Crude Distillation: Petroleum Refining Engineering 2012 - 2013
Diunggah oleh
die_10 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
19 tayangan22 halamanCrude distillation is the first process in a petroleum refinery. It involves heating crude oil to separate it into various hydrocarbon fractions like light naphtha, kerosene, diesel, and atmospheric residue through fractional distillation. The distillation process takes place in large distillation columns under vacuum conditions. Crude desalting may also be required to remove dissolved salts from crude oil before distillation to prevent corrosion.
Deskripsi Asli:
Crude Distillation
Judul Asli
Crude Distillation
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniCrude distillation is the first process in a petroleum refinery. It involves heating crude oil to separate it into various hydrocarbon fractions like light naphtha, kerosene, diesel, and atmospheric residue through fractional distillation. The distillation process takes place in large distillation columns under vacuum conditions. Crude desalting may also be required to remove dissolved salts from crude oil before distillation to prevent corrosion.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
19 tayangan22 halamanCrude Distillation: Petroleum Refining Engineering 2012 - 2013
Diunggah oleh
die_1Crude distillation is the first process in a petroleum refinery. It involves heating crude oil to separate it into various hydrocarbon fractions like light naphtha, kerosene, diesel, and atmospheric residue through fractional distillation. The distillation process takes place in large distillation columns under vacuum conditions. Crude desalting may also be required to remove dissolved salts from crude oil before distillation to prevent corrosion.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 22
Crude Distillation
Petroleum Refining Engineering
2012 - 2013
Crude Oil Receiving
• Crude oil is received and stored in a floating roof
tank
• Roof is made floating over the oil to avoid loss of
hydrocarbon vapors and low boiling factions
• The roof also floats up and down to compensate
for the breathing of operation during pumping in
and out of the tank
• Crude oil received from tank cars, pipelines or
tanker ships may contain water
• This water must settle in the receiving tank
before oil accounting is started
Floating Roof Tank
Crude Distillation
• The first process in the refinery
• Topping unit or atmospheric distillation unit
• Receives the highest flow rate
• Usually runs at 60% of the design feed rate
• Seasonal temperature changes should be
accounted for
• Capacity range: 10,000 BPSD to 400,000 BPSD
(1,400 – 56,000 tpd)
Distillation Products
• CDU produces products that have to be
processed in downstream processes
• Typical distillation prodcuts
– Gases
– Light straight run naphtha (light gasoline)
– Heavy naphtha (heavy gasoline or military jet fuel)
– Kerosene (light distillate or jet fuel)
– Light gas oil (LGO or diesel)
– Heavy gas oil (HGO
– Atmospheric residue or topped crude
Distillation Process
• Crude – products heat exchange
• Crude heating
• Distillation columns, 30 to 50 trays
• Steam function
– Stripping light hydrocarbons
– Lowering the partial pressure of hydrocarbon vapors
– Tower energy balance
• Condenser and reflux
• Pumparounds
– Cold reflux
– Heat removal
– Reduces vapor flow rate
Operation of CDU
• Degree of fractionation is determined by the
gap or overlap between two adjacent side
streams
• Ideally there should be no overlap between
products
• Gap or overlap
Cut Points
• Cut points are controlled by the overhead vapor temperature
and flow rate of products fro column or side strippers
• Amount of naphtha is determined by the dew point of
naphtha at its partial pressure
• Changing the draw rate of product affects the cut point of the
heavier product below it
– Lowering kerosene draw flow rate will lower its end point
(lighter) and will affect the initial cut point of LGO
• Side stream rate affects the temperature at the withdrawal
tray, lowers the internal reflux, affect the degree of
fractionation
Pressure and Temperature
• Pressure is controlled by the back pressure of
the reflux drum
– 0.2 – 0.34 barg (3-5 psig)
– Flash zone pressure is usualy 0.34 – 0.54 bar
higher than the top tray
• Overhead temperature must be 14 – 17 oC
higher than the dew point of water at columns
overhead pressure
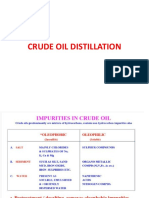
Crude Oil Desalting
• Some brine is associated with oil in form of
fine water droplets emulsified in crude oil
• Salt content cab be as high as 2000 PTB and
should be lowered to 2 – 5 PTB
• Salt can cause
– deposition in tubes in furnaces and HEX
– Corrosion problems
– Catalyst poisoning
Types of Salts in Crude Oil
• Free water and emulsified water
• Salts are mostly dissolved in fine water
droplets
• Salts are mostly magnesium, calcium and
sodium chlorides
Desalting Process
• Water-oil emulsion has to be broken
• Water washing
• Heating
• Coalescence
– Droplets size 1 – 10 micron
– Achieved by electrostatic field
• Settling
Electrostatic Desalter
Desalter Operation
• Temperature: increasing temperature lowers
density and viscosity. settling rate is increased
with temperature
• Washing water ratio
• Water level: raising water level reduces settling
time for water droplets. If too high it can reach
the electrode
• Washing water injection point: water is injected
at the mixing valve. Sometimes to avoid salt
deposition injection is done after the crude pump
Desalter Operation
• Demuslifier injection rate: added after the crude
pump or before mixing valve at 3 – 10 ppm of the
crude
• Type of washing water: soft water to prevent
scaling. Slitely acidic (pH 6). Free from hydrogen
sulfide and ammonia. Distillation overhead or
process water can be used
• Pressure drop in mixing valve: compromise
between better mixing and emulsion stabilization
Vacuum Distillation
• To extract more products from atmospheric
reside
• Produces
– Light vacuum gas oil (LVGO)
– Medium vacuum gas oil (MVGO)
– Heavy vacuum gas oil (HVGO)
– Vacuum residue
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Emission Estimation Technique Manual AU 2012Dokumen49 halamanEmission Estimation Technique Manual AU 2012János NegyeliczkyBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Note 11-Production and FacilitiesDokumen59 halamanLecture Note 11-Production and FacilitiesMOHAMAD IJAM SIREGAR BIN MULIA MoeBelum ada peringkat
- Planning in Oil and Gas FieldsDokumen44 halamanPlanning in Oil and Gas FieldsJairo CortesBelum ada peringkat
- Equipment Cost EstimationDokumen3 halamanEquipment Cost EstimationLaras Wuri D.100% (1)
- Journal of Loss Prevention in The Process Industries: Souvik Biswas, Benjamin J. FischerDokumen11 halamanJournal of Loss Prevention in The Process Industries: Souvik Biswas, Benjamin J. FischerkrazylionBelum ada peringkat
- Makum Coal FieldDokumen26 halamanMakum Coal Fieldsalim123456789100% (2)
- 113005Dokumen22 halaman113005Mohd Nizamuddin Mohamad NoorBelum ada peringkat
- Construction ManualDokumen278 halamanConstruction ManualUnnikrishnan NairBelum ada peringkat
- 1 PMHB Complete PDFDokumen357 halaman1 PMHB Complete PDFTayyiba ImranBelum ada peringkat
- Spe 59458 MSDokumen9 halamanSpe 59458 MSvaishnav2Belum ada peringkat
- 05 1 - EPC GE PTC 3 PR 00182 - Rev D7 Equipment Protection & Preservation ProcedureDokumen50 halaman05 1 - EPC GE PTC 3 PR 00182 - Rev D7 Equipment Protection & Preservation ProcedureHaianh PhamBelum ada peringkat
- BI Course Ebook PDFDokumen22 halamanBI Course Ebook PDFQorina AzizahBelum ada peringkat
- API HandbookDokumen60 halamanAPI HandbookKwamina23Belum ada peringkat
- Planning Notes Installation Manual EnUS 9007200510368139Dokumen17 halamanPlanning Notes Installation Manual EnUS 9007200510368139ionutenacheBelum ada peringkat
- Petronas Technical StandardsDokumen9 halamanPetronas Technical Standardsfaiz yatimBelum ada peringkat
- Schiehallion Loyal Decommissioning Phase1 ESIA PDFDokumen83 halamanSchiehallion Loyal Decommissioning Phase1 ESIA PDFBehrang BaghernejadBelum ada peringkat
- H2S Impact EvaluationDokumen38 halamanH2S Impact EvaluationharyonodanielBelum ada peringkat
- 60.0601 Performance Monitoring and ReportingDokumen105 halaman60.0601 Performance Monitoring and ReportingHtoo Htoo KyawBelum ada peringkat
- Baijan Savalan Flaresim 03022015 RevaDokumen25 halamanBaijan Savalan Flaresim 03022015 Revabldp03Belum ada peringkat
- Engineer ContractingDokumen114 halamanEngineer ContractingAndrew ReidBelum ada peringkat
- EML - PML - MPL-What Is The DiferenceDokumen1 halamanEML - PML - MPL-What Is The DiferenceprooptikiBelum ada peringkat
- PTS 18.21.02Dokumen32 halamanPTS 18.21.02满令强Belum ada peringkat
- CO2 Storage Atlas Norwegian SeaDokumen60 halamanCO2 Storage Atlas Norwegian SeaJim HungBelum ada peringkat
- Petrochemicals: Onshore Engineering and Construction Project ReferencesDokumen62 halamanPetrochemicals: Onshore Engineering and Construction Project ReferencesGurnam SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7 ProductionDokumen35 halamanChapter 7 ProductionDeniz AkoumBelum ada peringkat
- Risk Management Guide For Major Industrial AccidDokumen404 halamanRisk Management Guide For Major Industrial AccidDaisy100% (1)
- Offshore Facilities Life-Saving Appliance Requirements (Amendments/Supplements To Solas and Associated Lsa)Dokumen17 halamanOffshore Facilities Life-Saving Appliance Requirements (Amendments/Supplements To Solas and Associated Lsa)Gilang AdhityaBelum ada peringkat
- Piping Work 5Dokumen17 halamanPiping Work 5Sastra WinataBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering 003-Civil Structural Design Criteria On ShoreDokumen22 halamanEngineering 003-Civil Structural Design Criteria On Shoremarin cristian100% (1)
- Dep-30.00.60.16-Valve AnalysisDokumen62 halamanDep-30.00.60.16-Valve AnalysisStephen Maloba100% (1)
- Client: BMT India Document: Terms of References For Quantitative Risk Assessment StudyDokumen10 halamanClient: BMT India Document: Terms of References For Quantitative Risk Assessment StudyAnurag BholeBelum ada peringkat
- HF Alkylation and NExOCTANE Tech For Gasoline ProductionDokumen42 halamanHF Alkylation and NExOCTANE Tech For Gasoline ProductionUsama Shakil0% (1)
- Appropriate Contracting Strategy For Fast TrackDokumen7 halamanAppropriate Contracting Strategy For Fast TrackAsebaho BadrBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Management Group Project: Case Study Petrom S.ADokumen14 halamanStrategic Management Group Project: Case Study Petrom S.AsofiaBelum ada peringkat
- Journal of Loss Prevention in The Process Industries: O.N. Aneziris, I.A. Papazoglou, M. Konstantinidou, Z. NivolianitouDokumen13 halamanJournal of Loss Prevention in The Process Industries: O.N. Aneziris, I.A. Papazoglou, M. Konstantinidou, Z. NivolianitouPawan ChaturvediBelum ada peringkat
- CHAPTER 4 Jan 2022 Natural Gas 2Dokumen67 halamanCHAPTER 4 Jan 2022 Natural Gas 2Intan HoranBelum ada peringkat
- Top-Seal Integrity Assessment For Primary Recovery, Waterflood, Eor and Co2 StorageDokumen13 halamanTop-Seal Integrity Assessment For Primary Recovery, Waterflood, Eor and Co2 StorageronelbarafaeldiegoBelum ada peringkat
- GS 08 50208 SMDS Wax Plant Expansion PPD RevB1 PDFDokumen28 halamanGS 08 50208 SMDS Wax Plant Expansion PPD RevB1 PDFodunze1Belum ada peringkat
- PTS 18.52.08Dokumen60 halamanPTS 18.52.08azrai danialBelum ada peringkat
- Iia Global Internal Audit Standards Public Comment Draft English v2Dokumen132 halamanIia Global Internal Audit Standards Public Comment Draft English v2harshimadushaniBelum ada peringkat
- The Gorgon LNG ProjectDokumen10 halamanThe Gorgon LNG ProjectthawdarBelum ada peringkat
- Approach To LUP Under Comah RegsDokumen62 halamanApproach To LUP Under Comah Regsharlan11Belum ada peringkat
- 1-4-2 Scheduling Techniques For ConstructionDokumen47 halaman1-4-2 Scheduling Techniques For ConstructionVũ Thị Hà TrangBelum ada peringkat
- UD06737B-A Baseline Fingerprint Time Attendance Termimal User Manual V1.1.1 20180502Dokumen144 halamanUD06737B-A Baseline Fingerprint Time Attendance Termimal User Manual V1.1.1 20180502davaasuren jargalsaihanBelum ada peringkat
- TGM - Comman Municipal Sold Waste Management - 160910 - NK PDFDokumen232 halamanTGM - Comman Municipal Sold Waste Management - 160910 - NK PDFLalitMohanSenapatiBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Manager ResponsibilityDokumen2 halamanEngineering Manager Responsibilitymyusuf_engineerBelum ada peringkat
- Floating LNG September 2012 WebDokumen8 halamanFloating LNG September 2012 WebnazeemlngBelum ada peringkat
- LNG Process PresentationDokumen27 halamanLNG Process PresentationArmel BrissyBelum ada peringkat
- Oil Gas Refining BasicDokumen114 halamanOil Gas Refining BasicChức Văn100% (1)
- Petronas Technical Standards: Drainage & Sewer Systems For Onshore FacilitiesDokumen52 halamanPetronas Technical Standards: Drainage & Sewer Systems For Onshore FacilitiesvinothBelum ada peringkat
- PTS 20161DDokumen66 halamanPTS 20161DronelbarafaeldiegoBelum ada peringkat
- Developing Correlations For The Properties of Petroleum Fuels and Their FractionsDokumen13 halamanDeveloping Correlations For The Properties of Petroleum Fuels and Their Fractionsmurdanetap957Belum ada peringkat
- Technical Report - Discharge Facilities For Oil Recovered at Sea PDFDokumen356 halamanTechnical Report - Discharge Facilities For Oil Recovered at Sea PDFSurya Chala PraveenBelum ada peringkat
- Fpso Revamp For A Marginal Field Ea-SpeDokumen34 halamanFpso Revamp For A Marginal Field Ea-Spe고병석Belum ada peringkat
- Cost Effective Integrated Gas Plant Design Sulfinol MDokumen2 halamanCost Effective Integrated Gas Plant Design Sulfinol Mamirho3ein100% (1)
- Metallic Materials - Selected Standards: ManualDokumen102 halamanMetallic Materials - Selected Standards: ManualThiruppathirajanBelum ada peringkat
- Crude Oil DistillationDokumen109 halamanCrude Oil Distillationshreshth chawlaBelum ada peringkat
- CDUDokumen17 halamanCDUmitpgandhiBelum ada peringkat
- Crude DistillationDokumen32 halamanCrude DistillationIzziyyahBelum ada peringkat
- Marine Lubricants Information Bulletin: Viscosity ClassificationsDokumen4 halamanMarine Lubricants Information Bulletin: Viscosity Classificationsdie_1Belum ada peringkat
- Jan Trocki Pres EngDokumen28 halamanJan Trocki Pres Engdie_1Belum ada peringkat
- Research Highlights in New Catalytic Technologies: 1.theme DescriptionDokumen13 halamanResearch Highlights in New Catalytic Technologies: 1.theme Descriptiondie_1Belum ada peringkat
- Base Oil Manufacturing Hydroprocessing (Amy Claxton, ICIS)Dokumen36 halamanBase Oil Manufacturing Hydroprocessing (Amy Claxton, ICIS)die_1Belum ada peringkat
- Criterion Catalyst Increase YieldDokumen2 halamanCriterion Catalyst Increase Yielddie_1Belum ada peringkat
- Patra SK: No. Type Responsible Target Date Status Recommendations No and DescriptionDokumen4 halamanPatra SK: No. Type Responsible Target Date Status Recommendations No and Descriptiondie_1Belum ada peringkat
- Lube BAse Oil (S-Oil)Dokumen6 halamanLube BAse Oil (S-Oil)die_1Belum ada peringkat
- Oil Refining and ProductsDokumen15 halamanOil Refining and Productsdie_1Belum ada peringkat
- CEPSA Good Reference For ZeoliteDokumen29 halamanCEPSA Good Reference For Zeolitedie_1Belum ada peringkat
- Midw Technology As A Drop-In Catalyst SolutionDokumen11 halamanMidw Technology As A Drop-In Catalyst Solutiondie_1Belum ada peringkat
- Hydrocracking CatalystsDokumen8 halamanHydrocracking Catalystsdie_1Belum ada peringkat
- Catalyst DeactivationDokumen20 halamanCatalyst Deactivationdie_1Belum ada peringkat
- Msds of TccaDokumen5 halamanMsds of Tccadie_1Belum ada peringkat
- Voltro II Electrical Insulating Oil 4 2018Dokumen2 halamanVoltro II Electrical Insulating Oil 4 2018die_1Belum ada peringkat
- Renoil High Viscosity White Mineral OilsDokumen2 halamanRenoil High Viscosity White Mineral Oilsdie_1Belum ada peringkat
- Selecting TEMA Heat Exchangers - Alfa LavalDokumen2 halamanSelecting TEMA Heat Exchangers - Alfa Lavaldie_1Belum ada peringkat
- DR FCC PDFDokumen7 halamanDR FCC PDFAle SanzBelum ada peringkat
- Factors Affecting Drug Absorption PDFDokumen2 halamanFactors Affecting Drug Absorption PDFRobBelum ada peringkat
- Hydraulic Fracturing Theory and Practice: R. D. Barree Barree & Associates LLCDokumen18 halamanHydraulic Fracturing Theory and Practice: R. D. Barree Barree & Associates LLCmoorpvrBelum ada peringkat
- Lectureone Introduction To BioChE - 2Dokumen20 halamanLectureone Introduction To BioChE - 2desalegn abera100% (1)
- BR Int LD Id Inspiration 55-70plusDokumen11 halamanBR Int LD Id Inspiration 55-70plustarkett tBelum ada peringkat
- TDS OF H-408 Silicone Adjuvant For AgricultureDokumen2 halamanTDS OF H-408 Silicone Adjuvant For AgricultureAda FuBelum ada peringkat
- 5MF 10MFDokumen8 halaman5MF 10MFRodrigo Pessoa VespaBelum ada peringkat
- 905 3SDokumen4 halaman905 3SyasafyBelum ada peringkat
- PAMG-PA3 5052 Aluminum Honeycomb: DescriptionDokumen2 halamanPAMG-PA3 5052 Aluminum Honeycomb: Descriptionsahiljain_146Belum ada peringkat
- B.tech Labmanual - FinalDokumen99 halamanB.tech Labmanual - FinalSumathi JeganathanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4 (Ceramic Matrix Composites)Dokumen34 halamanChapter 4 (Ceramic Matrix Composites)Sri TharanBelum ada peringkat
- Msds FormaldehydeDokumen6 halamanMsds Formaldehydemkhurram79Belum ada peringkat
- Part 7 StoichiometryDokumen59 halamanPart 7 Stoichiometryjasumin91Belum ada peringkat
- GROUP 3 - LABORATORY REPORT 4 - Compounds With Hydroxyl GroupDokumen18 halamanGROUP 3 - LABORATORY REPORT 4 - Compounds With Hydroxyl GroupJESSIE FREDRICK DALANIELBelum ada peringkat
- Nanofabrication For Pattern Transfer Purpose.: Etching Is Done Either in "Dry" or "Wet" MethodsDokumen19 halamanNanofabrication For Pattern Transfer Purpose.: Etching Is Done Either in "Dry" or "Wet" MethodsPRAVEEN MBelum ada peringkat
- Process Pipeline Repair ClampsDokumen4 halamanProcess Pipeline Repair ClampsHeru SuryoBelum ada peringkat
- Mass Spectral Databases For LC-MS - and GC-MS-based Metabolomics PDFDokumen13 halamanMass Spectral Databases For LC-MS - and GC-MS-based Metabolomics PDFciborg1978Belum ada peringkat
- EASA Part-66 Exam Questions of Module 07 Standart Practices - Part IIDokumen19 halamanEASA Part-66 Exam Questions of Module 07 Standart Practices - Part IISteven J. SelcukBelum ada peringkat
- Pe Fir Handbook 1 2Dokumen237 halamanPe Fir Handbook 1 2Salman JoBelum ada peringkat
- Tugas 1 PPADokumen29 halamanTugas 1 PPAlulalalaBelum ada peringkat
- Evaporation Rate of Solvents PDFDokumen2 halamanEvaporation Rate of Solvents PDFsyamlokBelum ada peringkat
- OR Water TreatmentDokumen13 halamanOR Water Treatmentafif ginandarBelum ada peringkat
- WPS Vessel 1Dokumen4 halamanWPS Vessel 1Naqqash SajidBelum ada peringkat
- AEtrium-2 Brochure V7 PDFDokumen4 halamanAEtrium-2 Brochure V7 PDFThomas DylanBelum ada peringkat
- Iron Oxide NanoparticlesDokumen25 halamanIron Oxide NanoparticlesGöksun GüvenBelum ada peringkat
- Major Intermediates in Organophosphate Synthesis (PCL, Pocl, PSCL, and Their Diethyl Esters) Are Anticholinesterase Agents Directly or On ActivationDokumen7 halamanMajor Intermediates in Organophosphate Synthesis (PCL, Pocl, PSCL, and Their Diethyl Esters) Are Anticholinesterase Agents Directly or On ActivationYancy JuanBelum ada peringkat
- Brewing Salts and How To Adjust The Water For Your BeerDokumen10 halamanBrewing Salts and How To Adjust The Water For Your BeerMario JammaersBelum ada peringkat
- Isensee Robert W1943Dokumen17 halamanIsensee Robert W1943DŨNG VŨ NGUYỄN TUẤNBelum ada peringkat
- Hazen - William Coeficiente FBEDokumen10 halamanHazen - William Coeficiente FBEOrlandoBelum ada peringkat
- CFM SPM 70-48-00Dokumen8 halamanCFM SPM 70-48-00ZakiHaunaBelum ada peringkat