Mitral Stenosis With Multiple Left Atrium Thrombus: A Case Report
Diunggah oleh
Lisa ElfiraJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Mitral Stenosis With Multiple Left Atrium Thrombus: A Case Report
Diunggah oleh
Lisa ElfiraHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Mitral Stenosis with Multiple Left Atrium Thrombus: a Case Report
R. Afifah, L. Elfira, D. Reyhani, R. D. W. Satiti
Departement of Cardiology and Vascular Medicine
Faculty of Medicine Andalas University/ Dr. M Djamil General Hospital, Padang
Introduction:
Mitral stenosis is form of valvular disease characterized by narrowing of the mitral valve
orifice. This disease have high prevalency in developing countries. The most common cause
of mitral stenosis is rheumatic mitral stenosis which often associated with thrombus formation
in the left atrium (LA).
Case Illustration:
We reported the case of a 47-year-old female presented with progressive dyspnea with an
increased of severity within a month. She had a 7 month history of dyspnea d’effort, orthopnea
and paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea. From physical examinations found JVP 5+0 cm H2O,
inspection ictus cordis is not visible, palpation ictus cordis palpable 2 finger lateral LMCS 6th
ICS, percussion upper 2nd ICS, right right sternal border, left 2 finger lateral LMCS 6th ICS,
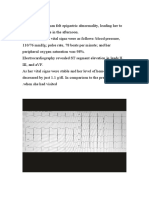
and auscultation S1 S2 ireguler, diastolic minimal 2/4 on apex, gallop (-), murmur (-). ECG
showed AF with QRS rate 90-100x, normal axis, QRS duration 0,08 s, inverted T wave at V4-
V6, no LVH or RVH was found. Echocardiography revealed mitral stenosis severe, AR mild,
TR mild e.c RHD, multiple thrombus on left atrial, and myxoma on interatrial septum with
pedicle. Patient then diagnosed with mitral stenosis with multiple left atrial thrombus. She
received UFH, furosemide, beta blocker, angiotensin receptor blocker, and warfarin during
hospitalization.
Discussion:
The cause of mitral stenosis are, rhemautic fever, scarring and fusion of valve apparatus, rarely
congenital, and female. Mitral stenosis in this patient probably caused by rheumatic fever.
Two-third of all patient with mitral stenosis are female. Dyspnea d’effort, orthopnea,
paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, and chest palpitation are useful signs that point to diagnostic.
Echocardiography will usually reveal the diagnostic.
Left Atrial thrombus caused by the primary antiphospholipid syndrome causing critical
functional mitral stenosis, usually seen in severe mitral stenosis caused by rheumatic fever
with atrial fibrillation. The clinical diagnosis of LA thrombus confirmed with
echocardiography with transesophageal approach as the best choice. It also helps in guiding
therapy designed to reduce thromboembolic risk.
Management of these patient are anticoagulant and thrombolytic therapy that help in the
prevention of its further progression. It can cause potential life threatening embolism and
circulatory collapse. Therefore these patient need urgent surgical removal of thrombus with
correction of the underlying cause and produces long term survival .
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Mitral Stenosis With Multiple Left Atrial TrombusDokumen1 halamanMitral Stenosis With Multiple Left Atrial TrombusfarhanomeBelum ada peringkat
- Aranda 1998Dokumen5 halamanAranda 1998Sarly FebrianaBelum ada peringkat
- UMS20 Medical 20 Short 20 and 20 Long 20 Cases 20 Record 20 Second 20 EditiDokumen132 halamanUMS20 Medical 20 Short 20 and 20 Long 20 Cases 20 Record 20 Second 20 EditiUchiha AnzarBelum ada peringkat
- Atrial Septal Defect: Dr. AninditaDokumen30 halamanAtrial Septal Defect: Dr. AninditaDadangNoviantoBelum ada peringkat
- L-R ShuntDokumen88 halamanL-R ShuntnanohaniwiekoBelum ada peringkat
- Cha Pte R 1 1 Con Ge Nit Al Heart DiseasesDokumen70 halamanCha Pte R 1 1 Con Ge Nit Al Heart DiseasessanjivdasBelum ada peringkat
- EBSTEIN'S ANOMALY Dhini - Maju 17 Juli 2014Dokumen29 halamanEBSTEIN'S ANOMALY Dhini - Maju 17 Juli 2014Azizi PranokoBelum ada peringkat
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDokumen6 halamanCongenital Heart DiseaseSamah KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Acn-IiDokumen80 halamanNursing Acn-IiMunawar100% (6)
- CHD by GetasewDokumen35 halamanCHD by Getasewshimeles teferaBelum ada peringkat
- Particularities of Scimitar Syndrome in Adult PatientsDokumen5 halamanParticularities of Scimitar Syndrome in Adult PatientsIJAR JOURNALBelum ada peringkat
- Atrial Septal Defects: Presented by Dr. Maysa Abdul Haq Directed by Dr. Ali Halabi Jordan Hospital 11-9-2005Dokumen36 halamanAtrial Septal Defects: Presented by Dr. Maysa Abdul Haq Directed by Dr. Ali Halabi Jordan Hospital 11-9-2005Joe JosephBelum ada peringkat
- Lutembacher's Syndrome - A Case ReportDokumen2 halamanLutembacher's Syndrome - A Case ReportInternational Journal of Clinical and Biomedical Research (IJCBR)Belum ada peringkat
- Mitral Valve...Dokumen4 halamanMitral Valve...ikbal rambalinoBelum ada peringkat
- Massive Pulmonary Embolism: A Case Report and Review of LiteratureDokumen6 halamanMassive Pulmonary Embolism: A Case Report and Review of LiteratureCATHERINE SIENNA ALTARBelum ada peringkat
- A Case of Ruptured Coronary Sinus of ValsalvaDokumen19 halamanA Case of Ruptured Coronary Sinus of Valsalvajb_blasurca100% (1)
- Aortic Atresia With Normally Developed Left Ventricle in A Young AdultDokumen3 halamanAortic Atresia With Normally Developed Left Ventricle in A Young AdultUmmul HidayahBelum ada peringkat
- Congenital Heart Disease Types and TreatmentsDokumen9 halamanCongenital Heart Disease Types and Treatmentsdr_alfuBelum ada peringkat
- Poster Presentation CCRA Malang 2014Dokumen3 halamanPoster Presentation CCRA Malang 2014alfarobi yogiBelum ada peringkat
- Case OneDokumen5 halamanCase Oneola nagarBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiac LipomDokumen4 halamanCardiac LipomCiprian MarianBelum ada peringkat
- K7 - Penyakit Jantung Katub-ANNDokumen38 halamanK7 - Penyakit Jantung Katub-ANNXeniel AlastairBelum ada peringkat
- RVOT Stenting in TOF PatientDokumen31 halamanRVOT Stenting in TOF PatientHannaTashiaClaudiaBelum ada peringkat
- Study of Correlation of Left Atrial Size and Atrial Fibrillation in Rheumatic Mitral Valve DiseaseDokumen3 halamanStudy of Correlation of Left Atrial Size and Atrial Fibrillation in Rheumatic Mitral Valve DiseaseRaita Faza AmaliaBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 17a VHDDokumen70 halamanLecture 17a VHDKishan ArrumugamBelum ada peringkat
- OutDokumen4 halamanOutMaria Zarah MenesesBelum ada peringkat
- Valvular heart disease diagnosis and treatmentDokumen38 halamanValvular heart disease diagnosis and treatmentDumora FatmaBelum ada peringkat
- The P Wave Holds CluesDokumen3 halamanThe P Wave Holds CluesJorge L Quispe LópezBelum ada peringkat
- A 38 Year Old Woman With Global Aphasia and MigraiDokumen4 halamanA 38 Year Old Woman With Global Aphasia and MigraiAchmad Dodi MeidiantoBelum ada peringkat
- Hipertensioni Arterial Sekondar AutosavedDokumen80 halamanHipertensioni Arterial Sekondar AutosavedFlo FlaBelum ada peringkat
- Vol08 1 87-88strDokumen2 halamanVol08 1 87-88strAry-Adhi PutrantoBelum ada peringkat
- 15 FullDokumen3 halaman15 FullAdi ParamarthaBelum ada peringkat
- Tetralogy of FallotDokumen3 halamanTetralogy of FallotKamal FauzeBelum ada peringkat
- Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT)Dokumen15 halamanHereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT)MarshallBelum ada peringkat
- Congenital Heart Disease in CatsDokumen5 halamanCongenital Heart Disease in Catsmatias66Belum ada peringkat
- Reversed Carvallo's SignDokumen3 halamanReversed Carvallo's SignrxrkBelum ada peringkat
- Anaesthetic Management of A Patient With Sick Sinus Syndrome For Exploratory LaparotomyDokumen4 halamanAnaesthetic Management of A Patient With Sick Sinus Syndrome For Exploratory LaparotomyaldyBelum ada peringkat
- Presented by Dona Mathew MSC (N) Govt - College of Nursing KottayamDokumen221 halamanPresented by Dona Mathew MSC (N) Govt - College of Nursing KottayamSumathi GopinathBelum ada peringkat
- 4 Valvular Heart Disease ICMPD (Autosaved)Dokumen30 halaman4 Valvular Heart Disease ICMPD (Autosaved)mus zaharaBelum ada peringkat
- Ortners Syndrome Case Series and Literature ReviewDokumen8 halamanOrtners Syndrome Case Series and Literature Reviewc5qwqy8vBelum ada peringkat
- Abstract Avrtcad2vd MuhammadakhiruddinDokumen2 halamanAbstract Avrtcad2vd MuhammadakhiruddinNanank Akhiruddin SyamsaBelum ada peringkat
- Pulmonary HypertensionDokumen63 halamanPulmonary HypertensionChrishan Shivanthan100% (4)
- Penyakit Katup Jantung: Dr. Tjatur Winarsanto SPPD Rs CiremaiDokumen59 halamanPenyakit Katup Jantung: Dr. Tjatur Winarsanto SPPD Rs CiremaianisamayaBelum ada peringkat
- Cardio Vascular DisordersDokumen62 halamanCardio Vascular DisordersUday Kumar100% (1)
- Congenital Heart DeseasesDokumen54 halamanCongenital Heart DeseasesAntony100% (1)
- Aortic Regurgitation: Causes, Symptoms, and TreatmentDokumen12 halamanAortic Regurgitation: Causes, Symptoms, and TreatmentSanjeet SahBelum ada peringkat
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus Presenting in Old Age: Chi-Ling Hang, and Thompson SullebargerDokumen3 halamanPatent Ductus Arteriosus Presenting in Old Age: Chi-Ling Hang, and Thompson SullebargerQuindo Isaac Santana FontalvoBelum ada peringkat
- The Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Valve SteDokumen6 halamanThe Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Valve SteNiarti Ulan SariBelum ada peringkat
- Kuliah Sem 4 '13 THX Intervensi KVDokumen39 halamanKuliah Sem 4 '13 THX Intervensi KVDesti Ratna PutriBelum ada peringkat
- Giant Left Atrial Appendage Aneurysm and Right Ventricular Diverticulum: A Very Rare AssociationDokumen4 halamanGiant Left Atrial Appendage Aneurysm and Right Ventricular Diverticulum: A Very Rare AssociationIJAR JOURNALBelum ada peringkat
- Case Report - An Uncommon Association of Ebstein's Anomaly and Rheumatic Mitral StenosisDokumen4 halamanCase Report - An Uncommon Association of Ebstein's Anomaly and Rheumatic Mitral StenosisRJMBelum ada peringkat
- A Case Report of Pseudo Wellenssyndrome in Patient WithpulmonaryembolismDokumen5 halamanA Case Report of Pseudo Wellenssyndrome in Patient WithpulmonaryembolismIJAR JOURNALBelum ada peringkat
- Pulmonary ValveDokumen4 halamanPulmonary ValveHaris RashidBelum ada peringkat
- Cureus 0010 00000002642 PDFDokumen6 halamanCureus 0010 00000002642 PDFMuhammad Nur Ardhi LahabuBelum ada peringkat
- Case ReportDokumen3 halamanCase ReportRuchi VatwaniBelum ada peringkat
- Valvular Heart Disease 2Dokumen46 halamanValvular Heart Disease 2Topea BogdanBelum ada peringkat
- Reentry Mechanism and Case Report of AVRT AblationDokumen2 halamanReentry Mechanism and Case Report of AVRT AblationNanank Akhiruddin SyamsaBelum ada peringkat
- Fetal Cardiology: A Practical Approach to Diagnosis and ManagementDari EverandFetal Cardiology: A Practical Approach to Diagnosis and ManagementBelum ada peringkat
- American Heart Association Guide to Auscultating the HeartDokumen42 halamanAmerican Heart Association Guide to Auscultating the HeartHananya ManroeBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture III Valvular Heart Diseases and EndocarditisDokumen43 halamanLecture III Valvular Heart Diseases and EndocarditisShahd KhatibBelum ada peringkat
- USMLE Step 1 NBME Top Concepts 2021Dokumen475 halamanUSMLE Step 1 NBME Top Concepts 2021dalia khamoBelum ada peringkat
- Role of Diagnostic Point-Of-Care Ultrasound in Preoperative Optimization: A Narrative ReviewDokumen5 halamanRole of Diagnostic Point-Of-Care Ultrasound in Preoperative Optimization: A Narrative ReviewdrsubramanianBelum ada peringkat
- MD8 ManualDokumen23 halamanMD8 ManualCESAR AUGUSTO ARIAS MOLANOBelum ada peringkat
- Short Answer: Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular SystemDokumen23 halamanShort Answer: Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular SystemRafael CastilloBelum ada peringkat
- Human Anat 2 Year Volume 4Dokumen122 halamanHuman Anat 2 Year Volume 4HARSHINI PANDIANBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Physiology of HeartDokumen69 halamanAnatomy and Physiology of HeartRitu Arun Kaushik100% (1)
- Acute Rheumatic FeverDokumen51 halamanAcute Rheumatic FeverFaedil Ichsan CiremaiBelum ada peringkat
- List of Video Lectures Available in Our Video BankDokumen25 halamanList of Video Lectures Available in Our Video Bankzeeshannajeeb80% (10)
- Cardiac Valve Replacement Surgery: Indications and GuidelinesDokumen25 halamanCardiac Valve Replacement Surgery: Indications and GuidelinesJamalul AdilBelum ada peringkat
- Medicine Revision E6.5 (Medicalstudyzone - Com)Dokumen209 halamanMedicine Revision E6.5 (Medicalstudyzone - Com)Diya B johnBelum ada peringkat
- 0505 1545 Kronzon - EchoDopplerAssessment NEWDokumen26 halaman0505 1545 Kronzon - EchoDopplerAssessment NEWekafithraBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of Mitral ValveDokumen6 halamanAnatomy of Mitral ValvesrhubanbabuBelum ada peringkat
- Essentials of Operative Cardiac SurgeryDokumen134 halamanEssentials of Operative Cardiac SurgeryJan CoveliersBelum ada peringkat
- Test Bank For Ekg Plain and Simple 3rd Edition EllisDokumen8 halamanTest Bank For Ekg Plain and Simple 3rd Edition Elliscanebrutalfniy66Belum ada peringkat
- Dr. Madaan Anatomy MCQ 2-2 (Muhadharaty)Dokumen46 halamanDr. Madaan Anatomy MCQ 2-2 (Muhadharaty)Joseph Brima SambaBelum ada peringkat
- HCMP Multimodality ImagingDokumen16 halamanHCMP Multimodality ImagingMathew McCarthyBelum ada peringkat
- Se Non-IschaemicDokumen40 halamanSe Non-IschaemicRui FonteBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiovascular NotebookDokumen140 halamanCardiovascular NotebookChantal CarnesBelum ada peringkat
- Equine Diagnostic Ultrasound PDFDokumen556 halamanEquine Diagnostic Ultrasound PDFSara Perez PastranaBelum ada peringkat
- Taibah University Interns: Umm Al - Qura University SLE Questions 2 EditionDokumen531 halamanTaibah University Interns: Umm Al - Qura University SLE Questions 2 EditionFammo Moidu100% (2)
- Standardized Echo Report Rev1Dokumen38 halamanStandardized Echo Report Rev1dgina8800100% (1)
- Cardiac MurmursDokumen53 halamanCardiac MurmursdrgashokBelum ada peringkat
- 02 Case Presentation On Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDokumen20 halaman02 Case Presentation On Rheumatic Heart Diseaseamit80% (10)
- Lvot o IiDokumen179 halamanLvot o Iimona300Belum ada peringkat
- First Description of TVD in Basset HoundDokumen4 halamanFirst Description of TVD in Basset HoundFlorencia SeneseBelum ada peringkat
- Pediatrics ImpDokumen233 halamanPediatrics Impملك عيسى100% (1)
- Mitral Stenosis Case ReportDokumen25 halamanMitral Stenosis Case ReportnindaBelum ada peringkat
- GL Valvole CardiacheDokumen49 halamanGL Valvole CardiacheAFA.BLSBelum ada peringkat