolina Gonzalez BuitragoBelum ada peringkat
- Refuerzo 2 Ev. 1ºESODokumen4 halamanRefuerzo 2 Ev. 1ºESOYair De La PeñaBelum ada peringkat
- Relación Tema 3. Sistemas de Ecuaciones Lineales y No Lineales. Problemas. SolucionesDokumen3 halamanRelación Tema 3. Sistemas de Ecuaciones Lineales y No Lineales. Problemas. SolucionesE&GBelum ada peringkat
- Práctica Unidad III (La Derivada) Cálculo 251 UASD Abril 2018Dokumen6 halamanPráctica Unidad III (La Derivada) Cálculo 251 UASD Abril 2018Jorge Frank UreñaBelum ada peringkat
- Guia de Matemã - Ticas I Mstar para Extraordinario y RegularizacionDokumen7 halamanGuia de Matemã - Ticas I Mstar para Extraordinario y RegularizacionСелия СмBelum ada peringkat
- Hoja 1 Ejercicios Unidad 4 Inecuaciones y Sistemas-1Dokumen2 halamanHoja 1 Ejercicios Unidad 4 Inecuaciones y Sistemas-1Ilham Alabbassi elhadriBelum ada peringkat
- Taller 1 - Unidad 2 CálculoDokumen1 halamanTaller 1 - Unidad 2 CálculoJuan Pablo Rodriguez EsparzaBelum ada peringkat
- Ejercitación Unidad2 Parte3Dokumen2 halamanEjercitación Unidad2 Parte3Milagros PeironeBelum ada peringkat
- Matematicas V Clam PDFDokumen33 halamanMatematicas V Clam PDFgromeroprofesorBelum ada peringkat
- Matematicas VDokumen33 halamanMatematicas VgromeroprofesorBelum ada peringkat
- Práctica Final Cálculo I (Mat - 250) UASD Agosto 2023 VeranoDokumen5 halamanPráctica Final Cálculo I (Mat - 250) UASD Agosto 2023 VeranoYuleidi GuillenBelum ada peringkat
- Libro 5º-Segunda ParteDokumen14 halamanLibro 5º-Segunda ParteFacu GonzBelum ada peringkat
- Ht12 Ecuaciones Exponenciales Logaritmicas 2017 1Dokumen2 halamanHt12 Ecuaciones Exponenciales Logaritmicas 2017 1Kevin SantillanBelum ada peringkat
- Ejercicios Resultos Del Tema 5Dokumen5 halamanEjercicios Resultos Del Tema 5Jose MarinBelum ada peringkat
- 6 Ejercicios de Repaso EcuacionesDokumen2 halaman6 Ejercicios de Repaso EcuacionesSara PerezBelum ada peringkat
- Guia 2 Ecuaciones Con SoluciónDokumen4 halamanGuia 2 Ecuaciones Con SoluciónpazBelum ada peringkat
- Taller Sistemas EcuacionesDokumen3 halamanTaller Sistemas EcuacionesNico Chikit0Belum ada peringkat
- Teorema Del Residuo y Del FactorDokumen2 halamanTeorema Del Residuo y Del FactorErik Unam RamirezBelum ada peringkat
- Apuntes - MAT II 2021-22Dokumen78 halamanApuntes - MAT II 2021-22myj5kqtpw9Belum ada peringkat
- Ecuaciones de Primer GradoDokumen3 halamanEcuaciones de Primer GradoLuis SalazarBelum ada peringkat
- Relación Tema 6. Sistemas de Ecuaciones Lineales. Problemas. Soluciones y ResueltosDokumen3 halamanRelación Tema 6. Sistemas de Ecuaciones Lineales. Problemas. Soluciones y ResueltosE&GBelum ada peringkat
- TALLER 3 Matematicas Clei 6 PDFDokumen2 halamanTALLER 3 Matematicas Clei 6 PDFDiego QuinteroBelum ada peringkat
- TALLER 3 Matematicas Clei 6 PDFDokumen2 halamanTALLER 3 Matematicas Clei 6 PDFDiego QuinteroBelum ada peringkat
- 2ESO MAT - Actividades Fase 1 Revisado RosaDokumen3 halaman2ESO MAT - Actividades Fase 1 Revisado RosaGuillem Amorós RuizBelum ada peringkat
- S2.+Guía+ +3Dokumen2 halamanS2.+Guía+ +3Ashley PérezBelum ada peringkat
- Calculo I Trabajos PracticosDokumen9 halamanCalculo I Trabajos PracticosChristian Ariel MaculusBelum ada peringkat
- U6 ECUACIONESvvhDokumen5 halamanU6 ECUACIONESvvhFrancisco JesúsBelum ada peringkat
- Guia 4Dokumen4 halamanGuia 4Azcurra JeremiasBelum ada peringkat
- Practico DerivadaDokumen4 halamanPractico DerivadaAle JuradoBelum ada peringkat
- ÁlgebraDokumen10 halamanÁlgebraGerson Barrientos ChávezBelum ada peringkat
- Tarea Unidad IIIDokumen3 halamanTarea Unidad IIImauri soldierBelum ada peringkat
- Tarea Unidad IIIDokumen3 halamanTarea Unidad IIImauri soldierBelum ada peringkat
- Workbook of The Basic Math Modulet - Wilton OltmannsDokumen122 halamanWorkbook of The Basic Math Modulet - Wilton OltmannsJoan Manuel Jimenez ZorrillaBelum ada peringkat
- Semana 11 Matematica 1 Ucss 2019-IDokumen4 halamanSemana 11 Matematica 1 Ucss 2019-Ivecode5292Belum ada peringkat
- i-MAT DECIMODokumen4 halamani-MAT DECIMOFabio LargoBelum ada peringkat
- Ejercicios Limites1Dokumen9 halamanEjercicios Limites1segundojesusBelum ada peringkat
- Guía de EstudioDokumen45 halamanGuía de EstudioDaniel MoyaBelum ada peringkat
- MatemÁticas 2º eDokumen3 halamanMatemÁticas 2º edieczamoravBelum ada peringkat
- Ejercicio de Repaso-2 ParcialDokumen2 halamanEjercicio de Repaso-2 Parciallisandro lawaisseBelum ada peringkat
- Ejercicios Calculo Diferencial Jun18Dokumen7 halamanEjercicios Calculo Diferencial Jun18Adriana Luna AldacoBelum ada peringkat
- Reactivos de CalculoDokumen6 halamanReactivos de CalculoAdriana Luna AldacoBelum ada peringkat
- Ejercicios Calculo Diferencial Jun18Dokumen7 halamanEjercicios Calculo Diferencial Jun18Adriana Luna AldacoBelum ada peringkat
- Ejercicios de Calculo DiferencialDokumen6 halamanEjercicios de Calculo DiferencialAdriana Luna AldacoBelum ada peringkat
- Ejercicios de Calculo DiferencialDokumen6 halamanEjercicios de Calculo DiferencialAdriana Luna AldacoBelum ada peringkat
- Ejercicios de Calculo DiferencialDokumen6 halamanEjercicios de Calculo DiferencialAdriana Luna AldacoBelum ada peringkat
- Guia de Matemáticas en BachilleratoDokumen18 halamanGuia de Matemáticas en BachilleratoAdriana Luna AldacoBelum ada peringkat
- Ejercicios de Calculo DiferencialDokumen6 halamanEjercicios de Calculo DiferencialAdriana Luna AldacoBelum ada peringkat
- Reactivos Prueba Enlace - OPERATIVA 2008Dokumen37 halamanReactivos Prueba Enlace - OPERATIVA 2008dgp266753% (15)
- Guía Temario Del CDDokumen8 halamanGuía Temario Del CDMiguel Angel Espinoza ZarateBelum ada peringkat
- Geometria Analitica Suceciones Relacion y FuncionDokumen6 halamanGeometria Analitica Suceciones Relacion y FuncionRafael RojasBelum ada peringkat
- Trabajo de InvestigaciónDokumen10 halamanTrabajo de InvestigaciónMayerlin Gonzalez0% (1)
- DerivadaDokumen1 halamanDerivadaEdwin BlancoBelum ada peringkat
- Grafos JuegosDokumen5 halamanGrafos JuegosJosé Augusto Siles Ramírez100% (1)
- 4.5 Metodos NúmericosDokumen9 halaman4.5 Metodos NúmericosKalel Dodi YasharBelum ada peringkat
- Mate 2 U2-2Dokumen23 halamanMate 2 U2-2henry castroBelum ada peringkat
- 4-Regla de L'Hopital 4Dokumen17 halaman4-Regla de L'Hopital 4Pio Jose valdiviaBelum ada peringkat
- Matrices - Operaciones Con Matrices y Método Reduccion de MatricesDokumen35 halamanMatrices - Operaciones Con Matrices y Método Reduccion de MatricesAlexandraBelum ada peringkat
- Clase 3 Tipos de Matrices.Dokumen7 halamanClase 3 Tipos de Matrices.Alexis GrijalvaBelum ada peringkat
- PracticaRelaciones y Funciones (I)Dokumen3 halamanPracticaRelaciones y Funciones (I)gr_al3xBelum ada peringkat
- Antiderivadas o IntegralesDokumen10 halamanAntiderivadas o IntegralesAnder Jose Moya GomezBelum ada peringkat
- Art 4Dokumen18 halamanArt 4RICARDO LUCIO MAMANI SUCABelum ada peringkat
- Algoritmo de DijkstraDokumen5 halamanAlgoritmo de DijkstraRobertico35Belum ada peringkat
- Sec 5.1 La Funcion Logaritmo NaturalDokumen36 halamanSec 5.1 La Funcion Logaritmo Naturaljose21820% (1)
- Captura de Pantalla 2022-07-21 A La(s) 14.34.54Dokumen10 halamanCaptura de Pantalla 2022-07-21 A La(s) 14.34.54DAVID SALOMON CASTILLA SANTACOLOMABelum ada peringkat
- Tarea 2 Seminario EstructuraDokumen5 halamanTarea 2 Seminario EstructuraMARIA ISABEL LOPEZ RAMOSBelum ada peringkat
- AN Cap 2Dokumen21 halamanAN Cap 2Erick GomezBelum ada peringkat
- GrafosDokumen12 halamanGrafosloquitochapi93Belum ada peringkat
- Tarea 3Dokumen10 halamanTarea 3mariaBelum ada peringkat
- Ejercicios Completos Algebra Tema 2Dokumen25 halamanEjercicios Completos Algebra Tema 2Carlos RestrepoBelum ada peringkat
- COMPUTACIÓNDokumen4 halamanCOMPUTACIÓNfiorela reynosoBelum ada peringkat
- 2do MATERIAL LIMITESDokumen13 halaman2do MATERIAL LIMITESruben ruuizBelum ada peringkat
- Trabajoautonomo#2Dokumen4 halamanTrabajoautonomo#2SAUL BOLIVAR SARMIENTO CARCHIBelum ada peringkat
- Opf PDFDokumen21 halamanOpf PDFHUAYTA CONTRERAS DEYVIDBelum ada peringkat
- Sem 4 DerivadasDokumen39 halamanSem 4 DerivadasCés Avi CelBelum ada peringkat
- ProroutDokumen97 halamanProroutMiguel LealBelum ada peringkat