Motherboard
Diunggah oleh
Aimee HernandezDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Motherboard
Diunggah oleh
Aimee HernandezHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
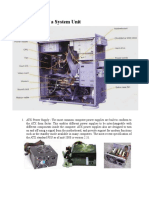
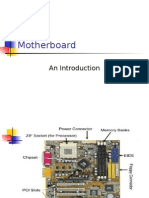
The Motherboard - A large printed printed circuit board that connects all the parts
together. Most of the computer’s ports are located on the motherboard. It also holds some
lesser chips such as the Chipset (which is actually one chip. It used to be multiple chips, but
on modern platforms the functions of these chips have been either moved directly onto the
CPU, or onto one chip which is surface mounted to the motherboard.) It holds a socket for
the CPU, slots for RAM, as well as various other connectors for expansion, including PCIe,
USB and SATA. It also holds the CPU voltage regulation module as well as other power
delivery circuitry. Features and exact expansion and ports vary from one model to another. It
is the primary determiner of features on the computer.
CPU Cooler - This is usually a heatsink with a fan on it, however it can also sometimes
be a watercooling system. Its role is to dissipate heat from the CPU into the air.
Random Access Memory (RAM) - This is where data relating to what you are currently
doing is stored. It is a very fast-access type of memory, but it is volatile, meaning that it is not
for long term storage, and loses all the data it holds when powered off. RAM is made in chips,
but each chip holds very little. In desktops and laptops, there are multiple chips that are
surface mounted to a PCB that is inserted into RAM slots on the motherboard. In laptops, it
is sometimes surface mounted directly to the motherboard.
The Graphics Card or Video Card - This is different from a GPU. The GPU (Graphics
Processing Unit) is the chip that handles graphics processing in a particular computer. The
GPU is surface mounted to the Graphics Card, but the graphics card also has power delivery
circuitry, cooling, and video output ports.
The Power Supply - The name is self-explanatory. It supplies power to the different
components in a computer. It is usually internal, but sometimes can be an external brick, in
which case the motherboard contains additional power delivery circuitry.
Hard Disk Drives - Slow, long-term data storage. They are inexpensive, so usually used
as a secondary drive to store large amounts of data that does not need to be accessed quickly.
Mass Storage Device
If you were surprised that your computer's memory is actually not where your epic archive of college-era
MP3s lives, the computer's mass storage device has you covered. This is where data is actually written,
stored and accessed for the long term, whether it's your old phone's 32-gigabyte SD card or your new
laptop's 1-terabyte of hard-disk storage. When a computer needs to access program or app data or bring
up a file that you saved six months (or six years) ago, that data comes from its storage device.
Keyboard
The keyboard is one of the main ways to communicate with a computer. There are many different types
of keyboards, but most are very similar and allow you to accomplish the same basic tasks.
Mouse
The mouse is another important tool for communicating with computers. Commonly known as
a pointing device, it lets you point to objects on the screen, click on them, and move them.
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) - This term is often erroneously used to refer to a
computer tower. It is the primary chip that performs most of the computing tasks of a the
computer. Major manufacturers are Intel and AMD. It is the primary determiner of a
computer’s performance.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Filipino Folk SongsDokumen7 halamanFilipino Folk SongsAimee Hernandez100% (2)
- Expansion SlotDokumen18 halamanExpansion SlotFazrul RosliBelum ada peringkat
- Motherboard ArchitectureDokumen15 halamanMotherboard ArchitectureAbhishek DebBelum ada peringkat
- Computer SoftwareDokumen12 halamanComputer SoftwareNaomi Nyambaso100% (1)
- Musical Instruments of IndonesiaDokumen3 halamanMusical Instruments of IndonesiaAimee HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Musical Instruments of IndonesiaDokumen3 halamanMusical Instruments of IndonesiaAimee HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Musical Instruments of IndonesiaDokumen3 halamanMusical Instruments of IndonesiaAimee HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Otherhardware Updated Js2019 Clo1 Week3Dokumen54 halamanOtherhardware Updated Js2019 Clo1 Week3somerandomhedgehog100% (1)
- 23 Computer Application Commerce Unit-02Dokumen42 halaman23 Computer Application Commerce Unit-02Kishore KrishnanBelum ada peringkat
- Practical # 01: Introduction To Computers, Parts of Computers and Architecture of Computer Tools: 1.1 What Is Computer?Dokumen13 halamanPractical # 01: Introduction To Computers, Parts of Computers and Architecture of Computer Tools: 1.1 What Is Computer?funny videosBelum ada peringkat
- Components of System UnitDokumen8 halamanComponents of System UnitIvan Louie Cruto100% (1)
- Types of Computer & Their PartsDokumen6 halamanTypes of Computer & Their PartsImtiaz AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- What Is A MotherboardDokumen3 halamanWhat Is A MotherboardAnonymous 9QDHkmBelum ada peringkat
- The MotherboardDokumen39 halamanThe MotherboardGenevev Reyes100% (1)
- Motherboard Components... CSEDokumen28 halamanMotherboard Components... CSEAtulay Mahajan100% (1)
- 079 CMT pr-1Dokumen8 halaman079 CMT pr-1Aarunain PandavdraBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Hardware ComponentsDokumen59 halamanComputer Hardware ComponentsJason EchevariaBelum ada peringkat
- Essential Motherboard Parts GuideDokumen28 halamanEssential Motherboard Parts GuideJohn Adams Budomo100% (2)
- Computer Ports and Its TypesDokumen18 halamanComputer Ports and Its TypesLUCKYBelum ada peringkat
- Bongkar Laptop Cq41Dokumen15 halamanBongkar Laptop Cq41Andrian AdeBelum ada peringkat
- Motherboard components and portsDokumen32 halamanMotherboard components and portsAnanduBelum ada peringkat
- Motherboard and Other PartsDokumen32 halamanMotherboard and Other PartsJom's Mijares100% (1)
- MotherboardDokumen30 halamanMotherboardJhan Rhoan Salazar100% (1)
- Hard Ware Note BookDokumen22 halamanHard Ware Note BookSrini VasuluBelum ada peringkat
- Hard DiskDokumen3 halamanHard DiskBILAL ZAFARBelum ada peringkat
- BIOS or Basic Input Output SystemDokumen5 halamanBIOS or Basic Input Output SystemIssan VillaruelBelum ada peringkat
- Motherboard Guide: Learn Components & FunctionsDokumen4 halamanMotherboard Guide: Learn Components & Functionsliezle munezBelum ada peringkat
- Storage Devices and Multimedia DevicesDokumen25 halamanStorage Devices and Multimedia DevicesJoevertVillartaBentulanBelum ada peringkat
- Complete Guide For Computer Hardware NewbiesDokumen47 halamanComplete Guide For Computer Hardware NewbiesMicky PautuBelum ada peringkat
- The Cpu: Central Processing UnitDokumen26 halamanThe Cpu: Central Processing Unitjim_finn_1Belum ada peringkat
- MS Office 2007 - NotesDokumen89 halamanMS Office 2007 - NotesmanuBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Hardware Repairing Course - Computer Hardware Repairing Institute - Computer Hardware Repairing Training Delhi Tilak NagarDokumen4 halamanComputer Hardware Repairing Course - Computer Hardware Repairing Institute - Computer Hardware Repairing Training Delhi Tilak NagarRakesh MahajanBelum ada peringkat
- Computer 1 With Applications: Introduction To ComputersDokumen23 halamanComputer 1 With Applications: Introduction To ComputersDonna Hernandez100% (1)
- Motherboard SlidesDokumen21 halamanMotherboard Slidesmubiru mosesBelum ada peringkat
- What is RAM? A guide to Random Access Memory types, features and moreDokumen25 halamanWhat is RAM? A guide to Random Access Memory types, features and moreSayyan Shaikh100% (1)
- Introduction to Computer Components and ProgrammingDokumen50 halamanIntroduction to Computer Components and ProgrammingNaim EastbulletBelum ada peringkat
- Parts of ComputerDokumen8 halamanParts of ComputerAn Rose AdepinBelum ada peringkat
- Seagate Command ReferenceDokumen17 halamanSeagate Command ReferenceTrevor HallBelum ada peringkat
- How Motherboard WorksDokumen12 halamanHow Motherboard Worksrez hablo100% (1)
- Unit 1 Computer System (2) (1) - 1629266582Dokumen61 halamanUnit 1 Computer System (2) (1) - 1629266582Nischal ChaudharyBelum ada peringkat
- 01 Computer LiteracyDokumen19 halaman01 Computer LiteracyGadi Fosta100% (1)
- Hardware BibleDokumen123 halamanHardware BibleMitko JosifoskiBelum ada peringkat
- PC Troubleshooting Tips #2Dokumen10 halamanPC Troubleshooting Tips #2Roger EmbalsadoBelum ada peringkat
- Module Photo PDFDokumen21 halamanModule Photo PDFINTERSOFT khansirBelum ada peringkat
- The Component of System UnitDokumen52 halamanThe Component of System UnitgtBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Organization and Architecture Chapter 2Dokumen49 halamanComputer Organization and Architecture Chapter 2Kirubel EsayasBelum ada peringkat
- Abhi PROJECT REPORTDokumen89 halamanAbhi PROJECT REPORTDependra KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 Assembly Language and ProgrammingDokumen85 halamanChapter 4 Assembly Language and ProgrammingPetra Kalasa100% (1)
- 15 Safety Precautions for Working with ElectricityDokumen14 halaman15 Safety Precautions for Working with ElectricitySayyan ShaikhBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Information Technology: DR Dharmendra Kumar KanchanDokumen83 halamanIntroduction To Information Technology: DR Dharmendra Kumar KanchanSadhika KatiyarBelum ada peringkat
- Easy Technical Guide To Understand PC Motherboard, Troubleshoot Problems and Its Repair: PART - IIIDokumen3 halamanEasy Technical Guide To Understand PC Motherboard, Troubleshoot Problems and Its Repair: PART - IIIAnonymous lPvvgiQjRBelum ada peringkat
- Explain The Concept of Information TechnologyDokumen38 halamanExplain The Concept of Information TechnologyGiovanni SlackBelum ada peringkat
- F3 Serial Port Diagnostic ModesDokumen497 halamanF3 Serial Port Diagnostic ModesEugen0% (1)
- Magnetic Tape NotesDokumen3 halamanMagnetic Tape NotesTanay NemadeBelum ada peringkat
- Computer - Hardware - Diagnosing & Fixing Motherboard FaultsDokumen4 halamanComputer - Hardware - Diagnosing & Fixing Motherboard Faultsscribdraza786Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 Operating SystemDokumen79 halamanChapter 1 Operating SystemMekuanint Aschalew100% (1)
- HDD ExpertDokumen3 halamanHDD Expertmehdi bibiBelum ada peringkat
- Multifunction Peripherals for PCs: Technology, Troubleshooting and RepairDari EverandMultifunction Peripherals for PCs: Technology, Troubleshooting and RepairBelum ada peringkat
- The Case - It Holds Everything Inside It. I Seriously Hope You AlreadyDokumen5 halamanThe Case - It Holds Everything Inside It. I Seriously Hope You AlreadyVasii CiuciuBelum ada peringkat
- Inside A ComputerDokumen7 halamanInside A ComputerMiguel Angel Acosta ReinosoBelum ada peringkat
- Why Is It Important To Understand Computer Parts?Dokumen19 halamanWhy Is It Important To Understand Computer Parts?Tina PoquizBelum ada peringkat
- PC Repair Troubleshooting Course ManualDokumen73 halamanPC Repair Troubleshooting Course Manualyogeshdhuri22Belum ada peringkat
- Capslet Week 3 Quarter 2 Ict-7: Inside A ComputerDokumen9 halamanCapslet Week 3 Quarter 2 Ict-7: Inside A ComputerDA9 AMADBelum ada peringkat
- HEALTH FITNESS TESTS & STI SYMPTOMSDokumen6 halamanHEALTH FITNESS TESTS & STI SYMPTOMSAimee HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- MotherboardDokumen2 halamanMotherboardAimee Hernandez100% (1)
- Four Types of Business LetterDokumen1 halamanFour Types of Business LetterAimee HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Kami Po Ang Patrol SampaguitaDokumen1 halamanKami Po Ang Patrol SampaguitaAimee HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- ToDokumen2 halamanToAimee HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Rice Cooker: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDokumen15 halamanRice Cooker: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchAimee HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- CpuDokumen1 halamanCpuAimee HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- CpuDokumen1 halamanCpuAimee HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Da Hub Computer Cafe - Ate Ai Taas NG Store Koh PinagkurusanDokumen7 halamanDa Hub Computer Cafe - Ate Ai Taas NG Store Koh PinagkurusanAimee HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- CpuDokumen1 halamanCpuAimee HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Da Hub Computer Cafe - Ate Ai Taas NG Store Koh PinagkurusanDokumen7 halamanDa Hub Computer Cafe - Ate Ai Taas NG Store Koh PinagkurusanAimee HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Da Hub Computer Cafe - Ate Ai Taas NG Store Koh PinagkurusanDokumen7 halamanDa Hub Computer Cafe - Ate Ai Taas NG Store Koh PinagkurusanAimee HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- QuestionaireDokumen1 halamanQuestionaireAimee HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Rice Cooker: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDokumen15 halamanRice Cooker: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchAimee HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Uri NG LathalainDokumen1 halamanUri NG LathalainAimee HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Uri NG LathalainDokumen1 halamanUri NG LathalainAimee HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Factors that Cause Depression and Impact School Performance in Grade 10 StudentsDokumen9 halamanFactors that Cause Depression and Impact School Performance in Grade 10 StudentsAimee HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Factors that Cause Depression and Impact School Performance in Grade 10 StudentsDokumen9 halamanFactors that Cause Depression and Impact School Performance in Grade 10 StudentsAimee HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- 1Dokumen6 halaman1Aimee HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Summary of Tale ChunyangDokumen1 halamanSummary of Tale ChunyangAimee HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- PampanitikanDokumen3 halamanPampanitikanAimee HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Filipino ComposerDokumen10 halamanFilipino ComposerAimee HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- The Tale of The Woodcutter and TheTigerDokumen3 halamanThe Tale of The Woodcutter and TheTigerAimee HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- ToolsDokumen2 halamanToolsAimee HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Musical Instruments of IndonesiaDokumen2 halamanMusical Instruments of IndonesiaAimee HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- 3vsb Should Be Volts Motherboard - Google SearchDokumen2 halaman3vsb Should Be Volts Motherboard - Google Searchoff emBelum ada peringkat
- Book 1Dokumen6 halamanBook 1Whitney Del RosarioBelum ada peringkat
- Steve Jobs: Co-founder of Apple ComputerDokumen2 halamanSteve Jobs: Co-founder of Apple ComputerAlejandro Angel AgudeloBelum ada peringkat
- Motherboard and BIOSDokumen21 halamanMotherboard and BIOSPinky ParreñoBelum ada peringkat
- Android Model Compare - Urovo I6300 and EDA 50 Updated 02072018Dokumen1 halamanAndroid Model Compare - Urovo I6300 and EDA 50 Updated 02072018yashavanta shettyBelum ada peringkat
- NEUST Student Profile Prepared by FacultyDokumen10 halamanNEUST Student Profile Prepared by FacultyCedrixe MadridBelum ada peringkat
- Compaq Presario 515 Inventec Volna Amd Uma - 6050a2258701 - Rev Ax1Dokumen53 halamanCompaq Presario 515 Inventec Volna Amd Uma - 6050a2258701 - Rev Ax1Yonny Javier VivasBelum ada peringkat
- Laptop Pricelist July 2020Dokumen28 halamanLaptop Pricelist July 2020mtirones01Belum ada peringkat
- Debug 1214Dokumen238 halamanDebug 1214scumpicade2003Belum ada peringkat
- Mi Boys Hub Pricelist As of Feb 26, 2020Dokumen3 halamanMi Boys Hub Pricelist As of Feb 26, 2020Reynald CordovillaBelum ada peringkat
- PC power supply voltages in the form of DC currentDokumen8 halamanPC power supply voltages in the form of DC currentsoegyBelum ada peringkat
- Via Mvp3 AT: System BoardDokumen63 halamanVia Mvp3 AT: System Boardbats bengueBelum ada peringkat
- QualiPoc Android - Product Family OverviewDokumen20 halamanQualiPoc Android - Product Family OverviewteajeeBelum ada peringkat
- Combined Movements of The 2 Forwards: Training Session 5Dokumen3 halamanCombined Movements of The 2 Forwards: Training Session 5karim50% (2)
- ADDRESSDokumen9 halamanADDRESSshweta singhBelum ada peringkat
- Dev ListDokumen7 halamanDev ListDion AureBelum ada peringkat
- Graphics Certification TableDokumen25 halamanGraphics Certification Tableamits_3Belum ada peringkat
- Entrevista Top Notch 1 Nivel 3Dokumen3 halamanEntrevista Top Notch 1 Nivel 3Christian MinaBelum ada peringkat
- ITC Assignment 1Dokumen3 halamanITC Assignment 1Abdul SindhiBelum ada peringkat
- SCMH Brochure2a 25-1 (145) CorrectDokumen2 halamanSCMH Brochure2a 25-1 (145) CorrectAnonymous DPWGxzpWBelum ada peringkat
- Tys Iphone Help - Tys Iphone Help - Jailbreak 5.0Dokumen7 halamanTys Iphone Help - Tys Iphone Help - Jailbreak 5.0jolly.jok3rBelum ada peringkat
- Technical FeasibilityDokumen4 halamanTechnical FeasibilityGil John AwisenBelum ada peringkat
- Chave de Ativação Windows 10 Não ApagarDokumen1 halamanChave de Ativação Windows 10 Não ApagarRoberto SouzaBelum ada peringkat
- Jarir Shopping Guide QatarDokumen84 halamanJarir Shopping Guide QatarErayBelum ada peringkat
- s8 Ultra Sim Watch ArticleDokumen3 halamans8 Ultra Sim Watch ArticleLion KingBelum ada peringkat
- BIOS Settings for Harman International Vix00 and Vix000 ConsolesDokumen5 halamanBIOS Settings for Harman International Vix00 and Vix000 ConsolesGerry DamsikiBelum ada peringkat
- Black Box Series 2 Mid Tower Case User ManualDokumen2 halamanBlack Box Series 2 Mid Tower Case User ManualfsuffiottiBelum ada peringkat
- Spanish Layout Keyboard StockDokumen1 halamanSpanish Layout Keyboard StockBlas PerezBelum ada peringkat
- All Prices Subject To Change Without Prior Notice. All Items Subject To Availability - 1604704947Dokumen19 halamanAll Prices Subject To Change Without Prior Notice. All Items Subject To Availability - 1604704947LIBC DasmariñasBelum ada peringkat
- Lista Notebook Iva PDFDokumen2 halamanLista Notebook Iva PDFabel BritezBelum ada peringkat