Stainless Steel Crown
Diunggah oleh
Myrna Abalos0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
78 tayangan2 halamanThis document discusses early childhood caries and treatment options such as zirconia crowns and stainless steel crowns. Zirconia crowns are fully tooth-colored ceramic crowns that are esthetically pleasing and impermeable to staining. Anterior zirconia crowns involve creating a subgingival feather edge margin and passive seating with luting cement. Posterior zirconia crowns require a supragingival preparation to avoid tissue maceration. Stainless steel crowns are indicated for restoring primary molars requiring large restorations, in children with rampant caries, or after pulp therapy. They have higher survival rates than other restorative materials and involve occlusal and sub
Deskripsi Asli:
INDICATIONS, CONTRAINDICATIONS, AND TOOTH PREPARATION
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniThis document discusses early childhood caries and treatment options such as zirconia crowns and stainless steel crowns. Zirconia crowns are fully tooth-colored ceramic crowns that are esthetically pleasing and impermeable to staining. Anterior zirconia crowns involve creating a subgingival feather edge margin and passive seating with luting cement. Posterior zirconia crowns require a supragingival preparation to avoid tissue maceration. Stainless steel crowns are indicated for restoring primary molars requiring large restorations, in children with rampant caries, or after pulp therapy. They have higher survival rates than other restorative materials and involve occlusal and sub
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
78 tayangan2 halamanStainless Steel Crown
Diunggah oleh
Myrna AbalosThis document discusses early childhood caries and treatment options such as zirconia crowns and stainless steel crowns. Zirconia crowns are fully tooth-colored ceramic crowns that are esthetically pleasing and impermeable to staining. Anterior zirconia crowns involve creating a subgingival feather edge margin and passive seating with luting cement. Posterior zirconia crowns require a supragingival preparation to avoid tissue maceration. Stainless steel crowns are indicated for restoring primary molars requiring large restorations, in children with rampant caries, or after pulp therapy. They have higher survival rates than other restorative materials and involve occlusal and sub
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
Early Childhood Caries (ECC) Other Names: overall or 0.5 – 1.
25 mm on all planes of the
Baby Bottle Caries tooth.
Baby Bottle Tooth Decay Use a fine thin tapered diamond – create a
Nursing Caries feather edge margin 1-2 mm subgingivally.
Nursing Bottle Syndrome Make sure NO subgingival shoulders or ledges
Milk Bottle Syndrome remain.
Infant Tooth Decay FINGER PRESSURE ONLY!!
NO “SNAP FIT”
White Spots – Early ECC (check pictures) Load crowns with high performance luting
Moderate ECC (check pictures) cement (Ceramir), Resin Cement, RMGI or GI and
Advanced ECC (check pictures) passively seat crown.
Tack cure when applicable and begin final clean-
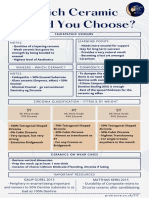
Zirconia Crowns up.
All Ceramic Crowns
Fully “WHITE” or Tooth Colored Posterior Stainless Steel Crown Restoration
PREFABRICATED Important Factors to be Considered When
Choosing the Restorative Material for the Child
Ceramic crowns especially designed for children.
Patient.
These crowns are made of solid ZIRCONIA, a
o Age
biocompatible material that has only been used
o Caries Risk
in high-end, adult cosmetic dentistry.
o Cooperation of the child
Composed entirely of one solid tooth-colored
material, they look extremely esthetically
Stainless Steel Crown vs. Amalgam
acceptable, both from the front view and on the
(8-year longitudinal clinical study)
inside of the mouth.
Survival Rate
Each crown is glazed with a tint of natural color,
o SSC – after 8 years – 80%
making them very smooth, shiny and
o Amalgam – after 1 year – 80%
impermeable to staining.
-After 4-5 years – 40%
(EZ-Pedo Co.)
Replacement Rate
o SSC – 4 out of 66 crowns had to be
Anterior Zirconia Crowns (Nu-Smile)
replaced.
Use a fine thin tapered diamond – create a
o Amalgam – 38 out of 66 amalgam
feather edge margin 1-2mm subgingivally.
restorations had to be re-filled.
Make sure NO subgingival shoulders or ledges
remain.
Reasons for replacement
Check fit and alignment. 1. Defects like fractures or marginal splitting.
Load crowns with high performance luting 2. Occurrence of new lesions or secondary
cement (Ceramir), Resin Cement, RMGI or GI and caries.
passively seat crown.
Tack cure when applicable and begin final clean- Stainless Steel Crowns
up. Indications:
o Primary molars requiring large
Zirconia Primary Posterior Crowns (NuSmile ZR Posterior multisurface restoration.
Crowns) o Children with rampant caries
Case Selection: o Teeth after pulp therapy
o Utilize anytime a standard SSC would be o Teeth with developmental anomalies like
used. those exhibiting hypoplastic anomalies,
o AVOID cases with severe crowding or malformed teeth.
severe mesial-distal space loss. o Fractured primary molars
o Some clinical crown remaining. o As an abutment for space maintainer
o Single crown placement is best for o In children with bruxism
beginning cases. o Restoration of hypoplastic young
Carefully PREP tooth SUPRAGINGIVALLY to avoid permanent teeth.
tissue MASCERATION. Reduce the tooth 20%
Types of Stainless Steel Crowns
Pre-Crimped (cervical is trimmed, see pics)
Pre-Festooned (occlusal portion is
festooned/polished)
Pre-Crimped and Festooned
Stainless Steel Crown Restoration
1.0 – 1.5 mm reduction occlusal (see pic)
1.0 mm subgingival reduction (see pic)
Trim cervical portion of SSC if there is blanching
of the gingiva.
If SSC rocks, check occlusal reduction if it is
adequate. If not, reduce more in the occlusal.
After occlusal reduction, check if there is
blanching again. If there is, repeat cervical
reduction of SSC.
Crimp the cervical crown margins.
Load crowns with high performance luting
cement (Ceramir), Resin Cement, RMGI or GI and
passively seat crown.
Tack cure when applicable and begin final clean-
up.
Yung iba na nakalagay dito sa SSC, sa picture ko
lang binase. Dun kasi sa ZIRCONIA crowns range
ang binigay niya sa reduction. Pero same lang ata.
Nagkataon lang iba sa picture
Correct niyo na lang if may mali THANKS!
Manarang <3
END OF LECTURE
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Semi-Permanent Restorations of Anterior Teeth PedoDokumen27 halamanSemi-Permanent Restorations of Anterior Teeth PedoFourthMolar.com100% (1)
- Od 1 PrelimDokumen4 halamanOd 1 Prelimnoelah salcedoBelum ada peringkat
- EnamelDokumen139 halamanEnamelA.Vikram ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- Crowns in Pediatric DentistryDokumen126 halamanCrowns in Pediatric Dentistrydrdeepikajoash16Belum ada peringkat
- 4-Enamel 2Dokumen12 halaman4-Enamel 2ahmedfawakh0Belum ada peringkat
- The Tooth-Coloured Inlay/Onlay Restorations - A ReviewDokumen7 halamanThe Tooth-Coloured Inlay/Onlay Restorations - A ReviewpoojaBelum ada peringkat
- The Art of FermentationDokumen2 halamanThe Art of Fermentationnatalia.levit1Belum ada peringkat
- Ss Crownss 2019 PDFDokumen48 halamanSs Crownss 2019 PDFAnkita AroraBelum ada peringkat
- Pediatric Preformed Metal Crowns - An Update Indi KontraDokumen4 halamanPediatric Preformed Metal Crowns - An Update Indi KontralulukzBelum ada peringkat
- Stainless Steel Crowns: IndicationsDokumen4 halamanStainless Steel Crowns: IndicationsMustafa TambawalaBelum ada peringkat
- Embryology: Odontogenesis Odontogenesis - Origin and Tissue Formation of TeethDokumen2 halamanEmbryology: Odontogenesis Odontogenesis - Origin and Tissue Formation of TeethRosette GoBelum ada peringkat
- JD v7 Id1143bbDokumen3 halamanJD v7 Id1143bbShaileshBelum ada peringkat
- Gypsum ProductsDokumen4 halamanGypsum ProductsJEANASHLEY PUNZALANBelum ada peringkat
- Treatment Planning For Restorations of Vital & Non-Vital TeethDokumen25 halamanTreatment Planning For Restorations of Vital & Non-Vital Teethjquin3Belum ada peringkat
- Department of Pediatric and Preventive DentistryDokumen25 halamanDepartment of Pediatric and Preventive DentistryAparna YadavBelum ada peringkat
- CDS Exam Cue CardsDokumen10 halamanCDS Exam Cue CardsMohammed KhalfanBelum ada peringkat
- Nterior Estorations: Choose A Job You Love and You Will Never Have To Work A Day in Your LifeDokumen20 halamanNterior Estorations: Choose A Job You Love and You Will Never Have To Work A Day in Your LifeABBelum ada peringkat
- Stainless Steel CrownsDokumen117 halamanStainless Steel CrownsRishuchawla100% (1)
- Operative 20 VeneersDokumen21 halamanOperative 20 VeneersInneke SutantoBelum ada peringkat
- Crowns Theory ClassDokumen39 halamanCrowns Theory ClassHrishida PBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 6, Amalgam Restorations (2) - Outline - HandoutDokumen7 halamanLecture 6, Amalgam Restorations (2) - Outline - HandoutJustDen09Belum ada peringkat
- Tooth Preparation For AmalgamDokumen84 halamanTooth Preparation For AmalgamParidhi GargBelum ada peringkat
- Enamel DR RiazDokumen76 halamanEnamel DR RiazDevaraj ManicamBelum ada peringkat
- All Ceramic Restorations PDFDokumen6 halamanAll Ceramic Restorations PDFMahdy AlShammariBelum ada peringkat
- Stainless Steel DSCDokumen7 halamanStainless Steel DSChrpt2hdrpwBelum ada peringkat
- All Ceramic Restorations (Why, When & HOW) : Dr. Mostafa NoorDokumen7 halamanAll Ceramic Restorations (Why, When & HOW) : Dr. Mostafa NoorAbdelrahman GalalBelum ada peringkat
- Kelas 1 Klasifikasi PreparasiDokumen40 halamanKelas 1 Klasifikasi Preparasidorayaki baeBelum ada peringkat
- Retainers in FPDDokumen77 halamanRetainers in FPDNiaz Ahammed100% (1)
- Handouts - Dr. Ahmed Leithey - Management of Endodontically Treated TeethDokumen8 halamanHandouts - Dr. Ahmed Leithey - Management of Endodontically Treated TeethAbdelfattah EL KadyBelum ada peringkat
- Crown 6 (Dralaa)Dokumen6 halamanCrown 6 (Dralaa)Abdullah EmadBelum ada peringkat
- Rebuilding Tooth Enamel and How Much of It Is Actually Possible .Dokumen9 halamanRebuilding Tooth Enamel and How Much of It Is Actually Possible .chandanpreetBelum ada peringkat
- Class I, II & VI Amalgam RestorationDokumen2 halamanClass I, II & VI Amalgam RestorationSahil SraBelum ada peringkat
- Curs 1 - LOC - ENGDokumen62 halamanCurs 1 - LOC - ENGmariaBelum ada peringkat
- Which Ceramic Should You Choose?: Feldspathic Veneers Notes: Learning PointsDokumen1 halamanWhich Ceramic Should You Choose?: Feldspathic Veneers Notes: Learning PointsJazBelum ada peringkat
- Ortopedie MaxDokumen71 halamanOrtopedie Maxainura antonBelum ada peringkat
- Occlusal Rims FabDokumen8 halamanOcclusal Rims FabSalon LamichhaneBelum ada peringkat
- Histologi GigiDokumen96 halamanHistologi GigichickenwingsBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 5, Amalgam Restorations (1) - Outline-HandoutDokumen6 halamanLecture 5, Amalgam Restorations (1) - Outline-HandoutJustDen09100% (1)
- Stainless Steel Crowns PDFDokumen4 halamanStainless Steel Crowns PDFLuciaTrinovenaLaseBelum ada peringkat
- My EnamelDokumen130 halamanMy EnamelKush PathakBelum ada peringkat
- Methods of Gaining SpaceDokumen39 halamanMethods of Gaining SpaceDr. Sushil KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Week 8 NotesDokumen5 halamanWeek 8 NotesDelaney IslipBelum ada peringkat
- Class V Cavity Preparation For Amaglam Indications: 1-CariesDokumen6 halamanClass V Cavity Preparation For Amaglam Indications: 1-CariesSamer AlRefaayBelum ada peringkat
- Biologic Considerations of Enamel Structure and Its Clinical Significance in Practice of Operative DentistryDokumen25 halamanBiologic Considerations of Enamel Structure and Its Clinical Significance in Practice of Operative DentistryNofal MundathoduBelum ada peringkat
- Crown Fixed ProsDokumen6 halamanCrown Fixed ProsMoamel AltaieBelum ada peringkat
- Amalgam Class ViDokumen14 halamanAmalgam Class ViJamaica Faith RamonBelum ada peringkat
- Indirect Intra Coronal RestorationsDokumen38 halamanIndirect Intra Coronal Restorationssamar yousif mohamedBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction and Enamel 24092014 Oral Histology and PhysiologyDokumen87 halamanIntroduction and Enamel 24092014 Oral Histology and PhysiologyJamal NaimBelum ada peringkat
- Laminates AND Veneers: Dr. Sakshi Rawal Department of Prosthodontics MDS II YearDokumen76 halamanLaminates AND Veneers: Dr. Sakshi Rawal Department of Prosthodontics MDS II Yearsapna100% (2)
- Diff Betwn Inlay and Amalgam CavityDokumen7 halamanDiff Betwn Inlay and Amalgam CavityVinisha Vipin Sharma100% (1)
- 125 Session 2Dokumen95 halaman125 Session 2ovov711Belum ada peringkat
- EnamelDokumen59 halamanEnamelMohammed rezgallahBelum ada peringkat
- Laminados de Porcelana 1Dokumen72 halamanLaminados de Porcelana 1Eduardo SáenzBelum ada peringkat
- Finish Lines in FPDDokumen28 halamanFinish Lines in FPDEazhil Raj100% (1)
- Demineralization and CariesDokumen5 halamanDemineralization and CariesDevin Chun Yue KwanBelum ada peringkat
- Esthetic Crowns For Primary Teeth A Review PDFDokumen7 halamanEsthetic Crowns For Primary Teeth A Review PDFSan SanBelum ada peringkat
- 2 - Human Dentition IntroDokumen71 halaman2 - Human Dentition IntroozyiamandsBelum ada peringkat
- MCQs in Oral Surgery: A comprehensive reviewDari EverandMCQs in Oral Surgery: A comprehensive reviewPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (6)
- "What Is A Concept Map?" by (Novak & Cañas, 2008)Dokumen4 halaman"What Is A Concept Map?" by (Novak & Cañas, 2008)WanieBelum ada peringkat
- KAHOOT - Assignment 4.1 Lesson PlanDokumen3 halamanKAHOOT - Assignment 4.1 Lesson PlanJan ZimmermannBelum ada peringkat
- A Study of Consumer Behavior in Real Estate Sector: Inderpreet SinghDokumen17 halamanA Study of Consumer Behavior in Real Estate Sector: Inderpreet SinghMahesh KhadeBelum ada peringkat
- Reliability Technoology For Submarine Repeaters PDFDokumen8 halamanReliability Technoology For Submarine Repeaters PDFbolermBelum ada peringkat
- Playwriting Pedagogy and The Myth of IntrinsicDokumen17 halamanPlaywriting Pedagogy and The Myth of IntrinsicCaetano BarsoteliBelum ada peringkat
- MasterMind 1 Unit 5 Extra LifeSkills Lesson 2Dokumen2 halamanMasterMind 1 Unit 5 Extra LifeSkills Lesson 2Hugo A FEBelum ada peringkat
- Research ProposalDokumen45 halamanResearch ProposalAaliyah Marie AbaoBelum ada peringkat
- Philosophy of Jnanadeva - As Gleaned From The Amrtanubhava (B.P. Bahirat - 296 PgsDokumen296 halamanPhilosophy of Jnanadeva - As Gleaned From The Amrtanubhava (B.P. Bahirat - 296 PgsJoão Rocha de LimaBelum ada peringkat
- United States Court of Appeals, Third CircuitDokumen1 halamanUnited States Court of Appeals, Third CircuitScribd Government DocsBelum ada peringkat
- Great Is Thy Faithfulness - Gibc Orch - 06 - Horn (F)Dokumen2 halamanGreat Is Thy Faithfulness - Gibc Orch - 06 - Horn (F)Luth ClariñoBelum ada peringkat
- Signalling in Telecom Network &SSTPDokumen39 halamanSignalling in Telecom Network &SSTPDilan TuderBelum ada peringkat
- K9G8G08B0B SamsungDokumen43 halamanK9G8G08B0B SamsungThienBelum ada peringkat
- Fire Art Case StudyDokumen15 halamanFire Art Case StudyKimberlyHerring100% (1)
- Writing - Hidden Curriculum v2 EditedDokumen6 halamanWriting - Hidden Curriculum v2 EditedwhighfilBelum ada peringkat
- Digital TransmissionDIGITAL TRANSMISSIONDokumen2 halamanDigital TransmissionDIGITAL TRANSMISSIONEla DerarajBelum ada peringkat
- Forever Living Presentation PDFDokumen34 halamanForever Living Presentation PDFCasey Rion100% (1)
- Case AnalysisDokumen25 halamanCase AnalysisGerly LagutingBelum ada peringkat
- E1979017519 PDFDokumen7 halamanE1979017519 PDFAnant HatkamkarBelum ada peringkat
- Tamil and BrahminsDokumen95 halamanTamil and BrahminsRavi Vararo100% (1)
- Thermal Systems: Introduction To Heat TransferDokumen33 halamanThermal Systems: Introduction To Heat TransferParas SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 INTRODUCTION TO PRESTRESSED CONCRETEDokumen15 halamanChapter 4 INTRODUCTION TO PRESTRESSED CONCRETEyosef gemessaBelum ada peringkat
- Anindya Anticipatory BailDokumen9 halamanAnindya Anticipatory BailYedlaBelum ada peringkat
- Re CrystallizationDokumen25 halamanRe CrystallizationMarol CerdaBelum ada peringkat
- BedDokumen17 halamanBedprasadum2321Belum ada peringkat
- Catastrophe Claims Guide 2007Dokumen163 halamanCatastrophe Claims Guide 2007cottchen6605100% (1)
- DND Homebrew Ideas V1 - The HomebreweryDokumen3 halamanDND Homebrew Ideas V1 - The HomebreweryKalazans CardialBelum ada peringkat
- Del Monte Usa Vs CaDokumen3 halamanDel Monte Usa Vs CaChe Poblete CardenasBelum ada peringkat
- 206f8JD-Tech MahindraDokumen9 halaman206f8JD-Tech MahindraHarshit AggarwalBelum ada peringkat
- Batch 4 PPTDokumen20 halamanBatch 4 PPTAbhi ShekBelum ada peringkat
- ''Want To Learn To Speak Latin or Greek This (2018) Summer''Dokumen10 halaman''Want To Learn To Speak Latin or Greek This (2018) Summer''ThriwBelum ada peringkat