2 Mark PDF
Diunggah oleh
Yshbalaram0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
13 tayangan2 halamanJudul Asli
2 mark.pdf
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
13 tayangan2 halaman2 Mark PDF
Diunggah oleh
YshbalaramHak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
1. Differentiate overload and short circuit.
When there is a short circuit, the impedance at the fault point is almost
zero and the voltage at the point is zero. The short circuit current is very high.
While an overload means the load is higher than the rated load which is
specified as the safe load. Thus the current is also higher than the safe designed
rated value. The overload does not cause damage instantly but if persists for long
time, can cause damage to the system.
2. List the different types of earthing.
▪ Solid or effective grounding
▪ Resistance grounding
▪ Reactance grounding
▪ Resonant grounding
3. Define pick up value in relay.
It is the minimum value of an actuating quantity at which relay starts
operating. In most of the relays actuating quantity is current in the relay coil and
pickup value of current is indicated along with the relay.
4. State the various methods of Backup Protection.
The various methods used for the backup protection are classified as,
▪ Relay Backup Protection.
▪ Breaker Backup Protection.
▪ Remote Backup Protection.
▪ Centrally Co-ordinate Backup Protection
5. Discuss why earth wire is provided in overhead transmission line?
It is a shielding method of protection against lightning over-voltage hitting
directly the phase wires. The earth wire or wires are kept above the phase
conductors such that the ‘shielding angle’ is about 30*. This reduces the
probability of direct lightning strokes hitting the phase conductors, and the
probability of hitting the earth wire and getting discharged to earth is more. Note
that this is effective only if the tower footing resistance is also low or else ‘back-
flash-over’ may occur. It is able to reduce slightly the induced over-voltages also.
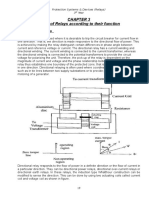
6. Describe why a shading ring is provide in an induction disc relay?
This coil is usually energized by current flowing in the single coil wound on a
magnetic structure containing an air gap. The air-gap fluxes produce by the
initializing current is split into two flux displace in time-space and by a shaded
ring. The shaded ring is made up of the copper ring that encircles the part of the
pole face of each pole.
The magnetic field develops from the current produces the flux in the portion of
the iron ring surrounded by the ring to lag in phase by 40° to 50° behind the flux
in the unshaded portion of the pole.
7. Define under frequency relay?
If frequency decreases then there is unbalance in the impedances. But the
torque exerted on the rotor is anti- clockwise. This operates the relay if frequency
decreases beyond the setting. This is known as under frequency relay
8. Define negative sequence relays?
These relays are also called as phase unbalance relay. Because these relay
provides protection against negative sequence components of unbalanced currents
existing due to unbalanced loads or phase to phase faults.
9. Discuss the difficulties in differential protection?
• The impedance of the pilot cables generally causes a slight difference
between the currents at the two ends of the section to be protected, then
the small differential current flowing through the relay may cause it to
operate even under no fault conditions.
• Pilot cable capacitance causes incorrect operation of the relay when a
large current flows
• Accurate matching of current transformers cannot be achieved due to
pilot
10. List the merits of mho relay?
The main advantages of the MHO relays are
▪ Faster Protection.
▪ Simpler Co-ordination.
▪ Inherent directional Characteristics
▪ Less effect of amount of generation of fault levels, fault current
magnitudes.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Why A Shading Ring Is Provide in An Induction Disc Relay?Dokumen2 halamanWhy A Shading Ring Is Provide in An Induction Disc Relay?YshbalaramBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionDari EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Ee2402 Protection and SwitchgearDokumen12 halamanEe2402 Protection and SwitchgearVasudha SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Ee1302 Protection and SwitchgearDokumen12 halamanEe1302 Protection and SwitchgearMukesh Kumar0% (1)
- Boat Maintenance Companions: Electrics & Diesel Companions at SeaDari EverandBoat Maintenance Companions: Electrics & Diesel Companions at SeaBelum ada peringkat
- قسم الوقاية - الجزء الثانيDokumen14 halamanقسم الوقاية - الجزء الثانيوليد موسىBelum ada peringkat
- Lec # 23 Over Current ProtectionDokumen51 halamanLec # 23 Over Current ProtectionAnamika Khan100% (1)
- Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Question Bank Ee2402 Protection and SwitchgearDokumen16 halamanDepartment of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Question Bank Ee2402 Protection and SwitchgearSweqZBelum ada peringkat
- Insulation Co-ordination in High-voltage Electric Power SystemsDari EverandInsulation Co-ordination in High-voltage Electric Power SystemsPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (5)
- Lecture 5 Fuses and ArrestersDokumen23 halamanLecture 5 Fuses and ArrestersSyed KhizarBelum ada peringkat
- Overcurrent ProtectionDokumen32 halamanOvercurrent ProtectionminlwintheinBelum ada peringkat
- EE1302 Protection and Switchgear-SignedDokumen12 halamanEE1302 Protection and Switchgear-SignedarivurpBelum ada peringkat
- Protection System Design For SubstationDokumen35 halamanProtection System Design For SubstationTimon Tim100% (1)
- PBC Slide 2Dokumen53 halamanPBC Slide 2Arnold SBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7Dokumen8 halamanChapter 7Ahmed Said GhonimyBelum ada peringkat
- High and Low Impedance ProtectionDokumen4 halamanHigh and Low Impedance ProtectionSankalp TiwariBelum ada peringkat
- RelaysReliability PDFDokumen8 halamanRelaysReliability PDFcazzocazzocazzoBelum ada peringkat
- Paper 1Dokumen9 halamanPaper 1Hana AliBelum ada peringkat
- Protection Systems TransformerDokumen14 halamanProtection Systems Transformerrajabharath12Belum ada peringkat
- Switches &MODsDokumen14 halamanSwitches &MODsZack GroothouseBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7Dokumen15 halamanChapter 7Khaled RabeaBelum ada peringkat
- 87T Protection SchemeDokumen12 halaman87T Protection Schemedskymaximus100% (1)
- PSP - HKDokumen10 halamanPSP - HKHarsh KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3Dokumen10 halamanChapter 3nassim.1979Belum ada peringkat
- RelaysDokumen7 halamanRelaysRajeev RawatBelum ada peringkat
- Differential RelayDokumen24 halamanDifferential RelayMortuzaBelum ada peringkat
- SGP PPT1Dokumen100 halamanSGP PPT1Anley NigissieBelum ada peringkat
- Insulation Co OrdinationDokumen4 halamanInsulation Co OrdinationVasudha SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Distance Relay PspsDokumen33 halamanDistance Relay PspsAdhiBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 3 APPARATUS PROTECTION (Switchgear and Protection)Dokumen17 halamanUnit 3 APPARATUS PROTECTION (Switchgear and Protection)sujithBelum ada peringkat
- PirDokumen31 halamanPirdilipelineBelum ada peringkat
- Relays - Open ElectricalDokumen5 halamanRelays - Open Electricalstalin63Belum ada peringkat
- On RelaysDokumen99 halamanOn RelaysHimanshu RajBelum ada peringkat
- 02 - Notes Overcurrent ProtectionDokumen9 halaman02 - Notes Overcurrent ProtectionM Kumar Marimuthu100% (1)
- RelayDokumen29 halamanRelayVivek KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Notes21 ProtectionDokumen22 halamanNotes21 ProtectionJerome SantosBelum ada peringkat
- Lighning ArresterDokumen24 halamanLighning ArresterBharath AradhyaBelum ada peringkat
- Psps Unit 1 QBDokumen9 halamanPsps Unit 1 QBNaveen RajBelum ada peringkat
- 2 Mark 16 Mark With Answer 2Dokumen83 halaman2 Mark 16 Mark With Answer 2Senthil Ilangovan100% (1)
- EE6701 NotesDokumen83 halamanEE6701 NotesJaya ShreeBelum ada peringkat
- Transformer Protection - 1Dokumen51 halamanTransformer Protection - 1Naveed Rabbani100% (1)
- Protection and Switchgear Important QuestionsDokumen38 halamanProtection and Switchgear Important QuestionsAkhil Surya0% (1)
- FusesDokumen8 halamanFusescatherinejeanasBelum ada peringkat
- PSP by Atif Group-7Dokumen41 halamanPSP by Atif Group-7Awais khanBelum ada peringkat
- What Is A Surge Arrester?Dokumen8 halamanWhat Is A Surge Arrester?Vihang DholakiyaBelum ada peringkat
- How To Calculate Stabilizing Resistor For High Impedance Differential Protection - Electrical4uDokumen7 halamanHow To Calculate Stabilizing Resistor For High Impedance Differential Protection - Electrical4usridharanBelum ada peringkat
- Long Transmission Lines: Since Long Lines Are Highly Subjected To Power Swings (Load SheddingDokumen4 halamanLong Transmission Lines: Since Long Lines Are Highly Subjected To Power Swings (Load Sheddingkrishna chaitanyaBelum ada peringkat
- Distribution OverDokumen3 halamanDistribution OverPaolo CasungcadBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Notes: Switchgear and ProtectionDokumen20 halamanLecture Notes: Switchgear and ProtectionAkula VeerrajuBelum ada peringkat
- Reduced Distance RelayingDokumen12 halamanReduced Distance Relayingmmorgenwaine9Belum ada peringkat
- Lecture Notes: Switchgear and ProtectionDokumen20 halamanLecture Notes: Switchgear and ProtectionMohammed AL-MaaitahBelum ada peringkat
- GROUP 7 Types of Distance ProtectionDokumen18 halamanGROUP 7 Types of Distance ProtectionJohn Rey RillonesBelum ada peringkat
- Sinha Power Plant QuestionDokumen14 halamanSinha Power Plant QuestionRaihanBelum ada peringkat
- Svcet: Unit - 4 Principles of Circuit BreakersDokumen13 halamanSvcet: Unit - 4 Principles of Circuit Breakersparvesh kumarBelum ada peringkat
- Conventional and Non-Conventional SourcesDokumen12 halamanConventional and Non-Conventional SourcesAkhtarBelum ada peringkat
- PSP BY Atif Group-7Dokumen38 halamanPSP BY Atif Group-7Awais khanBelum ada peringkat
- 5-Transmission and DistributionDokumen38 halaman5-Transmission and DistributionCaribBelum ada peringkat
- Hse Ems Enviornmental PolicyDokumen7 halamanHse Ems Enviornmental Policyshaquan josephsBelum ada peringkat
- HT Xlpe CableDokumen21 halamanHT Xlpe CablePritam SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Desigo SystemDokumen9 halamanDesigo Systemcindy .(00000050761)Belum ada peringkat
- Maruti Esteem Mpi Engine PDFDokumen18 halamanMaruti Esteem Mpi Engine PDFVaandu PiplupBelum ada peringkat
- ASME Sec. VIII - Multiple Openings - Boiler and Pressure Vessel Engineering - Eng-TipsDokumen4 halamanASME Sec. VIII - Multiple Openings - Boiler and Pressure Vessel Engineering - Eng-TipsarjunBelum ada peringkat
- RMIPA Port Master PlanDokumen362 halamanRMIPA Port Master Planjoncpasierb100% (6)
- Pix CarsDokumen149 halamanPix CarsRicardo AssunçãoBelum ada peringkat
- Solar Based Grass CutterDokumen6 halamanSolar Based Grass CutterTTBelum ada peringkat
- Technical Specification of VSK PDFDokumen28 halamanTechnical Specification of VSK PDFmaran.suguBelum ada peringkat
- Design and Fabrication of Stair Climber TrolleyDokumen21 halamanDesign and Fabrication of Stair Climber TrolleyAnonymous 1mMOyt9zBelum ada peringkat
- 80ZV 2Dokumen12 halaman80ZV 2mhmd_saad100% (2)
- Penggantian Relay Dist Ke LCD & Progress Koordinasi Penghantar Dan PembangkitDokumen11 halamanPenggantian Relay Dist Ke LCD & Progress Koordinasi Penghantar Dan PembangkitCahyo Tri HartoyoBelum ada peringkat
- V B TDokumen12 halamanV B TAshish KatariaBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 5. Neutron LoggingDokumen72 halamanLecture 5. Neutron LoggingDimash AbdrakhmanovBelum ada peringkat
- Flow Testing BrochureDokumen12 halamanFlow Testing BrochureImadBelum ada peringkat
- Selected Bibliography On Brickmaking in Developing CountriesDokumen4 halamanSelected Bibliography On Brickmaking in Developing CountriesRobert PetrutBelum ada peringkat
- Smart Energy Coordination of Autonomous ResidentiaDokumen13 halamanSmart Energy Coordination of Autonomous ResidentiaAhmed SabriBelum ada peringkat
- C4 Tech Spec Issue 2Dokumen5 halamanC4 Tech Spec Issue 2Дмитрий КалининBelum ada peringkat
- Thrust BearingsDokumen112 halamanThrust BearingsMohammad Ali ZamanBelum ada peringkat
- ItysDokumen32 halamanItysciohaniBelum ada peringkat
- Inplan - Ingenieurtechnik - Eng Thermal Oil BoilerDokumen6 halamanInplan - Ingenieurtechnik - Eng Thermal Oil BoilerMeilvy Rahmadani Pane0% (1)
- Answer Key - CWT 1Dokumen2 halamanAnswer Key - CWT 1Areeb AbbaxiBelum ada peringkat
- Off Grid PV Systems Design GuidelinesDokumen24 halamanOff Grid PV Systems Design Guidelinestantiba100% (1)
- EE2002 Lab Manual Fall 2013Dokumen15 halamanEE2002 Lab Manual Fall 2013Alex KeddyBelum ada peringkat
- 11 de Thi Vao Lop 10 Mon Tieng Anh Audio KeyDokumen47 halaman11 de Thi Vao Lop 10 Mon Tieng Anh Audio Keythuy Linh100% (1)
- CoatingDokumen16 halamanCoatingPubg fansBelum ada peringkat
- Abdul Rasheed (2019-Me-34) Thermodynamic AssignmentDokumen6 halamanAbdul Rasheed (2019-Me-34) Thermodynamic AssignmentAbdul Rasheed GhaziBelum ada peringkat
- How To Read PWHTchartDokumen10 halamanHow To Read PWHTchartAkhilesh Kumar100% (3)
- CPCI Designing With Precast Concrete Structural Solutions PDFDokumen44 halamanCPCI Designing With Precast Concrete Structural Solutions PDFMarie Fe Fortuno Bermido100% (1)