UNIT III: India's Engagements With China Long Questions
Diunggah oleh
vaibhavi sharma pathak0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
164 tayangan6 halamanDelhi University Framework political science, Indian Foreign Policy, India-China relations framework
Judul Asli
China Exam Framework for Tellis
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniDelhi University Framework political science, Indian Foreign Policy, India-China relations framework
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
164 tayangan6 halamanUNIT III: India's Engagements With China Long Questions
Diunggah oleh
vaibhavi sharma pathakDelhi University Framework political science, Indian Foreign Policy, India-China relations framework
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 6
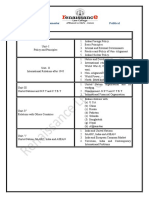
Expected questions are as follows
UNIT III: India’s engagements with China
Long questions
1. Examine the areas of conflict and cooperation in the India-China relations. (2017)
2. Analyse the continuities and changes in the India-China relations.
3. In the context of recent developments, analyse the economic and security
dimensions in India-China relations.
4. Discuss major challenges confronting India-China relationship. (2018)
Short notes
1. Panchsheel (2017)
2. Doklam crisis
3. Sino-Indian border dispute
....................................…
Discuss india-china relations with special reference to doklam dispute (Lib)
China’s growing stature in world politics is likely to undermine india’s influence.
Discuss. 2017
Synopsis
1. Pre-independence era: Harsh V. Pant
2. Nehru era till 1964: Harsh V. Pant
3. Till 1988: Harsh V. Pant
4. Since 1988 Convergences and divergences : Ashley J. Tellis and Sean Mirski
5. Latest developments: Sanjana Gogna and Wu Lin/Srikanth Kondapalli
Part I: Global Order
a) Changing Global Order
b) International Economic System
c) Global Non-proliferation system
Part II: Regional Security
a) Asian security
b) Stability in South Asia
Part III: Security in the Global Commons
a) Security in the Maritime Commons
b) Space security
c) Technology/Cyber security
Part IV: Non-traditional security
a) The search for energy security
b) Environmental issues
Introduction
1. India and China grew under American hegemony
2. India’s economic growth has not yet reached China’s economic growth
3. Both want peaceful international environment
India-China convergence India-China divergence
1. Recovering pre-eminence as 1.Contrast in respective political
international entities of consequence regimes
2. For multipolar world 2.Territorial disputes
3. Avoiding the costs of contributing to 3.Geopolitical rivalries
global public goods
4. Protection of hard won sovereignty
PART I: GLOBAL ORDER
(a) Changing Global Order
India-China convergence India-China divergence
1.For a multipolar world 1.For China, State>Individuals
For India, State=Individuals
2.Both increasingly integrated to US led
international order
3.Globalisation as a positive and inevitable 2.Clash on India’s claim to
event permanent seat in UNSC
4.Suspicion of NGOs 3.US+India following
containment of China policy
5.Caution with technologies
6.Both feel underrepresented in key
international bodies
7.International legal institutions are
important but they should not impinge on
national sovereignty
(b) International Economic System
India-China convergence India-China divergence
1.For open economic order 1.Benefits of LPG more to China
2.Dissatisfied by the BOP in many global 2.WB’s push for clean and
institutions transparent govt. is a major
challenge to China
3.Fear of rising protectionism among 3.Future of PSUs bleak in India,
developed countries whereas in China it is bright
4.For substantive state controls in domestic 4.China prefers multi-currency
economic system system (Yuan). India prefers
Dollar supremacy
5.Want to increase presence of national 5. China favours regional Free
currencies at global level Trade Agreements over WTO
agreements. India is more
welcoming of WTO supervision
(c) Global non-proliferation system
India-China convergence India-China divergence
1.Both believe in non-proliferation 1.China has no problem with
nuclear ambitions of North Korea
and Pakistan but has problem with
Iran.
2.For India, NPT is discriminatory
3.China oppose special
concessions given to India in spite
of being an outlier to NSG.
PART II: REGIONAL SECURITY
(a) Asian Security
India-China convergence India-China divergence
1.For both sovereignty is central 1.Military presence of USA in
Taiwan, Japan and South China
Sea not liked by China
2.Both for economic development of the 2.For India, military assistance to
region third party only under UN
guidance. China is silent about it.
3.Both for international cooperation and 3.India is hesitant about too much
collective security measures closeness with both US and China
4.For Asian security, non-military
instruments are important
(b) Stability in South Asia
India-China convergence India-China divergence
1.Both want stable and peaceful S.Asia 1.Promotion of democracy in the
region
2.Importance of Indian Ocean Region as 2.China’s interest to become part
sealine of communication of S.Asia is a new claim
3.For reforms in Myanmar and 3.India is against proximity of
Afghanistan Pakistan and China
4.Concerned about climate challenges and 4.China is against US interference
drug trafficking in the region in the region
PART III: SECURITY IN THE GLOBAL COMMONS
(a) Security in the maritime commons
India-China convergence India-China divergence
1.Global maritime system like UN 1.China is against third party
Convention on the Law of the Sea is arbitration. India has no problem
important for both India and China
2.Oppose USA’s unfettered access 2.India believes that the USA’s
Navy is providing an important
global public good by maintaining
maritime order and stability.
China is not in favour of this
3.Dispute resolution through diplomatic
negotiations
4.Justify use of force to defend one’s
territorial sovereignty
(b) Space security
India-China convergence India-China divergence
1.Both see space security as important 1.China’s space programmes are
of military nature, India’s focus
on civilian
2.Both for International Space Regime 2.China’s pace of space
development faster
3.China’s areas of scope wider.
India’s focus areas are imagery,
surveillance, position and
navigation, communication
system
4.Biggest threat to China is USA.
Biggest threat to India is China
(c) Cyber security
India-China convergence India-China divergence
1.Steadily growing cyberspace programs 1.China for technological
autonomy. India wants industry
and technology to be under
government guidance
2.Face similar threats: Hacking, illegal 2.In India, internet freedom is
online activities, cyber terrorism, more
militarization of cyberspace, espionage
3.Both for legal regime to guide cyber 3.For India, if its territory is used
world in cyber-crime, then the state must
take the responsibility. For China,
this is unfair and unrealistic
expectations on the state
4.Both for multilateral and bilateral
engagements on this issue
5.Both recognise importance of ‘Public-
Private Partnerships’
6.Both unaware on how to deal with NSAs
in cyber crimes
7.Both for more regulations
PART IV: NON-TRADITIONAL SECURITY
(a) The search for energy security
India-China convergence India-China divergence
1.Both will experience high and raising 1.China has the potential for self-
rates of energy consumption reliance. India far from it
2.Both heavily rely on coal for its energy 2.The state in China has more
security autonomy to take decisions for
energy security. The Indian state
is under the pressure of
democracy
3.Both are optimistic about making use of 3.China’s domestic production
their domestic gas reserves but with its and efficiency higher
challenges
4.Commercial concerns are important for 4.China is adopting latest designs
national energy companies to protect N-plants, India is slow
in this front
5. Both feel “International Energy 5.In India the opposition to
Agency” to be more democratic in nuclear energy is visible, in China
structure it is absent
6.Both are concerned about piracy and 6.In China, National Energy
safeguarding their energy assets Companies are more in state
control
7.India is dependent upon US
naval forces to secure its sea lines
of communication, decrease in US
naval power is increasing India’s
vulnerability
(b) Environmental issues
India-China convergence India-China divergence
1.Both seek to balance economic growth 1.China has spent significant
with environmental responsibility amount on environment friendly
measures. India is still vacillating
between green technologies
strategies and no strategy at all
2.Problem of pollution
3.Both blame developed countries for
environmental degradation
4.Both seek solution through international
negotiations
5.Both believe in “Common but
differentiated responsibilities”
CONCLUSION
India and China relation is a complex dynamic of cooperation and
competition
Wuhan meeting emphasised on strengthening communication between
militaries to avoid confrontation like Doklam
Promotion of Indian exports to China: Agricultural + pharmaceutical
products
Joint project in Afghanistan: Training of Afghan diplomats
India’s NSG membership opposed by China as India has not signed NPT
UN’s terror designation to Pakistan based groups like Lashkar-e-Taiba,
Jaish-e-Mohammad faced opposition from China but later agreed. In
May 2019, India witnessed a huge diplomatic win when China allowed
Azhar Masood to be designated as a terrorist by UNSC.
India’s opposition to OBOR initiative of China
China critical (highly concerned) about abrogation of Article 370 by
India and wants the UNSC to intervene
To resolve differences peacefully and through prolonged dialogue
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Internal SecurityDokumen38 halamanInternal SecuritySabareesh MohandasBelum ada peringkat
- Envall Hall India JapanDokumen10 halamanEnvall Hall India JapanalokBelum ada peringkat
- Pol 3178Dokumen7 halamanPol 3178kverret6299Belum ada peringkat
- International Relation Byjus PDFDokumen13 halamanInternational Relation Byjus PDFArnav MishraBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7 Security in Contemporary WorldDokumen12 halamanChapter 7 Security in Contemporary WorldKartik KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Ch.-5 - India and Other Countries New Words With Their MeaningsDokumen10 halamanCh.-5 - India and Other Countries New Words With Their MeaningsSujeet KulkarniBelum ada peringkat
- International Relations f971577cDokumen6 halamanInternational Relations f971577cSarvesh KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Quad A To ZDokumen3 halamanQuad A To ZYASHWANT SINGHBelum ada peringkat
- Qatar Crises: 1. What Are The Issues Addressed?Dokumen7 halamanQatar Crises: 1. What Are The Issues Addressed?syed haseebBelum ada peringkat
- Atmanirbhar Ias: NewspaperDokumen7 halamanAtmanirbhar Ias: NewspaperzionSBelum ada peringkat
- IR Notes-Final 3Dokumen283 halamanIR Notes-Final 3iusamashaiq10Belum ada peringkat
- SecurityDokumen9 halamanSecurityLaura Torres ErolesBelum ada peringkat
- Sunday Extra Class POLDokumen5 halamanSunday Extra Class POLradhikabathla8Belum ada peringkat
- Challenges To National Security of PakistanDokumen3 halamanChallenges To National Security of PakistanWaqas AslamBelum ada peringkat
- Challenges To National Security of PakistanDokumen3 halamanChallenges To National Security of PakistanWaqas AslamBelum ada peringkat
- Logical Reasoning Sectional TestDokumen15 halamanLogical Reasoning Sectional TestAditya HiremathBelum ada peringkat
- PSIR Paper 2Dokumen72 halamanPSIR Paper 2Yasha SahuBelum ada peringkat
- India-US Relations Under Biden Administration: PM ModiDokumen15 halamanIndia-US Relations Under Biden Administration: PM Modipushpak deshmukhBelum ada peringkat
- Ser No Subject Page No: Part-I: IntroDokumen14 halamanSer No Subject Page No: Part-I: IntroshubhamBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Challenges in India by Parth Sachdev1Dokumen18 halamanStrategic Challenges in India by Parth Sachdev1Abhishek PatiyalBelum ada peringkat
- CH 4 India's External RelationsDokumen95 halamanCH 4 India's External RelationsKEERAVANI73% (15)
- Gs - I, Ii, Iii, and Iv: Mains Questions (Topic Wise)Dokumen50 halamanGs - I, Ii, Iii, and Iv: Mains Questions (Topic Wise)kumarBelum ada peringkat
- CSPHCL JE General Awareness Old PaperDokumen5 halamanCSPHCL JE General Awareness Old Paperflyingz2810Belum ada peringkat
- Foreign PolicyDokumen14 halamanForeign PolicyHira iQbalBelum ada peringkat
- International Relations by Roastedgeographer YtDokumen234 halamanInternational Relations by Roastedgeographer YtMahalaxmi kasyapBelum ada peringkat
- Santoshkumar.C.: Veeresh .P. ArakeriDokumen9 halamanSantoshkumar.C.: Veeresh .P. ArakeriAnaveer S JBelum ada peringkat
- PyqsDokumen50 halamanPyqsAdarshBelum ada peringkat
- Current Affairs SyllabusDokumen16 halamanCurrent Affairs SyllabusBadar AhsanBelum ada peringkat
- Structure: 403 Princip Es O # I A N Foreign PolicyDokumen18 halamanStructure: 403 Princip Es O # I A N Foreign PolicyAparajita ChaudhuriBelum ada peringkat
- Continuing Challenges in Enforcement of The 2016 Arbitral Award On The West Philippine SeaDokumen4 halamanContinuing Challenges in Enforcement of The 2016 Arbitral Award On The West Philippine SeaChristian GuingcangcoBelum ada peringkat
- All India Senior School Certificate Examination Marking Scheme - 2016 Subject: Political Science 59/2/1Dokumen10 halamanAll India Senior School Certificate Examination Marking Scheme - 2016 Subject: Political Science 59/2/1Ahmed KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Sino-Indian War 2Dokumen14 halamanSino-Indian War 2Namra NasirBelum ada peringkat
- PolSci MS PDFDokumen8 halamanPolSci MS PDFHemaline RoseBelum ada peringkat
- Political Science On International PoliciesDokumen89 halamanPolitical Science On International PoliciesIshitaBelum ada peringkat
- Indo-Us RelationsDokumen11 halamanIndo-Us RelationshimanshiBelum ada peringkat
- India USA RelationDokumen11 halamanIndia USA RelationShubham MeghwalBelum ada peringkat
- OICDokumen4 halamanOICZeeshan DanishBelum ada peringkat
- China An Opportunity or A Threat To Asea PDFDokumen9 halamanChina An Opportunity or A Threat To Asea PDFAbdullah HussainBelum ada peringkat
- Test 5Dokumen13 halamanTest 5Tanya GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Main Examination General Studies (Paper-Iii) : Theme SecurityDokumen4 halamanMain Examination General Studies (Paper-Iii) : Theme SecurityJayendran devBelum ada peringkat
- India's Foreign Policy: Changing Dynamics: ContextDokumen4 halamanIndia's Foreign Policy: Changing Dynamics: ContextAshis Kumar MohantyBelum ada peringkat
- Summary of Elizabeth C. Economy's The World According to ChinaDari EverandSummary of Elizabeth C. Economy's The World According to ChinaBelum ada peringkat
- CBSE Class 12 Political Science Marking Scheme Question Paper 2022-23Dokumen8 halamanCBSE Class 12 Political Science Marking Scheme Question Paper 2022-23Sanjani kumariBelum ada peringkat
- PolSci MSDokumen8 halamanPolSci MSArnav DhamneBelum ada peringkat
- Thayer, Southeast Asia Amid Global ImpactsDokumen49 halamanThayer, Southeast Asia Amid Global ImpactsCarlyle Alan ThayerBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 How Can We Work For The Good of Society in SingaporeDokumen4 halamanChapter 3 How Can We Work For The Good of Society in SingaporeAlexisBelum ada peringkat
- M S Political Science Sample Paper 1Dokumen7 halamanM S Political Science Sample Paper 1kanakbaisla68Belum ada peringkat
- ChickFilA 4190projectDokumen1 halamanChickFilA 4190projectjaymoney20Belum ada peringkat
- MS-Set-V, XII PSDokumen4 halamanMS-Set-V, XII PSShad ChoudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Holslag, Jonathan (2008), China's New Security Policy For Africa, BICCS Asia Paper, Vol 3Dokumen13 halamanHolslag, Jonathan (2008), China's New Security Policy For Africa, BICCS Asia Paper, Vol 3artenda100% (3)
- Sino-Indian Border Dispute Group Discussion Short Points PDFDokumen1 halamanSino-Indian Border Dispute Group Discussion Short Points PDFCherryBelum ada peringkat
- VIII Social Science Sample PaperDokumen3 halamanVIII Social Science Sample PaperTaranjeet SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Std. 9 Subject: History Ch. 5 - India and Other Countries Textual AnswersDokumen3 halamanStd. 9 Subject: History Ch. 5 - India and Other Countries Textual AnswersSufyan AliBelum ada peringkat
- Section A: Class X Exam 2021-22 (TERM - II) Social ScienceDokumen5 halamanSection A: Class X Exam 2021-22 (TERM - II) Social ScienceMANTRA JANIBelum ada peringkat
- PWSDiscDokumen4 halamanPWSDiscThe Telugu ChannelBelum ada peringkat
- International Relations Notes by Ayesha Younas Paper 1 & 2Dokumen271 halamanInternational Relations Notes by Ayesha Younas Paper 1 & 2Mahzad Sareer100% (5)
- Chapter 3 Political Science Class 12 PDFDokumen7 halamanChapter 3 Political Science Class 12 PDFSharad ChauhanBelum ada peringkat
- Thesis Topic: Manish Kumar Yadav. Email: Cell No:+91-9871256919Dokumen56 halamanThesis Topic: Manish Kumar Yadav. Email: Cell No:+91-9871256919Kama LapizlasuliBelum ada peringkat
- "Super 30": (2 Marks)Dokumen9 halaman"Super 30": (2 Marks)aaryan28februaryBelum ada peringkat
- Book Review: The Resolution of ConflictDokumen6 halamanBook Review: The Resolution of Conflictvaibhavi sharma pathakBelum ada peringkat
- Federalism Ronald WattsDokumen133 halamanFederalism Ronald Wattsvaibhavi sharma pathakBelum ada peringkat
- Track II Diplomacy or "Backchannel Diplomacy" H Istory: Joseph V. MontvilleDokumen4 halamanTrack II Diplomacy or "Backchannel Diplomacy" H Istory: Joseph V. Montvillevaibhavi sharma pathakBelum ada peringkat
- Conflict Transformation:: New RoutesDokumen36 halamanConflict Transformation:: New Routesvaibhavi sharma pathakBelum ada peringkat
- War, Theories of Causes, TypesDokumen10 halamanWar, Theories of Causes, Typesvaibhavi sharma pathakBelum ada peringkat
- Peaceful World: Galtung's WorksDokumen4 halamanPeaceful World: Galtung's Worksvaibhavi sharma pathakBelum ada peringkat
- Dem - Post Communist StatesDokumen9 halamanDem - Post Communist Statesvaibhavi sharma pathakBelum ada peringkat
- Human Security NotesDokumen12 halamanHuman Security Notesvaibhavi sharma pathakBelum ada peringkat
- Buddhism NotesDokumen34 halamanBuddhism Notesvaibhavi sharma pathakBelum ada peringkat
- TISS Entrance For Master's.Dokumen7 halamanTISS Entrance For Master's.vaibhavi sharma pathakBelum ada peringkat
- Marxist Approach To Study Nationalism in IndiaDokumen16 halamanMarxist Approach To Study Nationalism in Indiavaibhavi sharma pathakBelum ada peringkat
- 2017 Indian Political ThoughtDokumen2 halaman2017 Indian Political Thoughtvaibhavi sharma pathakBelum ada peringkat
- Jnu SyllabusDokumen2 halamanJnu Syllabusvaibhavi sharma pathakBelum ada peringkat
- Liberal Perspective On ColonialismDokumen19 halamanLiberal Perspective On Colonialismvaibhavi sharma pathakBelum ada peringkat
- Buddhism Article Ignou Philosophy of BDokumen11 halamanBuddhism Article Ignou Philosophy of Bvaibhavi sharma pathakBelum ada peringkat
- Delhi University NotesDokumen8 halamanDelhi University Notesvaibhavi sharma pathakBelum ada peringkat
- Walter Andersen and Karti Bajpai InterviewsDokumen9 halamanWalter Andersen and Karti Bajpai Interviewsvaibhavi sharma pathakBelum ada peringkat
- 2017 Question PaperDokumen2 halaman2017 Question Papervaibhavi sharma pathakBelum ada peringkat
- VIVEKANAND - Indian Political ThoughtDokumen32 halamanVIVEKANAND - Indian Political Thoughtvaibhavi sharma pathak100% (1)
- BOOK - Ideologies of The Raj - Metcalf and Metcalf PDFDokumen252 halamanBOOK - Ideologies of The Raj - Metcalf and Metcalf PDFvaibhavi sharma pathak100% (1)
- TAGORE - Indian Political ThoughtDokumen21 halamanTAGORE - Indian Political Thoughtvaibhavi sharma pathakBelum ada peringkat
- Political Ideas of Shanti ParvaDokumen9 halamanPolitical Ideas of Shanti Parvavaibhavi sharma pathakBelum ada peringkat
- India's Foreign Relations - Jayanta Kumar RayDokumen831 halamanIndia's Foreign Relations - Jayanta Kumar Rayvaibhavi sharma pathakBelum ada peringkat
- BI410 Plant Developmental BiologyDokumen41 halamanBI410 Plant Developmental BiologyLaisla CagliariBelum ada peringkat
- Resonant Excitation of Coherent Cerenkov Radiation in Dielectric Lined WaveguidesDokumen3 halamanResonant Excitation of Coherent Cerenkov Radiation in Dielectric Lined WaveguidesParticle Beam Physics LabBelum ada peringkat
- 01.performing Hexadecimal ConversionsDokumen11 halaman01.performing Hexadecimal ConversionsasegunloluBelum ada peringkat
- Indus River Valley Civilization ObjectivesDokumen4 halamanIndus River Valley Civilization ObjectivesArslan AsifBelum ada peringkat
- Micro Fibra Sintetica at 06-MapeiDokumen2 halamanMicro Fibra Sintetica at 06-MapeiSergio GonzalezBelum ada peringkat
- FSU7533 Digital Marketing & Social Media Career Advancement Certification (Including Voucher) ETPDokumen2 halamanFSU7533 Digital Marketing & Social Media Career Advancement Certification (Including Voucher) ETPcBelum ada peringkat
- Jacksonville's Taste 2012Dokumen100 halamanJacksonville's Taste 2012Ali KhanBelum ada peringkat
- The Sacred Bee: Ancient Egypt: by Planet Bee FoundationDokumen4 halamanThe Sacred Bee: Ancient Egypt: by Planet Bee Foundationsoha elmahdyBelum ada peringkat
- Jurczyk Et Al-2015-Journal of Agronomy and Crop ScienceDokumen8 halamanJurczyk Et Al-2015-Journal of Agronomy and Crop ScienceAzhari RizalBelum ada peringkat
- "Written Statement": Tanushka Shukla B.A. LL.B. (2169)Dokumen3 halaman"Written Statement": Tanushka Shukla B.A. LL.B. (2169)Tanushka shuklaBelum ada peringkat
- Suspension Mansons 2Dokumen45 halamanSuspension Mansons 2Andres Silva67% (3)
- Handbook For Inspection of Ships and Issuance of Ship Sanitation CertificatesDokumen150 halamanHandbook For Inspection of Ships and Issuance of Ship Sanitation CertificatesManoj KumarBelum ada peringkat
- EpitheliumDokumen48 halamanEpitheliumdrpankaj28100% (1)
- Form A HypothesisDokumen2 halamanForm A Hypothesismrshong5bBelum ada peringkat
- BY DR Muhammad Akram M.C.H.JeddahDokumen32 halamanBY DR Muhammad Akram M.C.H.JeddahMuhammad Akram Qaim KhaniBelum ada peringkat
- Lease of Playground To A SchoolDokumen2 halamanLease of Playground To A SchoolSutapaBelum ada peringkat
- Paras Vs ComelecDokumen2 halamanParas Vs ComelecAngel VirayBelum ada peringkat
- Sow English Year 4 2023 2024Dokumen12 halamanSow English Year 4 2023 2024Shamien ShaBelum ada peringkat
- ProjectDokumen1 halamanProjectDevil KingBelum ada peringkat
- Discuss Both Views Introduction PracticeDokumen3 halamanDiscuss Both Views Introduction PracticeSang NguyễnBelum ada peringkat
- 1.2.7 Cell Membrane Structure and FunctionDokumen5 halaman1.2.7 Cell Membrane Structure and FunctionAYUSH ALTERNATE67% (3)
- French Art of Not Giving A F-CK Chapter SamplerDokumen19 halamanFrench Art of Not Giving A F-CK Chapter SamplerAllen & UnwinBelum ada peringkat
- Economic and Product Design Considerations in MachiningDokumen29 halamanEconomic and Product Design Considerations in Machininghashir siddiquiBelum ada peringkat
- MLHP Final ListDokumen36 halamanMLHP Final Listswapnitha tummaBelum ada peringkat
- WLP Math Week 4 Q4Dokumen4 halamanWLP Math Week 4 Q4JUDELYN O. DOMINGOBelum ada peringkat
- Vince - Michael - Intermediate - Language Assive 1Dokumen5 halamanVince - Michael - Intermediate - Language Assive 1Николай КолевBelum ada peringkat
- Tectos Falsos Stretch Caracteristicas TecnicasDokumen37 halamanTectos Falsos Stretch Caracteristicas TecnicasVadymBelum ada peringkat
- PCU 200 Handbook 2018-19 PDFDokumen177 halamanPCU 200 Handbook 2018-19 PDFVica CapatinaBelum ada peringkat
- Adult Development and LeadershipDokumen28 halamanAdult Development and LeadershipUsama dawoudBelum ada peringkat
- Human Resource Management in The Hospitality Industry Is FullyDokumen14 halamanHuman Resource Management in The Hospitality Industry Is FullykiahBelum ada peringkat