Lab 13-1: Web Server Footprinting Using Tool
Diunggah oleh
Karen Garza0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
58 tayangan7 halamanHACKING
Judul Asli
CEH V10-57
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHACKING
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
58 tayangan7 halamanLab 13-1: Web Server Footprinting Using Tool
Diunggah oleh
Karen GarzaHACKING
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 7
Web server Footprinting
It includes footprinting focused on the web server using different tools such as
Netcraft, Maltego, and httprecon, etc. Results of Web server footprinting brings server
name, type, operating system and running application and other information about
the target website.
Lab 13-1: Web Server Footprinting using Tool
Web Server Footprinting
Download and install ID Server tool.
1. Enter URL or IP address of the target server
Figure 13-04 ID Serve Application
Page 393 of 503
Enter the Query The Server/button.
Figure 13-05 Generating Query
2. Copy the Extracted information.
Figure 13-06 Extracted Information
Information such as Domain name, open ports, Server type and other information
are extracted.
Page 394 of 503
Mirroring a Website
As defined earlier, mirroring a website is the process mirroring the entire website in
the local system. If the entire website is downloaded onto the system, it enables is
attacker to use, inspect the website, directories, structure and to find other
vulnerabilities from this downloaded mirrored website copy. Instead of sending
multiple copies to a web server, this is a way to find vulnerabilities on a website.
Vulnerability Scanning
Vulnerability Scanners are automated utilities which are specially developed to detect
vulnerabilities, weakness, problems, and holes in an operating system, network,
software, and applications. These scanning tools perform deep inspection of scripts,
open ports, banners, running services, configuration errors, and other areas.
Session Hijacking
Attacker by intercepting, altering and using a Man-in-the-Middle attack to hijack a
session. The attacker uses the authenticated session of a legitimate user without
initiating a new session with the target.
Hacking Web Passwords
Password Cracking is the method of extracting the password to gain authorized access
to the target system in the guise of a legitimate user. Password cracking may be
performed by social engineering attack or cracking through tempering the
communication and stealing the stored information.
Password Attacks are classified into the following types: -
Non-Electronic Attacks
Active Online Attacks
Passive Online Attacks
Default Password
Offline Attack
Countermeasures
The basic recommendation for securing the web server from internal and external
attacks and other threat is the place the web server in a secure zone where security
devices such as firewalls, IPS, and IDS are deployed, filtering and inspecting the traffic
destined to the web server. Placing the web server into an isolated environment such
as DMZ protect it from threats.
Figure 13-07 Web Server Deploymen
Page 395 of 503
Detecting Web Server Hacking Attempts
There are several techniques that are being used to detect any intrusion or unexpected
activity in a web server such as Website change detection system detects for a hacking
attempt by using scripting which is focused on inspecting changes made by executable
files. Similarly, hashes are periodically compared to detect modification.
Defending Against Web Server Attacks
Auditing Ports.
Disabling insecure and unnecessary ports.
Using Port 443 HTTPS over port 80 HTTP.
Encrypted traffic.
Server Certificate
Code Access Security Policy
Disable tracing
Disable Debug compiles
Mind Map
Page 396 of 503
Patch Management
Patches and Hotfixes
As we know, Patches and Hotfixes are required to remove vulnerabilities, bugs, and
issues in a software release. Hotfixes are updates which fix these issues whereas
patches are the pieces of software that is specially designed for fixing the issue. A
hotfix is referred to a hot system, specially designed for a live production environment
where fixes have been made outside a normal development and testing to address the
issue.
Patches must be to download from official websites, home sites and application and
Operating system vendors. The recommendation is to register or subscribe to receive
alerts about latest patches and issues.
These patches can be download in the following way:
Manual Download from Vendor
Auto-Update
Patch Management
Patch management is an automated process which ensures the installation of required
or necessary patches on a system. Patch management process detects the missing
security patches, find out a solution, downloads the patch, test the patch in an isolated
environment, i.e., testing machine, and then deploy the patch onto systems.
Page 397 of 503
Lab 13-2: Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer (MBSA)
The Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer is a Windows-based Patch management tool
powered by Microsoft. MBSA identify the missing security updates and common
security misconfigurations. MBSA 2.3 release adds support for Windows 8.1, Windows
8, Windows Server 2012 R2, and Windows Server 2012. Windows 2000 will no longer
be supported with this release.
Procedure:
MBSA is capable of scanning Local system, remote system, and range of the computer.
Figure 13-08 Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer
Select the scanning options as required
Page 398 of 503
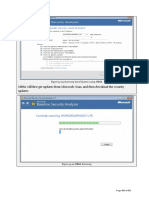
Figure 13-09 Scanning Local System using MBSA
MBSA will first get updates from Microsoft, Scan, and then download the security
updates.
Figure 13-10 MBSA Scanning
Page 399 of 503
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Security Testing MatDokumen9 halamanSecurity Testing MatLias JassiBelum ada peringkat
- Brian - Ashworth: Assessment Event 1 - Assess Network Security Threats and Vulnerabilities To Identify Risk (VM)Dokumen6 halamanBrian - Ashworth: Assessment Event 1 - Assess Network Security Threats and Vulnerabilities To Identify Risk (VM)parkbenchbruceBelum ada peringkat
- Securing Application Deployment with Obfuscation and Code Signing: How to Create 3 Layers of Protection for .NET Release BuildDari EverandSecuring Application Deployment with Obfuscation and Code Signing: How to Create 3 Layers of Protection for .NET Release BuildBelum ada peringkat
- Cybersecurity Essentials Chapter 7Dokumen13 halamanCybersecurity Essentials Chapter 7Samuel AmureBelum ada peringkat
- Reverse Honey TrapDokumen8 halamanReverse Honey TrapelabirBelum ada peringkat
- Securing Web PortalsDokumen12 halamanSecuring Web PortalsPietro VivoliBelum ada peringkat
- Cyber Unit 5 - 1627632179 - 1697003597Dokumen10 halamanCyber Unit 5 - 1627632179 - 1697003597xyz705638Belum ada peringkat
- Digital Malware Analysis - V2Dokumen33 halamanDigital Malware Analysis - V2apgnascimento96Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter - 1.1: Threats and Their SourcesDokumen10 halamanChapter - 1.1: Threats and Their SourcesAlex LeeBelum ada peringkat
- ETHICAL HACKING GUIDE-Part 3: Comprehensive Guide to Ethical Hacking worldDari EverandETHICAL HACKING GUIDE-Part 3: Comprehensive Guide to Ethical Hacking worldBelum ada peringkat
- Secured N-Tier Attack Detection and Prevention MechanismDokumen8 halamanSecured N-Tier Attack Detection and Prevention MechanismseventhsensegroupBelum ada peringkat
- SPE For NAS Getting Started GuideDokumen23 halamanSPE For NAS Getting Started GuideImtiazuddin MohammedBelum ada peringkat
- Security+ 601 Test 2Dokumen61 halamanSecurity+ 601 Test 2Kalen StarBelum ada peringkat
- Report On OWASP What Is OWASP?: Deep Nandu BED-C-48Dokumen4 halamanReport On OWASP What Is OWASP?: Deep Nandu BED-C-48deep nanduBelum ada peringkat
- DNCT703 Network and Cloud Security UpdatedDokumen13 halamanDNCT703 Network and Cloud Security UpdatedAnchal SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Demystifying Penetration TestingDokumen35 halamanDemystifying Penetration TestingAnderson MoreiraBelum ada peringkat
- Day 3Dokumen3 halamanDay 3parthmanitripathi1Belum ada peringkat
- Kaspersky Lab Whitepaper Systems Management Eng FinalDokumen3 halamanKaspersky Lab Whitepaper Systems Management Eng FinalchaitanyaBelum ada peringkat
- Endpoint Security (Ch10)Dokumen15 halamanEndpoint Security (Ch10)Areej OmarBelum ada peringkat
- Proactive Network Defence 7CS017Dokumen15 halamanProactive Network Defence 7CS017Anchal SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Penetration Testing Fundamentals-2: Penetration Testing Study Guide To Breaking Into SystemsDari EverandPenetration Testing Fundamentals-2: Penetration Testing Study Guide To Breaking Into SystemsBelum ada peringkat
- Installation and Use RightsDokumen6 halamanInstallation and Use RightsSofian ChenBelum ada peringkat
- There Are Several Ways To Manage A Secured SiteDokumen2 halamanThere Are Several Ways To Manage A Secured SiteBatrisyia SainiBelum ada peringkat
- Security Operations Center - Analyst Guide: SIEM Technology, Use Cases and PracticesDari EverandSecurity Operations Center - Analyst Guide: SIEM Technology, Use Cases and PracticesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- Hunting for MalwareDokumen15 halamanHunting for MalwareadvajayltiwariBelum ada peringkat
- 15067CEM ResitDokumen20 halaman15067CEM Resithoney arguellesBelum ada peringkat
- 5 SecurityTestingDokumen10 halaman5 SecurityTestingIlham AbBelum ada peringkat
- Threat Modelling and Pen Testing On Google GruyereDokumen32 halamanThreat Modelling and Pen Testing On Google Gruyerekartike tiwariBelum ada peringkat
- Pentest Workplan: Information Gathering and Vulnerability AnalysisDokumen5 halamanPentest Workplan: Information Gathering and Vulnerability AnalysisLe ChauveBelum ada peringkat
- Privacy Information For Installation Features: Collection of Information About Your ComputerDokumen14 halamanPrivacy Information For Installation Features: Collection of Information About Your ComputerBob CaronBelum ada peringkat
- Windows HardeningDokumen36 halamanWindows Hardeningomarelmoktar19869795Belum ada peringkat
- 01 - Security EssentialsDokumen34 halaman01 - Security EssentialsMan ModiBelum ada peringkat
- Symantec Web Gateway 5.0 Getting Started Guide enDokumen69 halamanSymantec Web Gateway 5.0 Getting Started Guide enAmar KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Symantec™ Protection Engine For Network Attached Storag 8.1 Getting Started GuideDokumen12 halamanSymantec™ Protection Engine For Network Attached Storag 8.1 Getting Started GuideRobertFeneaBelum ada peringkat
- A Practical Guide To Web Application SecurityDokumen10 halamanA Practical Guide To Web Application SecurityStillward Laud Mark-MillsBelum ada peringkat
- Network Security Vulnerabilities and Best PracticesDokumen13 halamanNetwork Security Vulnerabilities and Best PracticesRishikaa RamBelum ada peringkat
- Establishing Application SecurityDokumen6 halamanEstablishing Application SecurityKarl Alvin Reyes HipolitoBelum ada peringkat
- Detection and Evasion of Web Application AttacksDokumen66 halamanDetection and Evasion of Web Application AttacksNancy PeterBelum ada peringkat
- Datasheet MWS1000Dokumen6 halamanDatasheet MWS1000ducquang89Belum ada peringkat
- Unit IIIDokumen84 halamanUnit IIIYogita TiwariBelum ada peringkat
- Deep Security 96 SP1 Install Guide Basic enDokumen88 halamanDeep Security 96 SP1 Install Guide Basic enmkavinmcaBelum ada peringkat
- Avira Vir Server: SupportDokumen19 halamanAvira Vir Server: SupportHassanBelum ada peringkat
- Courseproject Websecurity Final LeviwelshansDokumen11 halamanCourseproject Websecurity Final Leviwelshansapi-282901577Belum ada peringkat
- Securing Websites: Top TipsDokumen17 halamanSecuring Websites: Top TipsatraidezBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 2 Application Security Another - PG 1 - 15Dokumen15 halamanUnit 2 Application Security Another - PG 1 - 15VishalBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 2 Application Security AnotherDokumen27 halamanUnit 2 Application Security AnotherVishalBelum ada peringkat
- Web Server Vulnerabilities And Security Measures: Members: Vũ Hoàng Đinh Hoàng Phi Instructor: Msc Nguyễn DuyDokumen23 halamanWeb Server Vulnerabilities And Security Measures: Members: Vũ Hoàng Đinh Hoàng Phi Instructor: Msc Nguyễn Duynewlife439Belum ada peringkat
- Security in System DevelopmentDokumen33 halamanSecurity in System DevelopmentYusifsuleimanBelum ada peringkat
- Ceh Chap8 QuizletDokumen2 halamanCeh Chap8 QuizletlynnverbBelum ada peringkat
- Important Question Ethical HackingDokumen27 halamanImportant Question Ethical Hackingsuthojuakhil21Belum ada peringkat
- Secure Software Notes On Operating SystemsDokumen6 halamanSecure Software Notes On Operating SystemsVarun MohunahBelum ada peringkat
- WP Bsa Windows Server SC Lores enDokumen16 halamanWP Bsa Windows Server SC Lores enDigital MultipayBelum ada peringkat
- WP Hacme Bank v2 User GuideDokumen74 halamanWP Hacme Bank v2 User GuideCesar Fabian MlBelum ada peringkat
- MS Sec Boot Ref Des WP v1Dokumen19 halamanMS Sec Boot Ref Des WP v1lndyaBhaiBelum ada peringkat
- Srs 360Dokumen11 halamanSrs 360Abhishek Kumar67% (9)
- Halliburton's Firewall Case StudyDokumen34 halamanHalliburton's Firewall Case StudyPranjal GharatBelum ada peringkat
- Getting Started SNAC12.1Dokumen30 halamanGetting Started SNAC12.1krisk_28Belum ada peringkat
- Incident Response Process Preparation GuideDokumen14 halamanIncident Response Process Preparation GuidevanessaBelum ada peringkat
- 1.4.1.1 Lab - Researching Network Attacks and Security Audit ToolsDokumen4 halaman1.4.1.1 Lab - Researching Network Attacks and Security Audit Toolssafwan eshamasulBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Honeypots 1. High-Interaction HoneypotsDokumen2 halamanTypes of Honeypots 1. High-Interaction HoneypotsKaren GarzaBelum ada peringkat
- MBSA Will First Get Updates From Microsoft, Scan, and Then Download The Security UpdatesDokumen1 halamanMBSA Will First Get Updates From Microsoft, Scan, and Then Download The Security UpdatesKaren GarzaBelum ada peringkat
- Ceh V10-54-3Dokumen2 halamanCeh V10-54-3Karen GarzaBelum ada peringkat
- Ceh V10-55-3Dokumen2 halamanCeh V10-55-3Karen GarzaBelum ada peringkat
- Advantages Disadvantages: 3. Stateful Multilayer Inspection FirewallDokumen2 halamanAdvantages Disadvantages: 3. Stateful Multilayer Inspection FirewallKaren GarzaBelum ada peringkat
- Ceh V10-52-2Dokumen1 halamanCeh V10-52-2Karen GarzaBelum ada peringkat
- Ceh V10-56-6Dokumen1 halamanCeh V10-56-6Karen GarzaBelum ada peringkat
- Patch Management: Patches and HotfixesDokumen1 halamanPatch Management: Patches and HotfixesKaren GarzaBelum ada peringkat
- Ceh V10-58-7Dokumen1 halamanCeh V10-58-7Karen GarzaBelum ada peringkat
- Go To Windows 7 Machine 5. Open Command Prompt 6. Generate Some Traffic Like FTPDokumen1 halamanGo To Windows 7 Machine 5. Open Command Prompt 6. Generate Some Traffic Like FTPKaren GarzaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 12: Evading IDS, Firewall and HoneypotsDokumen1 halamanChapter 12: Evading IDS, Firewall and HoneypotsKaren GarzaBelum ada peringkat
- CEH v10 Module 21 - References ESDokumen7 halamanCEH v10 Module 21 - References ESKaren GarzaBelum ada peringkat
- Ceh V10-52-1Dokumen1 halamanCeh V10-52-1Karen GarzaBelum ada peringkat
- Back To Windows Server 2016 and Observe The LogsDokumen1 halamanBack To Windows Server 2016 and Observe The LogsKaren GarzaBelum ada peringkat
- Evading Firewalls: Firewall IdentificationDokumen2 halamanEvading Firewalls: Firewall IdentificationKaren GarzaBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 13-1: Web Server Footprinting Using ToolDokumen1 halamanLab 13-1: Web Server Footprinting Using ToolKaren GarzaBelum ada peringkat
- Web Server Misconfiguration VulnerabilitiesDokumen1 halamanWeb Server Misconfiguration VulnerabilitiesKaren GarzaBelum ada peringkat
- Web Application Concepts: Server AdministratorDokumen1 halamanWeb Application Concepts: Server AdministratorKaren GarzaBelum ada peringkat
- IIS Web Server Architecture: Components of IIS Protocol ListenerDokumen1 halamanIIS Web Server Architecture: Components of IIS Protocol ListenerKaren GarzaBelum ada peringkat
- Ceh V10-57-4Dokumen1 halamanCeh V10-57-4Karen GarzaBelum ada peringkat
- Web Server Misconfiguration VulnerabilitiesDokumen1 halamanWeb Server Misconfiguration VulnerabilitiesKaren GarzaBelum ada peringkat
- Go To Windows 7 Machine 5. Open Command Prompt 6. Generate Some Traffic Like FTPDokumen1 halamanGo To Windows 7 Machine 5. Open Command Prompt 6. Generate Some Traffic Like FTPKaren GarzaBelum ada peringkat
- Enter The Query The Server/buttonDokumen1 halamanEnter The Query The Server/buttonKaren GarzaBelum ada peringkat
- Fragmentation Attack: Denial-Of-Service Attack (Dos)Dokumen2 halamanFragmentation Attack: Denial-Of-Service Attack (Dos)Karen GarzaBelum ada peringkat
- Ceh V10-55-3Dokumen2 halamanCeh V10-55-3Karen GarzaBelum ada peringkat
- Ceh V10-56-6Dokumen1 halamanCeh V10-56-6Karen GarzaBelum ada peringkat
- Fragmentation Attack: Denial-Of-Service Attack (Dos)Dokumen2 halamanFragmentation Attack: Denial-Of-Service Attack (Dos)Karen GarzaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 13: Hacking Web Servers: Technology BriefDokumen1 halamanChapter 13: Hacking Web Servers: Technology BriefKaren GarzaBelum ada peringkat
- Evading Firewalls: Firewall IdentificationDokumen2 halamanEvading Firewalls: Firewall IdentificationKaren GarzaBelum ada peringkat
- IIS Web Server Architecture: Components of IIS Protocol ListenerDokumen1 halamanIIS Web Server Architecture: Components of IIS Protocol ListenerKaren GarzaBelum ada peringkat
- Uplink Epon OLT Software Release Notes SummaryDokumen31 halamanUplink Epon OLT Software Release Notes SummaryAhmed Mah PamuNgkasBelum ada peringkat
- Manual de Reparação - GM VectraDokumen1 halamanManual de Reparação - GM Vectramurilokioshi12Belum ada peringkat
- JavaScript Book Without Projects Code v1Dokumen84 halamanJavaScript Book Without Projects Code v1yeechienBelum ada peringkat
- Web Management Tools and Web PortalsDokumen29 halamanWeb Management Tools and Web Portalsحيدر بداوي العتابيBelum ada peringkat
- Project ReportDokumen58 halamanProject ReportDikshant ChitaraBelum ada peringkat
- JDK UpgradeDokumen11 halamanJDK UpgradeBhavani Ommi100% (1)
- Chura Liya Hai Tumne - Yaadon Ki BaraatDokumen6 halamanChura Liya Hai Tumne - Yaadon Ki BaraatAbhishek Chakraborty0% (1)
- ProScan ManualDokumen68 halamanProScan ManualIng Jesus SantiagoBelum ada peringkat
- Study On How Dark Web Facilitate Cyber Security Experts To Improve Business SecuritDokumen8 halamanStudy On How Dark Web Facilitate Cyber Security Experts To Improve Business SecuritIJRASETPublicationsBelum ada peringkat
- Real Estate SEO StudyDokumen18 halamanReal Estate SEO StudyMNRealtor100% (6)
- User Manual - DOCEANE SUPRA 1: Categories Upload Type ProductDokumen1 halamanUser Manual - DOCEANE SUPRA 1: Categories Upload Type Productjtr dtyuhBelum ada peringkat
- Sesi 3 PKPDokumen14 halamanSesi 3 PKPNuraihan HashimBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Office Add-In DevelopmentDokumen40 halamanAdvanced Office Add-In DevelopmentReadoneBelum ada peringkat
- CCNA Security v2.0 Final Exam Answers 100 1 PDFDokumen26 halamanCCNA Security v2.0 Final Exam Answers 100 1 PDFLêTrungĐức100% (3)
- Digital Entrepreneurship Program: Course-Career-IncomeDokumen15 halamanDigital Entrepreneurship Program: Course-Career-IncomeSuyog PatilBelum ada peringkat
- KozjakDokumen6 halamanKozjakĐuka ObođanBelum ada peringkat
- WD Lab ManualDokumen78 halamanWD Lab ManualTom JerryBelum ada peringkat
- 315 Libros Gratis de TraducciónDokumen207 halaman315 Libros Gratis de TraducciónTraducător Autorizat Marilena Iordache100% (1)
- 50 Ways To Get Online Tutoring Students 2021 1Dokumen16 halaman50 Ways To Get Online Tutoring Students 2021 1Gaia Wellness CompanyBelum ada peringkat
- (Rapidleech) (D) Ifile It - PHPDokumen5 halaman(Rapidleech) (D) Ifile It - PHPAditya Ryu ArzoBelum ada peringkat
- Midterm EmpotechDokumen2 halamanMidterm EmpotechJessy BascoBelum ada peringkat
- Sama AjaxDokumen17 halamanSama Ajaxernestohp7Belum ada peringkat
- Computer StudiesDokumen17 halamanComputer StudiesMJAY GRAPHICSBelum ada peringkat
- Resume Refinement System Using Semantic AnalysisDokumen3 halamanResume Refinement System Using Semantic AnalysisInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyBelum ada peringkat
- MATHEMATICS in The Web PDFDokumen236 halamanMATHEMATICS in The Web PDFalsamixersBelum ada peringkat
- 300 High Qulity SEO Backlink With 20 edu gov linksDokumen6 halaman300 High Qulity SEO Backlink With 20 edu gov linksddesignsindia40% (5)
- Google Nonfiction ReadingDokumen6 halamanGoogle Nonfiction ReadingNick wolerdyBelum ada peringkat
- Etech q2 Mod4 How To Manage An Online ICT Project For Social ChangeDokumen34 halamanEtech q2 Mod4 How To Manage An Online ICT Project For Social ChangeRochelle VentirezBelum ada peringkat
- Meili SearchDokumen13 halamanMeili Searchtuandat09112002Belum ada peringkat
- Wonderful Law of Attraction Book PDFDokumen300 halamanWonderful Law of Attraction Book PDFNeil Bryan N. MoninioBelum ada peringkat