Switchgear Presentation
Diunggah oleh
Ahmad Yaseen100%(1)100% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (1 suara)
140 tayangan2 halamanimportant
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Iniimportant
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
100%(1)100% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (1 suara)
140 tayangan2 halamanSwitchgear Presentation
Diunggah oleh
Ahmad Yaseenimportant
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
Switchgear presentation
1. 1. Nadir Baloch T.A 175 Switchgear & Maintenance
2. 2. SWITCHGEAR switchgear is the combination of electrical disconnect switches, fuses or
circuit breakers used to control, protect and isolate electrical equipment. Switchgear is used
both to de-energize equipment to allow work to be done and to clear faults downstream.
3. 3. Switchgear
4. 4. Types: LV Switchgear MV Switchgear Generally electrical switchgear rated upto 1 KV is
termed as low voltage switchgear The most common use of LV switchgear is in LV
distribution board.
5. 5. THE ROLE OF SWITCHGEAR IS : ELECTRICAL PROTECTION SAFE ISOLATION
FROM LIVE PARTS LOCAL OR REMOTE SWITCHING The basic functions of Switchgear
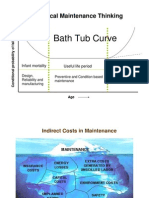
6. 6. Periodic Maintenance Preventive Maintenance a) 2 yearly Maintenance b) 4 yearly
Maintenance Importance Of PM Through such PM, troubles can be detected in the Early
stages and corrective actions can be taken before extensive damage occurs.
7. 7. The most common use of LV switchgear is in LV distribution board. This system has the
following parts Incomer The incomer feeds incoming electrical power to the incomer bus. The
switchgear used in the incomer should have a main switching device. The switchgear
devices attached with incomer should be capable of withstanding abnormal current for a
short specific duration in order to allow downstream devices to operate. Generally Air Circuit
Breakers are preferably used as interrupting device. Sub – Incomer These sub – incomers
draw power from main incomer bus and feed this power to feeder bus Feeders Different
feeders are connected to the feeder bus to feeds different loads like, motor loads, lighting
loads, industrial machinery loads, air conditioner loads, transformer cooling system loads etc.
8. 8. Main Transformer Incomer
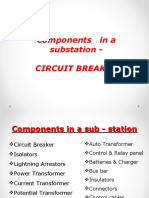
9. 9. Main Components Of Switchgears
10. 10. Busbar Busbar is a strip or bar of copper, brass or aluminium that conducts electricity
within a switchboard, distribution board, substation, The cross-sectional size of the busbar
determines the maximum amount of current Used to interconnect the loads and sources of
electrical power.
11. 11. Busbar Specification Manufacturer: Nova Magrini Gallilio Type of Busbar : Copper (
Insulated with Silver coated joints) Busbar Rating : 1500 Amp Method Of Cleaning : Clean
with Lint Free Cloth Busbar Dimensions : 2*100*8 mm Busbar Maintenance Full Bus Bar
Inspection check for overheating signs, visual inspection of Cu plate and nut bolts. cleaning
of incoming/outgoing spouts. Remove dust with vacuum cleaner. Cleaning and lubricating
mechanical links with contact grease. Check operating mechanism of shutter. Contact
Resistance of Electrical joints. Check IR to earth and between phases on busbar and
outgoing circuits @ 2500V
12. 12. Air Circuit Breaker (ACB) A circuit breaker is an automatically operated electrical switch
designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by overload or short circuit. Its
basic function is to detect a fault condition and interrupt current flow
13. 13. This type of circuit breakers, is those kind of circuit breaker which operates in air at
atmospheric pressure. ACBs are still preferable choice up to voltage 15 KV It is also
good choice to avoid the risk of oil fire, in case of oil circuit breaker. Operation Of ACB The
first objective is usually achieved by forcing the arc into contact with as large an area as
possible of insulating material. Every air circuit breaker is fitted with a chamber surrounding
the contact. This chamber is called ‘arc chute’. The arc is driven into it. If inside of the arc
chute is suitably shaped, and if the arc can be made conform to the shape, the arc chute wall
will help to achieve cooling.
14. 14. Air Circuit Breakers : Charging method Circuit breaker closing springs may be
compressed manually or by means of a small electric motor. The closing coil is charged by
manual charging handle. For closing, first charge the spring by using the charging handle
15. 15. Maintenance of Air Circuit Breaker LV Circuit Breakers operating at 600 volt and below,
should be inspected Maintained every 1 to 4 years depending on their services and
operating Conditions. Conditions that make frequency maintenance and inspection are
necessary: High humidity and High temp Dusty or Dirty Atmosphere Corrosive
Atmosphere
16. 16. Inspection & Cleaning Insulating parts including bushing should be cleaned of dust
Clean & inspect Arc Chutes for Cracks, Broken Parts . Replace Damage Parts Inspect
Breaker Operating Mechanism for loose hardware & missing or broken etc Examine for
wears Check Rack in/ out mechanism for normel operation Lubricate if necessary
Check tightness of all terminations Contacts maintenance Arcing contacts to be verified for
burn off To be adjusted or exchanged that arc contacts simultaneoslu when closing
Permissible tolerance 1mm Adjust lead of arcing contacts from main contacts such that when
arc contacts Meet then distance between
17. 17. Insulation Resistance Test (Megger) Load and line conductors should disconnected from
the breaker to make Test. IR between phases and phases w.r.t ground with breaker closed.
the result is compared against manufacturer/ pervious data For breaker being tested. Cycling
the breaker On & Off the breaker several times to check the correct operation Of breaker.
Verify For Loop Check Insert circuit breaker at test position and on & off the breaker from
remote location
18. 18. Current Transformer A current transformer (CT) is used for measurement of alternating
electric currents
19. 19. Current transformer are used in electrical power system for stepping down currents of the
system for metering and protection purpose. A CT functions with the same basic working
principle of electrical power transformer CT steps down rated system current to 1 Amp or 5
Amp. Because the relays and meters are generally designed for 1 Amp, 5 Amp and 110V
20. 20. Relay Relays is automatic device which senses an abnormal condition of electrical circuit
and closes its contacts. these contacts in turns close and complete the circuit breaker trip
coil circuit hence make the circuit breaker tripped
21. 21. Protective Relay Testing Why do we use protective relays? Their main duty is to isolate a
faulty section within few cycles Periodic Maintenance Testing After a relay is commissioned
it’s important to carry out regular maintenance tests. Some of the advantages of such
testing can be stated as, it will pin point a defective relay before it fails to act during a fault
Methods of Testing Steady State: steady state testing is for checking the relay pick up.
Injected current, voltage. when the current is raised and then fluctuated around pick up.
Dynamic state Time for relay operation is measured.
22. 22. Freja 300 The FREJA 300 relay testing system is a computer-aided relay testing system
by injecting current and voltage.
23. 23. Testing Principles There are two main principles as primary injection and secondary
injection. • Primary injection- High current is injected to primary side of the CT. Test carried
out covers CT, conductors, relay and sometimes circuit breaker as well. The relay unit has to
be isolated from the power system. Usually this principle is used at commissioning and also
if the secondary of the CT is not accessible. • Secondary injection - Relay is disconnected
from the CT and the stepped down current is directly injected to relay.
24. 24. General Precautions to be taken Check the Electrical Isolation First During maintenance
Earth MUST be connected Before maintenance of breaker spring must be discharge. Don’t
use compressed air on breaker Don’t use file or emery paper for contacts cleaning
Inspection Inside Switchgear Room Switchgear environment (switch room access and
surrounds, including fence and external walls if outdoors. Signs of water Signs of
unauthorized access Condition of firefighting equipment and warning notices General
Housekeeping
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Internal Audit Checklist ISO 14001Dokumen9 halamanInternal Audit Checklist ISO 14001Yasir Zoha100% (3)
- Internal Audit Checklist ISO 14001Dokumen9 halamanInternal Audit Checklist ISO 14001Yasir Zoha100% (3)
- GENUS Clock Gating Timing CheckDokumen17 halamanGENUS Clock Gating Timing Checkwasimhassan100% (1)
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionDari EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- DD 3600 3500 3000 Parts CatalogDokumen46 halamanDD 3600 3500 3000 Parts CatalogAndres Fdo Mora D100% (2)
- Electrical Substation Switch Yard General EquipmentsDokumen22 halamanElectrical Substation Switch Yard General EquipmentsAnand SwamiBelum ada peringkat
- Maintenance & Repair: ElectricalDokumen27 halamanMaintenance & Repair: ElectricalmeloshhkaBelum ada peringkat
- Comprehensive Electrical System Maintenance ChecklistsDokumen5 halamanComprehensive Electrical System Maintenance ChecklistsAshwinSiddaramaiahBelum ada peringkat
- Maintenance of Low Voltage Circuit BreakersDokumen2 halamanMaintenance of Low Voltage Circuit BreakersJuvencio MolinaBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Maintenance of Electrical Installation: Ayan Ghose Junior Engineer Ranaghat Electrical Section, PWDDokumen13 halamanElectrical Maintenance of Electrical Installation: Ayan Ghose Junior Engineer Ranaghat Electrical Section, PWDnatureayanBelum ada peringkat
- EDOC - Protective Relay Testing and Maintenance OverviewDokumen13 halamanEDOC - Protective Relay Testing and Maintenance OverviewEl Comedor BenedictBelum ada peringkat
- Primary Vs Secondary Injection Testing For Circuit BreakersDokumen9 halamanPrimary Vs Secondary Injection Testing For Circuit BreakersEmma TillanoBelum ada peringkat
- Significance of Protection SystemDokumen46 halamanSignificance of Protection Systemgurdeep100% (1)
- EDOC - 10 Critical Tests For New Power Circuit BreakersDokumen7 halamanEDOC - 10 Critical Tests For New Power Circuit BreakersEl Comedor BenedictBelum ada peringkat
- Frequency of Maintenance TestingDokumen5 halamanFrequency of Maintenance TestingIsmael AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Switch Gear1Dokumen35 halamanSwitch Gear1Subhasish MahapatraBelum ada peringkat
- Transformer Oil Purification / Filtration Process / ProcedureDokumen27 halamanTransformer Oil Purification / Filtration Process / ProcedurekaaisBelum ada peringkat
- Current Transformer OperationDokumen6 halamanCurrent Transformer Operationsurya892Belum ada peringkat
- Pres18 - Testing and Maintenance 2-02Dokumen41 halamanPres18 - Testing and Maintenance 2-02Vishwanath TodurkarBelum ada peringkat
- Transformer - Construction, Working, Types & ApplicationDokumen11 halamanTransformer - Construction, Working, Types & ApplicationDeepakDeepBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet in e SPCL Electrical Drgs Hec r2 1) PCC Panels 04513, Rev-2, (General Note, Bom, BBC For Pccs of Ltss-17 To Ltss-21)Dokumen10 halamanWorksheet in e SPCL Electrical Drgs Hec r2 1) PCC Panels 04513, Rev-2, (General Note, Bom, BBC For Pccs of Ltss-17 To Ltss-21)nidnitrkl051296Belum ada peringkat
- HVPE Operation and MaintenanceDokumen116 halamanHVPE Operation and MaintenanceMinerva AbantoBelum ada peringkat
- LV Catalogue 2017Dokumen132 halamanLV Catalogue 2017Ariel DimacaliBelum ada peringkat
- Conditioning Monitoring of TransformerDokumen5 halamanConditioning Monitoring of TransformerAnonymous lEmZKBXiv100% (1)
- EME 308 AssignmentDokumen4 halamanEME 308 AssignmentVictorBelum ada peringkat
- Maintenance of Meduim Voltage Circuit BreakersDokumen2 halamanMaintenance of Meduim Voltage Circuit BreakershafizgBelum ada peringkat
- Substation LayoutDokumen4 halamanSubstation LayoutJitendra MahidaBelum ada peringkat
- Testing HVCB 1Dokumen6 halamanTesting HVCB 1rmatspBelum ada peringkat
- What Is REF (Restricted Earth Fault Protection) On Transformer?Dokumen8 halamanWhat Is REF (Restricted Earth Fault Protection) On Transformer?ashutosh2009Belum ada peringkat
- UniMasr.com 79e3983af376cc3e0a3c7adef354815eDokumen60 halamanUniMasr.com 79e3983af376cc3e0a3c7adef354815eBala MBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical TransformerDokumen19 halamanElectrical Transformer164ec1f5100% (1)
- Breaker Failure ProtectionDokumen3 halamanBreaker Failure ProtectionvipulkumarjainBelum ada peringkat
- Comprehensive Electrical System Maintenance ChecklistsDokumen12 halamanComprehensive Electrical System Maintenance ChecklistsFarrukh Nadeem100% (1)
- Erection Procedures For Medium Voltage Switchgear - EEP PDFDokumen5 halamanErection Procedures For Medium Voltage Switchgear - EEP PDFMoucha JustdoitBelum ada peringkat
- Voltage Control Techniques Session 1Dokumen23 halamanVoltage Control Techniques Session 1Sumit SinghBelum ada peringkat
- O&M TransformerDokumen47 halamanO&M TransformerAshish PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Module 19 - MV SwitchgearDokumen58 halamanModule 19 - MV SwitchgearDipayan DasBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Switchgear and SafetyDokumen16 halamanElectrical Switchgear and SafetyAli Khamis100% (1)
- SubstationsDokumen34 halamanSubstationsBeen Carlo De JasminBelum ada peringkat
- ZLAC8015Dokumen9 halamanZLAC8015THANAWATBelum ada peringkat
- Note Switchgear PDFDokumen36 halamanNote Switchgear PDFNur FatihahBelum ada peringkat
- 3 - Transformer FaultDokumen4 halaman3 - Transformer FaultJoseph FaresBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Manual Switchgear and Protection SapDokumen46 halamanLab Manual Switchgear and Protection SapYash MaheshwariBelum ada peringkat
- Transformer BsetDokumen31 halamanTransformer Bsetrahat100% (1)
- Upptcl Training (Ee)Dokumen27 halamanUpptcl Training (Ee)AakashBelum ada peringkat
- Branch Feeder Monitor BFM Ii: Operation and Installation ManualDokumen111 halamanBranch Feeder Monitor BFM Ii: Operation and Installation ManualJean MelendezBelum ada peringkat
- Medium-Voltage Switchgear and Circuit BreakersDokumen17 halamanMedium-Voltage Switchgear and Circuit BreakersJeremy Orajay0% (1)
- Important TermsDokumen45 halamanImportant TermsrameshsmeBelum ada peringkat
- LV Underground Cable JointingDokumen11 halamanLV Underground Cable JointingQais Alsafasfeh100% (2)
- ProtocolsDokumen9 halamanProtocolsSantanu RoutBelum ada peringkat
- SGP 01 To 06Dokumen118 halamanSGP 01 To 06Sanyam BajpaiBelum ada peringkat
- Bus BArDokumen822 halamanBus BArCHANDER SINGH WARKADE100% (1)
- 04 Transformer Maintenance#Dokumen17 halaman04 Transformer Maintenance#aimiza100% (1)
- 132 GssDokumen40 halaman132 GssSonu Lovesforu100% (1)
- Inspection of MCC - EEPDokumen3 halamanInspection of MCC - EEPwaseemBelum ada peringkat
- Neutral Earth Resistor PDFDokumen15 halamanNeutral Earth Resistor PDFYume YumeBelum ada peringkat
- Power Transformer MaintenanceDokumen27 halamanPower Transformer MaintenanceBIKASH SAHBelum ada peringkat
- Lucy Ring MainDokumen12 halamanLucy Ring MainfndprojectBelum ada peringkat
- Micom P341Dokumen425 halamanMicom P341Vel MuruganBelum ada peringkat
- Schneider Ect128 - Design and Use of Current-Limiting Fuse - 1Dokumen30 halamanSchneider Ect128 - Design and Use of Current-Limiting Fuse - 1lbk50100% (1)
- Maintainence of Circuit BreakerDokumen34 halamanMaintainence of Circuit Breakeramirtha_s2238Belum ada peringkat
- Knowledge is "Real Power": Introduction to Power QualityDari EverandKnowledge is "Real Power": Introduction to Power QualityBelum ada peringkat
- Torque Prod Ac DrivesDokumen32 halamanTorque Prod Ac DrivesThanigaivelu SubrmanianBelum ada peringkat
- First Aid Course GeneralDokumen5 halamanFirst Aid Course GeneralAhmad YaseenBelum ada peringkat
- Risk-Based Thinking IN ISO 9001:2015:: How Understanding Risk Improves Quality in Your OrganizationDokumen12 halamanRisk-Based Thinking IN ISO 9001:2015:: How Understanding Risk Improves Quality in Your OrganizationAhmad Yaseen100% (2)
- INTERNET Effect On Social Relations and BehaviourDokumen7 halamanINTERNET Effect On Social Relations and BehaviourAhmad YaseenBelum ada peringkat
- Traction: Yasmin Samy Fouad Mohammed AttiaDokumen20 halamanTraction: Yasmin Samy Fouad Mohammed AttiaAhmad YaseenBelum ada peringkat
- Cognitive DissonanceDokumen6 halamanCognitive DissonanceAhmad YaseenBelum ada peringkat
- PASSDokumen1 halamanPASSAhmad YaseenBelum ada peringkat
- ID No.: 4D190084: Prepared By: Yasmin Samy FouadDokumen10 halamanID No.: 4D190084: Prepared By: Yasmin Samy FouadAhmad YaseenBelum ada peringkat
- Zeus Product BrochureDokumen8 halamanZeus Product BrochureAdmiral KunkkaBelum ada peringkat
- Atatürk'S Principles and History of Revolution Ii: Military Coups in The History of The Turkish RepublicDokumen3 halamanAtatürk'S Principles and History of Revolution Ii: Military Coups in The History of The Turkish RepublicAhmad YaseenBelum ada peringkat
- Military CoupsDokumen4 halamanMilitary CoupsAhmad YaseenBelum ada peringkat
- Brazil: The Mais Médicos ProgrammeDokumen16 halamanBrazil: The Mais Médicos ProgrammeAhmad YaseenBelum ada peringkat
- Covering CapDokumen6 halamanCovering CapAhmad YaseenBelum ada peringkat
- The Impact of The Internet On Social BehaviorDokumen6 halamanThe Impact of The Internet On Social BehaviorAhmad YaseenBelum ada peringkat
- Atatürk'S Principles and History of Revolution Ii: Military Coups in The History of The Turkish RepublicDokumen3 halamanAtatürk'S Principles and History of Revolution Ii: Military Coups in The History of The Turkish RepublicAhmad YaseenBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Overcurrent Protective Device Ratings You Must Properly Select PDFDokumen8 halaman3 Overcurrent Protective Device Ratings You Must Properly Select PDFAhmad YaseenBelum ada peringkat
- Products Comparison List - Jarir Bookstore, Not Just A BookstoreDokumen3 halamanProducts Comparison List - Jarir Bookstore, Not Just A BookstoreAhmad YaseenBelum ada peringkat
- بشرى لمرضى السكر PDFDokumen3 halamanبشرى لمرضى السكر PDFAhmad YaseenBelum ada peringkat
- Ems An Implementation Guide For Small and Medium Sized Organizations 2ndedDokumen201 halamanEms An Implementation Guide For Small and Medium Sized Organizations 2ndedAhmad YaseenBelum ada peringkat
- Qms Iso 9001 2015 TrainingDokumen7 halamanQms Iso 9001 2015 TrainingAhmad YaseenBelum ada peringkat
- Tejoury Company Profile - 2017.Dokumen16 halamanTejoury Company Profile - 2017.Ahmad YaseenBelum ada peringkat
- Substations & Switchgears Transformers Power Converters: Electrical Equipment & Bulk MaterialsDokumen2 halamanSubstations & Switchgears Transformers Power Converters: Electrical Equipment & Bulk MaterialsAhmad YaseenBelum ada peringkat
- The Basics of Arc Flash Article GE Industrial Solutions 0Dokumen3 halamanThe Basics of Arc Flash Article GE Industrial Solutions 0rajinikanth19Belum ada peringkat
- Assessment ManualDokumen14 halamanAssessment ManualAhmad YaseenBelum ada peringkat
- Policy For Live Work On System OPSAF-01-001 Issue 4Dokumen7 halamanPolicy For Live Work On System OPSAF-01-001 Issue 4Ahmad YaseenBelum ada peringkat
- 11m7 PDF en PDFDokumen1 halaman11m7 PDF en PDFAhmad YaseenBelum ada peringkat
- 50263dbb2fb8547 Ek PDFDokumen5 halaman50263dbb2fb8547 Ek PDFAhmad YaseenBelum ada peringkat
- U.S. Department of Labor Occupational Safety and Health AdministrationDokumen71 halamanU.S. Department of Labor Occupational Safety and Health AdministrationSAYEDBelum ada peringkat
- Sawdust in Service PanelDokumen8 halamanSawdust in Service PanelAhmad YaseenBelum ada peringkat
- QLD Plan Draft Review Raw DataDokumen242 halamanQLD Plan Draft Review Raw DataRohit Jain100% (1)
- BF254 BF255Dokumen3 halamanBF254 BF255rrr2013Belum ada peringkat
- DocumentationDokumen44 halamanDocumentation19-512 Ratnala AshwiniBelum ada peringkat
- Professional Development Objectives Related To Modalities Specific TopicsDokumen3 halamanProfessional Development Objectives Related To Modalities Specific TopicsCris100% (1)
- CH 4 Naac PPT 07-12Dokumen13 halamanCH 4 Naac PPT 07-12Arshad MohammedBelum ada peringkat
- Review Problems On Gas TurbineDokumen9 halamanReview Problems On Gas TurbinejehadyamBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation 1Dokumen22 halamanPresentation 1AILYN PECASALESBelum ada peringkat
- Trend Trading StocksDokumen64 halamanTrend Trading Stockssasi717100% (1)
- Family School Project Lesson Plan AstrologyDokumen3 halamanFamily School Project Lesson Plan Astrologyapi-529488210Belum ada peringkat
- FCC O Cials Denounce Lawmakers' Attempts To Censor NewsroomsDokumen52 halamanFCC O Cials Denounce Lawmakers' Attempts To Censor NewsroomsKeithStewartBelum ada peringkat
- Rise of Al JazeeraDokumen1 halamanRise of Al Jazeeraইlish ProductionsBelum ada peringkat
- (IGC 2024) 2nd Circular - 0630Dokumen43 halaman(IGC 2024) 2nd Circular - 0630VictoriaBelum ada peringkat
- Fbla Scavenger Hunt 1Dokumen3 halamanFbla Scavenger Hunt 1api-472648158Belum ada peringkat
- T10 - PointersDokumen3 halamanT10 - PointersGlory of Billy's Empire Jorton KnightBelum ada peringkat
- Market Challengers StrategiesDokumen19 halamanMarket Challengers Strategiestobbob007100% (20)
- Pesud Abadi Mahakam Company Profile Abdul Basith-DikonversiDokumen48 halamanPesud Abadi Mahakam Company Profile Abdul Basith-DikonversiAndi HafizBelum ada peringkat
- English Assignment - October 6, 2020 - Group AssignmentDokumen3 halamanEnglish Assignment - October 6, 2020 - Group AssignmentDaffa RaihanBelum ada peringkat
- 28 ESL Discussion Topics Adult StudentsDokumen14 halaman28 ESL Discussion Topics Adult StudentsniallBelum ada peringkat
- Faculty Vitae 1. Name: C.TamilselviDokumen2 halamanFaculty Vitae 1. Name: C.Tamilselvisadeeskumar.dBelum ada peringkat
- Cross System Create Supplier ProcessDokumen14 halamanCross System Create Supplier ProcesssakthiroboticBelum ada peringkat
- Biography of Anna HazareDokumen4 halamanBiography of Anna HazareGenesis FirstBelum ada peringkat
- Ijrpr2741 Study On Investor Perception Towards Stock Market InvestmentDokumen19 halamanIjrpr2741 Study On Investor Perception Towards Stock Market InvestmentAbhay RanaBelum ada peringkat
- AC AMMETER / Moving Iron: Model AECDokumen33 halamanAC AMMETER / Moving Iron: Model AECRoonar Aponte NoaBelum ada peringkat
- Construction of Perimeter Fence of BFP NHQ PDFDokumen133 halamanConstruction of Perimeter Fence of BFP NHQ PDFYalla ChaitanyaBelum ada peringkat
- NCP81205Dokumen1 halamanNCP81205Tom TomBelum ada peringkat
- MSS SP 69pdfDokumen18 halamanMSS SP 69pdfLaura CaballeroBelum ada peringkat
- Taxonomy: Family StaphylococcaceaeDokumen40 halamanTaxonomy: Family StaphylococcaceaeMarissa Terrado SorianoBelum ada peringkat
- Tip Sheet March 2017Dokumen2 halamanTip Sheet March 2017hoangvubui4632Belum ada peringkat