FM Syllandsg Sept19 June20 PDF
Diunggah oleh
Breakfree Michigan (breakfree38)Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
FM Syllandsg Sept19 June20 PDF
Diunggah oleh
Breakfree Michigan (breakfree38)Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Financial
Management (FM)
Syllabus and study guide
September 2019 to June 2020
Financial Management (FM)
Summary of content
Introduction
1. Intellectual levels
2. Learning hours and educational
recognition
3. Guide to ACCA examination structure
4. Guide to ACCA examination
assessment
Financial Management syllabus
5. Relational diagram linking Financial
Management with other exams
6. Overall aim of the syllabus
7. Main capabilities
8. Rationale
9. Approach to examining the syllabus
10. The syllabus
Financial Management study
guide
11. Detailed study guide
© ACCA 2019-2020 All rights reserved.
Financial Management (FM)
1.Intellectual levels 2.Learning hours and
The syllabus is designed to
education
progressively broaden and deepen the recognition
knowledge, skills and professional
values demonstrated by the student on The ACCA qualification does not
their way through the qualification. prescribe or recommend any particular
number of learning hours for
The specific capabilities within the examinations because study and
detailed syllabuses and study guides are learning patterns and styles vary greatly
assessed at one of three intellectual or between people and organisations. This
cognitive levels: also recognises the wide diversity of
personal, professional and educational
Level 1: Knowledge and circumstances in which ACCA students
comprehension find themselves.
Level 2: Application and analysis
Level 3: Synthesis and evaluation As a member of the International
Federation of Accountants, ACCA seeks
Very broadly, these intellectual levels to enhance the education recognition of
relate to the three cognitive levels at its qualification on both national and
which the Applied Knowledge, international education frameworks, and
the Applied Skills and the Strategic with educational authorities and partners
Professional exams globally. In doing so, ACCA aims to
are assessed. ensure that its qualification is recognised
and valued by governments, regulatory
Each subject area in the detailed study authorities and employers across all
guide included in this document is given sectors. To this end, ACCA qualification
a 1, 2, or 3 superscript, denoting is currently recognised on the education
intellectual level, marked at the end of frameworks in several countries. Please
each relevant learning outcome. This refer to your national education
gives an indication of the intellectual framework regulator for further
depth at which an area could be information.
assessed within the examination.
However, while level 1 broadly equates Each syllabus is organised into main
with Applied Knowledge, level 2 subject area headings which are further
equates to Applied Skills and level 3 to broken down to provide greater detail on
Strategic Professional, some lower level each area.
skills can continue to be assessed as
the student progresses through each
level. This reflects that at each stage of
study there will be a requirement to
broaden, as well as deepen capabilities.
It is also possible that occasionally some
higher level capabilities may be
assessed at lower levels
© ACCA 2019-2020 All rights reserved.
Financial Management (FM)
3.Guide to ACCA answers, just as they would use these
tools in the workplace. These
examination assessment methods allow ACCA to
structure and focus on testing students’ technical and
application skills, rather than, for
delivery mode example, their ability to perform simple
calculations.
The structure and delivery mode of
examinations varies. Strategic Professional
Strategic Business Leader is ACCA’s
Applied Knowledge case study examination at Strategic
The Applied Knowledge examinations Professional and is examined as a
contain 100% compulsory questions to closed book exam of four hours,
encourage candidates to study across including reading, planning and
the breadth of each syllabus. These are reflection time which can be used
assessed by a two-hour computer based flexibly within the examination. There is
examination. no pre-seen information and all exam
related material, including case
Applied Skills information and exhibits are available
The Corporate and Business Law exam within the examination. Strategic
is a two-hour computer-based objective Business Leader is an exam based on
test examination for English and Global. one main business scenario which
For the format and structure of the involves candidates completing several
Corporate and Business Law or tasks within which additional material
Taxation variant exams, refer to the may be introduced. All questions are
‘Approach to examining the syllabus’ in compulsory and each examination will
section 9 of the relevant syllabus and contain a total of 80 technical marks and
study guide. 20 Professional Skills marks.
The other Strategic Professional exams
The other Applied Skills examinations are all of three hours and 15 minutes
(PM, TX-UK, FR, AA, and FM) duration. All contain two Sections and
contain a mix of objective and longer all questions are compulsory. These
type questions with a duration of three exams all contain four professional
hours for 100 marks. These are marks.
assessed by a three hour computer-
based exam. Prior to the start of each For September and December 2019
exam there will be time allocated for sessions, all Strategic Professional
students to be informed of the exam exams will be assessed by paper based
instructions. examination. From March 2020, these
exams will become available by
The longer (constructed response) computer based examination. More
question types used in the Applied Skills detail regarding what is available in your
exams (excluding Corporate and market will be on the ACCA global
Business Law) require students to website.
effectively mimic what they do in the
workplace. Students will need to use a With Applied Knowledge and Applied
range of digital skills and demonstrate Skills exams now assessed by computer
their ability to use spreadsheets and based exam, ACCA is committed to
word processing tools in producing their
© ACCA 2019-2020 All rights reserved.
Financial Management (FM)
continuing on its journey to assess all
exams within the ACCA Qualification
using this delivery mode.
The question types used at Strategic
Professional again require students to
effectively mimic what they would do in
the workplace and, with the move to
CBE, these exams again offer ACCA the
opportunity to focus on the application of
knowledge to scenarios, using a range
of tools – spreadsheets, word
processing and presentations - not only
enabling students to demonstrate their
technical and professional skills but also
their use of the technology available to
today’s accountants.
ACCA encourages students to take time
to read questions carefully and to plan
answers but once the exam time has
started, there are no additional
restrictions as to when candidates may
start producing their answer.
Time should be taken to ensure that all
the information and exam requirements
are properly read and understood.
The pass mark for all ACCA
Qualification examinations is 50%.
© ACCA 2019-2020 All rights reserved.
Financial Management (FM)
4.Guide to ACCA generally examine the Finance Act
which was passed in the previous year.
examination Therefore, exams falling in the period 1
assessment June 2019 to 31 March 2020 will
examine the Finance Act 2018 and any
ACCA reserves the right to examine any examinable legislation which is passed
learning outcome contained within the outside the Finance Act before 31 July
study guide. This includes knowledge, 2018.
techniques, principles, theories, and
concepts as specified. For the financial For additional guidance on the
accounting, audit and assurance, law examinability of specific tax rules and
and tax exams except where indicated the depth in which they are likely to be
otherwise, ACCA will publish examined, reference should be made to
examinable documents once a year to the relevant Finance Act article written
indicate exactly what regulations and by the examining team and published on
legislation could potentially be assessed the ACCA website.
within identified examination sessions.
None of the current or impending
For most examinations (not tax), devolved taxes for Scotland, Wales, and
regulations issued or legislation passed Northern Ireland is, or will be,
on or before 31 August annually, will be examinable.
examinable from 1 September of the
following year to 31 August of the year
after that. Please refer to the
examinable documents for the exam
(where relevant) for further information.
Regulation issued or legislation passed
in accordance with the above dates may
be examinable even if the effective date
is in the future.
The term issued or passed relates to
when regulation or legislation has been
formally approved.
The term effective relates to when
regulation or legislation must be applied
to an entity transactions and business
practices.
The study guide offers more detailed
guidance on the depth and level at
which the examinable documents will be
examined. The study guide should
therefore be read in conjunction with the
examinable documents list.
For UK tax exams, examinations falling
within the period 1 June to 31 March will
© ACCA 2019-2020 All rights reserved.
Financial Management (FM)
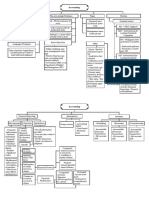
5.Relational diagram linking Financial Management
with other exams
This diagram shows links between this exam and other exams preceding or
following it. Some exams are directly underpinned by other exams such as
Advanced Financial Management by Financial Management. This diagram indicates
where students are expected to have underpinning knowledge and where it would
be useful to review previous learning before undertaking study.
6.Overall aim of the syllabus
This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide
detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session.
The aim of the syllabus is to develop the knowledge and skills expected of a finance
manager, in relation to investment, financing, and dividend policy decisions.
© ACCA 2019-2020 All rights reserved.
Financial Management (FM)
7.Main capabilities
On successful completion of this exam, candidates should be able to:
A Discuss the role and purpose of the financial management function
B Assess and discuss the impact of the economic environment on financial
management
C Discuss and apply working capital management techniques
D Carry out effective investment appraisal
E Identify and evaluate alternative sources of business finance
F Discuss and apply principles of business and asset valuations
G Explain and apply risk management techniques in business.
This diagram illustrates the flows and links between the main capabilities of the
syllabus and should be used as an aid to planning teaching and learning in a
structured way.
© ACCA 2019-2020 All rights reserved.
Financial Management (FM)
8.Rationale
The syllabus for Financial Management
is designed to equip candidates with the
skills that would be expected from a
finance manager responsible for the
finance function of a business. It
prepares candidates for more advanced
and specialist study in Advanced
Financial Management.
The syllabus, therefore, starts by
introducing the role and purpose of the
financial management function within a
business. Before looking at the three
key financial management decisions of
investing, financing, and dividend policy,
the syllabus explores the economic
environment in which such decisions are
made.
The next section of the syllabus is the
introduction of investing decisions. This
is done in two stages - investment in
(and the management of) working
capital and the appraisal of long-term
investments.
The next area introduced is financing
decisions. This section of the syllabus
starts by examining the various sources
of business finance, including dividend
policy and how much finance can be
raised from within the business. It also
looks at the cost of capital and other
factors that influence the choice of the
type of capital a business will raise. The
principles underlying the valuation of
business and financial assets, including
the impact of cost of capital on the value
of business, is covered next.
The syllabus finishes with an
introduction to, and examination of, risk
and the main techniques employed in
managing such risk.
© ACCA 2019-2020 All rights reserved.
Financial Management (FM)
9.Approach to
examining the
syllabus
The syllabus is assessed by a three-
hour computer based examination.
All questions are compulsory. The exam
will contain both computational and
discursive elements.
Some questions will adopt a
scenario/case study approach.
Prior to the start of the exam candidates
are given an extra 10 minutes to read
the exam instructions.
Section A of the computer-based exam
comprises 15 objective test questions of
2 marks each plus additional content as
per below.
Section B of the computer-based exam
comprises three questions each
containing five objective test questions
plus additional content as per below.
Section C of the exam comprises two
20-mark constructed response
questions. The two 20-mark questions
will mainly come from the working
capital management, investment
appraisal and business finance areas of
the syllabus. The section A and section
B questions can cover any areas of the
syllabus.
Candidates are provided with a formulae
sheet and tables of discount and annuity
factors.
© ACCA 2019-2020 All rights reserved.
Financial Management (FM)
10.The syllabus 2. Allowing for inflation and taxation in
DCF
3. Adjusting for risk and uncertainty in
A Financial management function investment appraisal
1. The nature and purpose of financial 4. Specific investment decisions (lease
management or buy, asset replacement, capital
rationing)
2. Financial objectives and relationship
with corporate strategy
E Business finance
3. Stakeholders and impact on
corporate objectives 1. Sources of, and raising, business
finance
4. Financial and other objectives in not-
for-profit organisations 2. Estimating the cost of capital
3. Sources of finance and their relative
B Financial management costs
environment
4. Capital structure theories and
1. The economic environment for practical considerations
business
5. Finance for small- and medium-
2. The nature and role of financial sized entities (SMEs)
markets and institutions
3. The nature and role of money F Business valuations
markets
1. Nature and purpose of the valuation
of business and financial assets
C Working capital management
2. Models for the valuation of shares
1. The nature, elements and
importance of working capital 3. The valuation of debt and other
financial assets
2. Management of inventories,
accounts receivable, accounts 4. Efficient market hypothesis (EMH)
payable and cash and practical considerations in the
valuation of shares
3. Determining working capital needs
and funding strategies
G Risk management
D Investment appraisal 1. The nature and types of risk and
approaches to risk management
1. Investment appraisal techniques
© ACCA 2019-2020 All rights reserved.
Financial Management (FM)
2. Causes of exchange rate differences
and interest rate fluctuations
3. Hedging techniques for foreign
currency risk
4. Hedging techniques for interest rate
risk
© ACCA 2019-2020 All rights reserved.
Financial Management (FM)
11.Detailed study guide i) ratio analysis, using appropriate
ratios such as return on
capital employed, return on
A Financial management equity, earnings per share and
dividend per share
function
ii) changes in dividends and share
prices as part of total
1. The nature and purpose of
shareholder return.
financial management
e) Explain ways to encourage the
a) Explain the nature and purpose of
achievement of stakeholder
financial management.[1]
objectives, including: [2]
i) managerial reward schemes
b) Explain the relationship between such as share options and
financial management and financial performance-related pay
and management accounting.[1] ii) regulatory requirements such as
corporate governance codes of
2. Financial objectives and the best practice and stock
relationship with corporate exchange listing regulations.
strategy
4. Financial and other objectives in
a) Discuss the relationship between not-for-profit organisations
financial objectives, corporate
objectives and corporate strategy.[2] a) Discuss the impact of not-for-profit
status on financial and other
objectives.[2]
b) Identify and describe a variety of
financial objectives, including: [2] b) Discuss the nature and importance
i) shareholder wealth maximisation of Value for Money as an objective
ii) profit maximisation in not-for-profit organisations.[2]
iii) earnings per share growth.
c) Discuss ways of measuring the
achievement of objectives in not-for-
3. Stakeholders and impact on
profit organisations.[2]
corporate objectives
a) Identify the range of stakeholders
B Financial management
and their objectives. [2]
environment
b) Discuss the possible conflict 1. The economic environment for
between stakeholder objectives. [2] business
c) Discuss the role of management in a) Identify and explain the main
meeting stakeholder objectives, macroeconomic policy targets.[1]
including the application of agency
theory.[2] b) Define and discuss the role of fiscal,
monetary, interest rate and
d) Describe and apply ways of exchange rate policies in achieving
measuring achievement of corporate macroeconomic policy targets.[1]
objectives including:[2]
© ACCA 2019-2020 All rights reserved.
Financial Management (FM)
c) Explain how government economic b) Explain the role of banks and other
policy interacts with planning and financial institutions in the operation
decision-making in business.[2] of the money markets.[2]
d) Explain the need for, and the c) Explain the characteristics and role
interaction with, planning and of the principal money market
decision-making in business of: [1] instruments:[2]
i) competition policy i) interest-bearing instruments
ii) government assistance for ii) discount instruments
business iii) derivative products.
iii) green policies
iv) corporate governance C Working capital
regulation.[2] management
2. The nature and role of financial
markets and institutions 1. The nature, elements and
importance of working capital
a) Identify the nature and role of money
and capital markets, both nationally a) Describe the nature of working
and internationally.[2] capital and identify its elements.[1]
b) Explain the role of financial b) Identify the objectives of working
intermediaries.[1] capital management in terms of
liquidity and profitability, and discuss
c) Explain the functions of a stock the conflict between them.[2]
market and a corporate bond
market.[2] c) Discuss the central role of working
capital management in financial
d) Explain the nature and features of management.[2]
different securities in relation to the
risk/return trade-off.[2] 2. Management of inventories,
accounts receivable, accounts
3. The nature and role of money payable and cash
markets
a) Explain the cash operating cycle and
a) Describe the role of the money
the role of accounts payable and
markets in:[1]
accounts receivable.[2]
i) providing short-term liquidity to
the private sector and the public b) Explain and apply relevant
sector accounting ratios, including: [2]
i) current ratio and quick ratio
ii) providing short-term trade ii) inventory turnover ratio, average
finance collection period and average
payable period
iii) allowing an organisation to
iii) sales revenue/net working
manage its exposure to foreign
capital ratio.
currency risk and interest rate
risk. c) Discuss, apply and evaluate the use
of relevant techniques in managing
inventory, including the Economic
© ACCA 2019-2020 All rights reserved.
Financial Management (FM)
Order Quantity model and Just-in- i) the length of the working capital
Time techniques.[2] cycle and terms of trade
ii) an organisation’s policy on the
d) Discuss, apply and evaluate the use level of investment in current
of relevant techniques in managing assets
accounts receivable, including: iii) the industry in which the
i) assessing creditworthiness [1] organisation operates.
ii) managing accounts receivable [1]
iii) collecting amounts owing [1] b) Describe and discuss the key factors
iv) offering early settlement in determining working capital
discounts [2] funding strategies, including:[2]
v) using factoring and invoice i) the distinction between
discounting [2] permanent and fluctuating
vi) managing foreign accounts current assets
receivable.[2] ii) the relative cost and risk of short-
term and long-term finance
e) Discuss and apply the use of iii) the matching principle
relevant techniques in managing iv) the relative costs and benefits of
accounts payable, including: aggressive, conservative and
i) using trade credit effectively [1] matching funding policies
ii) evaluating the benefits of v) management attitudes to risk,
early settlement and bulk previous funding decisions and
purchase discounts [2] organisation size.[1]
iii) managing foreign accounts
payable.[1]
D Investment appraisal
f) Explain the various reasons for
holding cash, and discuss and apply 1. Investment appraisal techniques
the use of relevant techniques in
managing cash, including:[2] a) Identify and calculate relevant cash
i) preparing cash flow forecasts to flows for investment projects.[2]
determine future cash flows and
cash balances b) Calculate payback period and
ii) assessing the benefits of discuss the usefulness of payback
centralised treasury as an investment appraisal
management and cash control method.[2]
iii) cash management models, such
as the Baumol model and the c) Calculate discounted payback and
Miller-Orr model discuss its usefulness as an
iv) investing short-term. investment appraisal method.[2]
3. Determining working capital d) Calculate return on capital
needs and funding strategies employed (accounting rate of
return) and discuss its usefulness
a) Calculate the level of working capital as an investment appraisal
investment in current assets and method.[2]
discuss the key factors determining
this level, including:[2] e) Calculate net present value and
discuss its usefulness as an
investment appraisal method.[2]
© ACCA 2019-2020 All rights reserved.
Financial Management (FM)
f) Calculate internal rate of return and ii) adjusted payback [1]
discuss its usefulness as an iii) risk-adjusted discount rates. [2]
investment appraisal
method.[2] 4. Specific investment decisions
(Lease or buy, asset
g) Discuss the superiority of replacement, capital rationing)
discounted cash flow (DCF)
methods over non-DCF methods.[2] a) Evaluate leasing and borrowing to
buy using the before- and after-tax
h) Discuss the relative merits of NPV costs of debt.[2]
and IRR.[2]
b) Evaluate asset replacement
2. Allowing for inflation and decisions using equivalent annual
taxation in DCF cost and equivalent annual
benefit.[2]
a) Apply and discuss the real-terms
and nominal-terms approaches to c) Evaluate investment decisions
investment appraisal.[2] under single-period capital
rationing, including:[2]
b) Calculate the taxation effects of
relevant cash flows, including the i) the calculation of profitability
tax benefits of tax-allowable indexes for divisible investment
depreciation and the tax liabilities of projects
taxable profit.[2] ii) the calculation of the NPV of
combinations of non-divisible
c) Calculate and apply before- and investment projects
after-tax discount rates.[2] iii) a discussion of the reasons for
capital rationing.
3. Adjusting for risk and uncertainty
in investment appraisal E Business finance
a) Describe and discuss the difference 1. Sources of, and raising, business
between risk and uncertainty in finance
relation to probabilities and
increasing project life.[2]
a) Identify and discuss the range of
short-term sources of finance
b) Apply sensitivity analysis to
available to businesses, including:[2]
investment projects and discuss the
i) overdraft
usefulness of sensitivity analysis in
ii) short-term loan
assisting investment decisions.[2]
iii) trade credit
iv) lease finance.
c) Apply probability analysis to
investment projects and discuss the
b) Identify and discuss the range of
usefulness of probability analysis in
long-term sources of finance
assisting investment decisions.[2]
available to businesses, including:[2]
i) equity finance
d) Apply and discuss other techniques
ii) debt finance
of adjusting for risk and uncertainty
iii) lease finance
in investment appraisal, including:
iv) venture capital.
i) simulation [1]
© ACCA 2019-2020 All rights reserved.
Financial Management (FM)
c) Identify and discuss methods of i) application of the dividend
raising equity finance, including:[2] growth model and discussion of
i) rights issue its weaknesses
ii) placing ii) explanation and discussion of
iii) public offer systematic and unsystematic
iv) stock exchange listing. risk
iii) relationship between portfolio
d) Identify and discuss methods of theory and the capital asset
raising short- and long-term pricing model (CAPM)
Islamic finance, including[1] iv) application of the CAPM, its
assumptions, advantages and
i) major differences between disadvantages.
Islamic finance and the other
forms of business finance. b) Estimating the cost of debt:
ii) the concept of riba (interest) and i) irredeemable debt
how returns are made by ii) redeemable debt
Islamic financial securities. iii) convertible debt
iii) Islamic financial instruments iv) preference shares
available to businesses v) bank debt.
including:
i) murabaha (trade credit) c) Estimating the overall cost of capital
ii) ijara (lease finance) including:[2]
iii) mudaraba equity finance) i) distinguishing between average
iv) sukuk (debt finance) and marginal cost of capital
v) musharaka (venture ii) calculating the weighted average
capital). cost of capital (WACC) using
(note: calculations are not required) book value and market value
weightings.
e) Identify and discuss internal
sources of finance, including:[2] 3. Sources of finance and their
i) retained earnings relative costs
ii) increasing working capital
management efficiency a) Describe the relative risk-return
iii) the relationship between relationship and the relative costs of
dividend policy and the financing equity and debt.[2]
decision
iv) the theoretical approaches to, b) Describe the creditor hierarchy and
and the practical influences on, its connection with the relative costs
the dividend decision, including of sources of finance.[2]
legal constraints, liquidity,
shareholder expectations and c) Identify and discuss the problem of
alternatives to cash dividends. high levels of gearing.[2]
d) Assess the impact of sources of
2. Estimating the cost of capital finance on financial position,
financial risk and shareholder
a) Estimate the cost of equity wealth using appropriate measures,
including:[2] including:[2]
© ACCA 2019-2020 All rights reserved.
Financial Management (FM)
i) ratio analysis using statement of b) Describe the nature of the financing
financial position gearing, problem for small businesses in
operational and financial gearing, terms of the funding gap, the
interest coverage ratio and other maturity gap and inadequate
relevant ratios security.[2]
ii) cash flow forecasting
iii) leasing or borrowing to buy. c) Explain measures that may be taken
to ease the financing problems of
e) Impact of cost of capital on SMEs, including the responses of
investments including:[2] government departments and
i) the relationship between financial institutions.[1]
company value and cost of
capital. d) Identify and evaluate the financial
ii) the circumstances under which impact of sources of finance for
WACC can be used in SMEs, including sources already
investment appraisal referred to in syllabus section E1
iii) the advantages of the CAPM and also [2]
over WACC in determining a i) Business angel financing
project-specific cost of capital. ii) Government assistance
iv) the application of CAPM in iii) Supply chain financing
calculating a project-specific iv) Crowdfunding / peer-to-peer
discount rate. funding.
4. Capital structure theories and
practical considerations
F Business valuations
a) Describe the traditional view of 1. Nature and purpose of the
capital structure and its valuation of business and
assumptions.[2] financial assets
b) Describe the views of Miller and a) Identify and discuss reasons for
Modigliani on capital structure, both valuing businesses and financial
without and with corporate taxation, assets.[2]
and their assumptions.[2]
b) Identify information requirements for
c) Identify a range of capital market valuation and discuss the limitations
imperfections and describe their of different types of information.[2]
impact on the views of Miller and
Modigliani on capital structure.[2] 2. Models for the valuation of shares
d) Explain the relevance of pecking a) Discuss and apply asset-based
order theory to the selection of valuation models, including:[2]
sources of finance.[1] i) net book value (statement of
financial position) basis
5. Finance for small and medium ii) net realisable value basis
sized entities (SMEs) iii) net replacement cost basis.
a) Describe the financing needs of b) Discuss and apply income-based
small businesses.[2] valuation models, including:[2]
i) price/earnings ratio method
© ACCA 2019-2020 All rights reserved.
Financial Management (FM)
ii) earnings yield method. a) Describe and discuss different types
of foreign currency risk:[2]
c) Discuss and apply cash flow-based i) translation risk
valuation models, including:[2] ii) transaction risk
i) dividend valuation model and the iii) economic risk.
dividend growth model
ii) discounted cash flow basis. b) Describe and discuss different types
of interest rate risk:[1]
3. The valuation of debt and other i) gap exposure
financial assets ii) basis risk.
a) Discuss and apply appropriate 2. Causes of exchange rate
valuation methods to:[2] differences and interest rate
i) irredeemable debt fluctuations
ii) redeemable debt
iii) convertible debt a) Describe the causes of exchange
iv) preference shares. rate fluctuations, including:
i) balance of payments [1]
4. Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH) ii) purchasing power parity theory [2]
and practical considerations in iii) interest rate parity theory [2]
the valuation of shares iv) four-way equivalence.[2]
a) Distinguish between and discuss b) Forecast exchange rates using:[2]
weak form efficiency, semi-strong i) purchasing power parity
form efficiency and strong form ii) interest rate parity.
efficiency.[2]
c) Describe the causes of interest rate
b) Discuss practical considerations in fluctuations, including: [2]
the valuation of shares and i) structure of interest rates and
businesses, including:[2] yield curves
i) marketability and liquidity of ii) expectations theory
shares iii) liquidity preference theory
ii) availability and sources of iv) market segmentation.
information
iii) market imperfections and pricing 3. Hedging techniques for foreign
anomalies currency risk
iv) market capitalisation.
a) Discuss and apply traditional and
c) Describe the significance of investor basic methods of foreign currency
speculation and the explanations of risk management, including:
investor decisions offered by i) currency of invoice [1]
behavioural finance.[1] ii) netting and matching [2]
iii) leading and lagging [2]
iv) forward exchange contracts [2]
G Risk Management v) money market hedging [2]
vi) asset and liability management.[1]
1. The nature and types of risk and
approaches to risk management
© ACCA 2019-2020 All rights reserved.
Financial Management (FM)
b) Compare and evaluate traditional
methods of foreign currency risk
management.[2]
c) Identify the main types of foreign
currency derivatives used to hedge
foreign currency risk and explain
how they are used in hedging.[1]
(No numerical questions will be set on
this topic)
4. Hedging techniques for interest
rate risk
a) Discuss and apply traditional and
basic methods of interest rate risk
management, including:
i) matching and smoothing [1]
ii) asset and liability management [1]
iii) forward rate agreements.[2]
b) Identify the main types of interest
rate derivatives used to hedge
interest rate risk and explain how
they are used in hedging.[1]
(No numerical questions will be set on
this topic)
© ACCA 2019-2020 All rights reserved.
Financial Management (FM)
Summary of changes to Financial Management (FM)
ACCA periodically reviews its qualification syllabuses so that they fully meet the
needs of stakeholders such as employers, students, regulatory and advisory bodies
and learning providers.
Amendments /additions
There have been no amendments to the Financial Management (FM) study guide
from the 2018 – 2019 study guide.
© ACCA 2019-2020 All rights reserved.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Performance Management (PM) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen20 halamanPerformance Management (PM) : Syllabus and Study GuideЛюба ИвановаBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Management (PM) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen20 halamanPerformance Management (PM) : Syllabus and Study GuideЛюба ИвановаBelum ada peringkat
- Financial Reporting (FR) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen19 halamanFinancial Reporting (FR) : Syllabus and Study GuideDenzil FBelum ada peringkat
- Taxation - United Kingdom (TX-UK) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen26 halamanTaxation - United Kingdom (TX-UK) : Syllabus and Study GuideChandraBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Business Reporting (SBR) (UK) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen18 halamanStrategic Business Reporting (SBR) (UK) : Syllabus and Study GuidedeltaeagleBelum ada peringkat
- Taxation TX (MYS) SyllandSG Dec 2019 - Sep 2020 FINAL PDFDokumen25 halamanTaxation TX (MYS) SyllandSG Dec 2019 - Sep 2020 FINAL PDFSarah See0% (1)
- Financial Management (FM) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen19 halamanFinancial Management (FM) : Syllabus and Study GuideAbir AllouchBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Taxation - United Kingdom (ATX-UK) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen26 halamanAdvanced Taxation - United Kingdom (ATX-UK) : Syllabus and Study GuideJonathan GillBelum ada peringkat
- Taxation - Pakistan (TX-PKN) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen31 halamanTaxation - Pakistan (TX-PKN) : Syllabus and Study GuideHassan KhawajaBelum ada peringkat
- F5 Performance Management PDFDokumen19 halamanF5 Performance Management PDFmuhammad saadBelum ada peringkat
- SBL - Sept 19-June 20 - 021019 PDFDokumen25 halamanSBL - Sept 19-June 20 - 021019 PDFDevendra GonsalvesBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Business Leader (SBL) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen25 halamanStrategic Business Leader (SBL) : Syllabus and Study GuideCường Lê TựBelum ada peringkat
- Financial Reporting (FR) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen18 halamanFinancial Reporting (FR) : Syllabus and Study GuidePatricio Villegas JungeBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Audit and Assurance (AAA) (INT) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen21 halamanAdvanced Audit and Assurance (AAA) (INT) : Syllabus and Study GuideIssa BoyBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Business Reporting (SBR) (UK) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen18 halamanStrategic Business Reporting (SBR) (UK) : Syllabus and Study GuideMohammad MohamudBelum ada peringkat
- FM - Sept 22-June 23 SG FinalDokumen20 halamanFM - Sept 22-June 23 SG FinalIshmealBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Audit and Assurance (AAA) (UK) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen21 halamanAdvanced Audit and Assurance (AAA) (UK) : Syllabus and Study Guidepallavi hasandasaniBelum ada peringkat
- Accaafm SLDokumen21 halamanAccaafm SLRitesh KashyapBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Business Reporting (SBR-UK) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen19 halamanStrategic Business Reporting (SBR-UK) : Syllabus and Study GuideAlishaBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Financial Management (AFM) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen19 halamanAdvanced Financial Management (AFM) : Syllabus and Study GuideMy CaoBelum ada peringkat
- Taxation - United Kingdom (TX-UK) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen23 halamanTaxation - United Kingdom (TX-UK) : Syllabus and Study GuideAlex RomarioBelum ada peringkat
- Corporate and Business Law (LW-SGP) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen16 halamanCorporate and Business Law (LW-SGP) : Syllabus and Study GuideJonathan GillBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Business Reporting (Sbr-Int) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen19 halamanStrategic Business Reporting (Sbr-Int) : Syllabus and Study GuideRish RajBelum ada peringkat
- Corporate and Business Law (LW-ENG) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen16 halamanCorporate and Business Law (LW-ENG) : Syllabus and Study GuideHassan FarazBelum ada peringkat
- Financial Reporting (FR) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen21 halamanFinancial Reporting (FR) : Syllabus and Study GuideAbir KaushalBelum ada peringkat
- Corporate and Business Law (LW-GLO) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen16 halamanCorporate and Business Law (LW-GLO) : Syllabus and Study GuideChampion ShonahBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Management (PM) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen19 halamanPerformance Management (PM) : Syllabus and Study GuideDilli Ram PokhrelBelum ada peringkat
- SBR UK - Sept 22-June 23 - FinalDokumen19 halamanSBR UK - Sept 22-June 23 - FinalAbbishekBelum ada peringkat
- PM - Sept 22-June 23Dokumen19 halamanPM - Sept 22-June 23MILAND SAVINGS &LOANBelum ada peringkat
- PM - Sept 22-June 23 - Final Updated LW 28 - 4Dokumen19 halamanPM - Sept 22-June 23 - Final Updated LW 28 - 4Zampy AlisBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Business Reporting (SBR-INT) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen19 halamanStrategic Business Reporting (SBR-INT) : Syllabus and Study GuidendifrekeBelum ada peringkat
- LW GLO - Syll_SG Sept 23-Aug 24Dokumen16 halamanLW GLO - Syll_SG Sept 23-Aug 24S RaihanBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Business Leader (SBL) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen28 halamanStrategic Business Leader (SBL) : Syllabus and Study GuideProKiller270Belum ada peringkat
- SBR Uk Syllabusandstudyguide Sept23 June24Dokumen21 halamanSBR Uk Syllabusandstudyguide Sept23 June24tunlinoo.067433Belum ada peringkat
- Audit and Assurance (AA) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen19 halamanAudit and Assurance (AA) : Syllabus and Study Guidepallavi hasandasaniBelum ada peringkat
- Taxation - United Kingdom (TX-UK) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen27 halamanTaxation - United Kingdom (TX-UK) : Syllabus and Study Guidepallavi hasandasaniBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Audit and Assurance (AAA-INT) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen23 halamanAdvanced Audit and Assurance (AAA-INT) : Syllabus and Study GuideFatima HasanBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Business Leader (SBL) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen23 halamanStrategic Business Leader (SBL) : Syllabus and Study GuideJayendra KatariyaBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Taxation - United Kingdom (ATX-UK) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen23 halamanAdvanced Taxation - United Kingdom (ATX-UK) : Syllabus and Study GuideAnwar JumoortyBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Taxation - United Kingdom (ATX-UK) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen25 halamanAdvanced Taxation - United Kingdom (ATX-UK) : Syllabus and Study GuideIsavic AlsinaBelum ada peringkat
- Taxation (TX) - United Kingdom (UK)Dokumen27 halamanTaxation (TX) - United Kingdom (UK)Enkhbold DamdinsurenBelum ada peringkat
- TX-UK Syllabus - J22-M23 FinalDokumen27 halamanTX-UK Syllabus - J22-M23 FinalAcca BooksBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Audit and Assurance (AAA-INT) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen23 halamanAdvanced Audit and Assurance (AAA-INT) : Syllabus and Study GuideNehaBelum ada peringkat
- Taxation - Singapore (TX-SGP) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen18 halamanTaxation - Singapore (TX-SGP) : Syllabus and Study GuidesadasdBelum ada peringkat
- APM - Sept 22 - June 23 SG FinalDokumen20 halamanAPM - Sept 22 - June 23 SG FinalnothingBelum ada peringkat
- Corporate and Business Law (LW-ENG) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen15 halamanCorporate and Business Law (LW-ENG) : Syllabus and Study GuideAdeel Mukhtar EYBelum ada peringkat
- Corporate and Business Law (LW-GLO) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen16 halamanCorporate and Business Law (LW-GLO) : Syllabus and Study GuideNjeri TimothysBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Management (PM) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen20 halamanPerformance Management (PM) : Syllabus and Study GuideMaryam KazmiBelum ada peringkat
- Atx Uk Syllanstudyguide June22 March23Dokumen23 halamanAtx Uk Syllanstudyguide June22 March23Anish JainBelum ada peringkat
- LW ENG - Sept 22-Aug 23 FinalDokumen16 halamanLW ENG - Sept 22-Aug 23 FinalLuv MeBelum ada peringkat
- Corporate and Business Law (LW) - EnglishDokumen16 halamanCorporate and Business Law (LW) - EnglishEnkhbold Damdinsuren100% (1)
- Audit and Assurance (AA)Dokumen19 halamanAudit and Assurance (AA)Enkhbold DamdinsurenBelum ada peringkat
- tx-hkg-j23-d23 Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen18 halamantx-hkg-j23-d23 Syllabus and Study GuidemyheartfallsinnewyorkBelum ada peringkat
- TX-uk j23-m24 Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen25 halamanTX-uk j23-m24 Syllabus and Study Guidehunaid.ayeshaBelum ada peringkat
- Apm Syllabusandstudyguide Sept23 June24Dokumen19 halamanApm Syllabusandstudyguide Sept23 June24Myo NaingBelum ada peringkat
- Aaa-Int-Syllabusandstudyguide-Sept23-June24 - FINALDokumen23 halamanAaa-Int-Syllabusandstudyguide-Sept23-June24 - FINALabdullahdap9691Belum ada peringkat
- ATX MYS D23 To Sep 24 - FINALDokumen22 halamanATX MYS D23 To Sep 24 - FINALfengfa2000Belum ada peringkat
- Atx-Uk j23-m24 Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen23 halamanAtx-Uk j23-m24 Syllabus and Study GuideAnonymous MeBelum ada peringkat
- Atx-Hkg-J23-D23 Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen19 halamanAtx-Hkg-J23-D23 Syllabus and Study GuidemyheartfallsinnewyorkBelum ada peringkat
- List of Lending Institutions Shortlisted To Be Partners of MUDRA Bank Name Public Sector BanksDokumen6 halamanList of Lending Institutions Shortlisted To Be Partners of MUDRA Bank Name Public Sector BanksSANJAY SINGH RATHOREBelum ada peringkat
- Bank's Mudra Loan FormDokumen4 halamanBank's Mudra Loan FormRAM NAIDU CHOPPABelum ada peringkat
- Abhishek Soni: Curriculam Vitae Sub: - For Industrial Training Career ObjectiveDokumen2 halamanAbhishek Soni: Curriculam Vitae Sub: - For Industrial Training Career ObjectiveSANJAY SINGH RATHOREBelum ada peringkat
- Wages 1 Apr 16Dokumen4 halamanWages 1 Apr 16SANJAY SINGH RATHOREBelum ada peringkat
- 155743Dokumen1 halaman155743SANJAY SINGH RATHOREBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Management (PM) : Syllabus and Study GuideDokumen20 halamanPerformance Management (PM) : Syllabus and Study GuideSANJAY SINGH RATHOREBelum ada peringkat
- The Square and Cube of First 100 NumbersDokumen1 halamanThe Square and Cube of First 100 NumbersMOHD MOBEEN KHAN76% (42)
- Chapter 22 ArensDokumen12 halamanChapter 22 Arensrahmatika yaniBelum ada peringkat
- ESOPDokumen8 halamanESOPKiran GvBelum ada peringkat
- Branches and AgenciesDokumen10 halamanBranches and AgenciesSol Guimary0% (1)
- Sast Regulations, 2011Dokumen28 halamanSast Regulations, 2011Ekansh TiwariBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Business ImplementationDokumen3 halamanIntroduction To Business ImplementationRellie Castro100% (1)
- Corporate Social Responsibility and A Modern Firm CSR Leads TO Competitive Advantage AND Sustainable DevelopmentDokumen33 halamanCorporate Social Responsibility and A Modern Firm CSR Leads TO Competitive Advantage AND Sustainable DevelopmentdebashismeisterBelum ada peringkat
- Abhinay Saket & Associates: Source For Payment of DividendDokumen2 halamanAbhinay Saket & Associates: Source For Payment of DividendAbhinay KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Investing in Comp Etitive Methods: By: Fiona Caramba-Coker For: Dr. Fred DemiccoDokumen31 halamanInvesting in Comp Etitive Methods: By: Fiona Caramba-Coker For: Dr. Fred DemiccosusmritiBelum ada peringkat
- The Motley Fool Million Dollar PortfolioDokumen6 halamanThe Motley Fool Million Dollar Portfoliomvamsidhar0% (1)
- Ration Analysis: 7.3 Parties Interested in Ratio AnalysisDokumen17 halamanRation Analysis: 7.3 Parties Interested in Ratio AnalysisMuhammad NoumanBelum ada peringkat
- CGMA Business Partnering Report PDFDokumen28 halamanCGMA Business Partnering Report PDFmyt3169371Belum ada peringkat
- Final PPT of IndusInd BankDokumen14 halamanFinal PPT of IndusInd BanktruptiBelum ada peringkat
- Demerger - News - Bajaj - Auto PDFDokumen16 halamanDemerger - News - Bajaj - Auto PDFRavi ChandraBelum ada peringkat
- Commissioner of Internal Revenue v. Procter and Gamble G.R. L-66838Dokumen11 halamanCommissioner of Internal Revenue v. Procter and Gamble G.R. L-66838Dino Bernard LapitanBelum ada peringkat
- Week 4 Practice Questions 1Dokumen17 halamanWeek 4 Practice Questions 1Gabriel Abdillah100% (1)
- Aphria Class Action Amended Securities Fraud Complaint 5.28.19Dokumen90 halamanAphria Class Action Amended Securities Fraud Complaint 5.28.19Teri Buhl100% (1)
- Accounting Concept Maps 5Dokumen18 halamanAccounting Concept Maps 5Ashley Levy San Pedro100% (1)
- Examination About Investment 8Dokumen3 halamanExamination About Investment 8BLACKPINKLisaRoseJisooJennieBelum ada peringkat
- 1 CFA RC - Report & Appendix (National Economics University)Dokumen34 halaman1 CFA RC - Report & Appendix (National Economics University)Trần TùngBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Lessons On Business Longevity From The Oldest Company in The WorldDokumen3 halaman3 Lessons On Business Longevity From The Oldest Company in The WorldVhasco SiagianBelum ada peringkat
- wealthAR 2016 2017Dokumen160 halamanwealthAR 2016 2017sharkl123Belum ada peringkat
- Partnership Case Digest (1800 Teague vs. Martin-1816 Co Pitco Vs YuloDokumen20 halamanPartnership Case Digest (1800 Teague vs. Martin-1816 Co Pitco Vs YuloNhoj Liryc TaptagapBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Fundamentals Of: Accountancy, Business and Management IIDokumen23 halamanIntroduction To Fundamentals Of: Accountancy, Business and Management IIAlbert Gaddiel CobicoBelum ada peringkat
- Module 6 Agency ProblemsDokumen6 halamanModule 6 Agency ProblemsRod Jessen A. VillamorBelum ada peringkat
- NoticeDokumen4 halamanNoticejasmin coBelum ada peringkat
- Forms of Business Organization ComparisonDokumen18 halamanForms of Business Organization ComparisonEthan Manuel Del ValleBelum ada peringkat
- Accounting For Partnership and Corporation Solman Baysa Lupisan 2014 Chapter 9Dokumen17 halamanAccounting For Partnership and Corporation Solman Baysa Lupisan 2014 Chapter 9AlexanderJacobVielMartinezBelum ada peringkat
- Business Organizations Syllabus BreakdownDokumen13 halamanBusiness Organizations Syllabus Breakdowneeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeee50% (2)
- The Cost of Capital: Answers To Seleected End-Of-Chapter QuestionsDokumen9 halamanThe Cost of Capital: Answers To Seleected End-Of-Chapter QuestionsZeesun12Belum ada peringkat
- BNLIDokumen3 halamanBNLIsisalim nurBelum ada peringkat