Types of Unemployment
Diunggah oleh
Alexandra0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
14 tayangan2 halamanunemployment types.
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Iniunemployment types.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
14 tayangan2 halamanTypes of Unemployment
Diunggah oleh
Alexandraunemployment types.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
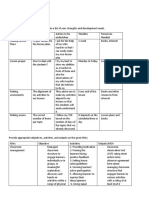
Types of unemployment
No. Types Explanation
1. Frictional / Search Occurs when people are in between jobs, entering or re-
unemployment entering the labour force.
Examples:
1. When students are looking for that first job.
2. When mothers are returning to the workforce.
3. When workers are fired, or
4. Laid off due to business-specific reasons.
2. Structural Arises due to structural changes in the economy of a country.
unemployment Examples:
1. When an industry’s replacement of machinery workers
with robots, those that don’t learn how to manage the
robots that replaced them need retraining for other jobs.
3. Cyclical Occurs when there is a lack of jobs because of a downswing
unemployment in a business cycle or a recession.
4. Seasonal Arises due to seasonal variation in the activities of particular
unemployment industries.
Industries where seasonal unemployment is common include
farming, tourism, and construction.
Examples:
1. Resort workers
2. Ski instructors,
3. Ice cream vendors
4. People who harvest crops.
5. Construction workers are laid off in the winter
6. School employees
5. Technological Occurs because of changes in the techniques of production.
unemployment Examples:
1. Workers who lack the adequate skills and education in
agricultural sector are laid off, in favour of modern
machinery.
6. Classical Caused when wages are ‘too’ high.
unemployment (Real Example,
wage / induced) 1. When workers themselves were blamed for not accepting
lower wages, or for asking for too high wages.
7. Long – term Occurs for those actively looking for a job for over 27 weeks.
unemployment
8. Underemployment People who work part-time, but they really want to work full
time if they could find a full-time job.
9. Regional Occurs when structural unemployment affects local areas of
unemployment an economy.
Agricultural, fishing, tourism, and other industries are
dependent on their geographical boundaries, the weather, and
consumer demand.
10. Voluntary Happens when a worker decides to leave a job because it is
unemployment no longer financially fulfilling.
Example:
1. Worker whose take-home pay is less than his cost of living.
11. Involuntary This is considered as a major problem than voluntary
unemployment employment because utility enhancing household choices are
reflected by voluntary unemployment.
12. Demand deficient Happens especially during a recession.
unemployment When there is a reduction in the demand for the company’s
products or services, they will most likely cut back too on their
production, making it unnecessary to retain a wide workforce
within the organization. In effect, workers are laid off.
13. Chronic Occurs when a country has unemployment for the long term.
unemployment Main reasons for chronic unemployment in underdeveloped
countries:
1. Low capital formation.
2. High population growth.
3. Under-utilization and primitive stage of technology.
14. Disguised / Hidden This is associated with abundant manpower, when employees
unemployment with very minimal or zero marginal productivity are removed,
it would not affect the total output.
15. Casual In industries where workers are appointed on day to day basis
unemployment such as agriculture, construction, catering etc. have more
chances for unemployment as they recruit employees on a
contract basis can be terminated at any time.
Once the contract of worker ends at specified time, then he
needs to find a new job in the same industry which has started
somewhere else.
Example, in film industry where the junior artist works at times
required.
16. Residual The unemployment that remains in periods of full employment,
unemployment as a result of those mentally, physically, or emotionally unfit to
work.
Examples:
1. Those people who are unable to work because of physical
or mental disabilities.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Sevis Id:: Department of Homeland SecurityDokumen3 halamanSevis Id:: Department of Homeland SecurityButssy100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Managing Organizational Change A Multiple Perspectives Approach 3rd Edition Palmer Test Bank DownloadDokumen24 halamanManaging Organizational Change A Multiple Perspectives Approach 3rd Edition Palmer Test Bank DownloadNancy Johnson100% (20)
- Handbook of Criminal Justice AdministrationDokumen520 halamanHandbook of Criminal Justice AdministrationGarry Grosse100% (3)
- ThaiDokumen1 halamanThaiAlexandraBelum ada peringkat
- The French AlphabetDokumen1 halamanThe French AlphabetAlexandraBelum ada peringkat
- ILTDokumen2 halamanILTAlexandraBelum ada peringkat
- Type WarehouseDokumen1 halamanType WarehouseAlexandraBelum ada peringkat
- ILTDokumen2 halamanILTAlexandraBelum ada peringkat
- Who Do U LoveDokumen1 halamanWho Do U LoveAlexandraBelum ada peringkat
- Bùhǎo Means 'Not Good'. ("Bu" Means 'No' or 'Not'.) ChineseDokumen3 halamanBùhǎo Means 'Not Good'. ("Bu" Means 'No' or 'Not'.) ChineseAlexandraBelum ada peringkat
- Differences Between Financial Accounting and Management AccountingDokumen2 halamanDifferences Between Financial Accounting and Management AccountingAlexandra100% (1)
- Momo LandDokumen2 halamanMomo LandAlexandraBelum ada peringkat
- Bùhǎo Means 'Not Good'. ("Bu" Means 'No' or 'Not'.) ChineseDokumen3 halamanBùhǎo Means 'Not Good'. ("Bu" Means 'No' or 'Not'.) ChineseAlexandraBelum ada peringkat
- How To Talk About The OrderDokumen7 halamanHow To Talk About The Orderqlipoth1100% (1)
- ASEAN Work Plan On Youth 2021 2025Dokumen94 halamanASEAN Work Plan On Youth 2021 2025Gregor CleganeBelum ada peringkat
- Arithmetic Lesson PlanDokumen3 halamanArithmetic Lesson PlanKennethBelum ada peringkat
- What It Means To Lead During A Crisis Schoenberg PDFDokumen26 halamanWhat It Means To Lead During A Crisis Schoenberg PDFsukandeBelum ada peringkat
- Rhea Mae A. Padrique: Learning Activity Sheets in NumeracyDokumen15 halamanRhea Mae A. Padrique: Learning Activity Sheets in NumeracyLea YaonaBelum ada peringkat
- NHS IGCSE Curriculum-HandbookDokumen83 halamanNHS IGCSE Curriculum-HandbookDavid Musila ToywaBelum ada peringkat
- Reading Lesson PlanDokumen3 halamanReading Lesson Planapi-284572865Belum ada peringkat
- Anwar Al-Awlaki - The Life of Muhammad - Mecca Period - Transcript CD 1Dokumen15 halamanAnwar Al-Awlaki - The Life of Muhammad - Mecca Period - Transcript CD 1Md Naim Khan0% (1)
- Curriculum Vitae (CV) A. Personals Details and ContactsDokumen5 halamanCurriculum Vitae (CV) A. Personals Details and ContactsYustina Sawa100% (1)
- Chap 1 RevisedzDokumen11 halamanChap 1 RevisedzJobel PostradoBelum ada peringkat
- Mba Unb PDFDokumen2 halamanMba Unb PDFustino imoBelum ada peringkat
- Toag 11 4 297b 27547 PDFDokumen1 halamanToag 11 4 297b 27547 PDFSulabh ShresthaBelum ada peringkat
- Overview of Complementary, Alternative & Integrative MedicineDokumen34 halamanOverview of Complementary, Alternative & Integrative MedicineSaad MotawéaBelum ada peringkat
- Krashen's Input Hypothesis and English Classroom TeachingDokumen4 halamanKrashen's Input Hypothesis and English Classroom TeachingNagato PainwareBelum ada peringkat
- Fs 2 DLP Different Characteristics of VertebratesDokumen4 halamanFs 2 DLP Different Characteristics of VertebratesTerrence Mateo100% (1)
- Economics of Development: Fall 2009Dokumen57 halamanEconomics of Development: Fall 2009Wonseok ParkBelum ada peringkat
- Solutions Manual To Accompany College Physics 0321822420 9780321822420Dokumen35 halamanSolutions Manual To Accompany College Physics 0321822420 9780321822420clowneryanileness.y7qst100% (55)
- ICDSDokumen30 halamanICDSMadhu Ranjan100% (1)
- Self-Instructional Manual (SIM) For Self-Directed Learning (SDL)Dokumen109 halamanSelf-Instructional Manual (SIM) For Self-Directed Learning (SDL)Jelly Joy CampomayorBelum ada peringkat
- Brochure PDFDokumen10 halamanBrochure PDFKhairatun NisaBelum ada peringkat
- Innovations in Education - Remote Teaching-V8 - 1-164 - WEB PDFDokumen164 halamanInnovations in Education - Remote Teaching-V8 - 1-164 - WEB PDFScot WakeleyBelum ada peringkat
- Lbs PHD Final LoresDokumen15 halamanLbs PHD Final LoressaurabhpontingBelum ada peringkat
- Memorandum of Understanding TemplateDokumen3 halamanMemorandum of Understanding TemplateMARY ROSE CAGUILLOBelum ada peringkat
- Open Water Diver Course Quizz and Exam Answer SheetDokumen3 halamanOpen Water Diver Course Quizz and Exam Answer SheetDilza SZ0% (1)
- TOS 10 - 1st PERIODICAL TESTDokumen1 halamanTOS 10 - 1st PERIODICAL TESTJemar Quezon LifanaBelum ada peringkat
- Miss Joanna Molabola Grade 6Dokumen6 halamanMiss Joanna Molabola Grade 6Jinky BracamonteBelum ada peringkat
- ReportDokumen1 halamanReportLina AbuzeidBelum ada peringkat