ME8351 Manufacturing Technology-I Key Concepts
Diunggah oleh
Senthil Kumar Periyasamy100%(1)100% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (1 suara)
150 tayangan4 halamanME8351-Question Bank
Judul Asli
Question Bank for MFT(Two Mark Questions With Answers and PARTB Questions)
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniME8351-Question Bank
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
100%(1)100% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (1 suara)
150 tayangan4 halamanME8351 Manufacturing Technology-I Key Concepts
Diunggah oleh
Senthil Kumar PeriyasamyME8351-Question Bank
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 4
(
ME8351 Manufacturing Technology-I II Year – Mechanical Engineering (2019-2010)
UNIT-I –METAL CASTING PROCESSES
PART-A
1. Define Pattern & List the material used for pattern.
Pattern is a model of casting. Materials: Wood, Metal, Plaster, Plastic, Wax.
2. State the different types of Pattern.
Double piece Pattern, Match Plate, Loose Piece Pattern, Sweep Pattern, Segmental, Skeleton, Shell
Pattern.
3. What are the factors for selecting the pattern materials?
(i) Number of casting to be produced (ii) Quality of casting
(iii) Size & shape of the casting. (iv) Required surface finish.
4. What is pattern allowance?
Patterns are not made to correct size of the required casting. They are made slightly larger than the required casting.
This extra dimension given to the pattern is called pattern allowance.
5. What are the types of pattern allowance?
Machining allowance, Distortion allowance, Rapping Allowance, Draft Allowance.
6. List the types of Moulding tools.
Shovel Trowel, Slick, Bellows, Riddle, Rammer, Strike off Bar, Runner & Riser, Mallet, Gate cutter, Vent Rod,
Lifter.
7. What are the ingredients of Moulding Sand?
1. Sand2. Binder- Clay type, Organic, Inorganic 3.Additives-Reducing Agents, Fibrous, special additives.
8. Classify the Moulding sand.
(i) Natural Sand (ii) Synthetic Sand (iii) Special sand.
9. What are the properties of Moulding Sand?
Porosity, Plasticity, Adhesiveness, Cohesiveness, Refractories, Collapsibility.
10. What are the steps for preparing the Moulding sand ?
Mixing of Sand, Tempering of sand, Conditioning of sand.
11. What are the types of Moulding Sand?
Green Sand, Dry sand, Loam Sand, Facing Sand, Parting sand, Core Sand.
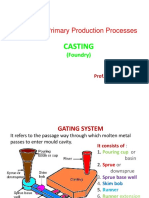
12. What are the components of Gating system?
Poring cup, Spure, Runner, Gate, Riser.
13. What are the types of Moulding methods?
Green Sand, Dry Sand, Loam Moulding, Bench Moulding, Floor Moulding, Pit Moulding, Sweep Moulding, Plate
moulding, Machine Moulding( Jolt Machine, Sand Slinger, Top & Bottom Squeezer.
14. What is meant by Core & Core print? (NOV/DEC 2012)
Core: It is used to make a hollow type casting. The core is placed in the mould and is removed after casting. Core
Print: A projection made in the pattern is called core print. It is used to form a core seat in the mould.
15. What are the types of core boxes?
Half Core box, Dump core box, Split core Box, Strickle core box, Gang Core Box.
16. What are core binders?
Binders are added with the core sand to bind the sand grain together. It give the strength and hardness to the core
and to prevent moisture absorption.
Types: (i) Oil Binders (Linseed Oil ) (ii) Water Soluble Binders: Starch, dextrin. (iii)Resin Binders: Phenol
Formaldehyde, Urea.
17. What are the types Core Ovens?
(i) Batch Type Oven (ii) Continuous Type Ovens (iii) Di –Electric Baking Ovens.
18. What are the different types of casting process?
(i) Sand Casting (ii) Gravity die casting (iii) Pressure Die casting-Hot & Cold Chamber
(iv) Centrifugal- Centrifuge, semi centrifuge (v) Continuous (vi) Chilled casting
19. What are Chaplet?
Chaplet is a metal location piece, inserted in a mould either to prevent core shifting its position or to give support to
a core.
20. What are the different types of Melting Furnace? (NOV/DEC 2012)
(i) Cupola Furnace (ii) Crucible Furnace- Pit type, coke fired stationery furnace, Oil fired Tilting Furnace
(ii)Electric Arc Furnace- Direct arc, Indirect, Induction Furnace.
21. Define Fettling of casting.
Cleaning of casting called as fettling- Trimming, Surface cleaning,
(
ME8351 Manufacturing Technology-I II Year – Mechanical Engineering (2019-2010)
22. List the casting defects.
Blow holes, Slabs, Honey combing, Shift, Cold shut, Fins, Run out, Rat Tail, Swell ,Blister.
23. List the Instruments used for measuring temperature in molten metal. Thermo electric Pyrometer, Optical
Pyrometer.
24. What is meant by grain fineness number?
A system developed by AFS (American Fineness Society) for rapidly expressing the average grain size of given
sand. It approximates the number of meshes per inch of that sieve that would just pass the sample if its grains of
uniform size. It is approximately proportional to the surface area per unit of weight of sand, exclusive of clay.
GFN= sum of products/ sum of precentages of sand retained on each sieve and pan
25. few applications of centrifugal casting
Pipes, Tubes, bushings, pulleys, nozzles and rings.
26. Define casting.
The parts obtained by pouring the molten metal into the mould cavity into required shape and allow it to solidify is
known as Castings.
27.What are the causes of misruns in casting? (APRIL/MAY 2016)
It is due to faulty moulding and faulty moulding box equipment.
28.What are chaplets? (APRIL/MAY 2016)
Chaplet is a metal location piece, inserted in a mould either to prevent core shifting its position or to give support to
a core.
29. What are the characteristics of a core? ((NOV/DEC 2016)
Refractoriness , permeability, collapsibility and strength.
30.Name the alloys which are generally die cast. Why are aluminium alloys preferably cast in cold chamber
die casting machines? (NOV/DEC 2016)
Zinc alloys, Aluminium alloys , Magnesium alloys & Copper alloys. Because Al- base alloys tend to alloy with the
steel plunger of the hot die casting machine.
PART-B
1. What are the pattern allowances? Explain briefly each.
2. Discuss the properties of moulding sand.
3. Explain the CO2 process of core making state its advantages and applications.
4. State the different type of mould. Write a short note on Green sand mould and shell moulding
5. Write a neat sketch of a cupola, Explain its operate.
6. Explain with a simple sketch how metal is melted in a Electric arc furnace.
7. What are the different types of furnace used in foundry? with neat sketches any one of them.
8. Explain briefly the various moulding method used in foundries.
9. Enumerate the continuous casting defects and suggest suitable remedies.
10. Explain the process of centrifugal casting with neat sketches.
11. Explain the investment casting process in detail.
12. Explain the two types of pressure die casting processes.
UNIT II -JOINING PROCESSES
PART-A
1. List the arc welding equipments.
Arc Welding Equipments,Earthing clamp,Welding generator(D.C),Protective shield Welding transformer (A.C),
Gloves, Electrode holder, Apron, Cable, Wire brush.
2. Sate the different types of electrode used in welding.
Electrode Types: Consumable electrode, Non consumable electrode.
Consumable Electrode: This type of electrode is not only used to produce the arc also provide filler material
during welding.
Bare electrode: Do not have any coating on their surface. It is rarely used to weld wrought iron and mild steel.
Lightly coated electrode: It is coated mainly due to increase arc stability. It have a coating layer of several
hundredths millimeter and is 1-5% of the electrode weight. This type of weld will affects with oxidation.
Heavily coated electrode: Covered with high quality of 1-3mm thick. The weight of this coating is from 15-30% of
electrode rod.
3. State the specification and choice of electrode.
Electrode are specified by length and diameter available up to 12mm diameter and 450mm long.
S. WORK PIECE ELECTRODE
N
1. Wrought Iron Low carbon steel rod
2. Cast Iron Cast iron rods
3. Mild steel M.s copper coated rod
4. Alloy steel Low- alloy steel of 0.25% carbon
5. Aluminium Cast aluminium alloy rod
6. Carbon steel Steel wireof 0.1% to 0.18% carbon and 0.0025 to 0.04%phosphor and
sulphur.
7. Copper casting Copper rod.
4. List the purpose of flux used in welding.
Flux coating is meant for (i) To produce a gas shield around the arc and molten metal due to this atmosphric
reaction is restricted, To increase strength of weld, Increase deposition efficiency.
5. What are the different types of Flames used in Gas Welding?
Neutral Flame- Welding of steel , Cast Iron, Aluminium, Copper, Carburising- Welding of alloy steels,Nickel and
Monel Metal, Oxidising Flame- Welding of Brass,Bronze,Maganese and steel.
6. List the equipments used in gas welding.
(i) Gas cylinders.(ii) Pressure regulators(iii) Pressure gauges.(iv) Hoses
(v) Welding torch.
7. Define solid State Welding.
It is the process of joining metals in solid state without melting them.Joining is done by the interatomic bonds
developed when the atoms of two surfaces are brought very close to each other.
8. What do you mean by TIG Welding?
Tungsten Inert gas Welding utilize Non consumable Tungsten Electrode.It produce only electric arc it cannot be act
as a filler metal.An inert gas like argon or Helium are used Through the nozzle.
9. What is meant by rightward and leftward welding techniques?
Right ward technique: Welding is carried out from left to right.It has no lateral movement.The blow pipe angle
should be 40 to 500 C.
Leftward Technique: Welding is carried out from right to leftt.It has lateral movement on sideways.The blow pipe
angle should be 30 to 400 C.
10. What do you mean by MIG Welding?
Metal Inert Gas Welding uses a consumable electrode which supplies continuously. A inert gas argon or Helium is
supplied to produce a gas shield which does not affect or react with the atmospheric air.
11. What do you mean by electro slag welding?
It is a processes of joining two thick metalsplates by the heat generated when electric arc passed through the molten
slag.
12. Define Arc crater.
Arc crater is depression in the molten metal created by the end of the welding electrodeduring the welding of metal.
13. Compare Arc and GAS Welding.
ARC: Heat is obtained from electric arc 4000°C, Electrode is used a filler rod, strength of the joint is more, filler
metal should be same as work material.
GAS: Heat is obtained from Gas flame 2300°C, Seperate filler metal is used, strength of the joint is less, filler metal
and work metal need not besame.
14. What is meant by “Carburising flame” in gas welding? (NOV/DEC 2012)
A flame that contains more acetylene than oxygen. This flame will burn at a lower temperature than the other
flames, and can add extra carbon to certain welds.
15.What is the role of flux in welding operation? (APRIL/MAY 2016)
Flux coating is meant for (i) To produce a gas shield around the arcand molten metal due to this atmosphric
reaction is restricted, To increase strength of weld, Increase deposition efficiency.
PART-B
1. Explain the various types of gas welding processes.
2. Explain the Components of manual metal arc welding with neat sketch.
3. Brief about three types of flames in oxy acetylene welding process.
4. ) Briefly explain the principle and working of Gas Tungsten arc welding process. Also list out its merits,
demerits and applications
5). Briefly explain the principle and working of Metal Gasc welding process. Also list out its merits,
demerits and applications
6) Briefly explain the principle and working of Submergible arc welding. Also list out its merits,
demerits and applications
7) Briefly explain the principle and working of Electro slag welding process. Also list out its merits,
demerits and applications
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- 18me45b Metal Casting Welding Model Question Paper 2Dokumen2 halaman18me45b Metal Casting Welding Model Question Paper 2Stalan JonathanBelum ada peringkat
- Manufacturing Technology-I - Department of Mechanical EngineeringDokumen4 halamanManufacturing Technology-I - Department of Mechanical EngineeringSoma SundaramBelum ada peringkat
- L 8-Extrusion PDFDokumen16 halamanL 8-Extrusion PDFkhaledmosharrafmukutBelum ada peringkat
- ME 2202 - PPP Casting-03Dokumen63 halamanME 2202 - PPP Casting-03Satyajeet SahooBelum ada peringkat
- 05 - Defects in Crystalline Solids PDFDokumen49 halaman05 - Defects in Crystalline Solids PDFFRANCESCA SARAZABelum ada peringkat
- MPI Unit IDokumen54 halamanMPI Unit IArun PatilBelum ada peringkat
- 15A03804 Power Plant EngineeringDokumen2 halaman15A03804 Power Plant EngineeringCharanTheja PBelum ada peringkat
- NV MCQ-4 PDFDokumen8 halamanNV MCQ-4 PDFTejas UpadhyeBelum ada peringkat
- Physics All IndiaDokumen17 halamanPhysics All IndiahiBelum ada peringkat
- REV12020 PhysicsDokumen4 halamanREV12020 Physicshari kroviBelum ada peringkat
- Types of PatternDokumen12 halamanTypes of PatternadamBelum ada peringkat
- 3 PDFDokumen199 halaman3 PDFsanku surya sai charanBelum ada peringkat
- Determinant CalculationsDokumen80 halamanDeterminant Calculationskunal vayaBelum ada peringkat
- Units and MeasurementsDokumen13 halamanUnits and MeasurementsNITHISH KUMAR.GBelum ada peringkat
- Cast Iron InoculationDokumen12 halamanCast Iron InoculationCaio Fazzioli TavaresBelum ada peringkat
- Defects LatestDokumen55 halamanDefects LatestJaddu MSDBelum ada peringkat
- Sheet Metal OperationsDokumen52 halamanSheet Metal OperationsthakruBelum ada peringkat
- Unconventional Machining ProcessesDokumen22 halamanUnconventional Machining ProcessesManivannan JeevaBelum ada peringkat
- Rapid Prototyping and ToolingDokumen3 halamanRapid Prototyping and Toolingappuanandh7811Belum ada peringkat
- Classxiiassignment201920Dokumen84 halamanClassxiiassignment201920Dhaval KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Crystal Structure and Noncrystalline MaterialsDokumen38 halamanCrystal Structure and Noncrystalline MaterialsAbo Abdo100% (1)
- CFD Question Bank for Aerospace ApplicationsDokumen3 halamanCFD Question Bank for Aerospace ApplicationsGanesh Natarajan SBelum ada peringkat
- Favor Calcular Integrales Por Álgebra y Sustitución Tan) : DX X X XDokumen1 halamanFavor Calcular Integrales Por Álgebra y Sustitución Tan) : DX X X XSantiago Javier Casallas HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- If A Line Makes Angles 90°, 135°, 45° With The X, y and Z-Axes Respectively, Find Its Direction CosinesDokumen2 halamanIf A Line Makes Angles 90°, 135°, 45° With The X, y and Z-Axes Respectively, Find Its Direction CosinesShreeBelum ada peringkat
- Electrochem 201516Dokumen81 halamanElectrochem 201516Mohd AminudinBelum ada peringkat
- RRB SirDokumen1 halamanRRB Sirprince alok KarBelum ada peringkat
- Question Paper For Class 12 PhysicsDokumen5 halamanQuestion Paper For Class 12 PhysicsShubham AsthanaBelum ada peringkat
- Biology - XI - Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - IntroductionDokumen47 halamanBiology - XI - Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - IntroductionSDO BSNL NALAGARHBelum ada peringkat
- X 7 Years (Sci) E-Sample NEWDokumen129 halamanX 7 Years (Sci) E-Sample NEWrishitjain1712Belum ada peringkat
- Machining Processes and Metrology Question PaperDokumen2 halamanMachining Processes and Metrology Question PaperHarshan ArumugamBelum ada peringkat
- 1261 XII Physics Support Material Study Notes and VBQ 2014 15Dokumen370 halaman1261 XII Physics Support Material Study Notes and VBQ 2014 15RajdeepBelum ada peringkat
- Solutions of Kinematics HC Verma Chapter 3Dokumen16 halamanSolutions of Kinematics HC Verma Chapter 3Wave Education100% (1)
- Chapter 3 ElectrochemistryDokumen8 halamanChapter 3 Electrochemistrymeshal retteryBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Physics-Important Questions: Shorts UNIT - 1 (Units and Dimensions)Dokumen4 halamanEngineering Physics-Important Questions: Shorts UNIT - 1 (Units and Dimensions)psatyasankarBelum ada peringkat
- Class XII Physics AssignmentDokumen28 halamanClass XII Physics AssignmentApex Institute100% (1)
- C16 Electrostatic Student1Dokumen81 halamanC16 Electrostatic Student1Faris Izzuddin RoslinBelum ada peringkat
- IC Engines-ClassificationDokumen21 halamanIC Engines-ClassificationChintu Santhu0% (1)
- Materials Science and Metallurgy EssentialsDokumen122 halamanMaterials Science and Metallurgy EssentialsYsv PavuluriBelum ada peringkat
- Kings: Manufacturing Technology - IiDokumen5 halamanKings: Manufacturing Technology - IiSaravanan MathiBelum ada peringkat
- Me8792 - Power Plant EngineeringDokumen48 halamanMe8792 - Power Plant EngineeringPalanivel Rajan A RBelum ada peringkat
- 3D GeometryDokumen111 halaman3D GeometryDipesh VermaBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment For UNIT IDokumen2 halamanAssignment For UNIT IParamasivam VeerappanBelum ada peringkat
- Class 11 Physics Notes 2023-24 Chapter 3 Motion in A Straight LineDokumen33 halamanClass 11 Physics Notes 2023-24 Chapter 3 Motion in A Straight Linenick tyagiBelum ada peringkat
- Branches of Physics & Uses of RadarDokumen19 halamanBranches of Physics & Uses of Radarmirza_2010Belum ada peringkat
- Physics: Aurora ClassesDokumen21 halamanPhysics: Aurora ClassesxentrixxBelum ada peringkat
- Extrusion and Drawing: Manufacturing ProcessesDokumen41 halamanExtrusion and Drawing: Manufacturing ProcessesEloisa Nher Hipolito100% (1)
- Physics Question BankDokumen11 halamanPhysics Question BankdevBelum ada peringkat
- CH 3 - Motion in A Straight Line Practice Sheet No. Questions AnswersDokumen3 halamanCH 3 - Motion in A Straight Line Practice Sheet No. Questions AnswersKrish PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Manufacturing Process 1 Question BankDokumen8 halamanManufacturing Process 1 Question Bankashok PradhanBelum ada peringkat
- 6 1 Formulae Ray OpticsDokumen14 halaman6 1 Formulae Ray OpticsNathanianBelum ada peringkat
- CLS Aipmt 16 17 XII Phy Study Package 6 SET 1 Chapter 8Dokumen24 halamanCLS Aipmt 16 17 XII Phy Study Package 6 SET 1 Chapter 8Kareena Gupta75% (4)
- RollingDokumen3 halamanRollingAhmad AnwarBelum ada peringkat
- XII NCERT Objective CH 1 Electric Charges and FieldsDokumen18 halamanXII NCERT Objective CH 1 Electric Charges and FieldskarishmaBelum ada peringkat
- MT MLMDokumen17 halamanMT MLMSundara MoorthyBelum ada peringkat
- Core Classification Materials CoresDokumen26 halamanCore Classification Materials CoresThulasi RamBelum ada peringkat
- Manufacturing Technology - I Unit - I: 2 Marks Question & AnswersDokumen15 halamanManufacturing Technology - I Unit - I: 2 Marks Question & AnswersSK NAGOOR VALI100% (1)
- Shop 160Dokumen26 halamanShop 160Jasmin AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Unit-I: 1. What Is Draft Allowance? How Is It Provided For Patterns?Dokumen19 halamanUnit-I: 1. What Is Draft Allowance? How Is It Provided For Patterns?Jegan ParamasivamBelum ada peringkat
- VSSUT Casting and Welding NotesDokumen199 halamanVSSUT Casting and Welding NoteshsemargBelum ada peringkat
- Mould & Core Material for the Steel FoundryDari EverandMould & Core Material for the Steel FoundryPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- Unit 2Dokumen190 halamanUnit 2Senthil Kumar PeriyasamyBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentalproengineer 130906080834 PDFDokumen213 halamanFundamentalproengineer 130906080834 PDFSenthil Kumar PeriyasamyBelum ada peringkat
- Manufacturing Processes: Iii Semester / Ii YearDokumen24 halamanManufacturing Processes: Iii Semester / Ii YearSenthil Kumar PeriyasamyBelum ada peringkat
- Metal Cutting Theory GuideDokumen229 halamanMetal Cutting Theory GuideSenthil Kumar PeriyasamyBelum ada peringkat
- ME8351 Manufacturing Technology Question BankDokumen10 halamanME8351 Manufacturing Technology Question BankSenthil Kumar PeriyasamyBelum ada peringkat
- HW Solutions For Period 3Dokumen10 halamanHW Solutions For Period 3dellibabu509Belum ada peringkat
- Me6402 mt2 Notes Rejinpaul PDFDokumen227 halamanMe6402 mt2 Notes Rejinpaul PDFSenthil Kumar PeriyasamyBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1Dokumen229 halamanUnit 1Senthil Kumar PeriyasamyBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanics of CuttingDokumen17 halamanMechanics of CuttingPercy RobertBelum ada peringkat
- III Unit Solids OkDokumen19 halamanIII Unit Solids OkMohammed ImranBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentalproengineer 130906080834 PDFDokumen213 halamanFundamentalproengineer 130906080834 PDFSenthil Kumar PeriyasamyBelum ada peringkat
- UNIT I Part IDokumen22 halamanUNIT I Part ISenthil Kumar PeriyasamyBelum ada peringkat
- IE6605-Production Planning and ControlDokumen11 halamanIE6605-Production Planning and Controll8o8r8d8s8i8v8Belum ada peringkat
- IE6605-Production Planning and ControlDokumen11 halamanIE6605-Production Planning and Controll8o8r8d8s8i8v8Belum ada peringkat
- ME2027 Question BankDokumen12 halamanME2027 Question BankSenthil Kumar Periyasamy0% (1)
- ME2027 Question BankDokumen12 halamanME2027 Question BankSenthil Kumar Periyasamy0% (1)
- Velammal Engineering College Machine Elements Design DocumentDokumen18 halamanVelammal Engineering College Machine Elements Design DocumentSenthil Kumar PeriyasamyBelum ada peringkat
- ARE - Design For Welding - AWS Resources For EngineersDokumen86 halamanARE - Design For Welding - AWS Resources For EngineersnelsonBelum ada peringkat
- Plastic Processing TechniqueDokumen8 halamanPlastic Processing TechniqueFirstEastern PerspectiveBelum ada peringkat
- Structural Welding Code Sheet Steel GuideDokumen4 halamanStructural Welding Code Sheet Steel Guideayub82Belum ada peringkat
- Welder Qualification MatrixDokumen1 halamanWelder Qualification MatrixRaghavan VenkatramanBelum ada peringkat
- Secondary Machining GuideDokumen17 halamanSecondary Machining GuideKimberley YorkBelum ada peringkat
- Position of Welds ComparisonDokumen3 halamanPosition of Welds ComparisonYuvaraj SathishBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 3 Extrusion Blow MoldingDokumen34 halamanLesson 3 Extrusion Blow MoldingAnonymous ExWAN2xjFJBelum ada peringkat
- CNC ProgrammingDokumen62 halamanCNC ProgrammingSanjog Maiti100% (1)
- Fusion Welding Techniques GuideDokumen16 halamanFusion Welding Techniques Guidevijju ajjuBelum ada peringkat
- 2017 Welding Training MaterialsDokumen24 halaman2017 Welding Training MaterialsAdnan Rana100% (2)
- O-Ring (Metric Size)Dokumen63 halamanO-Ring (Metric Size)Kamlesh DalavadiBelum ada peringkat
- Solidcast IranDokumen239 halamanSolidcast IranMario Farfan Cantoya NetoBelum ada peringkat
- CNC Programming Handbook Smid 195 - 293Dokumen99 halamanCNC Programming Handbook Smid 195 - 293Răzvan Iordache100% (1)
- A Brief Summary On Submerged Arc Welding Process and SAW Wires.20140121.222422Dokumen2 halamanA Brief Summary On Submerged Arc Welding Process and SAW Wires.20140121.222422quiltport77Belum ada peringkat
- Arc Welding ReportDokumen6 halamanArc Welding ReportYe Chonn100% (6)
- WPS Updated PDFDokumen2 halamanWPS Updated PDFRaja Muaz Ahmad KhanBelum ada peringkat
- The HandbookDokumen110 halamanThe HandbookChatree TaweekongBelum ada peringkat
- Table - QW-416 Welding Variables For Welder Performance PDFDokumen1 halamanTable - QW-416 Welding Variables For Welder Performance PDFAnonymous VohpMtUSNBelum ada peringkat
- History of Lathe From Beginning of Machine Tool InventionDokumen4 halamanHistory of Lathe From Beginning of Machine Tool Inventionകൂട്ടുകാരിയെ സ്നേഹിച്ച കൂട്ടുകാരൻBelum ada peringkat
- PQR Asme Ix - CompletedDokumen3 halamanPQR Asme Ix - CompletedCarlos Nombela Palacios100% (1)
- History of WeldingDokumen10 halamanHistory of WeldingGracie O. ChingBelum ada peringkat
- 14250A ch3 PDFDokumen82 halaman14250A ch3 PDFKamarul NizamBelum ada peringkat
- Teknik PengelasanDokumen84 halamanTeknik PengelasanluhurBelum ada peringkat
- Cycle Time Study Sheet: 14.61 7.12 Baratsuki: 249.29 242.17Dokumen1 halamanCycle Time Study Sheet: 14.61 7.12 Baratsuki: 249.29 242.17Frank RojasBelum ada peringkat
- Making Metal Dice Project OutlineDokumen1 halamanMaking Metal Dice Project Outlineapi-239142091Belum ada peringkat
- PT Perkasa Heavyndo Engineering Welder Qualification RecordsDokumen91 halamanPT Perkasa Heavyndo Engineering Welder Qualification RecordstskmechBelum ada peringkat
- Asme Sec Ix-2013 165Dokumen1 halamanAsme Sec Ix-2013 165Durgarao VasaBelum ada peringkat
- AnilDokumen7 halamanAnilanil kumarBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding and Preventing Common Casting Defects Like Hot TearsDokumen4 halamanUnderstanding and Preventing Common Casting Defects Like Hot TearsSachin KumbharBelum ada peringkat