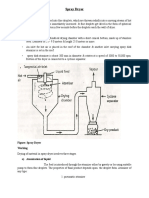
Lyophilisation
Diunggah oleh
VargheseJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Lyophilisation
Diunggah oleh
VargheseHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
The lyophilization process
Lyophilization is a process whereby a product is dried by removing the water under low
temperature and pressure.
Lyophilization involves the removal of water or other solvents from a given product by a
process called sublimation. This occurs when the ice of a frozen product converts directly to
the gaseous state without passing through the liquid phase. This enables the preparation of a
stable product that is easy to use and store at ambient temperatures.
A low pressure environment is pre-requisite to allow this process to take place. In order to
start the removal of water, the pressure inside the freeze dryer must be below the “triple point
value” for the product, whilst also maintaining the temperature of the sample below its freeze
point in the lyophilization process.
Pre-freezing – first stage of the lyophilization process
The sample is frozen, which means the water in the product is converted to ice, thereby the
phase has changed from liquid to solid.
Slow pre-freezing will produce lager ice crystals, which are easier to lyophilize, whilst fast
pre-freezing results in smaller crystals.
Primary drying – Second stage of the lyophilization process
In the second stage of lyophilization the sublimation process starts. The ice formed in the pre-
freeze step is removed from the sample by the direct transition of the “solid” ice to a vapour
without passing through a liquid phase. The resultant vapour is collected by the condenser,
which has a lower temperature and pressure than the product. The vapour is thus converted
back to ice on the condenser surface. The “energy” required for this process to occur is
provided by a gentle heating of the sample, which will start the sublimation process and
eventually the sample will dry.
If too much energy (heat) is applied to the sample during this stage the condenser of the
lyophilizer may not be able to condense the volume of vapours fast enough, the ice condenser
temperature will subsequently rise along with its vapor pressure, thus increasing the risk of
the sample melting.
Secondary drying – Third stage of the lyophilization process
Finally, any residual water present, which is strongly bound to the molecules of the sample, is
converted to vapour and removed from the sample.
This water has invariably a vapour pressure lower than that of water in its “free” form.
Removal of the water in this final stage of lyophilization will be performed at higher product
temperatures, consequently, any biological activity of the sample will not be impaired or
affected. This usually involves increasing the temperature and lowering the pressure to
provide enough energy to break down the molecular bonding. A process called desorption.
The advantages of lyophilization include:
Ease of processing a liquid, which simplifies aseptic handling
Enhanced stability of a dry powder
Removal of water without excessive heating of the product
Enhanced product stability in a dry state
Rapid and easy dissolution of reconstituted product doe to increased solubility
Disadvantages of lyophilization include:
Increased handling and processing time
Need for sterile diluent upon reconstitution
Cost and complexity of equipment
The lyophilization process generally includes the following steps:
Dissolving the drug and excipients in a suitable solvent, generally water for injection
(WFI).
Sterilizing the bulk solution by passing it through a 0.22 micron bacteria-retentive
filter.
Filling into individual sterile containers and partially stoppering the containers under
aseptic conditions.
Transporting the partially stoppered containers to the lyophilizer and loading into the
chamber under aseptic conditions.
Freezing the solution by placing the partially stoppered containers on cooled shelves
in a freeze-drying chamber or pre-freezing in another chamber.
Applying a vacuum to the chamber and heating the shelves in order to evaporate the
water from the frozen state.
Complete stoppering of the vials usually by hydraulic or screw rod stoppering
mechanisms installed in the lyophilizers.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Refrigerator Revelations: A User's Guide to Operation and MaintenanceDari EverandRefrigerator Revelations: A User's Guide to Operation and MaintenanceBelum ada peringkat
- LyoDokumen22 halamanLyoAjay Kumar100% (1)
- Lyophilization of Parenterals FinalDokumen25 halamanLyophilization of Parenterals FinalMostofa RubalBelum ada peringkat
- Freeze Drying GuideDokumen12 halamanFreeze Drying GuidePedro CostaBelum ada peringkat
- Freeze Drying: Presented By: MR - Prem Patil M.Pharm+Mba (1 Year)Dokumen33 halamanFreeze Drying: Presented By: MR - Prem Patil M.Pharm+Mba (1 Year)Hasif D. Müller100% (1)
- LypholizationDokumen19 halamanLypholizationNaeem Khan MalizaiBelum ada peringkat
- What Is LyophilizationDokumen6 halamanWhat Is LyophilizationMd.Tareque AbdullahBelum ada peringkat
- Seminar By: M.Akram Baig ROLL NO:100812Dokumen18 halamanSeminar By: M.Akram Baig ROLL NO:100812manindergupta2192705Belum ada peringkat
- Lyophilization ProcessDokumen1 halamanLyophilization ProcessАнастасия АлександроваBelum ada peringkat
- Lyophilization/Freeze Drying: Dr. Nasir AbbasDokumen12 halamanLyophilization/Freeze Drying: Dr. Nasir AbbasAdil AminBelum ada peringkat
- LyophillicityDokumen7 halamanLyophillicityNabeel KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of LyophilizationDokumen5 halamanPrinciples of Lyophilizationiqbalkhan62Belum ada peringkat
- A Review Article On Lyophilization Techniques Used in Pharmaceutical ManufacturingDokumen7 halamanA Review Article On Lyophilization Techniques Used in Pharmaceutical Manufacturingjanviverma356535Belum ada peringkat
- Basics of Lyophilisation - by Dhaval SurtiDokumen34 halamanBasics of Lyophilisation - by Dhaval SurtiM. S. ChikkamaniBelum ada peringkat
- Lyophilization BasicsDokumen7 halamanLyophilization Basicsj.k.kumar100% (2)
- Interim Project Report: Under Guidance ofDokumen10 halamanInterim Project Report: Under Guidance ofDeepak SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Freeze DryerDokumen5 halamanFreeze DryerSundaresanBelum ada peringkat
- Freeze Drying: DR - Sangeetha SubramanianDokumen21 halamanFreeze Drying: DR - Sangeetha SubramanianYoshita SinghBelum ada peringkat
- 6877 DryingDokumen21 halaman6877 DryingDrx Namdev KachareBelum ada peringkat
- Freeze Drying.1pptxDokumen10 halamanFreeze Drying.1pptxAbdull SamiBelum ada peringkat
- AssignmentDokumen4 halamanAssignmentSania SaeedBelum ada peringkat
- Freeze Drying / Lyophilization: Professor A B M FaroqueDokumen19 halamanFreeze Drying / Lyophilization: Professor A B M FaroqueSudipta MandolBelum ada peringkat
- Drying (Partial), Freeze Drying, Freeze Concentration, and Pasteurisation Class LectureDokumen61 halamanDrying (Partial), Freeze Drying, Freeze Concentration, and Pasteurisation Class Lecturenabil100% (1)
- DryingDokumen8 halamanDryingAjaya Kumar MohapatraBelum ada peringkat
- Drying Process Ppt. AmenDokumen18 halamanDrying Process Ppt. AmenCherry ObiasBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment 2Dokumen2 halamanAssessment 2Jasmine DelgadoBelum ada peringkat
- Principi Base Della Liofilizzazione - Carlo VecchioDokumen43 halamanPrincipi Base Della Liofilizzazione - Carlo VecchioYana Cadiatan100% (1)
- Lyophilization Process 1622495344Dokumen7 halamanLyophilization Process 1622495344maheshBelum ada peringkat
- Freeze DryingDokumen7 halamanFreeze Dryingbekku100% (1)
- Application of DryingDokumen31 halamanApplication of Dryinguzzal ahmedBelum ada peringkat
- Principle, Construction, Working, Uses, Merits and Demerits of Freeze Dryer - PharmaguidelineDokumen4 halamanPrinciple, Construction, Working, Uses, Merits and Demerits of Freeze Dryer - PharmaguidelineKaren Pachchigar 1Belum ada peringkat
- BCH 706 Lypholization 34587Dokumen27 halamanBCH 706 Lypholization 34587zshanali6236Belum ada peringkat
- Freeze-Drying: Improve This Article Reliable References Challenged RemovedDokumen23 halamanFreeze-Drying: Improve This Article Reliable References Challenged RemovedAgis Maulana PratamaBelum ada peringkat
- Freeze Drying: Presented by S.Kishore 15001A0841 Iv Btech Chemical EngineeringDokumen8 halamanFreeze Drying: Presented by S.Kishore 15001A0841 Iv Btech Chemical EngineeringChandaneswarkumar Boddani0% (1)
- Lyophilization DetailsDokumen33 halamanLyophilization Detailsj.k.kumar100% (4)
- Labconco Guide To Freeze DryingDokumen12 halamanLabconco Guide To Freeze DryingHector Pacheco AhumadaBelum ada peringkat
- Lyophilization PDFDokumen6 halamanLyophilization PDFrouss1906Belum ada peringkat
- Freeze Drying ReportDokumen23 halamanFreeze Drying ReportSanjana Bhattacharyya93% (14)
- Labogene Freezedrying WEBDokumen20 halamanLabogene Freezedrying WEBHagar SaeedBelum ada peringkat
- Spray Dryer & Freeze DryerDokumen20 halamanSpray Dryer & Freeze DryerHaroon RahimBelum ada peringkat
- 5 PengeringanDokumen14 halaman5 PengeringanAl Zahra Khas KempekBelum ada peringkat
- 4 Stages Complete Drying Process - Primarily From Freeze Drying Process-20190416023134-1 PDFDokumen2 halaman4 Stages Complete Drying Process - Primarily From Freeze Drying Process-20190416023134-1 PDFAzzwa ZubairiBelum ada peringkat
- Lyophilization/Freeze Drying - An Review: Article InfoDokumen12 halamanLyophilization/Freeze Drying - An Review: Article InfoavrupaveasyaBelum ada peringkat
- Process Control in Fruit Canning, Milk Frezzing and Vegetable FreezingDokumen37 halamanProcess Control in Fruit Canning, Milk Frezzing and Vegetable FreezingSharmina RituBelum ada peringkat
- Seminar Presentation On Freeze Drying: Prsented byDokumen26 halamanSeminar Presentation On Freeze Drying: Prsented byBibhuti B. RoulBelum ada peringkat
- Assignlent of Physical PharmacyDokumen8 halamanAssignlent of Physical PharmacyHamza amazonBelum ada peringkat
- General Principles of Freeze DryingDokumen12 halamanGeneral Principles of Freeze DryingAdnan HuskicBelum ada peringkat
- Dryers in Word FileDokumen5 halamanDryers in Word FileHaroon RahimBelum ada peringkat
- SUBLIMATIONDokumen4 halamanSUBLIMATIONSarim HassanBelum ada peringkat
- L Yo Phil IzationDokumen4 halamanL Yo Phil IzationFabianBelum ada peringkat
- Freeze Drying (Recovered)Dokumen20 halamanFreeze Drying (Recovered)DONA JOJOBelum ada peringkat
- By: Siddhartha RoyDokumen39 halamanBy: Siddhartha RoyrajagopalBelum ada peringkat
- KKKR3723 20182019 Utility Part 4 - EvaporationDokumen56 halamanKKKR3723 20182019 Utility Part 4 - EvaporationPutriBelum ada peringkat
- FPE20306-2019 - Chapter 3 - Evaporation - TheoryDokumen18 halamanFPE20306-2019 - Chapter 3 - Evaporation - TheoryAntonio MoncayoBelum ada peringkat
- Freeze DryingDokumen1 halamanFreeze DryingRazelle LaneBelum ada peringkat
- Sublimation PDFDokumen8 halamanSublimation PDFneha tariqBelum ada peringkat
- Vol. 5, Issue 11, November 2017, PharmaTutor, Paper-3Dokumen12 halamanVol. 5, Issue 11, November 2017, PharmaTutor, Paper-3asra kareemiBelum ada peringkat
- Lyophilization TechniqueDokumen21 halamanLyophilization TechniqueMd. Jewel100% (1)
- Foods 09 01488 v2Dokumen27 halamanFoods 09 01488 v2Dammak IlyesBelum ada peringkat
- ,!:@& F # T M - 5J - D GDJ :) N N 2wdup? O2 ÊDokumen2 halaman,!:@& F # T M - 5J - D GDJ :) N N 2wdup? O2 ÊVargheseBelum ada peringkat
- F&IP Lab Manual 4th YearDokumen173 halamanF&IP Lab Manual 4th YearVargheseBelum ada peringkat
- F&IP Lab Manual 4th YearDokumen173 halamanF&IP Lab Manual 4th YearVargheseBelum ada peringkat
- Full Adevrtisement FacultyDokumen18 halamanFull Adevrtisement FacultyVargheseBelum ada peringkat
- TopicsDokumen1 halamanTopicsVargheseBelum ada peringkat
- Y y Næ D K R R I Æ y Æ Ã Æ Wy y ¿ÆDokumen2 halamanY y Næ D K R R I Æ y Æ Ã Æ Wy y ¿ÆVargheseBelum ada peringkat
- CNS 377Dokumen2 halamanCNS 377VargheseBelum ada peringkat
- ) Ҕ Yҕ 'Ҕ (Ҕ) Ҕtϣɨ¤ Ċ Щ Ҕ) Ҕŭ Ҕҕҕ (Πҕ Ҕ Ҕ Ҕ 'Ҕ Ҕ 2 Ҕ Tкϟҕ *Ҕ Hyҕ) ) Ҕ) Ҕ) Ҕ ÷ɡȧǖ Ƥҕ Ҕ Ҕ Uҕ Ҕ 2Ҕ İѴѵѷҕ Ҕҕҕ2Ҕ Ҕ) Ҕҕ (Ҕш Ȃҕǐ 2Ł*Ҕ Ü4Ҕ Ҕ Ҕ' Ҕ Ҕz;Ǐї ɢҕă (Ҕ (4Ҕbҕ Yҕҕm9Tҕ Ҕ Ҕ (Ҕ 2Ҕ Ҕ 2RtñͿDokumen2 halaman) Ҕ Yҕ 'Ҕ (Ҕ) Ҕtϣɨ¤ Ċ Щ Ҕ) Ҕŭ Ҕҕҕ (Πҕ Ҕ Ҕ Ҕ 'Ҕ Ҕ 2 Ҕ Tкϟҕ *Ҕ Hyҕ) ) Ҕ) Ҕ) Ҕ ÷ɡȧǖ Ƥҕ Ҕ Ҕ Uҕ Ҕ 2Ҕ İѴѵѷҕ Ҕҕҕ2Ҕ Ҕ) Ҕҕ (Ҕш Ȃҕǐ 2Ł*Ҕ Ü4Ҕ Ҕ Ҕ' Ҕ Ҕz;Ǐї ɢҕă (Ҕ (4Ҕbҕ Yҕҕm9Tҕ Ҕ Ҕ (Ҕ 2Ҕ Ҕ 2RtñͿVargheseBelum ada peringkat
- C (CF V) ( Clnicnl?L) )Dokumen2 halamanC (CF V) ( Clnicnl?L) )VargheseBelum ada peringkat
- C (CC V) ( Clnicnl?L) )Dokumen2 halamanC (CC V) ( Clnicnl?L) )VargheseBelum ada peringkat
- Pharm IV Lab ManualDokumen125 halamanPharm IV Lab ManualVargheseBelum ada peringkat
- The Theory and Practice of Industrial Pharmacy 10-11Dokumen2 halamanThe Theory and Practice of Industrial Pharmacy 10-11VargheseBelum ada peringkat
- The Theory and Practice of Industrial Pharmacy by Lachman and Lieberman 1-3Dokumen3 halamanThe Theory and Practice of Industrial Pharmacy by Lachman and Lieberman 1-3VargheseBelum ada peringkat
- Science Week 5 QuizDokumen1 halamanScience Week 5 QuizJelou G. LunasBelum ada peringkat
- ThermodynamicsDokumen11 halamanThermodynamics.....Belum ada peringkat
- Laboratory ReportDokumen5 halamanLaboratory ReportRicanie CadornaBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Class 9 Chapter 1Dokumen75 halamanChemistry Class 9 Chapter 1Dhruv SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Astronaut Ice Cream, AnyoneDokumen6 halamanAstronaut Ice Cream, AnyoneNguyễn Lê Ti NaBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacognosy & PhytochemistryDokumen73 halamanPharmacognosy & PhytochemistryAsif Hasan Niloy100% (2)
- A Mathematical Model of Multi-Dimensional Freeze-Drying For Food ProductsDokumen13 halamanA Mathematical Model of Multi-Dimensional Freeze-Drying For Food ProductsEliana CárdenasBelum ada peringkat
- Inanimate Object EssayDokumen7 halamanInanimate Object Essayafibxejjrfebwg100% (2)
- 6.thermodynamics: Material Downloaded From SUPERCOP 1/8Dokumen8 halaman6.thermodynamics: Material Downloaded From SUPERCOP 1/8Abhinash MahapatroBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry Sba LabDokumen5 halamanChemistry Sba LabTawayna HemmingsBelum ada peringkat
- Sublimation of Benzoic Acid and The Determination of Its Melting PointDokumen3 halamanSublimation of Benzoic Acid and The Determination of Its Melting PointLorenz Rael Datay Cruz71% (7)
- 160) Chemistry Revised English PrintableDokumen103 halaman160) Chemistry Revised English PrintableKshitiz RajBelum ada peringkat
- Science 8 Q3 Week 3Dokumen12 halamanScience 8 Q3 Week 3Jetami Yuna GoBelum ada peringkat
- Conclusion Lab SeparationDokumen2 halamanConclusion Lab Separationnurul100% (1)
- Matter in Our SurroundingDokumen32 halamanMatter in Our SurroundingthinkiitBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 3-Sublimation and Melting Point DeterminationDokumen3 halamanExperiment 3-Sublimation and Melting Point DeterminationEmilyn Millares100% (4)
- Describe Ways On Proper Use Handling Solid, Liquid, Gas Found at Home and in SchoolDokumen7 halamanDescribe Ways On Proper Use Handling Solid, Liquid, Gas Found at Home and in SchoolShanel Silvano100% (2)
- Final CoachingDokumen137 halamanFinal CoachingEl Comedor BenedictBelum ada peringkat
- General Chemistry Grade 12 ModuleDokumen86 halamanGeneral Chemistry Grade 12 ModuleprincessssmtlbBelum ada peringkat
- FU - ART - Z.peng M.yuedong Y - 2009 - Energy Balance in DC Arc Plasma Melting FurnaceDokumen6 halamanFU - ART - Z.peng M.yuedong Y - 2009 - Energy Balance in DC Arc Plasma Melting FurnaceEduardo CandelaBelum ada peringkat
- Changes in Matter: Adapted From Chemical InteractionsDokumen18 halamanChanges in Matter: Adapted From Chemical Interactionsbabyu1Belum ada peringkat
- Short QuestionDokumen2 halamanShort QuestionRafey TahirBelum ada peringkat
- Phases of MatterDokumen5 halamanPhases of MatterMarivic MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- Sci 8 Q3 WK 3&4Dokumen2 halamanSci 8 Q3 WK 3&4ELVIS DOMINGOBelum ada peringkat
- PURIFICATION of Organic Compounds: 2. SublimationDokumen1 halamanPURIFICATION of Organic Compounds: 2. SublimationchinnagandiBelum ada peringkat
- Lyophilization: Senthamil Selvan TDokumen36 halamanLyophilization: Senthamil Selvan TbhuvaneshwaranBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 Kinetic Theory and DiffusionDokumen4 halamanChapter 1 Kinetic Theory and DiffusionKhondokar TarakkyBelum ada peringkat
- Phase Changes: Matter Exists in Three Physical StatesDokumen22 halamanPhase Changes: Matter Exists in Three Physical StatesCQChoongBelum ada peringkat
- Sublimation and Melting Point DeterminationDokumen3 halamanSublimation and Melting Point DeterminationRhone RoqueBelum ada peringkat
- Catalogo Maquinas Metalnox en PDFDokumen36 halamanCatalogo Maquinas Metalnox en PDFNils BickelBelum ada peringkat
- ICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation GuideDari EverandICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation GuideAndrew TeasdaleBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeDari EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (14)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincDari EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Well Integrity for Workovers and RecompletionsDari EverandWell Integrity for Workovers and RecompletionsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (3)
- AP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeDari EverandAP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsDari EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (3)
- Oxygen: The molecule that made the worldDari EverandOxygen: The molecule that made the worldPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (108)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactDari EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (5)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeDari EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (4)
- The Production of Volatile Oils and Perfumery Plants in the United StatesDari EverandThe Production of Volatile Oils and Perfumery Plants in the United StatesBelum ada peringkat
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingDari EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (10)
- Taste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodDari EverandTaste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (20)
- Guidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsDari EverandGuidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (1)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeDari EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- AP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeDari EverandAP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeBelum ada peringkat
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideDari EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideBelum ada peringkat
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactDari EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Tribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsDari EverandTribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeDari EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (90)
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsDari EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsBelum ada peringkat
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionDari EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)
- Essential Chemistry for Formulators of Semisolid and Liquid DosagesDari EverandEssential Chemistry for Formulators of Semisolid and Liquid DosagesPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)