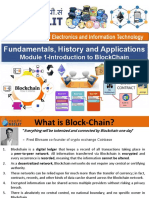
Cse1006 Blockchain-And-cryptocurrency-technologies TH 1.0 0 Blockchain and Cryptocurrency Technologies
Diunggah oleh
PRANAV KUMAR 17BEC04730 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
158 tayangan2 halamanhello
Judul Asli
Cse1006 Blockchain-And-cryptocurrency-technologies Th 1.0 0 Blockchain and Cryptocurrency Technologies
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Inihello
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
158 tayangan2 halamanCse1006 Blockchain-And-cryptocurrency-technologies TH 1.0 0 Blockchain and Cryptocurrency Technologies
Diunggah oleh
PRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473hello
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
L T P J C
CSE1006 Blockchain and Cryptocurrency Technologies
3 0 0 0 3
Pre-requisite This course has no formal pre-requisite Syllabus version
v. 1.0
Preamble
This course is an introductory course to Blockchain and crypto currency. It answers how Blockchain
and cryptocurrency work? What makes them different? How secure are they? How anonymous are
their users? What determines the price of them? Can cryptocurrencies be regulated? What might be
the future hold?
Course Objectives:
Understanding the mechanism of Blockchain and Cryptocurrency
Understanding why current implementations work
Understanding the necessary cryptographic background
Exploring applications of Blockchain to cryptocurrencies and beyond Understanding
limitations of current Blockchain
Introduction to recent research
Expected Course Outcome:
After successfully completing the course the student should be able to understand how
Blockchain works and the ideas, technologies sprouting from it.
Student Learning Outcomes (SLO): 9, 17
Module:1 Introduction to Cryptography & 5 hours SLO: 17
Cryptocurrencies
Cryptographic Hash Functions, Hash Pointers and Data Structures, Digital Signatures, Public Keys as
Identities, A Simple Cryptocurrency.
Module:2 How Blockchain Achieves & How to Store 7 hours SLO: 17
and Use
Decentralization-Centralization vs. Decentralization-Distributed consensus, Consensus without
identity using a block chain, Incentives and proof of work.
Simple Local Storage, Hot and Cold Storage, Splitting and Sharing Keys, Online Wallets and
Exchanges, Payment Services, Transaction Fees, Currency Exchange Markets.
Module:3 Mechanics of Bitcoin 5 hours SLO: 17
Bitcoin transactions, Bitcoin Scripts, Applications of Bitcoin scripts, Bitcoin blocks, The Bitcoin
network, Limitations and improvements.
Module:4 Bitcoin Mining 5 hours SLO: 17
The task of Bitcoin miners, Mining Hardware, Energy consumption and ecology, Mining pools,
Mining incentives and strategies
Module:5 Bitcoin and Anonymity 5 hours SLO: 9, 17
Anonymity Basics, How to De-anonymize Bitcoin, Mixing, Decentralized Mixing, Zerocoin and
Zerocash.
Module:6 Community, Politics, and Regulation 9 hours SLO: 9, 17
Consensus in Bitcoin, Bitcoin Core Software, Stakeholders: Who's in Charge, Roots of Bitcoin,
Governments Notice on Bitcoin, Anti Money Laundering Regulation, New York's BitLicense
Proposal.
Bitcoin as a Platform
Bitcoin as an Append only Log, Bitcoins as “Smart Property”, Secure Multi‐Party Lotteries in Bitcoin,
Bitcoin as Public Randomness, Source-Prediction Markets, and Real World Data Feeds.
Module:7 Altcoins and the Cryptocurrency Ecosystem 7 hours SLO: 17
Altcoins: History and Motivation, A Few Altcoins in Detail, Relationship Between Bitcoin and
Altcoins, Merge Mining-Atomic Cross‐chain Swaps-6 Bitcoin‐Backed Altcoins, “Side Chains”,
Ethereum and Smart Contracts.
Module:8 Recent Trends & applications 2 hours SLO: 17
Total Lecture hours: 45 hours
Text Book(s)
1. Narayanan, A., Bonneau, J., Felten, E., Miller, A., & Goldfeder, S. (2016). Bitcoin and
cryptocurrency technologies: a comprehensive introduction. Princeton University Press.
Reference Books
1. Antonopoulos, A. M. (2014). Mastering Bitcoin: unlocking digital cryptocurrencies. “O’Reilly Media,
Inc.".
2. Franco, P. (2014). Understanding Bitcoin: Cryptography, engineering and economics. John Wiley & Sons.
Mode of evaluation: CAT-1, CAT-2, FAT
Recommended by Board of Studies 10- 08-2018
Approved by Academic Council No. 52 Date 14-09-2018
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Trademen 4.2 - Cryptocurrency ExchangeDokumen6 halamanTrademen 4.2 - Cryptocurrency ExchangeRosa WatiBelum ada peringkat
- GE 301 Project FinalDokumen19 halamanGE 301 Project FinalAnonymous SzPXvT2fBelum ada peringkat
- Entity Data Generation Process by CQDokumen7 halamanEntity Data Generation Process by CQLuis Felipe MartinsBelum ada peringkat
- Top 20 Countries Found To Have The Most CybercrimeDokumen5 halamanTop 20 Countries Found To Have The Most CybercrimeAman Dheer KapoorBelum ada peringkat
- Cryptocurrency and BlockchainsssDokumen4 halamanCryptocurrency and BlockchainsssalexBelum ada peringkat
- Section 5.2 Cryptocurrency Beyond BitcoinDokumen20 halamanSection 5.2 Cryptocurrency Beyond BitcoinEmanBelum ada peringkat
- Bulihan, City of Malolos, Bulacan 3000: College of Information Technology and EngineeringDokumen12 halamanBulihan, City of Malolos, Bulacan 3000: College of Information Technology and EngineeringJefferson John JavenBelum ada peringkat
- A Note On Cryptocurrency Stabilisation Seigniorage SharesDokumen8 halamanA Note On Cryptocurrency Stabilisation Seigniorage SharesTomy1969Belum ada peringkat
- Cryptocurrency IEEE (Abstract)Dokumen1 halamanCryptocurrency IEEE (Abstract)Sharath Kumar KR100% (2)
- Jason Genge View On CryptocurrencyDokumen13 halamanJason Genge View On Cryptocurrencyjason simeon gengeBelum ada peringkat
- Cryptocurrency Optimization: 1 Import The LibrariesDokumen8 halamanCryptocurrency Optimization: 1 Import The LibrariesSamuel PeoplesBelum ada peringkat
- Cryptocurrencies Between Utopia and RealityDokumen9 halamanCryptocurrencies Between Utopia and RealityAvik BarmanBelum ada peringkat
- Bitcoin CryptocurrencyDokumen1 halamanBitcoin CryptocurrencyNikki KumariBelum ada peringkat
- Seminar On Crypto-Currency: LinkedinDokumen33 halamanSeminar On Crypto-Currency: LinkedinnitishBelum ada peringkat
- Cryptocurrency Public SpeakingDokumen8 halamanCryptocurrency Public SpeakingMuradBelum ada peringkat
- Blockchain Learning SyllabusDokumen4 halamanBlockchain Learning SyllabusHimanshu TomarBelum ada peringkat
- Zclassic - Investors GuideDokumen12 halamanZclassic - Investors GuideAnthonyBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 21 Cryptocurrency Article (ACCA + IFRS Box)Dokumen8 halamanChapter 21 Cryptocurrency Article (ACCA + IFRS Box)Kelvin Chu JYBelum ada peringkat
- Blockchain Technology Beyond Bitcoin: A Seminar Report OnDokumen30 halamanBlockchain Technology Beyond Bitcoin: A Seminar Report OnSanjeev KumarBelum ada peringkat
- @vtucode - in Module 4 2021 SchemeDokumen33 halaman@vtucode - in Module 4 2021 SchemeTejashree SathyaBelum ada peringkat
- Cryptocurrency Exchange DevelopmentDokumen10 halamanCryptocurrency Exchange DevelopmentTech analogBelum ada peringkat
- ReportDokumen74 halamanReportar15t0tleBelum ada peringkat
- Crypto Whitepaper SummaryDokumen2 halamanCrypto Whitepaper SummaryPJABelum ada peringkat
- Resistance Whitepaper v0.98 PDFDokumen58 halamanResistance Whitepaper v0.98 PDFSamuel McCullochBelum ada peringkat
- Top 5 Crypto Q4 2018Dokumen7 halamanTop 5 Crypto Q4 2018Petar SlapnicarBelum ada peringkat
- CRYPTOCURRENCYDokumen40 halamanCRYPTOCURRENCYRadhika JaiswalBelum ada peringkat
- Mini Project: Subject Code: 3IT31Dokumen3 halamanMini Project: Subject Code: 3IT31Foram Patel0% (1)
- Alternative Uses of The Blockchain I (2019!12!17 19-12-19 UTC)Dokumen42 halamanAlternative Uses of The Blockchain I (2019!12!17 19-12-19 UTC)nerviosus locusBelum ada peringkat
- CryptoDokumen24 halamanCryptoshivani.cs1995Belum ada peringkat
- Use of Blockchain Technology in General PDFDokumen15 halamanUse of Blockchain Technology in General PDFLoteriaespecialBelum ada peringkat
- AlliedCrowds Cryptocurrency in Emerging Markets DirectoryDokumen20 halamanAlliedCrowds Cryptocurrency in Emerging Markets DirectoryCrowdfundInsiderBelum ada peringkat
- Blockchain Seminar Report SummaryDokumen30 halamanBlockchain Seminar Report SummaryRishabh KumarBelum ada peringkat
- BITCOIN - The Final Piece of The Protocol PuzzleDokumen17 halamanBITCOIN - The Final Piece of The Protocol PuzzleeliforuBelum ada peringkat
- BBA (CA) - Networking Subject-Assignment and Important QuestionsDokumen12 halamanBBA (CA) - Networking Subject-Assignment and Important Questionsh.hersheys.here100% (1)
- Blockchain in 5 MinutesDokumen23 halamanBlockchain in 5 MinutesIsmael SotoBelum ada peringkat
- FYP PPT SubmissionDokumen15 halamanFYP PPT SubmissionJagesh SoniBelum ada peringkat
- Grayscale Ethereum Classic Investment Thesis March 2017Dokumen23 halamanGrayscale Ethereum Classic Investment Thesis March 2017Anonymous xD0eIUt9DFBelum ada peringkat
- Seminar Report BlockDokumen18 halamanSeminar Report BlockFieldartBelum ada peringkat
- M.Tech CSE 3rd Sem Introduction To Block Chain Unit 1 Lecture NotesDokumen39 halamanM.Tech CSE 3rd Sem Introduction To Block Chain Unit 1 Lecture Notesrupak05Belum ada peringkat
- BlockchainDokumen26 halamanBlockchainPranav BansalBelum ada peringkat
- Discovering Bitcoin's Public Topology and Influential NodesDokumen17 halamanDiscovering Bitcoin's Public Topology and Influential NodesNouman KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Ixc White Paper v3Dokumen7 halamanIxc White Paper v3IXC CoinBelum ada peringkat
- Feature Article Big Gae NewsDokumen7 halamanFeature Article Big Gae Newsapi-547871967Belum ada peringkat
- Crypto Currency: A Bright Future or Just A Fad?: IntroductionDokumen2 halamanCrypto Currency: A Bright Future or Just A Fad?: IntroductionAshi JainBelum ada peringkat
- Blockchain Notes B Tech AKTU by Krazy Kreation (Kulbhushan)Dokumen2 halamanBlockchain Notes B Tech AKTU by Krazy Kreation (Kulbhushan)RahulMondol100% (1)
- Blockchain Module1Dokumen10 halamanBlockchain Module1Pawan PrajapatiBelum ada peringkat
- 7 Best Tether Wallets to Store USDT SafelyDokumen12 halaman7 Best Tether Wallets to Store USDT SafelyHamid reza alaBelum ada peringkat
- Cryptocurrency: Name: Y.Raviteja HT - No: 17D91A05B8 Cse-4B 4 Year 1 SemesterDokumen14 halamanCryptocurrency: Name: Y.Raviteja HT - No: 17D91A05B8 Cse-4B 4 Year 1 SemesterMana PrabhasBelum ada peringkat
- Ripple CryptocurrencyDokumen5 halamanRipple CryptocurrencyRipple Coin NewsBelum ada peringkat
- Blockchain - The Accounting PerspectiveDokumen11 halamanBlockchain - The Accounting Perspectiveश्रेयंश राज नेपालBelum ada peringkat
- Synopsis NFT MarketplaceDokumen7 halamanSynopsis NFT MarketplaceRahul Ranjan SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Blockchain Technology FDP at IIIT DharwadDokumen517 halamanBlockchain Technology FDP at IIIT DharwadAnupam Tiwari100% (1)
- PointersDokumen62 halamanPointersRedheartkidBelum ada peringkat
- Beyond Binary Horizons Cryptocurrency and Blockchains Philosophical Odyssey in Uganda by Agatha MulungiDokumen91 halamanBeyond Binary Horizons Cryptocurrency and Blockchains Philosophical Odyssey in Uganda by Agatha MulungilubogoBelum ada peringkat
- How Can Cryptocurrency and Blockchain Technology Play A Role in Building Social and Solidarity FinanceDokumen25 halamanHow Can Cryptocurrency and Blockchain Technology Play A Role in Building Social and Solidarity FinanceP2P FoundationBelum ada peringkat
- Bank 2020 - Blockchain Powering The Internet of Value - Whitepaper PDFDokumen50 halamanBank 2020 - Blockchain Powering The Internet of Value - Whitepaper PDFIvan ArroyoBelum ada peringkat
- GitCoin (Cryptocurrency API) Project ReportDokumen65 halamanGitCoin (Cryptocurrency API) Project ReportShrey ChoubeyBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 BlockchainDokumen7 halamanChapter 2 BlockchainFarheen AkramBelum ada peringkat
- FinTech and Shadow Banks Loan ComparisonDokumen10 halamanFinTech and Shadow Banks Loan ComparisonHilmansyah AminBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Cardano Blockchain Step-By-Step GuideDokumen16 halamanWhat Is Cardano Blockchain Step-By-Step Guidesbosnic1Belum ada peringkat
- Summary of Paul Vigna & Michael J. Casey's The Truth MachineDari EverandSummary of Paul Vigna & Michael J. Casey's The Truth MachineBelum ada peringkat
- Computer - Communication: B.Tech-ECE Pranav Kumar 17BEC0473 Prof. Nandakumar SDokumen11 halamanComputer - Communication: B.Tech-ECE Pranav Kumar 17BEC0473 Prof. Nandakumar SPRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473Belum ada peringkat
- Computer - Communication: B.Tech-ECE Pranav Kumar 17BEC0473 Prof. Nandakumar SDokumen26 halamanComputer - Communication: B.Tech-ECE Pranav Kumar 17BEC0473 Prof. Nandakumar SPRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473100% (1)
- Computer - Communication: B.Tech-ECE Pranav Kumar 17BEC0473 Prof. Nandakumar SDokumen18 halamanComputer - Communication: B.Tech-ECE Pranav Kumar 17BEC0473 Prof. Nandakumar SPRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473Belum ada peringkat
- VL2019205005306 DaDokumen1 halamanVL2019205005306 DaPRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473Belum ada peringkat
- Computer - Communication: B.Tech-ECE Pranav Kumar 17BEC0473 Prof. Nandakumar SDokumen17 halamanComputer - Communication: B.Tech-ECE Pranav Kumar 17BEC0473 Prof. Nandakumar SPRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473Belum ada peringkat
- 17bec0813 VL2018195002346 Da02Dokumen5 halaman17bec0813 VL2018195002346 Da02PRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473Belum ada peringkat
- Batch No.: 14: School of Electronics EngineeringDokumen14 halamanBatch No.: 14: School of Electronics EngineeringPRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473Belum ada peringkat
- Computer - Communication: B.Tech-ECE Pranav Kumar 17BEC0473 Prof. Nandakumar SDokumen17 halamanComputer - Communication: B.Tech-ECE Pranav Kumar 17BEC0473 Prof. Nandakumar SPRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473Belum ada peringkat
- Circular 11 Course Registration Schedule Fall Semester 2020-2021Dokumen1 halamanCircular 11 Course Registration Schedule Fall Semester 2020-2021PRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473Belum ada peringkat
- Code of Conduct (10252)Dokumen1 halamanCode of Conduct (10252)PRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473Belum ada peringkat
- Low Power Floating Point Design AnalysisDokumen12 halamanLow Power Floating Point Design AnalysisPRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473Belum ada peringkat
- Technical 3Dokumen51 halamanTechnical 3PRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473Belum ada peringkat
- Circular 11 Course Registration Schedule Fall Semester 2020-2021Dokumen1 halamanCircular 11 Course Registration Schedule Fall Semester 2020-2021PRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473Belum ada peringkat
- Microcontrollers and Its Applications: Name: Atul Kumar Dwivedi Reg. No.-17BEC0813 Slot: G2Dokumen10 halamanMicrocontrollers and Its Applications: Name: Atul Kumar Dwivedi Reg. No.-17BEC0813 Slot: G2PRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473Belum ada peringkat
- Frequency Domain Techniques For Void Spectrum Detection in Cognitive Radio NetworkDokumen20 halamanFrequency Domain Techniques For Void Spectrum Detection in Cognitive Radio NetworkPRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473Belum ada peringkat
- School of Electronics Engineering: Fall Semester 2019-20 J Comp-Review III ECE4009 Wireless and Mobile CommunicationDokumen12 halamanSchool of Electronics Engineering: Fall Semester 2019-20 J Comp-Review III ECE4009 Wireless and Mobile CommunicationPRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473Belum ada peringkat
- Project Report: "Shannon Fannon Coding"Dokumen8 halamanProject Report: "Shannon Fannon Coding"PRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473Belum ada peringkat
- Technical 2Dokumen46 halamanTechnical 2PRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473Belum ada peringkat
- Technical 1Dokumen58 halamanTechnical 1PRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473Belum ada peringkat
- Cloze Passage and Para Jumbles: TCS Training Verbal AptitudeDokumen58 halamanCloze Passage and Para Jumbles: TCS Training Verbal AptitudePRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473Belum ada peringkat
- Vlsi System Design: FALL - (2019-20) Pranav Kumar 17BEC0473 Prof. Jagannadha Naidu K 15Dokumen12 halamanVlsi System Design: FALL - (2019-20) Pranav Kumar 17BEC0473 Prof. Jagannadha Naidu K 15PRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473Belum ada peringkat
- Reflecting BearDokumen1 halamanReflecting BearPRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473100% (1)
- Ethnus Consultancy Services Pvt. LtdDokumen33 halamanEthnus Consultancy Services Pvt. LtdPRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473Belum ada peringkat
- JPEG Image Compression Implemented in Matlab: by Michael ChristensenDokumen6 halamanJPEG Image Compression Implemented in Matlab: by Michael ChristensenChandan KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Gram Schmidt ProcessDokumen3 halamanGram Schmidt ProcessPRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473Belum ada peringkat
- Vlsi System Design: FALL - (2019-20) Pranav Kumar 17BEC0473 Prof. Jagannadha Naidu K 10Dokumen9 halamanVlsi System Design: FALL - (2019-20) Pranav Kumar 17BEC0473 Prof. Jagannadha Naidu K 10PRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473Belum ada peringkat
- Circular On Fall Semester 2020 - 2021 Course RegistrationDokumen1 halamanCircular On Fall Semester 2020 - 2021 Course RegistrationPRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473Belum ada peringkat
- Circular 9 Result Processing For Winter and Special Terms 2019-2020Dokumen1 halamanCircular 9 Result Processing For Winter and Special Terms 2019-2020PRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473Belum ada peringkat
- PageRank PDFDokumen1 halamanPageRank PDFPRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473Belum ada peringkat
- Software Development Cell: Faculty LoginDokumen3 halamanSoftware Development Cell: Faculty LoginPRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473Belum ada peringkat
- BTC 2014 Second Janch SuchiDokumen41 halamanBTC 2014 Second Janch SuchiChitransh Kumar SaxenaBelum ada peringkat
- DepEd Teacher 1 Job Application CertificationDokumen1 halamanDepEd Teacher 1 Job Application Certificationmarie joy CuestaBelum ada peringkat
- A Low-Cost Cross-Border Payment System Based On Auditable Cryptocurrency With Consortium Blockchain Joint Digital CurrencyDokumen14 halamanA Low-Cost Cross-Border Payment System Based On Auditable Cryptocurrency With Consortium Blockchain Joint Digital Currencypriya dharshiniBelum ada peringkat
- 1486047776053IizSOQRIHRhxh8qd PDFDokumen5 halaman1486047776053IizSOQRIHRhxh8qd PDFsanjeev raiBelum ada peringkat
- New Fast Recaptcha Free Coin Rotator AblDokumen20 halamanNew Fast Recaptcha Free Coin Rotator Ablalexbd9091Belum ada peringkat
- 2nd List SelectionDokumen2 halaman2nd List SelectionAyush AryanBelum ada peringkat
- 1k Real Hits (CALL OF DUTY)Dokumen85 halaman1k Real Hits (CALL OF DUTY)vieiradanilo00psBelum ada peringkat
- Car Insurance Management System ERDDokumen1 halamanCar Insurance Management System ERDFares MohamedBelum ada peringkat
- 03 Security User AuthenticationDokumen56 halaman03 Security User AuthenticationTrus AtholaBelum ada peringkat
- Accountstatementfrom01-10-2023To22-01-2024: AccountdetailsDokumen38 halamanAccountstatementfrom01-10-2023To22-01-2024: Accountdetailsr6540073Belum ada peringkat
- FollowingDokumen281 halamanFollowinggrazi.docemelBelum ada peringkat
- ARS FunctionsDokumen6 halamanARS FunctionskkuppachiBelum ada peringkat
- Web Security With SSLDokumen2 halamanWeb Security With SSLMangesh AbnaveBelum ada peringkat
- Notification BSFCSCL Asst Manager and Asst Accountant PostsDokumen2 halamanNotification BSFCSCL Asst Manager and Asst Accountant PostsJeshiBelum ada peringkat
- E-commerce Assignment Report FormatDokumen4 halamanE-commerce Assignment Report FormatyashBelum ada peringkat
- Bitcoin: Done By: Mohammad Ali Abu Shukur 20150269Dokumen10 halamanBitcoin: Done By: Mohammad Ali Abu Shukur 20150269Mohammad Abu-ShukurBelum ada peringkat
- Bank ChalanDokumen1 halamanBank ChalanDaniel Cyril50% (2)
- Final International Trade CourseworkDokumen3 halamanFinal International Trade CourseworkQuin RashellBelum ada peringkat
- NCVTCTSCertificateDokumen2 halamanNCVTCTSCertificateVINAY KUMAR BINDBelum ada peringkat
- MOOC Seminar Report CryptocurrencyDokumen14 halamanMOOC Seminar Report CryptocurrencyAbhi NavBelum ada peringkat
- Application For Change of Name or Address or AgeDokumen2 halamanApplication For Change of Name or Address or AgeHeera KardongBelum ada peringkat
- UPSRTC Ticket Booking ReturnDokumen1 halamanUPSRTC Ticket Booking ReturnNikhil Budhiraja100% (1)
- Alibaba's Taobao PT IBCDokumen16 halamanAlibaba's Taobao PT IBCnikkibalzarBelum ada peringkat
- Establishment Certificate for Lucky Stationary and OnlineDokumen1 halamanEstablishment Certificate for Lucky Stationary and OnlineLuckyGuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Userpass 1Dokumen12 halamanUserpass 1Benny SodikinBelum ada peringkat
- Statement XXXXXXXXXXX7726 29oct2022!19!58 UnlockedDokumen7 halamanStatement XXXXXXXXXXX7726 29oct2022!19!58 UnlockedS SelvarajBelum ada peringkat
- Aadhar Card AnnexDokumen1 halamanAadhar Card Annexvinu1175Belum ada peringkat
- NSC Assignment Mark Scheme Autumn 2018Dokumen5 halamanNSC Assignment Mark Scheme Autumn 2018Nixon MaharzanBelum ada peringkat
- TIN - Country Sheet RO enDokumen6 halamanTIN - Country Sheet RO encismaruBelum ada peringkat