Daily Lesson Log Grade 8 1.A
Diunggah oleh
Raymund AlilingHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Daily Lesson Log Grade 8 1.A
Diunggah oleh
Raymund AlilingHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
DAILY LESSON LOG (1st Quarter)
Teacher Learning Area Science
Teaching Dates Grade Level 8
Time
Section
I-OBJECTIVES
Content Standard: B. Performance Standard: Learning Competency/ies:
The learners demonstrate The learners should be able to develop a written (S8FE-Ia-15)
understanding of Newton’s three plan and implement a “Newton’s Olympics” The learners should be able to investigate
laws of motion and uniform the relationship between the amount of
circular motion. force applied and the mass of the object
to the amount of change in objects
motion.
Objectives:
1.Describe force.
2.Identify the different types of forces.
3.Identify the effects of forces on matter.
4.Distinguish between contact and
non-contact forces.
II-CONTENT Module I: FORCES AND MOTION
Lesson 1: BALANCED AND UNBALANCED FORCES
III- LEARNING RESOURCES
A. References
1. Teacher’s Guide Page/s : pp. 5 - 8
2. Learner’s Materials Pages : pp. 3
3. Textbook Pages:
4. Additional Materials from learning Resources(LR) portals:
B. Other Learning Resources https://goo.gl/images/oJnWpF
http://newtonowledge.weebly.com/newtons-first-law.html
https://goo.gl/images/1VDEvF
https://goo.gl/images/7TBmWe
https://goo.gl/images/GzNs8m
https://goo.gl/images/dgQTU2
IV- PROCEDURES
A. Reviewing previous lesson or presenting the Grouped the students and let them write ideas and concept about motion in the metacards
new lesson given to them. Let them post their output on the board.
Note:
Motion is a continuing change of place and position .The motion of an object is its
relative change in position with time. It is measured with respect to a point of
reference by an observer.
Change in motion is acceleration. Acceleration is caused by a net external force.
B. Establishing a purpose for the lesson -Introduce the new lesson (Let the learners read the objectives of the new lesson)
C. Presenting illustrative examples/instances of The teacher will place a ball or any object on top of a table and ask:
the lesson
a) Will this object move by itself?
b) How can we make this object move?
c) While it is moving, how can we make the object speed up or slow down?
d) How can make it stop?
e) How can we make it change its direction?
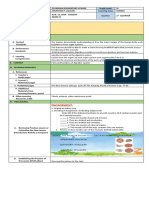
D. Discussing the new concepts and practicing Group the students and let them examine and analyze the pictures and tell something about
new skills#1 force.
( Group Activity Rubrics will be presented and revive by the students.)
1. Do you think they can move
1.
1. Do you think the foot can move
the ball?
2. Why you said so?
3. What causes the ball to move?
4. Does the picture shows contact
force? Noncontact force? Explain
2.
1. Do you think the elbow can move
the takyan?
2. Why you said so?
3. What causes the ball to move?
4. Does the picture shows contact
force? Noncontact force? Explain
3.
1. Do you think the cue ball can move
the balls?
2. Why you said so?
3. What causes the ball to move?
4. Does the picture shows contact
4. force? Noncontact force? Explain
Note:
A Force is commonly describe as the push and the pull which can set an object in
motion, speed it up or slow it down,or may even change direction of its motion.
A force acts on an object.A push and a pull on something-an object. Forces do not exist
in isolation from the object that experiences them.
A force has an agent-a specific identifiable cause.
A force is a vector quantity. If you push an object,you can push it either gently or very
hard. Similarly, you can push either left or right, up and down. To quantify push ,we
need to specify both magnitude and direction.
E. Discussing new concepts and new skills #2 Discuss force and its types.
There are four fundamental forces:
1.Gravitational Force- force attraction between two masses…such as the position of the stars
and the planet in the solar system
2.Electromagnetic Force- force that affect the charge particles…such as The electrons from the
clouds will travel towards the land –thunderbolts and the attraction between your hair and the
charge balloon.
3. Weak Force- the radioactive decay
4. Strong nuclear Force-binds protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.
The types of forces are:
1. tension force- the contact force exerted by a string or a wire which pulls an object.
2. normal force- force exerted by a surface (the agent) against an object that is pressing against
the surface
3. tensional force- the force that is transmitted through a rope, string or wire when pulled by
forces acting from opposite sides.
A force can either be contact or non-contact force. A contact force is present in surfaces in
contact with each othersuch as frictional force while non-contact force acts on bodies with
greater distances such as gravitational force, magnetic force and nuclear force.
The students can be provided a copy of figures below.
F. Developing mastery(guides formative A.Answer the following question
assessment) 1.What is force?
(a force is a push and a pull on an object)
2.What can a force do on an object?
(A force can make things move, stop, change state, change shape and change direction)
3.What are the four fundamental forces?
(the four fundamental forces are gravitational force, electromagnetic force, weak force and
strong nuclear force)
4.What are the types of forces?
(the types of forces are the tension force, normal force and frictional force)
5.How can you differentiate contact and non-contact force?
(a contact force is present in surfaces in contact with each other while non-contact force acts on
bodies with greater distances)
B. Present the following statement in class and ask the students if they agree or disagree with
them. Justify or explain their answer.
1. Force is needed to stop an object.
2. Force always results to motion.
3. Force can act even at a distance.
4. Objects have the tendency to remain at rest.
5. Objects have the tendency to resist change.
G. Making generalizations and abstractions Ask the student what they have learn in the lesson.
about the lesson What is force?
1. Force is a push or a pull.
2. Force can act on an object.
3. Force requires an agent
4. Force is a vector
What are the four fundamental forces:
1.Gravitational Force- force attraction between two masses…such as the position of the stars
and the planet in the solar system
2.Electromagnetic Force- force that affect the charge particles…such as The electrons from the
clouds will travel towards the land –thunderbolts and the attraction between your hair and the
charge balloon.
3. Weak Force- the radioactive decay
4. Strong nuclear Force-binds protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.
What are types of forces base on their agents are:
1. tension force- the contact force exerted by a string or a wire which pulls an object.
2. normal force- force exerted by a surface (the agent) against an object that is pressing against
the surface
3. tensional force- the force that is transmitted through a rope, string or wire when pulled by
forces acting from opposite sides.
What is the difference between contact and noncontact force?
A force can either be contact or non-contact force. A contact force is present in surfaces in
contact with each other such as frictional force while non-contact force acts on bodies with
greater distances such as gravitational force, magnetic force and nuclear force.
What can a force do on matter?
Force can make things move, stop, change state, change shape and change direction
H. Finding Practical applications of concepts Say: Now that you have learned that force can make things move, stop, change state, shape
and skills in daily living and direction. Can you give example where force had affected you and what kind of force is it?
I. Evaluation of Learning 1.Which best describes the effect of force on the motion of an object?
A. Force causes the object to change shape or mass.
B. Force causes the object to change speed or direction.
C. Force causes the object to experience gravity.
D. Force causes the object to experience balance.
2.A push and pull on an object is ___.
A. Weight
B. Force
C. friction
D. Matter
3. A force that acts where two objects touch
A. Contact Force
B. Non-contact Force
C. Balanced Force
D. Unbalanced Force
4. What is a force that opposes motion between objects that are in contact??
A. velocity
B. direction
C. friction
D. speed
J. Additional activities for application or
remediation
Study the pictures above.
1.What kind of force is shown contact or noncontact?
2. Make an arrow on the forces acting on the object?
V. REMARKS
VI. REFLECTION
A. No. of learners who earned B. No. of learners who scored C. Did the remedial lessons D. No. of learners who continue
80% in the evaluation: ________ below 80% who needs additional work?sNo. of learners who have to require remediation:
activities for remediation: _______ caught up with the lesson: ______ _________
E. Which of my teaching strategy/ies worked well? Why did these work?
F. What difficulties did I encounter with my principal or superior can help me solve?
G. What innovation or localized materials did I Use or discover which I wish to share with other teachers?
Date: ______________ Checked by: ____________________________________
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Science 8 1st Quarter DLL (By Day)Dokumen95 halamanScience 8 1st Quarter DLL (By Day)Rutchie LasqueBelum ada peringkat
- Science8 DLLDokumen156 halamanScience8 DLLMelanie Trinidad100% (1)
- Detailed Science Lesson Plan 1Dokumen2 halamanDetailed Science Lesson Plan 1Lorraine DonioBelum ada peringkat
- Science LESSON PLAN - Week 1Dokumen4 halamanScience LESSON PLAN - Week 1Kathryn Decena CentinalesBelum ada peringkat
- DLP Science g8Dokumen3 halamanDLP Science g8Krizzia Lovely Perez100% (1)
- 1ST Quarter Science Grade 8Dokumen99 halaman1ST Quarter Science Grade 8STEPHEN MILANBelum ada peringkat
- DLL Science 8Dokumen5 halamanDLL Science 8marichuBelum ada peringkat
- DLL Science 8 1st QuarterDokumen95 halamanDLL Science 8 1st QuarterRebecca Implica TuvillejaBelum ada peringkat
- DLL Science 8 1stDokumen119 halamanDLL Science 8 1stJESSAN DE PEDROBelum ada peringkat
- Science8 q1 Wk2Dokumen5 halamanScience8 q1 Wk2Lenie MateoBelum ada peringkat
- Force and Motion - Balance and Unbalance ForcesDokumen5 halamanForce and Motion - Balance and Unbalance ForcesJoanna Marie A. GripoBelum ada peringkat
- Science 8 Week 3 LP6Dokumen4 halamanScience 8 Week 3 LP6zandroBelum ada peringkat
- Division of Bohol Science 8 Quarter 1 - Week 3 (Day 1) : S8FE-Ia-16)Dokumen4 halamanDivision of Bohol Science 8 Quarter 1 - Week 3 (Day 1) : S8FE-Ia-16)Johndion A. RulomaBelum ada peringkat
- LP 3rd LawDokumen5 halamanLP 3rd LawRoan Joy BalbalosaBelum ada peringkat
- SCIENCE 8 Daily-Lesson-Log - 1ST DAYDokumen3 halamanSCIENCE 8 Daily-Lesson-Log - 1ST DAYRebecca Implica TuvillejaBelum ada peringkat
- Acceleration DLPDokumen3 halamanAcceleration DLPMark Anthony BesinalBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Exemplar Science Grade 8 Third CodocxDokumen4 halamanLesson Exemplar Science Grade 8 Third CodocxMa Carmela DanganBelum ada peringkat
- LESSON PLAN IN SCIENCE 8 (Second Demo)Dokumen3 halamanLESSON PLAN IN SCIENCE 8 (Second Demo)Lemuel Jr MitchaoBelum ada peringkat
- DLL Science 2017-2018Dokumen69 halamanDLL Science 2017-2018Luis100% (10)
- Development of Periodic Table Continuation DLP CalatravaDokumen6 halamanDevelopment of Periodic Table Continuation DLP CalatravaGwendolyn CalatravaBelum ada peringkat
- I. Objectives: Detailed Lesson Plan in Integrated Science 8Dokumen17 halamanI. Objectives: Detailed Lesson Plan in Integrated Science 8Janet PagulayanBelum ada peringkat
- Week 7 Grade8 DLL Edited NPFDokumen4 halamanWeek 7 Grade8 DLL Edited NPFMaám Rosemary B. LandanBelum ada peringkat
- DLL W3Dokumen7 halamanDLL W3JingjingAloComendadorBelum ada peringkat
- 11 08 19.co2Dokumen3 halaman11 08 19.co2ANGELIQUE DIAMALONBelum ada peringkat
- Bagay, Eurasia A. - DLP - Science 8 - Q3W3Dokumen2 halamanBagay, Eurasia A. - DLP - Science 8 - Q3W3asia bagayBelum ada peringkat
- Daily Lesson Log: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDokumen3 halamanDaily Lesson Log: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayKaren PolinarBelum ada peringkat
- 3rd COT DLPDokumen5 halaman3rd COT DLPCristine roqueroBelum ada peringkat
- Annotated COT 2Dokumen8 halamanAnnotated COT 2Tan QuimBelum ada peringkat
- DLL History of The Periodic TableDokumen14 halamanDLL History of The Periodic TableJann Kim MedenillaBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 8Dokumen14 halamanGrade 8Juliet Ileto Villaruel - Almonacid100% (1)
- LP CoT Science G8Dokumen2 halamanLP CoT Science G8Ramon Lord A. NerierBelum ada peringkat
- Earth ScienceDokumen4 halamanEarth ScienceHomemade BarquillosBelum ada peringkat
- Glenn's DLLDokumen6 halamanGlenn's DLLLovely Shiena C. AragoncilloBelum ada peringkat
- G8-Fidelity 1Dokumen4 halamanG8-Fidelity 1Emma T Sogo-anBelum ada peringkat
- Par Cot2 Lesson Plan (Autorecovered)Dokumen9 halamanPar Cot2 Lesson Plan (Autorecovered)Jeazel MosendoBelum ada peringkat
- DLP Sci8 W5-3Dokumen3 halamanDLP Sci8 W5-3Vanessa Joy SaavedraBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan About MatterDokumen4 halamanLesson Plan About MatterglaizaBelum ada peringkat
- Science 8 Q3 Week 4 - DLL BausinDokumen6 halamanScience 8 Q3 Week 4 - DLL Bausinsheryll BausinBelum ada peringkat
- Daily Lesson Log Science 8Dokumen5 halamanDaily Lesson Log Science 8NERISA S. SONIDOBelum ada peringkat
- Sci 8. DLL. Q1. W1 2Dokumen6 halamanSci 8. DLL. Q1. W1 2Marilou Cambronero SalazarBelum ada peringkat
- Infer That Waves Carry Energy : Group Rotations Are Valuable For Keeping The Whole Class EngagedDokumen10 halamanInfer That Waves Carry Energy : Group Rotations Are Valuable For Keeping The Whole Class EngagedRowena Sta MariaBelum ada peringkat
- COT - DLL - 2022 g8 Module 4Dokumen5 halamanCOT - DLL - 2022 g8 Module 4Chrisel Luat LopezBelum ada peringkat
- Regional Training of Teachers On The Critical Content of Science Grade 8Dokumen4 halamanRegional Training of Teachers On The Critical Content of Science Grade 8JADE L. SORZANO100% (1)
- Demo Lesson Plan AccelerationDokumen4 halamanDemo Lesson Plan Accelerationmarizel ortega100% (1)
- Republic of The Philippines: Department of Education Region IIIDokumen3 halamanRepublic of The Philippines: Department of Education Region IIIMichaelAbdonDomingoFavoBelum ada peringkat
- DLP For COT Round 3Dokumen7 halamanDLP For COT Round 3Karen PolinarBelum ada peringkat
- I. Objectives: (Write The LC Codes For Each)Dokumen8 halamanI. Objectives: (Write The LC Codes For Each)Cli P. ArmonioBelum ada peringkat
- Cot DLP Digestive System 1Dokumen4 halamanCot DLP Digestive System 1Jonathan Paguio Lalican Lpt100% (2)
- DLL Grade 8 WorkDokumen5 halamanDLL Grade 8 WorkIrish Joy Aguadera - NamuagBelum ada peringkat
- SCIENCE 8 Daily-Lesson-Log - 3rd DayDokumen3 halamanSCIENCE 8 Daily-Lesson-Log - 3rd DayRebecca Implica TuvillejaBelum ada peringkat
- DLP August 19,2019Dokumen2 halamanDLP August 19,2019Shane Catherine Besares100% (1)
- DLP G8 Q1 WK 3 D2 (12) JaneDokumen7 halamanDLP G8 Q1 WK 3 D2 (12) JaneCathy MoronioBelum ada peringkat
- Science 8 q1 w3Dokumen12 halamanScience 8 q1 w3Je-ann AcuBelum ada peringkat
- G8-Science-Daily Lesson Log DLL TemplateDokumen3 halamanG8-Science-Daily Lesson Log DLL TemplateDewson Pacudz100% (1)
- Science 8 q2 Wk2 Printed by TMTDokumen16 halamanScience 8 q2 Wk2 Printed by TMTgian triunfanteBelum ada peringkat
- 3rd Quarter DLP 11Dokumen4 halaman3rd Quarter DLP 11Jim Alesther LapinaBelum ada peringkat
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningDokumen8 halamanDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Instructional PlanningChona M. RosalitaBelum ada peringkat
- Daily Lesson Log Grade 8 1Dokumen4 halamanDaily Lesson Log Grade 8 1Ela Anjell AmparadoBelum ada peringkat
- q1 - DLL Day 1 Science 8Dokumen6 halamanq1 - DLL Day 1 Science 8Glemarie Joy EnriquezBelum ada peringkat
- Volcanic Eruption: Group 1Dokumen12 halamanVolcanic Eruption: Group 1Raymund AlilingBelum ada peringkat
- Daily Lesson Log Grade 8 37Dokumen2 halamanDaily Lesson Log Grade 8 37Raymund AlilingBelum ada peringkat
- Daily Lesson Log Grade 8 3bDokumen2 halamanDaily Lesson Log Grade 8 3bRaymund Aliling100% (2)
- Daily Lesson Log Grade 8 2aDokumen3 halamanDaily Lesson Log Grade 8 2aRaymund AlilingBelum ada peringkat
- Endogenic ProcessesDokumen33 halamanEndogenic ProcessesRaymund AlilingBelum ada peringkat
- Clothes and FashionDokumen2 halamanClothes and FashionRaymund AlilingBelum ada peringkat
- Jinyang Grade4 BDokumen31 halamanJinyang Grade4 BRaymund AlilingBelum ada peringkat
- Jinyang Grade4 BDokumen31 halamanJinyang Grade4 BRaymund AlilingBelum ada peringkat
- Jinyang Grade1Dokumen22 halamanJinyang Grade1Raymund AlilingBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Chapterwise Weightage - EAMCETDokumen2 halamanPhysics Chapterwise Weightage - EAMCETVenu GopalBelum ada peringkat
- Stress Distribution Around HolesDokumen1.008 halamanStress Distribution Around HolesffontanaBelum ada peringkat
- The Effect of Applied High Speed Balancing MethodDokumen16 halamanThe Effect of Applied High Speed Balancing MethodLong NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- PritiKotak (BARC) - Appln Miniature SPDokumen51 halamanPritiKotak (BARC) - Appln Miniature SPRamesh EthirajanBelum ada peringkat
- Kinematics 9702 Questions - 3Dokumen1 halamanKinematics 9702 Questions - 3Zeeshan AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1. Properties of SolidsDokumen14 halamanChapter 1. Properties of SolidsDeepak R BoradeBelum ada peringkat
- Wall Footing: Code ReferencesDokumen4 halamanWall Footing: Code ReferencesSupun Aravinda JayawardhaneBelum ada peringkat
- DIPPRDokumen8 halamanDIPPROmar AlmonteBelum ada peringkat
- CAESAR Load CaseDokumen15 halamanCAESAR Load Casevijayanmks100% (1)
- Latest Lifting LugDokumen8 halamanLatest Lifting Lugjagannadha varmaBelum ada peringkat
- BSc-Phys-Hon-CBCS (2020) PDFDokumen139 halamanBSc-Phys-Hon-CBCS (2020) PDFBikash DeyBelum ada peringkat
- Propellers NAME: A. Manish Kumar ROLLNO: 319106918066 Overlapping PropellersDokumen9 halamanPropellers NAME: A. Manish Kumar ROLLNO: 319106918066 Overlapping Propellersmanish alahariBelum ada peringkat
- Orbital MechanicsDokumen19 halamanOrbital MechanicsRajiv Vutukuri100% (2)
- Forces BookletDokumen14 halamanForces BookletDiana ArnoldBelum ada peringkat
- Tunnel Modeling in PLAXIS 3D: Richard Witasse, Principal Product ManagerDokumen12 halamanTunnel Modeling in PLAXIS 3D: Richard Witasse, Principal Product Managerclaudio pintoBelum ada peringkat
- B15 Vibrating StringDokumen4 halamanB15 Vibrating Stringconc oxygenBelum ada peringkat
- WWW - Ib.academy: Study GuideDokumen92 halamanWWW - Ib.academy: Study GuideHendrikEspinozaLoyolaBelum ada peringkat
- Solution: Chapter 5, Practice Problem 5/039Dokumen13 halamanSolution: Chapter 5, Practice Problem 5/039陳台Belum ada peringkat
- Pump Bypass ExampleDokumen4 halamanPump Bypass Exampleali aliBelum ada peringkat
- Angular Projectile MotionDokumen16 halamanAngular Projectile MotionwscienceBelum ada peringkat
- Diseño de Elementos en Tracción - LRFDDokumen263 halamanDiseño de Elementos en Tracción - LRFDAlejandro CardenasBelum ada peringkat
- New Version 3. Finite Element Simulation of Metal Cutting Using LS Dyna - Vishnu Vardhan Chandrasekaran (Vzc0009)Dokumen115 halamanNew Version 3. Finite Element Simulation of Metal Cutting Using LS Dyna - Vishnu Vardhan Chandrasekaran (Vzc0009)Kivanc SengozBelum ada peringkat
- Russian Code STAADDokumen34 halamanRussian Code STAADsriganesh07Belum ada peringkat
- Mse 255 Lecture 6Dokumen43 halamanMse 255 Lecture 6percydziksBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid Dynamics I M Usman HamidDokumen159 halamanFluid Dynamics I M Usman HamidNaik MuhamadBelum ada peringkat
- Presentasi Free VibrationDokumen48 halamanPresentasi Free VibrationadiBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 3heatengine PhysicDokumen3 halamanLab 3heatengine Physicapi-263500375Belum ada peringkat
- Axial Compressor SHEETDokumen2 halamanAxial Compressor SHEETpaulaBelum ada peringkat
- 7.prediction of Models On UhpcDokumen36 halaman7.prediction of Models On UhpcDarssni RavichandranBelum ada peringkat
- Sulit Dcc6213: Hydraulics and Hydrology / PksDokumen6 halamanSulit Dcc6213: Hydraulics and Hydrology / Pksmuhd haziqBelum ada peringkat