Sheet Piles Walls: Name Title
Diunggah oleh
Kristin Argosino0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
29 tayangan4 halamanasignment no.2
Judul Asli
foundation engineering
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Iniasignment no.2
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
29 tayangan4 halamanSheet Piles Walls: Name Title
Diunggah oleh
Kristin Argosinoasignment no.2
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 4
Xcdvfbghyrnb
Cold rolled sheet piling is less expensive, but
SHEET PILES WALLS provides less water resistance. Hot rolled
sheet piling is more traditional and provides
better water resistance.
INSTALLATION: Vibratory hammers are typically
used to install sheet piles. If soils are too
hard or dense. At certain sites where vibrations
are a concern, the sheets can be hydraulically
pushed into the ground.
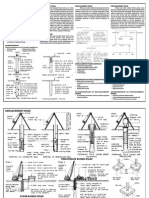
TYPES OF SHEET PILES
Reinforced concrete sheet piles are formed
Sheet Piles are sections of sheet materials with using precast concrete members. They are
interlocking edges that are installed in commonly used in permanent river embankments,
sequence to design depth along the planned canals and other marine structures.
excavation perimeter or seawall alignment.
Timber sheet piles generally used for short
FUNCTION: The interlocking edges that are driven spans in temporary structures, and to resist
into the ground to form a wall for permanent light lateral loads. The disadvantage of timber
(designed to provide a long service life) or piles is that they require preservative
temporary lateral earth retention and treatment and are not generally suitable for
excavation support with reduced groundwater soils consisting of stones.
inflow.
Steel sheet piles the most common form of sheet
MATERIALS: Sheet piles are also a sustainable piles as it has good resistance to high driving
option, because they are made of recycled steel stresses, excellent water-tightness, and can be
and the piles can often be reused. increased in length either by welding
DATE SUBMITTED RATINGor
ASSIGNEMNT NAME ARGOSINO, KRISTINEbolting.
MAE O. SEPTEMBER 24, 2019
NO.2
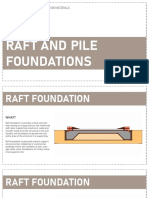
The Different Types of
TITLE Sheet piles, Cofferdams, Pile foundations and Drilled piers PROFESSOR’S SIGNATURE
PILE FOUNDATIONS INSTALLATION:
Displacement piling installation refers to the
method of driving piles into the ground without
first removing any of the soil or other
material.
Replacement piling installation refers to the
method of first digging out a hole, into which
the pile is then maneuvered.
TYPES OF PILE FOUNDATIONS
Pile foundations are deep foundations used for End Bearing Piles where, the bottom end of the
large structures and in situations where the pile rests on a layer of especially strong soil
soil at shallow depth is not suitable to resist or rock. The load of the building is
excessive settlement, resist uplift, etc. A transferred through the pile onto the strong
foundation is described as 'piled' when its layer. In a sense, this pile acts like a
depth is more than three times its breadth. column. The key principle is that the bottom
end rests on the surface which is the
FUNCTION: Principally used to transfer the loads intersection of a weak and strong layer. The
from superstructures, through weak, load therefore bypasses the weak layer and is
compressible strata or water onto stronger, more safely transferred to the strong layer.
compact, less compressible and stiffer soil or
rock at depth, increasing the effective size of Friction Piles work on a different principle.
a foundation and resisting horizontal loads. The pile transfers the load of the building to
They are typically used for large structures, the soil across the full height of the pile,
and in situations where soil is not suitable to by friction. In other words, the entire surface
prevent excessive settlement. of the pile, which is cylindrical in shape,
works to transfer the forces to the soil.
MATERIALS: They are formed by long, slender,
columnar elements typically made from steel or
reinforced concrete, or sometimes timber.
techniques. Once the desired tip elevation has
DRILLED PIERS been achieved, the drilled pier reinforcement
is set in place and the drilled shaft is filled
with concrete. Simply by excavating
cylindrical shafts into the ground and filling
them with concrete.
TYPES OF DRILLED PIERS
Straight-shaft end-bearing piers develop their
support from end-bearing on strong soil,
“hardpan” or rock. The overlying soil is
assumed to contribute nothing to the support
Drilled piers, also referred to as drilled of the load imposed on the pier.
piers, caissons or bored piles, are deep
foundation solutions. Straight-shaft side wall friction piers pass
through overburden soils that are assumed to
carry none of the load, and penetrate far
FUNCTION: Drilled shafts are typically designed enough into an assigned bearing stratum to
and constructed to support axial forces through develop design load capacity by side wall
a combination of side friction and end bearing friction between the pier and bearing stratum.
resistance. Drilled shafts are an economic
solution that can be installed in a variety of
Combination of straight shaft side wall
different ground conditions to accommodate
large axial, lateral and overturning forces. friction and end bearing piers are of the same
construction as the two mentioned above, but
MATERIALS: A drilled pier is a deep foundation with both side wall friction and end bearing
system that uses a large diameter concrete assigned a role in carrying the design load.
cylinder constructed by placing fresh concrete When carried into rock, this pier may be
and reinforcing steel into a drilled shaft. referred to as a socketed pier or a “drilled
pier with rock socket”.
INSTALLATION: Drilled piers are installed by
advancing an auger / drill tool to the required Belled or under reamed piers are piers with a
depth using open hole, casing, or slurry bottom bell or under ream. A greater percentage
of the imposed load on the pier top is assumed
to be carried by the base.
However, for practical and reasons of economy
COFFERDAMS most cofferdams are either rectangular or
circular. In general circular cofferdams offer
the advantage that they provide a more open
excavation over the entire plan area when
bracing is provided solely by ring beams.
However, installation of sheet piles in
circular cofferdams requires stricter
construction controls. Rectangular cofferdams
are simpler to construct but typically require
more complex internal bracing.
Cofferdam is an enclosure built within, or in TYPES OF COFFERDAMS
pairs across, a body of water to allow the Braced cofferdams are formed from a single wall
enclosed area to be pumped out. This pumping of sheet piles that is driven into the ground
creates a dry work environment so that the work to form a “box” around the excavation. The sheet
can be carried out safely. piles are then braced on the inside and the
interior is dewatered. It is primarily used for
FUNCTION: Commonly used for construction of bridge piers in shallow water (30 - 35 ft, 9 to
bridge piers and other support structures built 12m depth).
within water.
Cellular cofferdams are used only in those
MATERIALS: usually formed from sheet piles that circumstances where the excavation size
are supported by walers and internal braces, and precludes the use of cross-excavation bracing.
cross braces. Cofferdams are typically In this case, the cofferdam must be stable by
dismantled after permanent works are completed. virtue of its own resistance to lateral forces.
Since cofferdams are usually constructed within
water, the sheet piles are installed using pre- Double-walled sheet pile cofferdams are
constructed templates that permit the correct cofferdams comprising two parallel rows of
positioning of each sheet pile from a barge. sheet piles driven into the ground and
connected together by a system of tie rods at
INSTALLATION: A cofferdam can in essence be one or more levels. The space between the walls
constructed in almost any desirable shape. is generally filled with granular material such
as sand, gravel or broken rock.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- 2017-CE May PDFDokumen32 halaman2017-CE May PDFKristin Argosino100% (2)
- Pile Vs WellDokumen16 halamanPile Vs Wellgvgbabu100% (4)
- Presentation On FoundationsDokumen14 halamanPresentation On FoundationsShiwangi NagoriBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1-Pile Foundations-Lecture NoteDokumen79 halamanChapter 1-Pile Foundations-Lecture NoteManal EsmaelBelum ada peringkat
- HydraulicsDokumen8 halamanHydraulicsKristin ArgosinoBelum ada peringkat
- 30 - WELL CONTROL DATA SHEET For DRILLER'S METHODDokumen2 halaman30 - WELL CONTROL DATA SHEET For DRILLER'S METHODAseem PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- 10 Coiled Tubing Operation PDFDokumen51 halaman10 Coiled Tubing Operation PDFEdgar Ordoñez100% (6)
- I. Deep Foundation: A. PileDokumen7 halamanI. Deep Foundation: A. PileNikol CapulongBelum ada peringkat
- Deep Foundations: Kaidy DuarteDokumen22 halamanDeep Foundations: Kaidy DuarteCynthia XiuBelum ada peringkat
- Piling Tugasan1Dokumen29 halamanPiling Tugasan1MDanish AimanBelum ada peringkat
- Pile Foundation: P. N. SolankiDokumen68 halamanPile Foundation: P. N. Solankilokesh aggarwalBelum ada peringkat
- Deep FoundationsDokumen23 halamanDeep FoundationsMushaid Ali SyedBelum ada peringkat
- Pile Foundation: Classification of Pile FoundationsDokumen1 halamanPile Foundation: Classification of Pile FoundationsPrabhakar SvBelum ada peringkat
- BMC Shallow FoundationsDokumen6 halamanBMC Shallow Foundationsshenaz AfroseBelum ada peringkat
- CH-2 Types of Shallow FoundationsDokumen35 halamanCH-2 Types of Shallow Foundations19CE535 Mandar GawandeBelum ada peringkat
- Building FoundationDokumen5 halamanBuilding FoundationvictorBelum ada peringkat
- Deep FoundationDokumen74 halamanDeep FoundationShantanu PaulBelum ada peringkat
- EXCAVATIONDokumen16 halamanEXCAVATIONKashyap GoradiaBelum ada peringkat
- Deepfoundation 160805203054Dokumen51 halamanDeepfoundation 160805203054Mohammed HazemBelum ada peringkat
- Building FoundationDokumen5 halamanBuilding FoundationvictorBelum ada peringkat
- Deep Foundation: When Do We Use Deep Foundations?Dokumen7 halamanDeep Foundation: When Do We Use Deep Foundations?Cadfiles aasthaBelum ada peringkat
- Art306 Building and Construction Materials: Assignment IvDokumen19 halamanArt306 Building and Construction Materials: Assignment IvAbhishek SoniBelum ada peringkat
- GRP 2 - Soil - Foundation PilesDokumen74 halamanGRP 2 - Soil - Foundation PilesFELICITY MONTEFALCOBelum ada peringkat
- Anand Engineering College, Agra: Pile FoundationDokumen30 halamanAnand Engineering College, Agra: Pile Foundationtoluca28Belum ada peringkat
- Assignment #1 - MamornoDokumen19 halamanAssignment #1 - MamornoYna Hadassa A. MamornoBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1Dokumen57 halamanChapter 1Oromo Oromiya EtiophiaBelum ada peringkat
- BE CO4 H.A-compressedDokumen8 halamanBE CO4 H.A-compressedjd2saiBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment No: 3 Topic: Types of FoundationsDokumen6 halamanAssignment No: 3 Topic: Types of FoundationsShahzad AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Buildings-Types of FoundationsDokumen5 halamanBuildings-Types of FoundationsRonit ChariBelum ada peringkat
- CHAPTER 1 PILE FoundationDokumen57 halamanCHAPTER 1 PILE FoundationOromo Oromiya EtiophiaBelum ada peringkat
- Module 18, FounDokumen10 halamanModule 18, FounLeo DavifBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture - Week 1Dokumen85 halamanLecture - Week 1Asnil PrakashBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Pile FoundationsDokumen9 halamanTypes of Pile FoundationsAlex AnderBelum ada peringkat
- Pile Foundations 14-10-19Dokumen45 halamanPile Foundations 14-10-19Goutam NandiBelum ada peringkat
- Building ConstructionDokumen27 halamanBuilding ConstructionMelaku DinkuBelum ada peringkat
- Pilings and CaissonsDokumen8 halamanPilings and CaissonsJoshua C. JosonBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 14-15 Pile Foundation and Bearing Capacity in Sand and ClayDokumen14 halamanLecture 14-15 Pile Foundation and Bearing Capacity in Sand and ClayChauhdary Fazeel AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Literature Review. Sub-Structure/FoundationDokumen8 halamanLiterature Review. Sub-Structure/FoundationLillian KobusingeBelum ada peringkat
- 47 - Bithica Show Pile FoundationDokumen15 halaman47 - Bithica Show Pile FoundationGauri ChoudhariBelum ada peringkat
- Rock Mechanics For Engineering Geology Part2Dokumen194 halamanRock Mechanics For Engineering Geology Part2Leon Fourone100% (1)
- Module 3Dokumen149 halamanModule 3Owsu KurianBelum ada peringkat
- Types of FdnsDokumen41 halamanTypes of Fdnshiwotnesh girmaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7.PILEFOUNDDokumen42 halamanChapter 7.PILEFOUNDZsoloa adamBelum ada peringkat
- Pile Foundation Tos Assignment - 2 Amey DeshmukhDokumen13 halamanPile Foundation Tos Assignment - 2 Amey DeshmukhAmey Deshmukh100% (1)
- Topic 3: Foundation: CSE565 Construction Technology Ir DR Eddie LamDokumen11 halamanTopic 3: Foundation: CSE565 Construction Technology Ir DR Eddie Lamzhiliang yangBelum ada peringkat
- Foundation 2Dokumen34 halamanFoundation 2aamaniammuBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 1 Ceb 605Dokumen11 halamanAssignment 1 Ceb 605ShyamalBelum ada peringkat
- Types of FoundationDokumen52 halamanTypes of FoundationMARUFBelum ada peringkat
- Shakib Sir URP - FoundationDokumen48 halamanShakib Sir URP - FoundationHome Tutor Provider KhulnaBelum ada peringkat
- Jagannath University Faculty of Architecture and PlanningDokumen14 halamanJagannath University Faculty of Architecture and PlanningSheetal BaidBelum ada peringkat
- Application of Deep Foundation: (Yash Prabhat Priadarshi) (17-11-050)Dokumen45 halamanApplication of Deep Foundation: (Yash Prabhat Priadarshi) (17-11-050)Yash PrabhatBelum ada peringkat
- Piled Foundation ReportDokumen7 halamanPiled Foundation ReportDijo Mathews100% (1)
- Foundation Design LectureDokumen59 halamanFoundation Design LectureJamaica MarambaBelum ada peringkat
- Deep Foundations PDFDokumen15 halamanDeep Foundations PDFGaddam Padmaja ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Foundation Systems-Raft Foundation: 1. Definition, Purpose, & General AspectsDokumen7 halamanAdvanced Foundation Systems-Raft Foundation: 1. Definition, Purpose, & General Aspects18 FAISAL SHAH100% (1)
- Chapter 3 - Slide NotesfdsDokumen37 halamanChapter 3 - Slide Notesfdsa040201910Belum ada peringkat
- Factors Affecting Cast-In-situ Pile Foundation.Dokumen5 halamanFactors Affecting Cast-In-situ Pile Foundation.Gaurav Dhang100% (1)
- 2nd Sem FoundationDokumen35 halaman2nd Sem Foundationbicky agarwalBelum ada peringkat
- Foundation PilesDokumen123 halamanFoundation PilesPravindBelum ada peringkat
- Piles DesignDokumen12 halamanPiles Designn_sasanBelum ada peringkat
- 01 IntroductionDokumen26 halaman01 IntroductionJoshua OrcalesBelum ada peringkat
- Caisson: Guided By, Prof. S.C.JainDokumen68 halamanCaisson: Guided By, Prof. S.C.JainVAIBHAVBelum ada peringkat
- Math MeDokumen7 halamanMath MeKristin ArgosinoBelum ada peringkat
- Compute The Stadia Interval FactorDokumen7 halamanCompute The Stadia Interval FactorKristin ArgosinoBelum ada peringkat
- Simplified Steel DesignDokumen473 halamanSimplified Steel DesignKristin ArgosinoBelum ada peringkat
- Set 1 Problems PDFDokumen2 halamanSet 1 Problems PDFKristin Argosino0% (1)
- Stresses in Soil Mass Problem 1: Foundation Engineering 1Dokumen3 halamanStresses in Soil Mass Problem 1: Foundation Engineering 1Kristin ArgosinoBelum ada peringkat
- Fans and Blowers ReportDokumen49 halamanFans and Blowers ReportKristin ArgosinoBelum ada peringkat
- Name Title Kristine Mae O. Argosino: Procedures For Spectrum AnalysisDokumen3 halamanName Title Kristine Mae O. Argosino: Procedures For Spectrum AnalysisKristin ArgosinoBelum ada peringkat
- Name Title Kristine Mae O. Argosino: Procedures For Spectrum AnalysisDokumen3 halamanName Title Kristine Mae O. Argosino: Procedures For Spectrum AnalysisKristin ArgosinoBelum ada peringkat
- Basis of Bisection MethodDokumen31 halamanBasis of Bisection MethodKristin ArgosinoBelum ada peringkat
- CALENDARDokumen1 halamanCALENDARKristin ArgosinoBelum ada peringkat
- Newton-Raphson: Prepared By: Cielito V. Maligagli, RCEDokumen6 halamanNewton-Raphson: Prepared By: Cielito V. Maligagli, RCEKristin ArgosinoBelum ada peringkat
- Book 1Dokumen2 halamanBook 1Kristin ArgosinoBelum ada peringkat
- Part 3 4 SPECS CONTRACTSDokumen45 halamanPart 3 4 SPECS CONTRACTSKristin ArgosinoBelum ada peringkat
- Prestressed Concrete Design ObjectivesDokumen15 halamanPrestressed Concrete Design ObjectivesKristin ArgosinoBelum ada peringkat
- No.1 PrestressedDokumen10 halamanNo.1 PrestressedKristin ArgosinoBelum ada peringkat
- Modification Design of Stone Mastic Asphalt Using Polypropylene Film As Additives To BitumenDokumen5 halamanModification Design of Stone Mastic Asphalt Using Polypropylene Film As Additives To BitumenKristin ArgosinoBelum ada peringkat
- Argosino Martee Socio Eco IssuesDokumen4 halamanArgosino Martee Socio Eco IssuesKristin ArgosinoBelum ada peringkat
- Crane Stability and Ground PressureDokumen14 halamanCrane Stability and Ground PressureameerBelum ada peringkat
- CE322 Assignment 3Dokumen5 halamanCE322 Assignment 3PARAN, DIOSCURABelum ada peringkat
- Soil NailingDokumen215 halamanSoil Nailingphanisha100% (4)
- Filter Diaphragms PDFDokumen13 halamanFilter Diaphragms PDFZlatko BiočićBelum ada peringkat
- Atterberg Limits. DSDokumen18 halamanAtterberg Limits. DSGhulam Quadir KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Research TestDokumen13 halamanResearch TestOrnelAsperasBelum ada peringkat
- Price List - May 2019Dokumen96 halamanPrice List - May 2019maheshBelum ada peringkat
- Micro PilesDokumen17 halamanMicro PilesTrudeep DaveBelum ada peringkat
- Classification of SOIL V1.00 Sept2010Dokumen16 halamanClassification of SOIL V1.00 Sept2010kameshBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Sts02465Dokumen25 halamanSample Sts02465chondroc11Belum ada peringkat
- 7.3 Cone Penetration Testing: 7.2.3.2 Direct Design MethodsDokumen1 halaman7.3 Cone Penetration Testing: 7.2.3.2 Direct Design MethodsJihad HamdounBelum ada peringkat
- End - For TilesDokumen171 halamanEnd - For Tilesxinlok007Belum ada peringkat
- 隔离桩对基坑外既有隧道变形控制的优化分析 郑刚Dokumen11 halaman隔离桩对基坑外既有隧道变形控制的优化分析 郑刚He WeiBelum ada peringkat
- Schnabel Handbook FormattedDokumen21 halamanSchnabel Handbook FormattedJimmy ThomasBelum ada peringkat
- CGS - The Influence of Tailings Dam Failures On PracticeDokumen41 halamanCGS - The Influence of Tailings Dam Failures On PracticeAdnan KaderBelum ada peringkat
- NBS - 001 Structure Sample Specification 2019-03-29Dokumen23 halamanNBS - 001 Structure Sample Specification 2019-03-29Nay Win MaungBelum ada peringkat
- Tritech Petroleum Report On Lusi Volcano 2006Dokumen15 halamanTritech Petroleum Report On Lusi Volcano 2006Gilang RamadhanBelum ada peringkat
- (ASCE) GM.1943-5622.0001110 - Amit Kumar Das and Kousik Deb - XXXXXDokumen16 halaman(ASCE) GM.1943-5622.0001110 - Amit Kumar Das and Kousik Deb - XXXXXMUSTAFA KUBİLAY KELEŞOĞLUBelum ada peringkat
- History OF OIL RIGDokumen12 halamanHistory OF OIL RIGRubyYangHashimBelum ada peringkat
- Ded Jalan Toll Kunciran - Serpong: Borhole NoDokumen6 halamanDed Jalan Toll Kunciran - Serpong: Borhole NoAgus WahyudiBelum ada peringkat
- List of Dams and Reservoirs in India Statewise PDFDokumen9 halamanList of Dams and Reservoirs in India Statewise PDFVipin SajwanBelum ada peringkat
- Top Down MethodDokumen11 halamanTop Down MethodsinlekmBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding of Soil MechanicsDokumen27 halamanUnderstanding of Soil Mechanicsnimish.aquamarineBelum ada peringkat
- Antra - en - 2014-12Dokumen16 halamanAntra - en - 2014-12do1453Belum ada peringkat
- CE366 Fall17 SampleProblems 1Dokumen16 halamanCE366 Fall17 SampleProblems 1AbbasBelum ada peringkat
- Part I-Final Report On Soil InvestigationDokumen16 halamanPart I-Final Report On Soil InvestigationmangjuhaiBelum ada peringkat
- 09b PDFDokumen17 halaman09b PDFrazvan04061986Belum ada peringkat
- Reworked Acid Stim PresentationsDokumen4 halamanReworked Acid Stim PresentationsAzka Shinichi JrBelum ada peringkat