CH 2 How We See The Invisible World
Diunggah oleh
Isabella ChauDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
CH 2 How We See The Invisible World
Diunggah oleh
Isabella ChauHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Bio 15 Ch 2 How We See the Invisible World OS SG
Assigned reading: Introduction - Interactions of Light, Magnification, Resolution, and Contrast, Early Microscopes,
Brightfield Microscopes-Microscope Maintenance: Best Practices, Staining Microscopic Specimens - Flagella Staining
Key Tems:
Reflection van Leeuwenhoek. compound microscope objective lens ocular lens contrast
Absorbance interference oil immersion lens, Magnification. compound microscope
diaphragm. refraction resolution numerical aperture brightfield microscope
binocular objective lenses total magnification stage coarse focusing knob
fine focusing knob illuminator condenser lens staining fixation
wet mount smear simple staining differential stain mordant
counterstain gram-positive acid-fast stain gram-negative endospore
capsule staining Endospore staining flagella staining
1. Explain the difference between magnification and resolution.
2. Explain the difference between resolution and contrast.
3. Name two factors that affect resolution
4. Explain the difference between simple and compound microscopes.
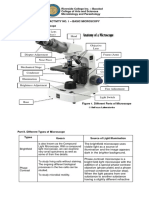
5. Be able to name the parts of the microscope in figure 2.12.
6. Why is immersion oil used and with which objective?
7. Explain why it is important to fix a specimen before viewing it under a light microscope.
8. Explain the difference between simple and differential staining.
9. Explain the role of Gram’s iodine in the Gram stain procedure.
10. Explain the role of alcohol in the Gram stain procedure.
11. What color are gram-positive and gram-negative cells, respectively, after the Gram stain procedure?
12. Why are acid-fast stains useful?
13. Is endospore staining an example of positive, negative, or differential staining?
14. What type of microscope do we use in the lab?
15. Explain the purpose of a smear and heat fixation in the preparation of a specimen for microscopic viewing.
16. Would a simple stain be a good technique to use when trying to determine the size of a bacterium? Why?
17. How do you determine the final magnification for an object you are looking at under the microscope?
18. What does it mean when a microscope has a resolution of 0.2nm?
19. If you built a light microscope having a total magnification of 5,000X, would it give you better, worse or the same
resolution as one that has a magnification of 1,000X? Why?
20. Why is fixing necessary for most staining procedures?
Review questions from Textbook: 1, 10, 12, 13, 16, 18, 20, 23, 24, 27, 28
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Lab 3Dokumen15 halamanLab 3aizen3881Belum ada peringkat
- F. Y. B. Sc. (Microbiology) Paper-II Question BankDokumen6 halamanF. Y. B. Sc. (Microbiology) Paper-II Question BankHaimil DeepKamal JoshiBelum ada peringkat
- Microscopy and Staining: LectureDokumen55 halamanMicroscopy and Staining: LectureDrYahia Al-Qoa'fyBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment For Microscopy, Staining, and ClassificationDokumen3 halamanAssignment For Microscopy, Staining, and ClassificationVia SongcalBelum ada peringkat
- Observing Microorganisms Through A MicroscopeSV PDFDokumen3 halamanObserving Microorganisms Through A MicroscopeSV PDFFelipe Andrés JorqueraBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Questions and Suggested SolutionsDokumen66 halamanBiology Questions and Suggested SolutionsEvansBelum ada peringkat
- Ch. 3 Observing Microorganisms Through A MicroscopeDokumen20 halamanCh. 3 Observing Microorganisms Through A MicroscopeYousef DosouqiBelum ada peringkat
- Bio 2 FinalDokumen12 halamanBio 2 FinalNovee Jane Arangote CeriñoBelum ada peringkat
- Microbiology and Microscopy Advanced: Seeing The Very SmallDokumen32 halamanMicrobiology and Microscopy Advanced: Seeing The Very SmallJasmine R. MaturanBelum ada peringkat
- Nanolithography and Device Fabrication: Fall 2020/2021 NilDokumen40 halamanNanolithography and Device Fabrication: Fall 2020/2021 NilRashail AshasBelum ada peringkat
- 2 Expt 1 Microscope Revised 2021Dokumen5 halaman2 Expt 1 Microscope Revised 2021Sam SamBelum ada peringkat
- Laboratory Lesson Activity No. 1 Introduction To The Light Microscope Guide Questions Variety of Light MicroscopeDokumen5 halamanLaboratory Lesson Activity No. 1 Introduction To The Light Microscope Guide Questions Variety of Light MicroscopeAbby LuceroBelum ada peringkat
- Labaratory QuestionsDokumen3 halamanLabaratory QuestionsIsabella SamsonBelum ada peringkat
- 2 Microscopy LabDokumen18 halaman2 Microscopy Lablux0008Belum ada peringkat
- By: Sunil Kumar: Important Questions From Ray OpticsDokumen3 halamanBy: Sunil Kumar: Important Questions From Ray OpticsNikhilesh PrasadBelum ada peringkat
- Activity 1 Microscopy and Slide PreparationmaddiDokumen5 halamanActivity 1 Microscopy and Slide PreparationmaddiIMMORTAL SOULBelum ada peringkat
- E290 Zool11 LaboratoryExerciseNo.1Dokumen4 halamanE290 Zool11 LaboratoryExerciseNo.1Ruth DiangBelum ada peringkat
- Concepts of Biology - Lab ManualDokumen43 halamanConcepts of Biology - Lab ManualUMMU MARDHIAH ABDUL HALIMBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 1 - MicrosDokumen9 halamanExperiment 1 - MicrosCOLLEEN GULLENBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Exercise 1 MICROSDokumen9 halamanLab Exercise 1 MICROSCrizzajen IsipBelum ada peringkat
- Microscopy Hand NotesDokumen10 halamanMicroscopy Hand NotesAmeeraBelum ada peringkat
- SBVC Microbiology Bio 270 Lab Manual 2022Dokumen137 halamanSBVC Microbiology Bio 270 Lab Manual 2022JiggaWhaaBelum ada peringkat
- Microscopy and StainingDokumen14 halamanMicroscopy and StainingEJ BarnuevoBelum ada peringkat
- Chem ProjectDokumen18 halamanChem ProjectRyan Joshi25% (4)
- Types of Coating Applied To Spectacle LensesDokumen4 halamanTypes of Coating Applied To Spectacle LensesSiva LoveBelum ada peringkat
- Bauer BSC3-3 Act2Dokumen3 halamanBauer BSC3-3 Act2John Vincent BauerBelum ada peringkat
- The Microscope: Summary of ExerciseDokumen18 halamanThe Microscope: Summary of Exerciserashmi_harryBelum ada peringkat
- Activity No. 1 The Use and Care of The MicroscopeDokumen7 halamanActivity No. 1 The Use and Care of The MicroscopeRheal P EsmailBelum ada peringkat
- Biology Lab Activity 1Dokumen6 halamanBiology Lab Activity 1Adrian Anthony Villaluz GasatayaBelum ada peringkat
- MicroscopesDokumen26 halamanMicroscopesKL JonesBelum ada peringkat
- ABRERA, Lucky Lynn R - Tools in Lab ACT-microparaDokumen9 halamanABRERA, Lucky Lynn R - Tools in Lab ACT-microparaLucky Lynn AbreraBelum ada peringkat
- Biochemical Engineering Lab ManualDokumen35 halamanBiochemical Engineering Lab ManualWazif Zakwan100% (1)
- Physics by Shahzad Ali CH 03016640404Dokumen2 halamanPhysics by Shahzad Ali CH 03016640404sajjad majeedBelum ada peringkat
- Module 1 MicrosDokumen8 halamanModule 1 MicrosmagwiBelum ada peringkat
- Laboratory-Activity-1 - Microscopy 2Dokumen5 halamanLaboratory-Activity-1 - Microscopy 2Khate CyrelleBelum ada peringkat
- MicroscopeDokumen4 halamanMicroscopeLili13Belum ada peringkat
- Introduction To The Microscope VIRTUAL LABDokumen5 halamanIntroduction To The Microscope VIRTUAL LABTianjia MaoBelum ada peringkat
- VIVA QuestionsDokumen3 halamanVIVA Questionsshruti chauhanBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDokumen18 halamanChemistry Investigatory ProjectLNCT PhotoClubBelum ada peringkat
- Microscopes by AmoebaDokumen3 halamanMicroscopes by AmoebaNailah DalidigBelum ada peringkat
- Bnoculars PerformanceDokumen15 halamanBnoculars Performancegbhat62Belum ada peringkat
- Clinical Pathology JournalDokumen68 halamanClinical Pathology JournalDhruv patelBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 2 Microscopy W23Dokumen15 halamanLab 2 Microscopy W23devaanshBelum ada peringkat
- 1 The MicroscopeDokumen42 halaman1 The MicroscopeKristine NicoleBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Report Microb Prac 1Dokumen16 halamanLab Report Microb Prac 1fatinBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmaceutical Microbiology Journal (PCI) 2021 (3) ModifiedDokumen72 halamanPharmaceutical Microbiology Journal (PCI) 2021 (3) ModifiedAishwarya PatilBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment No 1Dokumen3 halamanExperiment No 1Friolo, Prince Stephen P.Belum ada peringkat
- XII Unit Test 3 PhysicsDokumen2 halamanXII Unit Test 3 PhysicsSidharth TaylorBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Microscope PDFDokumen4 halamanIntroduction To Microscope PDFLaiza EboBelum ada peringkat
- 2 Micros PDFDokumen18 halaman2 Micros PDFKenny JosefBelum ada peringkat
- MONIS, Clemcy Pearl A. (Bacterial Simple Stain Procedure)Dokumen3 halamanMONIS, Clemcy Pearl A. (Bacterial Simple Stain Procedure)Clemcy Pearl MonisBelum ada peringkat
- Mic125 Lab ManualDokumen35 halamanMic125 Lab ManualAqilah NajwaBelum ada peringkat
- Dark Field MicrosDokumen4 halamanDark Field MicrosRukshan Widanagamage100% (3)
- 112 Ex3Dokumen20 halaman112 Ex3Francis SullanoBelum ada peringkat
- Cyto Unit 2Dokumen20 halamanCyto Unit 2Elyon Jirehel AlvarezBelum ada peringkat
- Bacte Lab - Prelim ExamDokumen30 halamanBacte Lab - Prelim ExamDanielle Anne LambanBelum ada peringkat
- E Nriching Our Lives Through Science:: Performance Task in General Biology 1Dokumen5 halamanE Nriching Our Lives Through Science:: Performance Task in General Biology 1Eirell Sanders100% (1)
- (07Q2W1) MicroscopeDokumen44 halaman(07Q2W1) MicroscopeAldwinC EspirituBelum ada peringkat
- Essential Reference Guide To Long Exposure Photography PDFDokumen53 halamanEssential Reference Guide To Long Exposure Photography PDFvincBelum ada peringkat
- Thin Layer Chromatography Unit 2Dokumen10 halamanThin Layer Chromatography Unit 2SathwikaBelum ada peringkat
- Distillation - WikipediaDokumen16 halamanDistillation - WikipediaAbhijith B ABBelum ada peringkat
- Invertebrate ZoologyDokumen9 halamanInvertebrate ZoologyKayl Dustin MalalisBelum ada peringkat
- Analytica Chimica ActaDokumen9 halamanAnalytica Chimica Actakuma2130Belum ada peringkat
- Cells Project For Grade 8Dokumen50 halamanCells Project For Grade 8Heidi KwonBelum ada peringkat
- Chm510 Laboratory ReportDokumen7 halamanChm510 Laboratory ReportafiqahBelum ada peringkat
- Cromatograma HPLCDokumen37 halamanCromatograma HPLCDarwin Andrés Taboada MartínezBelum ada peringkat
- Antigen and Antibody Reaction FinalDokumen77 halamanAntigen and Antibody Reaction FinalSharma MukeshBelum ada peringkat
- Microscopy Gram-Color: Stain Set For The Gram Staining MethodDokumen3 halamanMicroscopy Gram-Color: Stain Set For The Gram Staining MethodMuhammad AdhityaBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Modification: Mr. Kevin Francis E. MagaoayDokumen22 halamanCell Modification: Mr. Kevin Francis E. MagaoayDesiree Ann MarasiganBelum ada peringkat
- Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy: CHEMY 313 Analytical ChemistryDokumen7 halamanAtomic Absorption Spectroscopy: CHEMY 313 Analytical ChemistryJassim123 SabtBelum ada peringkat
- Viewing The Microbial WorldDokumen18 halamanViewing The Microbial Worldeapple kimBelum ada peringkat
- SPZ-50 Stereo Zoom Binocular Microscope On Stand LW & LED Ring Light - Aven ToolsDokumen3 halamanSPZ-50 Stereo Zoom Binocular Microscope On Stand LW & LED Ring Light - Aven ToolsAlim MardhiBelum ada peringkat
- Microscope Laboratory Activity 1Dokumen4 halamanMicroscope Laboratory Activity 1Ambot sa ImoBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of HPLCDokumen37 halamanFundamentals of HPLCrahatulislam100% (1)
- Radial ImmunodiffusionDokumen3 halamanRadial Immunodiffusionkiedd_04100% (5)
- Streak Plate Method - Principle, Types, Methods, UsesDokumen20 halamanStreak Plate Method - Principle, Types, Methods, UsesHerda CahyaningrumBelum ada peringkat
- g7 BrochureDokumen2 halamang7 BrochureThegoldenTigerBelum ada peringkat
- Analytical Presentation Sem 2Dokumen17 halamanAnalytical Presentation Sem 2MSc Part 2 OraganicBelum ada peringkat
- Microscopy Task A. Draw The Following: Hay Infusion (LPO and HPO)Dokumen5 halamanMicroscopy Task A. Draw The Following: Hay Infusion (LPO and HPO)JASMIN DAMIANBelum ada peringkat
- HPLC Column Void Volume - Pharmaceutical GuidelinesDokumen2 halamanHPLC Column Void Volume - Pharmaceutical GuidelinesManivannan KathirvelBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Structure Gizmo AnswersDokumen5 halamanCell Structure Gizmo Answerspaula-navas 13451Belum ada peringkat
- Recombination in BacteriaDokumen33 halamanRecombination in BacteriaThammana NishithareddyBelum ada peringkat
- D4001S Zymoclean Gel Dna Recovery Kit PDFDokumen9 halamanD4001S Zymoclean Gel Dna Recovery Kit PDFAndreea-Ioana PopaBelum ada peringkat
- BiochemistryDokumen5 halamanBiochemistryAngeline LimpiadaBelum ada peringkat
- Microbiology: TDR-300B PlusDokumen2 halamanMicrobiology: TDR-300B PlusZahid RasoolBelum ada peringkat
- Post-Lab Biochem 1aDokumen5 halamanPost-Lab Biochem 1aOla Anna GamutinBelum ada peringkat
- Bio-Rad NGC QuestDokumen24 halamanBio-Rad NGC QuestDivya DharshiniBelum ada peringkat
- Parts and Functions of A MicroscopeDokumen1 halamanParts and Functions of A MicroscopeDivine Josol CamposanoBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 4 Staining and Observation of MicroorganismsDokumen9 halamanLab 4 Staining and Observation of MicroorganismsNur NatashaBelum ada peringkat