Circuit Breaker
Diunggah oleh
Edinson Milton Gaona BarbozaHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Circuit Breaker
Diunggah oleh
Edinson Milton Gaona BarbozaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Circuit Breaker
The Circuit Breakers are automatic Switches which can interrupt fault currents.
The part of the Circuit Breakers connected in one phase is called the pole.
A Circuit Breaker suitable for three phase system is called a ‘triple-pole
Circuit Breaker. Each pole of the Circuit Breaker comprises one or more
interrupter or arc-extinguishing chambers. www.sayedsaad.com
The interrupters are mounted on support insulators. The interrupter encloses
a set of fixed and moving contact's
The moving contacts can be drawn apart by means of the operating links
of the operating mechanism. The operating mechanism of the Circuit Breaker
gives the necessary energy for opening and closing of contacts of the Circuit
Breakers.
The arc produced by the separation of current carrying contacts is interrupted by
a suitable medium and by adopting suitable techniques for arc extinction. The
Circuit Breaker can be classified on the basis of the arc extinction medium.
The Fault Clearing Process
During the normal operating condition the Circuit Breaker can be opened or
closed
by a station operator for the purpose of Switching and maintenance.
During the abnormal or faulty conditions the relays sense the fault and close
the trip circuit of the Circuit Breaker. Thereafter the Circuit Breaker opens.
The Circuit Breaker has two working positions, open and closed.
These correspond to open Circuit Breaker contacts and closed Circuit Breaker
contacts respectively.
The operation of automatic opening and closing the contacts is achieved by means
of the operating mechanism of the Circuit Breaker.
As the relay contacts close, the trip circuit is closed and the operating mechanism
of the Circuit Breaker starts the opening operation.
The contacts of the Circuit Breaker open and an arc is draw between them.
The arc is extinguished at some natural current zero of a.c. wave.
The process of current interruption is completed when the arc is extinguished
and the current reaches final zero value. The fault is said to be cleared.
The process of fault clearing has the following sequence:
1- Fault Occurs. As the fault occurs, the fault impedance being low,
the currents increase and the relay gets actuated.
The moving part of the relay move because of the increase in the operating
torque. The relay takes some time to close its contacts.
2 - Relay contacts close the trip circuit of the Circuit Breaker closes and trip coil is
energized.
3 - The operating mechanism starts operating for the opening operation.
The Circuit Breaker contacts separate.
4 - Arc is drawn between the breaker contacts. The arc is extinguished
in the Circuit Breaker by suitable techniques. The current reaches final zero
as the arc is extinguished and does not restrict again.
The Trip-Circuit
Fig (1) below illustrates the basic connections of the Circuit Breaker control for
the opening operation
STANDARD RATINGS OF CIRCUIT BREAKERS AND THEIR SELECTION
The characteristics of a Circuit Breaker including its operating devices and
auxiliary equipment that are used to determine the rating are:
(a) Rated characteristics to be given for all Circuit Breakers.
1. Rated voltage.
2. Rated insulation level.
3. Rated frequency.
4. rated current.
5. Rated short Circuit Breaking current.
6. Rated transient recovery voltage for terminal faults.
7. Rated short circuit making current.
8. Rated operating sequence.
9. Rated short time current.
www.sayedsaad.com
(b) Rated characteristics to be given in the Specific cases given below:
1 - Rated characteristics for short line faults for
three pole Circuit Breakers rated at 72.5 kV and
above, more than 12.5 kA rated short circuit breaking
current and designed for direct connection to overhead
transmission lines.
2 - Rated line charging breaking current, for three pole
Circuit Breakers rated at 72.5 kV and above and intended
for Switching over- head transmission lines.
3 - Rated supply voltage of closing and opening devices, where applicable.
4 - Rated supply frequency of closing and opening devices, where applicable.
5 - Rated pressure of compressed gas supply for operation and
Interruption, where applicable.
(c) Optional rated characteristics:
1. Rated out of phase breaking current.
2. Rated line charging breaking current, for three pole
Circuit Breakers rated at less than 72.5 kV and for single
pole Circuit Breakers.
3. Rated cable charging breaking current.
4. Rated single capacitor bank breaking current.
5. Rated small inductive breaking current.
6. Rated supply voltage of auxiliary circuits.
7. Rated supply frequency of auxiliary circuits
The type of the Circuit Breaker
The type of the Circuit Breaker is usually identified according to the medium of arc
extinction. The classification of the Circuit Breakers based on the medium of arc extinction
is as follows:www.sayedsaad.com
(1) Air break' Circuit Breaker. (Miniature Circuit Breaker).
(2) Oil Circuit Breaker (tank type of bulk oil)
(3) Minimum oil Circuit Breaker.
(4) Air blast Circuit Breaker.
(5) Vacuum Circuit Breaker.
(6) Sulphur hexafluoride Circuit Breaker. (Single pressure or
Double Pressure).
Type Medium Voltage, Breaking Capacity
1 – Air break Circuit Air at atmospheric (430 – 600) V– (5-15)MVA
Breaker pressure (3.6-12) KV - 500 MVA
2 – Miniature CB. Air at atmospheric (430-600 ) V
pressure
3 – Tank Type oil CB. Dielectric oil (3.6 – 12) KV
4 – Minimum Oil CB. Dielectric oil (3.6 - 145 )KV
5 – Air Blast CB. Compressed Air 245 KV, 35000 MVA
(20 – 40 ) bar up to 1100 KV, 50000 MVA
6 – SF6 CB. SF6 Gas 12 KV, 1000 MVA
36 KV , 2000 MVA
145 KV, 7500 MVA
245 KV , 10000 MVA
7 – Vacuum CB. Vacuum 36 KV, 750 MVA
8 – H.V.DC CB. Vacuum , SF6 Gas 500 KV DC
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- Daikin AG 31-002 Centrifugal Chiller Fundamentals Guide Vers 2.2Dokumen33 halamanDaikin AG 31-002 Centrifugal Chiller Fundamentals Guide Vers 2.2usmanafzal246Belum ada peringkat
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- การติดตั้งแผงโซล่าเซลล์ในบ้านรุปแบบวิธีการและเอกสารDokumen39 halamanการติดตั้งแผงโซล่าเซลล์ในบ้านรุปแบบวิธีการและเอกสารChanade WichasilpBelum ada peringkat
- Calculator Programmable ThermostatDokumen5 halamanCalculator Programmable Thermostataravoof84Belum ada peringkat
- Directional OverDokumen28 halamanDirectional OverEdinson Milton Gaona BarbozaBelum ada peringkat
- Cable Capacity of Conduits and TrunkingDokumen11 halamanCable Capacity of Conduits and TrunkingarunBelum ada peringkat
- Pra-Rancangan Pabrik Sabun Cair Dari Crude Palm Oil (Cpo) Dengan Kapasitas 20.000 Ton/TahunDokumen1 halamanPra-Rancangan Pabrik Sabun Cair Dari Crude Palm Oil (Cpo) Dengan Kapasitas 20.000 Ton/TahunNurulhafizBelum ada peringkat
- Abb Power T&D Company Inc.: Distribution Relay Divisions USADokumen48 halamanAbb Power T&D Company Inc.: Distribution Relay Divisions USAEdinson Milton Gaona BarbozaBelum ada peringkat
- REJ 52 - Protection Relay Operator's Manual: 1MRS750144-MUMDokumen48 halamanREJ 52 - Protection Relay Operator's Manual: 1MRS750144-MUMEdinson Milton Gaona BarbozaBelum ada peringkat
- Over-Current and Earth Fault ProtectionDokumen14 halamanOver-Current and Earth Fault ProtectionEdinson Milton Gaona BarbozaBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Substations: Electrical Network Comprises The Following RegionsDokumen2 halamanElectrical Substations: Electrical Network Comprises The Following RegionsEdinson Milton Gaona BarbozaBelum ada peringkat
- How The Sun Shines: John N BahcallDokumen11 halamanHow The Sun Shines: John N BahcallMike WilliamsBelum ada peringkat
- Data Sheet Enblock C10 Ver1.9Dokumen3 halamanData Sheet Enblock C10 Ver1.9paoly44Belum ada peringkat
- Get 6555Dokumen3 halamanGet 6555elsayedBelum ada peringkat
- 1189 E EUG 1 Manually Operated Synchronising CircuitsDokumen22 halaman1189 E EUG 1 Manually Operated Synchronising CircuitsSyed Mohammad NaveedBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Balanced and Un Balanced LoadDokumen20 halaman3 Balanced and Un Balanced LoadMohd Azlan HarunBelum ada peringkat
- Manual 3kW Off Grid VX Solar Inverter 120702Dokumen33 halamanManual 3kW Off Grid VX Solar Inverter 120702Stefan ArseneBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamental of Solar Cell/Photovoltaic Science and TechnologyDokumen42 halamanFundamental of Solar Cell/Photovoltaic Science and TechnologySultan ZahidBelum ada peringkat
- Vibrational Analysis: Dr. Mazhar Amjad GilaniDokumen23 halamanVibrational Analysis: Dr. Mazhar Amjad GilaniXarOonBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4: Vapor Power Cycle: DR Zurriati Mohd Ali FKMDokumen48 halamanChapter 4: Vapor Power Cycle: DR Zurriati Mohd Ali FKMHafiz ShamBelum ada peringkat
- ROE Questions FinalDokumen60 halamanROE Questions FinalAhmad TahirBelum ada peringkat
- Dyno StartDokumen2 halamanDyno StartbittibssiBelum ada peringkat
- 3WT Air Circuit Breaker Quick Selection GuideDokumen2 halaman3WT Air Circuit Breaker Quick Selection GuideDinuro DiBelum ada peringkat
- Uninterruptible Power Supply - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokumen1 halamanUninterruptible Power Supply - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAnkit DhimanBelum ada peringkat
- Study Material Class Xi Phy 2022-23Dokumen155 halamanStudy Material Class Xi Phy 2022-23It's all About fitnessBelum ada peringkat
- EVS Power BrochureDokumen10 halamanEVS Power BrochureGiga Primerindra SiraitBelum ada peringkat
- HESOP London Underground - Case Study - en - LDDokumen2 halamanHESOP London Underground - Case Study - en - LDHector RiveraBelum ada peringkat
- Compact NSX Lv429740Dokumen3 halamanCompact NSX Lv429740talibanindonesiaBelum ada peringkat
- MAN Oils - MAN Truck & BusDokumen1 halamanMAN Oils - MAN Truck & BusCB Filtros LtdaBelum ada peringkat
- New Microsoft Power Point PresentationDokumen39 halamanNew Microsoft Power Point PresentationSamBelum ada peringkat
- VLT Brake Resistor MCE101 Design Guide MG90O202Dokumen146 halamanVLT Brake Resistor MCE101 Design Guide MG90O202Sunil SinghBelum ada peringkat
- MOINindustriual Training Rashid AshrafDokumen54 halamanMOINindustriual Training Rashid AshrafUMAR MAJEED MIR 209-MEET-18Belum ada peringkat
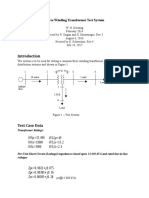
- Three Winding Transformer Test System-EPRI-2017-Rev4Dokumen18 halamanThree Winding Transformer Test System-EPRI-2017-Rev4Jorge TorresBelum ada peringkat
- MPPT Solar Charge Controller ML4830N15 InstructionsDokumen13 halamanMPPT Solar Charge Controller ML4830N15 InstructionsR techBelum ada peringkat
- Primitive Turbulence: Kinetics, Prandtl's Mixing Length, and Von K Arm An's ConstantDokumen12 halamanPrimitive Turbulence: Kinetics, Prandtl's Mixing Length, and Von K Arm An's ConstantHector BurgueñoBelum ada peringkat
- Battery Charge Lester ElectricalDokumen8 halamanBattery Charge Lester ElectricaldungnvbsBelum ada peringkat