Kines
Diunggah oleh
Djhica Nicolle TilosHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Kines
Diunggah oleh
Djhica Nicolle TilosHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
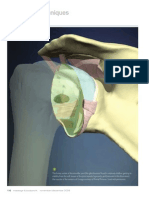
1. It is also known as the subacromial arch and considered as functional joint of sh 11.
11. Which carpal bone is also known as the semilunar bone.
complex.
Lunate
Suprahumeral joint
12. Which carpal bone is commonly fx.
2. Normal angle of torsion of the humerus.
Scaphoid
130-150 degrees
13. Intrinsic minus deformity involves which nerve.
3. Angle formed by the humeral head and the shaft of humerus.
Ulnar Nerve
Angle of inclination
14. Difficulty in assuming the ok sign is indicative of w/c pathology.
4. This mm. Is responsible in preventing the occurrence of sliding door paralysis of
Anterior interosseous nerve
the scapula.
15. What is the medial border of the anatomical snuffbox.
Trapezius
Extensor pollicis longus
5. This structure improves the congruency of the gh joint.
16. Biceps is the active flexor in al elbow positions and it is not affected by any elbow
Glenoid Labrum
positions.
6. It is the area of weakness between the superior and middle gh ligament.
False
Foramen of weitbrecht
7. This structure prevents or resist valgus stress in the elbow.
17. Pronator quadratus is the workhorse in your FA pronation.
Medial collateral Ligament
False ( Pronator teres)
8. This joint is primary affected in nursemaid elbow.
18. Anterior deltoid is the prime mover of SH flexion.
Proximal Radioulnar
True
9. What is the normal carrying angle in men.
19. The intrinsic plus position is the action of lumbricales.
5-10 degrees
True
10. This group of mm. is involved in your lateral epicondilitis.
20. Adductor pollicis is the only thenar mm. Supplied by ulnar nn.
Extensors
True
21. Axillary crutch palsy affects the axillary nerve. 30. Amputation of the thumb at the level of the CMC joint will lead to 90% loss of UE
function.
False ( Radial nerve)
False ( 10%)
22. Among the rotator cuff mm the subscapularis is the only internal rotator and
inserted to the greater tuberosity of humerus. 31. Initiator of elbow extension.
False ( supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis) Anconeus
23. The most unstable area of gh joint capsule is the inferior part. 32. The head of triceps that is active if there is resistance.
True Long head
24. Capitulum is longer than your trochlea. 33. Muscles that is always active as an elbow flexor with or w/o resistance and
whether the motion is rapid or slow.
False ( trochlea is longer)
Brachialis
25. SA anterior muscle is being supplied by long thoracic nn, injury to this nn will lead
to lateral winging of scapula 34. True about carrying angle of the elbow.
False ( medial winging) Increase in angle cause disturbance on median nerve
26. The scaphoid, lunate, and triquetrum articulate with the radius and ulna. 35. True about the kinematics of the elbow joint.
False ( radius only)
27. During radial deviation the distal row of the carpal bones slides laterally and 36. True about the cubital fosssa.
proximal row of the carpal bones slides medially.
Skin and fascia serve as roof of the fossa
True
Medial aspect of the fossa is formed by pronator teres
28. The grip strength is weak when the wrist is held in flexed position and stronger
From lateral to medial the content of cubital fossa
when the wrist is extended position.
37. Type of apprehension pattern where thumb is not necessary active.
True
Hook
29. The presence of the anatomical pulleys in the metacarpal and phalanges prevents
the bowstring effect of the flexor tendons durinf flexion of the fingers and wrist. 38. Feature of humerus.
True Olecranon process, coronoid and spiral groove
39. Carpal bones do not form part of the radiocarpal joint. Medial border of scapula
Trapezoid 50. This muscle responsible for upward rotation, adduction and depression of
scapula.
40. The chief muscle used for supination of FA with elbow extended.
Lower traps
Supinator muscle
41. Known as a pure elbow flexor.
Brachialis
42. Normal range of carrying angle.
10-15 degrees
43. The rectangular structure, sometimes referred to as the “SH summit”.
acromion
44. Posterior compartment of the FA is supplied by.
Radial nerve
45. Muscles innervated by the ulnar nerve.
All interossei
46. Commonly called tennis elbow. The focal point of pain will be palpated in bony
landmark of?
Lateral epicondyle of humerus
47. What muscle is innervated by branches of both the median and ulnar nerves.
Flexor digitorum profundos
48. Which muscle contributes to the rotator cuff.
Supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subs, teres minor
49. This insertion of SA muscle or saw muscle is at.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Axilla: Norah AlmudawiDokumen14 halamanThe Axilla: Norah AlmudawiF-med440 imamBelum ada peringkat
- Knee Joint PDFDokumen16 halamanKnee Joint PDFSiva ShanmugamBelum ada peringkat
- Radiography of Forearm and Upper ArmDokumen35 halamanRadiography of Forearm and Upper ArmsaurabhmhshwrBelum ada peringkat
- Biomechanics of Elbow ComplexDokumen9 halamanBiomechanics of Elbow ComplexKIARA VENICE DELGADOBelum ada peringkat
- Nerves of The Upper LimbDokumen8 halamanNerves of The Upper Limbananya mishraBelum ada peringkat
- Upper Extremity (Anatomy)Dokumen17 halamanUpper Extremity (Anatomy)Margareth Christine CusoBelum ada peringkat
- Condition Chart Shoulder ImpingementDokumen18 halamanCondition Chart Shoulder Impingementapi-547889945Belum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Physical Examination of The ShoulderDokumen13 halamanAnatomy and Physical Examination of The ShoulderbrunolazzariBelum ada peringkat
- 811 Anatomy of Shoulder JointDokumen51 halaman811 Anatomy of Shoulder JointAishwarya PatilBelum ada peringkat
- Topography of UPPER LIMBDokumen39 halamanTopography of UPPER LIMBCHANDRA0% (1)
- Human +muscles + PainDokumen28 halamanHuman +muscles + PainSaninan Mat100% (2)
- The Rotator Cuff (Myofascial Techniques)Dokumen4 halamanThe Rotator Cuff (Myofascial Techniques)Advanced-Trainings.com100% (3)
- Misfit Athletics Hspu Weakness Template 2.0Dokumen8 halamanMisfit Athletics Hspu Weakness Template 2.0Anonymous BEEeTPqiBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Toprank Review Academy - NursingDokumen14 halaman1 Toprank Review Academy - NursingLhara MañoBelum ada peringkat
- 22-Surface Anatomy of The Upper and Lower LimbsDokumen24 halaman22-Surface Anatomy of The Upper and Lower LimbsMiahz Tv100% (1)
- Ould R: Applied AnatomyDokumen4 halamanOuld R: Applied Anatomyayu feratywiBelum ada peringkat
- Managementofelbow Trauma:: Anatomy and ExposuresDokumen11 halamanManagementofelbow Trauma:: Anatomy and ExposuresMishael Diaz PoncecaBelum ada peringkat
- Hip InjuriesDokumen24 halamanHip InjuriessaadBelum ada peringkat
- Muscles of Arm & ShoulderDokumen4 halamanMuscles of Arm & ShoulderDavid BadaruBelum ada peringkat
- Spine LectureDokumen55 halamanSpine LectureLeoBelum ada peringkat
- Joints in The Upper Limb Cheat Sheet: by ViaDokumen1 halamanJoints in The Upper Limb Cheat Sheet: by ViaBELİS YILMAZBelum ada peringkat
- Hardware and Gadgets ExamDokumen4 halamanHardware and Gadgets ExamLian rose Del RosarioBelum ada peringkat
- MSK 7Dokumen72 halamanMSK 7Noor KhalidBelum ada peringkat
- Gross Anatomy of The Forearm: A CAL Package Designed By-Pratik SinhaDokumen24 halamanGross Anatomy of The Forearm: A CAL Package Designed By-Pratik Sinhaapi-19916399Belum ada peringkat
- Opa 220-230Dokumen11 halamanOpa 220-230Hijrana PutriBelum ada peringkat
- Muscles of The LimbsDokumen5 halamanMuscles of The LimbsCUESCANO, CRISTEL G. BSMT 2-ABelum ada peringkat
- 2.08 Brachial Region (Arm) - Compartments, Muscles, Nerves, and VesselsDokumen3 halaman2.08 Brachial Region (Arm) - Compartments, Muscles, Nerves, and VesselsDi CanBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 2 Skeletal Muscles Part 3Dokumen3 halamanUnit 2 Skeletal Muscles Part 3Sharva BhasinBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of The Elbow: Trauma and ReconstructionDokumen13 halamanAnatomy of The Elbow: Trauma and ReconstructionSrinivasBelum ada peringkat
- Spine LectureDokumen54 halamanSpine LectureDewi Lucy PrasetyaBelum ada peringkat
- Jathtrain00002 0050Dokumen11 halamanJathtrain00002 0050NeerajBelum ada peringkat
- Oia Keisha PDFDokumen7 halamanOia Keisha PDFJAN CAMILLE LENONBelum ada peringkat
- Wrist and Hand TransesDokumen5 halamanWrist and Hand TranseskatrizmaervillagantolBelum ada peringkat
- Rotator Cuff TearsDokumen5 halamanRotator Cuff TearsdrjorgewtorresBelum ada peringkat
- Arm 2021 - Students'Dokumen44 halamanArm 2021 - Students'Nkechukwu OgakwuBelum ada peringkat
- UL AnatomyDokumen34 halamanUL AnatomyMejBelum ada peringkat
- CAT Muscle Quick Study 121010.1 PDFDokumen4 halamanCAT Muscle Quick Study 121010.1 PDFPhilippe MamarilBelum ada peringkat
- Shoulder DynamicsDokumen17 halamanShoulder DynamicsShaista MunirBelum ada peringkat
- 02 Joints of Upper LimbDokumen28 halaman02 Joints of Upper LimbbnvjBelum ada peringkat
- Arm & Cubita Fossa 2024 - StudentsDokumen38 halamanArm & Cubita Fossa 2024 - Studentsmickylix139Belum ada peringkat
- High Yield AnatomyDokumen7 halamanHigh Yield AnatomyMaf BBelum ada peringkat
- President's Address: Trick MovementsDokumen3 halamanPresident's Address: Trick MovementsDr. Rushikesh K. Joshi100% (1)
- Anatomy and Biomechanics of The ThumbDokumen5 halamanAnatomy and Biomechanics of The ThumbAdosotoBelum ada peringkat
- Pubali Seminar FinalDokumen53 halamanPubali Seminar FinalPubali PalBelum ada peringkat
- Kinesiology Chap 6 TransesDokumen4 halamanKinesiology Chap 6 TranseschloegmndzBelum ada peringkat
- 15 - Mahima Bhatia - Radial Nerve InjuryDokumen19 halaman15 - Mahima Bhatia - Radial Nerve InjuryApoorvBelum ada peringkat
- Relations of Knee Joint: AnteriorlyDokumen100 halamanRelations of Knee Joint: AnteriorlysrisakthiBelum ada peringkat
- The Humerus - Proximal - Shaft - Distal - TeachMeAnatomyDokumen5 halamanThe Humerus - Proximal - Shaft - Distal - TeachMeAnatomymuhammad HaseebBelum ada peringkat
- 6288787c5b072 Bio2206l Exercise 7a Muscles of The Head Neck and ShouldersDokumen6 halaman6288787c5b072 Bio2206l Exercise 7a Muscles of The Head Neck and ShouldersKimBelum ada peringkat
- Shoulder DislocationsDokumen8 halamanShoulder DislocationsMuhammad Audi MuttaqinBelum ada peringkat
- Interphalangeal Joint (Hand Complex)Dokumen6 halamanInterphalangeal Joint (Hand Complex)VIRESH VBelum ada peringkat
- Impingment SyndromeDokumen10 halamanImpingment SyndromeJefri Aditiya SaragihBelum ada peringkat
- Upper Limb MusclesDokumen7 halamanUpper Limb MusclesAhmed ThabetBelum ada peringkat
- Rehabilitation of Elbow Trauma: Shrikant J. Chinchalkar, Bscot, Otr, CHT, Mike Szekeres, BscotDokumen12 halamanRehabilitation of Elbow Trauma: Shrikant J. Chinchalkar, Bscot, Otr, CHT, Mike Szekeres, BscotIoanaCamiiBelum ada peringkat
- 21-Knee JointDokumen61 halaman21-Knee JointRamesh KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Examen Fisico Manguito RotadorDokumen6 halamanExamen Fisico Manguito RotadorwilhelmBelum ada peringkat
- Applied Anatomy of The Wrist, Thumb and Hand: Joints, Joint Capsules and LigamentsDokumen10 halamanApplied Anatomy of The Wrist, Thumb and Hand: Joints, Joint Capsules and LigamentsroyvillafrancaBelum ada peringkat
- Muscles of The Gluteal RegionDokumen2 halamanMuscles of The Gluteal RegionYogi drBelum ada peringkat
- Special TestsDokumen5 halamanSpecial TestsVienGameBelum ada peringkat
- Elbow Anatomy & Biomechanics (Fornalski,)Dokumen11 halamanElbow Anatomy & Biomechanics (Fornalski,)Gloria Pg MontzeBelum ada peringkat
- Muscular System: Del Rosario, Elija Marie T. Care Giver NciiDokumen22 halamanMuscular System: Del Rosario, Elija Marie T. Care Giver NciiJun T. Del RosarioBelum ada peringkat
- Forearm Fractures FinalDokumen8 halamanForearm Fractures FinalApolinar González HernándezBelum ada peringkat
- Lec 11 UL Forarm Anterior CompartmentDokumen32 halamanLec 11 UL Forarm Anterior CompartmenthusseinBelum ada peringkat
- Mrcs Ana 4Dokumen206 halamanMrcs Ana 4Shahriar SakibBelum ada peringkat
- 07 Shoulder JointDokumen27 halaman07 Shoulder JointYara WaelBelum ada peringkat
- High Yield MCQs Part 001Dokumen233 halamanHigh Yield MCQs Part 001Imam-fulani AbdulazeezBelum ada peringkat
- Biceps Tendon PainDokumen16 halamanBiceps Tendon PainAuroraElizabethBelum ada peringkat
- Rematological ExaminationDokumen37 halamanRematological ExaminationAbdul BasitBelum ada peringkat
- A Modified Boytchev Procedure For Recurrent Anterior Dislocation of The Shoulder Khaled M Mostafa and Kamal El-GafaryDokumen9 halamanA Modified Boytchev Procedure For Recurrent Anterior Dislocation of The Shoulder Khaled M Mostafa and Kamal El-GafaryDebangshu KumarBelum ada peringkat
- The Epidemiology of Fractures in Children: Manuel Cassiano NevesDokumen20 halamanThe Epidemiology of Fractures in Children: Manuel Cassiano NevesAna-Maria DuleaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5 Skeletal SystemDokumen9 halamanChapter 5 Skeletal SystemClarisse Anne QuinonesBelum ada peringkat
- Skeletal Development of The Proximal Humerus in The Pediatric Population: MRI FeaturesDokumen10 halamanSkeletal Development of The Proximal Humerus in The Pediatric Population: MRI Featuresahmed doweidarBelum ada peringkat
- Musician Trigger PointsDokumen11 halamanMusician Trigger PointsLiviuBelum ada peringkat
- Gardner 1948Dokumen14 halamanGardner 1948mitroisergiuBelum ada peringkat
- Ortho Flashcards - RR Sn22Dokumen18 halamanOrtho Flashcards - RR Sn22Nayumi VillanuevaBelum ada peringkat
- Act. 4c The Appendicular Skeleton For STUDENTSDokumen15 halamanAct. 4c The Appendicular Skeleton For STUDENTSShane SayconBelum ada peringkat
- 1 ANT Anatomy of The Upper Limp TGDokumen129 halaman1 ANT Anatomy of The Upper Limp TGReath Gatkuoth DuothBelum ada peringkat
- Kellner Et Al. 2022 FaxinalipterusDokumen32 halamanKellner Et Al. 2022 Faxinalipterusmauricio.garciaBelum ada peringkat
- Upper Limb Lecture 1Dokumen45 halamanUpper Limb Lecture 1fdjkvfjvBelum ada peringkat
- Humeral Shaft Fractures and Radial Palsy PDFDokumen5 halamanHumeral Shaft Fractures and Radial Palsy PDFDan IonescuBelum ada peringkat
- Muscle OIADokumen3 halamanMuscle OIAVanessa TumangBelum ada peringkat
- Fractures of The Radius and Ulna: CPD ArticleDokumen10 halamanFractures of The Radius and Ulna: CPD ArticleMark Afandy Fitrah MBelum ada peringkat
- Periodic Paralysis Group 4 DraftDokumen10 halamanPeriodic Paralysis Group 4 DraftCassandra ColigadoBelum ada peringkat
- FRACTUREDokumen5 halamanFRACTUREKhiara Yapha AlfarBelum ada peringkat
- Pasifik Medikal CatalogueDokumen24 halamanPasifik Medikal CatalogueAr ZahBelum ada peringkat
- MIDTERM - 2 - Brunnstrum - Chapter 3 Traning Procedure For The Trunk and Upper Extremity - 03-14-22Dokumen12 halamanMIDTERM - 2 - Brunnstrum - Chapter 3 Traning Procedure For The Trunk and Upper Extremity - 03-14-22Mariane GumbanBelum ada peringkat
- Online Papers - June 2010 BatchDokumen105 halamanOnline Papers - June 2010 BatchBhavana HatwarBelum ada peringkat
- Subclavian ArteryDokumen8 halamanSubclavian ArteryPatalie HettihewaBelum ada peringkat