Audit 2 Process Approach
Diunggah oleh
Selvaraj Simiyon0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
9 tayangan2 halamanThis document outlines an approach for auditing an organization's quality management system (QMS). It discusses general questions that should be asked of every process, such as whether the process is defined and implemented properly. It then describes specific audit approaches, including evaluating customer focus, organizational leadership, QMS performance, process management, and continual improvement. The goal is to determine if the organization's processes are capable of meeting requirements and improving over time.
Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
clause 2 guide.docx
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniThis document outlines an approach for auditing an organization's quality management system (QMS). It discusses general questions that should be asked of every process, such as whether the process is defined and implemented properly. It then describes specific audit approaches, including evaluating customer focus, organizational leadership, QMS performance, process management, and continual improvement. The goal is to determine if the organization's processes are capable of meeting requirements and improving over time.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
9 tayangan2 halamanAudit 2 Process Approach
Diunggah oleh
Selvaraj SimiyonThis document outlines an approach for auditing an organization's quality management system (QMS). It discusses general questions that should be asked of every process, such as whether the process is defined and implemented properly. It then describes specific audit approaches, including evaluating customer focus, organizational leadership, QMS performance, process management, and continual improvement. The goal is to determine if the organization's processes are capable of meeting requirements and improving over time.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
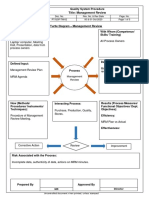
2 Process Auditing Approach
2.1 General Approach
When evaluating an organization's QMS, there are basic questions that should be asked of every
process, for example:
• Is the process appropriately determined?
• Is the process identified and appropriately defined, including for example process inputs, outputs,
resources and controls?
• Are Process Owner and Process User responsibilities assigned?
• Is the process implemented and maintained?
• Is the process effective in achieving the desired results?
Other questions could include:
• What is the process?
• What is it trying to achieve?
• Who is the customer of the process?
• Does the process address applicable customer specific requirements?
• Are Process User competencies identified?
• Is the process operating, as defined?
• What is the desired level of performance?
• Have process performance targets been established, including those specified by the customer?
• Have process measures (e.g. KPIs) been established and are mechanisms in place to collate and
analyze the data?
• What is the current level of performance?
• Is process performance regularly reviewed by top management?
• Where performance is not being achieved, are improvement plans in place?
2.2 Specific Approaches
There are a number of specific audit approaches that can be built into the audit plan to provide focus
on key elements of the QMS, including for example:
2.2.1 Customer Focus
The audit team should determine that customer satisfaction is being evaluated and appropriate
actions are taken by the organization based on available performance information (e.g.,
nonconformity data, corrective action requests, results of satisfaction surveys, complaints regarding
product quality, OTD, service provision, responsiveness to customer and internal requests) provided
by the organization's customers (e.g., scorecards, report cards).
2.2.2 Organizational Leadership
The Interview with top management should be used to evaluate:
• establishment and continued relevance of the organization's quality policy and objectives;
• establishment of performance measures aligned to quality objectives;
• QMS development, implementation, and continual improvement;
• top management commitment;
• QMS performance and effectiveness;
• performance to customer expectations (e.g., supplier rating, scorecard, audit results); and
• actions taken to address issues that are not meeting customer performance expectations.
2.2.3 QMS Performance and Effectiveness
The audit of QMS performance and effectiveness should include a review of the following:
• processing of customer complaints, customer feedback data (e.g., periodic performance reports
received from customers), and other relevant customer data (e.g., results of customer surveys);
• results and actions from internal and external audits of the QMS, including their associated records;
• stakeholder feedback (e.g., feedback from regulatory authorities or other interested parties);
• processing of process/product nonconformities, including review of associated corrective actions
and evaluation on the effectiveness of actions taken;
• processing of preventive actions, including evaluation on the effectiveness of actions taken;
• management review conduct, including associated records (e.g., process inputs/outputs, actions
taken);
• internal performance monitoring, measurement, reporting, and reviews against stakeholder and
internal performance objectives and targets, including continual improvement activities and
associated records;
• organization's current performance against targets, including customer specific targets and
associated records of applicable actions taken where targets are not being met; and
• the status and effectiveness of the organization's process performance improvement activities and
their outcomes related to product quality.
2.2.4 Process Management
The audit team should conduct QMS audits using a method that focuses on process performance and
effectiveness; this ensures that priority is given to the following:
• reviewing the organization's processes, their sequence and interactions, the identification of
functions and assignment of responsibilities, and performance against requirements and defined
measures, with focus on processes that directly impact the customer;
• reviewing the process for validation and approval of processes and process changes;
• reviewing the availability of resources and information required to operate and support associated
activities, including appropriate training and competency of personnel;
• reviewing the process-based management techniques, including the examination of process
measures (e.g., quality, takt time, cycle time, output effectiveness, control limits, process capability
determination);
• reviewing plans in place to ensure performance objectives/targets are monitored, measured, and
analyzed in order to realize the planned activities and achieve the planned results (e.g., verify
performance information availability, percentage of nonconforming parts/products, percentage OTD);
• reviewing applicable action taken when objectives/targets are not met to promote continual
improvement; and
• pursuing audit trails addressing customer concerns or requests for corrective actions, performance
against objectives, and relevant process controls.
NOTE:
The audit team should audit processes to sufficient depth and detail to evaluate if the organization's
processes are capable of meeting planned results and performance levels, including applicable
customer specific targets.
2.2.5 Continual Improvement
The audit team should evaluate the organization's interrelated processes and activities for continual
improvement of the QMS, its processes, their conformity, and effectiveness in order to:
• ensure focus on issues that are important to the organization, their customers, and regulatory
authorities; and
• determine the effectiveness of an organization's approach to continually improving process
performance.
NOTE:
The organization should be able to demonstrate that they have a structured approach to achieve
continual improvement of the QMS and its processes.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Internal Audit FindingsDokumen5 halamanInternal Audit FindingsHarie Bongky67% (6)
- Form - Supplier Corrective Action RequestDokumen1 halamanForm - Supplier Corrective Action RequestHarie BongkyBelum ada peringkat
- IATA Travel Agent HandbookDokumen32 halamanIATA Travel Agent HandbookCaro Seijas100% (7)
- Procedure For Management Review PDFDokumen5 halamanProcedure For Management Review PDFSelvaraj Simiyon50% (2)
- VT Teddy BearDokumen3 halamanVT Teddy BearSanyee DiehBelum ada peringkat
- NPT 1200 - R1 NotesDokumen28 halamanNPT 1200 - R1 NotesJaime Garcia De Paredes100% (4)
- Clause 2 GuideDokumen2 halamanClause 2 GuideSelvaraj SimiyonBelum ada peringkat
- Auditor - Guidance - 9100 - 2016Dokumen60 halamanAuditor - Guidance - 9100 - 2016Calvin DinhBelum ada peringkat
- Project Quality ManagementDokumen30 halamanProject Quality ManagementgkableBelum ada peringkat
- 9.0 Performance EvaluationDokumen5 halaman9.0 Performance EvaluationShailesh GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Operations Management Lesson 7Dokumen20 halamanOperations Management Lesson 7AshleyBelum ada peringkat
- Addressing RisksDokumen5 halamanAddressing RisksNaeemBelum ada peringkat
- Quality Audits: Presented By: K. Anupama M. Pharm (Q.A), 1 SemDokumen36 halamanQuality Audits: Presented By: K. Anupama M. Pharm (Q.A), 1 SemAnupama Katte100% (2)
- Guidance On Conforming To ISO9001Dokumen46 halamanGuidance On Conforming To ISO9001vethamanoBelum ada peringkat
- PMBOK Chapter 7 - QualityDokumen30 halamanPMBOK Chapter 7 - QualitylatehoursBelum ada peringkat
- Iso 9001:2000 Audit Checklist: 4 Quality Management System Status NotesDokumen9 halamanIso 9001:2000 Audit Checklist: 4 Quality Management System Status NotesManu Manu100% (1)
- 1.1. Management Review InputDokumen3 halaman1.1. Management Review InputCok Mayun WidyatmikaBelum ada peringkat
- Sop Management ReviewDokumen3 halamanSop Management ReviewItzel Acosta SalgadoBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 6 - QMSDokumen13 halamanLecture 6 - QMSIrfan MuddassirBelum ada peringkat
- ISO 9000 Auditor Training GuideDokumen127 halamanISO 9000 Auditor Training Guideravindra_jivani100% (1)
- Internal Audit QuestionsDokumen4 halamanInternal Audit QuestionsChristian ParkerBelum ada peringkat
- TQM Training: Total Quality Management BasicsDokumen20 halamanTQM Training: Total Quality Management BasicsLUIS JAVIER MURILLO FLORESBelum ada peringkat
- Total Quality Management: Mechanical Engineering Technology MET - 523TQMDokumen24 halamanTotal Quality Management: Mechanical Engineering Technology MET - 523TQMsubhan sibghatBelum ada peringkat
- NOTADokumen37 halamanNOTADuin Abd AzizBelum ada peringkat
- Project Quality ManagementDokumen13 halamanProject Quality ManagementVarun SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Measure Performance & Improve QualityDokumen25 halamanMeasure Performance & Improve Qualitylorenzo empleoBelum ada peringkat
- Strategy Evaluation & ControlDokumen63 halamanStrategy Evaluation & ControlAnjali BalakrishnanBelum ada peringkat
- Quality Audit: Presented By:-Sahil Jagdhane 214218011 Industrial Engineering and ManagementDokumen13 halamanQuality Audit: Presented By:-Sahil Jagdhane 214218011 Industrial Engineering and Managementdeepak tyagiBelum ada peringkat
- ISO Certification or IMSDokumen4 halamanISO Certification or IMSRajan VermaBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Implementation & ControlDokumen26 halamanStrategic Implementation & Controlaman27jaiswalBelum ada peringkat
- Strategy PPT Ch7Dokumen38 halamanStrategy PPT Ch7Habtamu mamoBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 25Dokumen12 halamanLecture 25HajraMalikBelum ada peringkat
- Project Quality ManagementDokumen42 halamanProject Quality ManagementsaviBelum ada peringkat
- Strategy PPT Ch7Dokumen38 halamanStrategy PPT Ch7yordiBelum ada peringkat
- 10 Quality ManagementDokumen19 halaman10 Quality ManagementMohamed LisaamBelum ada peringkat
- BBNP4103 Performance Appraisal: Topic 1 Introduction To Performance Appraisal by Valerie VickyDokumen61 halamanBBNP4103 Performance Appraisal: Topic 1 Introduction To Performance Appraisal by Valerie Vickyrenya1987Belum ada peringkat
- SUMMARY - Managerial ControlDokumen38 halamanSUMMARY - Managerial ControlSilmy AlfatirBelum ada peringkat
- BMG706 Assignment Report GuidelinesDokumen5 halamanBMG706 Assignment Report Guidelinesnhuyle270712Belum ada peringkat
- Quality Control Assurance SystemsDokumen9 halamanQuality Control Assurance SystemsSathi shBelum ada peringkat
- Management Review Procedure Ensures Continual ImprovementDokumen3 halamanManagement Review Procedure Ensures Continual ImprovementalexrferreiraBelum ada peringkat
- ISO 9001 2015 Management Review GuidanceDokumen3 halamanISO 9001 2015 Management Review GuidanceemanBelum ada peringkat
- Clause 9 - ExplanationDokumen12 halamanClause 9 - Explanations_agali2413Belum ada peringkat
- PrinciplesofManagement 15 Control Week12Dokumen38 halamanPrinciplesofManagement 15 Control Week12Joan AntonioBelum ada peringkat
- Internal Audit Key Performance IndicatorsDokumen21 halamanInternal Audit Key Performance IndicatorsHenry James Nepomuceno100% (1)
- CH 11 EvaluationDokumen9 halamanCH 11 EvaluationAnnisayuniarzBelum ada peringkat
- The Basic Concepts of Quality Management: Dr. Qin Su (Prof. Su) Tel:2667833Dokumen17 halamanThe Basic Concepts of Quality Management: Dr. Qin Su (Prof. Su) Tel:2667833ik_panditBelum ada peringkat
- 2.0 Quality Systems PDFDokumen23 halaman2.0 Quality Systems PDFAna Karen ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- Procedure For Management Review1Dokumen2 halamanProcedure For Management Review1Raja ManiBelum ada peringkat
- QA - QC ManualDokumen25 halamanQA - QC ManualMuhammad Bilal MughalBelum ada peringkat
- 4 Quality Management System: Date: 29 October 2008 Location: AssessorDokumen21 halaman4 Quality Management System: Date: 29 October 2008 Location: AssessordkhondeBelum ada peringkat
- Business Continuity Planning Audit Work Program Sample 3Dokumen19 halamanBusiness Continuity Planning Audit Work Program Sample 3Juan Pascual CosareBelum ada peringkat
- ISO Quality Systems GuideDokumen8 halamanISO Quality Systems GuidePrashant KadamBelum ada peringkat
- OBS 124 Unit 4 Organisational Control and ChangeDokumen55 halamanOBS 124 Unit 4 Organisational Control and Changeu22619942Belum ada peringkat
- Performance Evaluation & Management ReviewDokumen4 halamanPerformance Evaluation & Management ReviewSelvaraj SimiyonBelum ada peringkat
- Clause 9 GuideDokumen4 halamanClause 9 GuideSelvaraj SimiyonBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Audit ProcessDokumen66 halaman3 Audit ProcessSabiriene HaroonBelum ada peringkat
- MALA, A. - QuestionnaireDokumen4 halamanMALA, A. - QuestionnaireAmina Beth MalaBelum ada peringkat
- CDC UP Quality Management Practices GuideDokumen5 halamanCDC UP Quality Management Practices GuideRavi GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Qa QC PlanDokumen41 halamanQa QC PlanEng-TaYsEeRBelum ada peringkat
- Checklist QMS 9001 2008Dokumen3 halamanChecklist QMS 9001 2008bananasheep100% (1)
- Quality Management SystemDokumen7 halamanQuality Management SystemYousifBelum ada peringkat
- Module 5 - Quality and Internal Control in Food IndustryDokumen29 halamanModule 5 - Quality and Internal Control in Food IndustryMOHD ROSNIZAM BIN MOHD YUSOFF MoeBelum ada peringkat
- ISO 9001 Basic FundamentalDokumen35 halamanISO 9001 Basic FundamentalIstimawan_Bagus100% (2)
- Asq What Is A Quality PlanDokumen3 halamanAsq What Is A Quality PlanCloud RedfieldBelum ada peringkat
- Information Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Follow-up ProcessDari EverandInformation Systems Auditing: The IS Audit Follow-up ProcessPenilaian: 2 dari 5 bintang2/5 (1)
- ISO 45001 Current Status of DevelopmentDokumen18 halamanISO 45001 Current Status of Developmentali nordBelum ada peringkat
- 3X3 ISO 9001 2015 - RequirementsDokumen42 halaman3X3 ISO 9001 2015 - RequirementsSelvaraj SimiyonBelum ada peringkat
- ISO 45001 Current Status of DevelopmentDokumen18 halamanISO 45001 Current Status of Developmentali nordBelum ada peringkat
- ISO 9001 FDIS Transition Guide FINAL July 2015 PDFDokumen12 halamanISO 9001 FDIS Transition Guide FINAL July 2015 PDFsheina asuncionBelum ada peringkat
- IATF Transition Survey FeedbackDokumen19 halamanIATF Transition Survey FeedbackSelvaraj SimiyonBelum ada peringkat
- Iatf Stakeholder Event: 7 March 2018 London, UK Dr. Chris Owen (SMMT)Dokumen5 halamanIatf Stakeholder Event: 7 March 2018 London, UK Dr. Chris Owen (SMMT)Selvaraj SimiyonBelum ada peringkat
- IATF 16949 Systematic Review Team Process and Progress: Russ Hopkins Ford Motor CompanyDokumen4 halamanIATF 16949 Systematic Review Team Process and Progress: Russ Hopkins Ford Motor CompanySelvaraj SimiyonBelum ada peringkat
- Ford Letter Reporting of IATF 16949 Transition Audit StatusDokumen1 halamanFord Letter Reporting of IATF 16949 Transition Audit StatusSelvaraj SimiyonBelum ada peringkat
- 02 - IATF Stakeholder Conference 2017 - James Bruin - FINALDokumen15 halaman02 - IATF Stakeholder Conference 2017 - James Bruin - FINALSelvaraj SimiyonBelum ada peringkat
- FCA Reminder LetterDokumen1 halamanFCA Reminder LetterSelvaraj SimiyonBelum ada peringkat
- BMW Group. Transition Update and Current StatusDokumen4 halamanBMW Group. Transition Update and Current StatusSelvaraj SimiyonBelum ada peringkat
- Seguimiento de Partes InteresadasDokumen10 halamanSeguimiento de Partes InteresadasEfrain PerezBelum ada peringkat
- Iatf Stakeholder Conference: 13 September 2017 Oberursel, Germany Dale Hammer (IAOB)Dokumen3 halamanIatf Stakeholder Conference: 13 September 2017 Oberursel, Germany Dale Hammer (IAOB)Selvaraj SimiyonBelum ada peringkat
- Support and Resistance SimplifiedDokumen128 halamanSupport and Resistance Simplifieddodona7772494100% (7)
- 03 IATF Stakeholder Conference 2017 Ruediger Funke FINALDokumen11 halaman03 IATF Stakeholder Conference 2017 Ruediger Funke FINAL12ocaBelum ada peringkat
- IATF Stakeholder Conference 2017 SummaryDokumen6 halamanIATF Stakeholder Conference 2017 SummarySelvaraj SimiyonBelum ada peringkat
- Customer Satisfaction SurveyDokumen1 halamanCustomer Satisfaction Surveyanon_102149321Belum ada peringkat
- 04 - IATF Stakeholder Conference 2017 - Bachir Benrahal - FINALDokumen15 halaman04 - IATF Stakeholder Conference 2017 - Bachir Benrahal - FINALSelvaraj SimiyonBelum ada peringkat
- Form - Nonconforming Part DispositionDokumen1 halamanForm - Nonconforming Part DispositionSelvaraj SimiyonBelum ada peringkat
- Procedure - Quoting and OrdersDokumen2 halamanProcedure - Quoting and OrdersiresendizBelum ada peringkat
- Form - Design Control FormDokumen4 halamanForm - Design Control FormSelvaraj SimiyonBelum ada peringkat
- Form - Requisition FormDokumen1 halamanForm - Requisition FormSelvaraj SimiyonBelum ada peringkat
- Form - Supplier Quality Survey - Rev 0Dokumen3 halamanForm - Supplier Quality Survey - Rev 0Selvaraj SimiyonBelum ada peringkat
- Evaluation Form For SuppliersDokumen1 halamanEvaluation Form For SuppliersRichard ThodeBelum ada peringkat
- List Your Processes Here: Enter Full Name of CAR Form Here Enter Abbreviated Name of Your CAR Form HereDokumen4 halamanList Your Processes Here: Enter Full Name of CAR Form Here Enter Abbreviated Name of Your CAR Form HereSelvaraj SimiyonBelum ada peringkat
- Form - Calibration RecordDokumen1 halamanForm - Calibration Recordشادي الاخرسBelum ada peringkat
- Form - CAR LogDokumen49 halamanForm - CAR LogSelvaraj SimiyonBelum ada peringkat
- Electromagnetic Compatibility: Unit-1: Introduction To EmcDokumen28 halamanElectromagnetic Compatibility: Unit-1: Introduction To EmcShiva Prasad M100% (1)
- Fortiap SeriesDokumen41 halamanFortiap SeriesKamel BoumazaBelum ada peringkat
- Install Ansible On Mac OSXDokumen5 halamanInstall Ansible On Mac OSXNagendraBelum ada peringkat
- MPM2DZ CoursePack (2019)Dokumen254 halamanMPM2DZ CoursePack (2019)Hope ZhangBelum ada peringkat
- SAP Training SampleDokumen7 halamanSAP Training SampleMaria Patricia B. DequillaBelum ada peringkat
- General Instructions: Universite Du 7 Novembre A CarthageDokumen8 halamanGeneral Instructions: Universite Du 7 Novembre A Carthagemakram74Belum ada peringkat
- MicroeconometricsDokumen228 halamanMicroeconometricsaleber1962Belum ada peringkat
- VP Human Resources Director Operations in New York NY Resume Melanese MoodyDokumen2 halamanVP Human Resources Director Operations in New York NY Resume Melanese MoodyMelaneseMoodyBelum ada peringkat
- As 111423 KVS11 Um 911GB GB WW 2050-1Dokumen600 halamanAs 111423 KVS11 Um 911GB GB WW 2050-1Joko SusenoBelum ada peringkat
- Falcon Iii® Rf-7800V-Hh: VHF Networking HandheldDokumen2 halamanFalcon Iii® Rf-7800V-Hh: VHF Networking HandheldNicoleta NiţăBelum ada peringkat
- OracleCloudEstimate EDIDokumen1 halamanOracleCloudEstimate EDIArsenij KroptyaBelum ada peringkat
- Digital Banking UpdatesDokumen46 halamanDigital Banking Updatesvivek_anandBelum ada peringkat
- Authorization LetterDokumen4 halamanAuthorization LetterCherry Mae CarredoBelum ada peringkat
- UX Case Study - Streaming App (Next TV)Dokumen30 halamanUX Case Study - Streaming App (Next TV)Thanh Huy ĐoànBelum ada peringkat
- CV of Fairuz Areefin KhanDokumen2 halamanCV of Fairuz Areefin KhanAbu SaleahBelum ada peringkat
- Vdocuments - MX - ptc04 II Epon Access Hardware Installation Manualpdf PDFDokumen23 halamanVdocuments - MX - ptc04 II Epon Access Hardware Installation Manualpdf PDFJuan Ayala SizalimaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 4 - Cyber SecurityDokumen14 halamanUnit 4 - Cyber SecurityPradmohan Singh TomarBelum ada peringkat
- All mIRC CommandsDokumen4 halamanAll mIRC CommandsAbhishek KunalBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Linux Why There Are 100's of Linux OSDokumen20 halamanWhat Is Linux Why There Are 100's of Linux OSdizelBelum ada peringkat
- Wooldridge 2002 Rudiments of StataDokumen11 halamanWooldridge 2002 Rudiments of StataDineshBelum ada peringkat
- SentryGuide75 10sept2015Dokumen204 halamanSentryGuide75 10sept2015Adrian Calin RigoBelum ada peringkat
- Sg247851 - IBM ZOS Management Facility V2R3Dokumen614 halamanSg247851 - IBM ZOS Management Facility V2R3gborja8881331Belum ada peringkat
- Sod IvarDokumen41 halamanSod IvarSacha's ChannelBelum ada peringkat
- 6 AWOS Block DiagramDokumen2 halaman6 AWOS Block Diagramresdi yonoBelum ada peringkat
- HAMEG FA Oscilloscopes Why Analog EDokumen2 halamanHAMEG FA Oscilloscopes Why Analog EGeorgeBelum ada peringkat
- Ecf2 Module 2Dokumen6 halamanEcf2 Module 2Blackwolf SocietyBelum ada peringkat
- Asian Air Lines VisionDokumen13 halamanAsian Air Lines VisionMusaab QamarBelum ada peringkat