Material Requirements Plan (MRP)
Diunggah oleh
FitRi Ezery0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
48 tayangan2 halamanJob or Task Scheduling involves preparing a time and action calendar for each order from receipt to shipment. This includes scheduling tasks like planned cut dates and line loading dates, and assigning responsibilities. Material Resource Planning involves preparing material requirements based on samples and specifications and estimating costs. Production Loading defines which styles are loaded to production lines and in what quantities. Process Selection and Planning selects the necessary processes for orders based on customer requirements. Capacity Planning determines how much capacity to allocate to orders based on total factory capacity. Line Planning prepares daily production targets for lines after discussing with production. Follow Up and Execution involves executing plans and monitoring progress, expediting delays.
Deskripsi Asli:
ppc
Judul Asli
Nota
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniJob or Task Scheduling involves preparing a time and action calendar for each order from receipt to shipment. This includes scheduling tasks like planned cut dates and line loading dates, and assigning responsibilities. Material Resource Planning involves preparing material requirements based on samples and specifications and estimating costs. Production Loading defines which styles are loaded to production lines and in what quantities. Process Selection and Planning selects the necessary processes for orders based on customer requirements. Capacity Planning determines how much capacity to allocate to orders based on total factory capacity. Line Planning prepares daily production targets for lines after discussing with production. Follow Up and Execution involves executing plans and monitoring progress, expediting delays.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
48 tayangan2 halamanMaterial Requirements Plan (MRP)
Diunggah oleh
FitRi EzeryJob or Task Scheduling involves preparing a time and action calendar for each order from receipt to shipment. This includes scheduling tasks like planned cut dates and line loading dates, and assigning responsibilities. Material Resource Planning involves preparing material requirements based on samples and specifications and estimating costs. Production Loading defines which styles are loaded to production lines and in what quantities. Process Selection and Planning selects the necessary processes for orders based on customer requirements. Capacity Planning determines how much capacity to allocate to orders based on total factory capacity. Line Planning prepares daily production targets for lines after discussing with production. Follow Up and Execution involves executing plans and monitoring progress, expediting delays.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
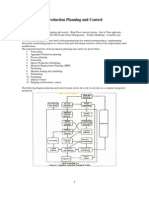
• Job or Task Scheduling: Preparation of time and action The forecast for individual end items
calendar for each order from order receiving to shipment. The
job schedule contains list of tasks to be processed for the styles. Sales orders
Against each tasks planner mentions when to start a task and
what is dead line for that task. Name of responsible person
(department) for the job is being listed. For example, scheduling
Inventories
planned cut date (PCD), line loading date.
Existing capacity
• Material Resource Planning (Inventory): Preparation
ofMaterial requirement sheet according to sample product and Material Requirements Plan (MRP)
buyer specification sheet. Consumption of material (fabric,
thread, button, and twill tape) is calculated and estimated cost
Plan for the production and purchase of
of each material.
the components used in making the items
in the MPS.
• Loading production: Planner defines which style to be loaded
to the production line and how much quantity to be loaded. End item requirements broken down
into specific components –
• Process selection & planning: Processes needed to complete
what to make or buy, and when
an order vary style to style. According to the order (customer) Level of details is high.
requirement PPC department select processes for the orders.
Sometime extra processes are eliminated to reduce cost of Planning horizon usually extends
production. from 3-18 months.
• Facility location: Where a company has multiple factories
(facilities) for production and factories are set for specific MRP
product, planner need to identify which facility will be most
suitable for new orders. Sometimes there may be a capacity Gross Requirement
shortage in a factory, in that case planner need to decide which
facility will selected for that oder Net Requirement
• Estimating quantity and costs of production: Planner estimate
daily production (units) according to the styles work content. Planned order Receipts
With the estimated production figure, production runs and
manpower involvement planner also estimate production cost Schedule Receipts
per pieces.
Project On Hand
Planned order Releases
• Capacity planning: PPC department plays a major role during
order booking. They decide (suggest) how much order they
should accept according to their production capacity. Allocating
of total capacity or deciding how much capacity to be used for
an order out of total factory capacity. Regularly updating Production Activity Control (PAC)
factories current capacity (production capacity).
Execution plan, detailing specific orders
to produce items from the MRP.
• Line planning: Preparing detailed line planning with daily
production target for the production line. Most cases line Responsible for planning and controlling
planning is made after discussing with production team and the flow of work through the factory.
Industrial engineers.
Planning horizon is very short (a day to a
month).
• Follow up and execution: Whatever plan is made is executed
by PPC department. PPC department keeps close look whether The level of detail is high since it is
everything is progressing according the plan. Chasing other
concerned with individual components,
department heads on daily basis to keep plan on track. They
update order wise completed tasks on the Time & action workstations and orders.
Calendar. When they found something is going to be late they
expedite and create an alarm about the delay. Plan are reviewed and revised daily.
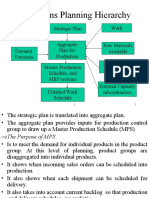
Inputs to MPS
The production plan Time Fences
Points in the planning horizon to define
the flexibility allowed in the MPS
Frozen Zone (closest to current date)
Capacity and materials committed to
customer orders,
forecast generally ignored
Senior management approval for changes
Slushy Zone
Less commitment of materials and capacity
Tradeoffs negotiated between marketing
and manufacturing
Liquid Zone – All changes allowed within
limits of the Production Plan
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Master Production Schedule TechniqueDokumen16 halamanMaster Production Schedule TechniqueSathiya Moorthy100% (1)
- 10 Steps To Precision Maintenance Reliability SuccessDokumen11 halaman10 Steps To Precision Maintenance Reliability SuccessElvis DiazBelum ada peringkat
- Factory Audit ReportDokumen33 halamanFactory Audit ReportMudit Kothari100% (1)
- Production Planning: Devaki NadkarniDokumen29 halamanProduction Planning: Devaki Nadkarnidsathiya100% (1)
- Projectmanagement 01Dokumen28 halamanProjectmanagement 01FitRi EzeryBelum ada peringkat
- PP Training Presentation M&MDokumen49 halamanPP Training Presentation M&MNikhil WaniBelum ada peringkat
- CH-2 Production Planning and ControlDokumen53 halamanCH-2 Production Planning and ControlSimon abebawBelum ada peringkat
- 2017 Walters Global Salary SurveyDokumen428 halaman2017 Walters Global Salary SurveyDebbie CollettBelum ada peringkat
- Production Planning ControlDokumen12 halamanProduction Planning ControlRaibatul AdawiyahBelum ada peringkat
- Research Project ReportDokumen21 halamanResearch Project ReportinternationalbankBelum ada peringkat
- Production Planning & ControlDokumen23 halamanProduction Planning & Controlrupa royBelum ada peringkat
- Cpim - MPR (Sop & MPS)Dokumen118 halamanCpim - MPR (Sop & MPS)Mohammad S. Abu SbeihBelum ada peringkat
- Practical Guide To Production Planning & Control [Revised Edition]Dari EverandPractical Guide To Production Planning & Control [Revised Edition]Penilaian: 1 dari 5 bintang1/5 (1)
- Workplace Housekeeping: Training Slides OnDokumen42 halamanWorkplace Housekeeping: Training Slides Onamit yadavBelum ada peringkat
- Material Requirement PlanningDokumen42 halamanMaterial Requirement PlanningBinodini SenBelum ada peringkat
- Aggregates Sales and Operations PlanningDokumen31 halamanAggregates Sales and Operations PlanningIan Kenneth MarianoBelum ada peringkat
- Production Planning and SchedulingDokumen46 halamanProduction Planning and SchedulingGaurav KatariaBelum ada peringkat
- Production Planning and ControlDokumen14 halamanProduction Planning and ControlMuthuvel M100% (1)
- The BEST PAPER CPM 26086235 A Palladium Group White PaperDokumen24 halamanThe BEST PAPER CPM 26086235 A Palladium Group White PaperColiveira_brBelum ada peringkat
- 6 - Master Production ScheduleDokumen30 halaman6 - Master Production ScheduleVishvajit KumbharBelum ada peringkat
- CH 5 Operations Planning & ControlDokumen64 halamanCH 5 Operations Planning & ControlYaredBelum ada peringkat
- OM Chapter FourDokumen58 halamanOM Chapter FourLakachew GetasewBelum ada peringkat
- Operations Management-Chapter FiveDokumen64 halamanOperations Management-Chapter FiveAGBelum ada peringkat
- Production Planning and Inventory Control: Dr. Mohammed OthmanDokumen34 halamanProduction Planning and Inventory Control: Dr. Mohammed OthmanYasser IsteitiehBelum ada peringkat
- Production Planning and Inventory ControlDokumen34 halamanProduction Planning and Inventory Controlmarah nimerBelum ada peringkat
- Material Requirements PlanningDokumen36 halamanMaterial Requirements PlanningKave MathiBelum ada peringkat
- Production Planning and ControlDokumen32 halamanProduction Planning and Controlsiddhi jainBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3-Master SchedulingDokumen54 halamanChapter 3-Master SchedulingVatsal PatelBelum ada peringkat
- P&OM Unit 3.1Dokumen48 halamanP&OM Unit 3.1Tom CruiseBelum ada peringkat
- Material and Procuction Management NotesDokumen68 halamanMaterial and Procuction Management NotesMwanza MaliiBelum ada peringkat
- FinalDokumen31 halamanFinalBhawesh WarudkarBelum ada peringkat
- OM Unit - IVDokumen78 halamanOM Unit - IVMani MjBelum ada peringkat
- 5 6298816525973323997 PDFDokumen120 halaman5 6298816525973323997 PDFKAMAL PATIBelum ada peringkat
- Materials Mgt-SIBM (Annexure)Dokumen47 halamanMaterials Mgt-SIBM (Annexure)DHRUV CHANCHALBelum ada peringkat
- Manufacturing & Operations Management, Materials & LogisticsDokumen17 halamanManufacturing & Operations Management, Materials & LogisticsZakir KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3Dokumen61 halamanChapter 3Caringal Christelle MaeBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Materials Requirement PlanningDokumen22 halaman3 Materials Requirement PlanningGangadhar TallaBelum ada peringkat
- Terms Definition Assemble-To-OrderDokumen2 halamanTerms Definition Assemble-To-OrderNivas KaruppananBelum ada peringkat
- Prodn - Ops - PLNG & Control-2019Dokumen42 halamanProdn - Ops - PLNG & Control-2019Raman KulkarniBelum ada peringkat
- Production Planning2Dokumen16 halamanProduction Planning2amity_acelBelum ada peringkat
- Om - Unit-Iv - PG IiDokumen99 halamanOm - Unit-Iv - PG IiaashutoshBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To PPICDokumen16 halamanIntroduction To PPICTian Nur MBelum ada peringkat
- Lect 3Dokumen38 halamanLect 3shashikantppediaBelum ada peringkat
- Module 04Dokumen16 halamanModule 04SAMRUDA SADANANDBelum ada peringkat
- Production Planning and ControlDokumen21 halamanProduction Planning and Controlrajya lakshmiBelum ada peringkat
- Week 11 & 12 (MRP - Information Technology & SCM, ERP)Dokumen27 halamanWeek 11 & 12 (MRP - Information Technology & SCM, ERP)HAMNA SYEDBelum ada peringkat
- Note Pdtmog - Operations Management Chapter 4Dokumen46 halamanNote Pdtmog - Operations Management Chapter 4muneergaming jaibBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 3 - Capacity PlanningDokumen18 halamanLesson 3 - Capacity Planningvycenapaula2004Belum ada peringkat
- Planning and Control of OperationsDokumen45 halamanPlanning and Control of Operationsanvita raoBelum ada peringkat
- Manufacturing Planning & SchedulingDokumen44 halamanManufacturing Planning & Schedulingbuntymth05Belum ada peringkat
- Week 11 & 12 (MRP - Information Technology & SCM, ERP)Dokumen27 halamanWeek 11 & 12 (MRP - Information Technology & SCM, ERP)HAMNA SYEDBelum ada peringkat
- Chap 6 - Resource Planning Systems PDFDokumen25 halamanChap 6 - Resource Planning Systems PDFNhi HoàiBelum ada peringkat
- Perencanaan Dan Pengendalian Produksi: Master Production SchedulingDokumen13 halamanPerencanaan Dan Pengendalian Produksi: Master Production SchedulinguddindjmBelum ada peringkat
- Unit IIIDokumen22 halamanUnit IIIdangerous saifBelum ada peringkat
- Sistemas de ProduccionDokumen114 halamanSistemas de ProduccionJA C FBelum ada peringkat
- Module 2: ERP Manufacturing Perspective: by Mrs. Shital H. MoreDokumen54 halamanModule 2: ERP Manufacturing Perspective: by Mrs. Shital H. MoreThamaraiselvi.M grdcs SCIBBelum ada peringkat
- Om Group Assignment 1Dokumen11 halamanOm Group Assignment 1motibtBelum ada peringkat
- Master Production ScheduleDokumen30 halamanMaster Production ScheduleRoland KouameBelum ada peringkat
- Aggregate Planning and Master Production Scheduling (MPS)Dokumen22 halamanAggregate Planning and Master Production Scheduling (MPS)Shveta HastirBelum ada peringkat
- Storage LocationsDokumen2 halamanStorage LocationsK Raghunatha ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- ME 4050 Lecture 11 MRP1-2 and ERPDokumen24 halamanME 4050 Lecture 11 MRP1-2 and ERPK ROHITH SINGH me12b031Belum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3. Sales & Operations Aggregate) PlanningDokumen47 halamanChapter 3. Sales & Operations Aggregate) PlanningsanjaykhatwaniBelum ada peringkat
- SCM-Module-5-Resource Planning - MRP 1 & IIDokumen24 halamanSCM-Module-5-Resource Planning - MRP 1 & IIMuhammed Husain MusaniBelum ada peringkat
- Production Planning & ControlDokumen44 halamanProduction Planning & ControlavgadekarBelum ada peringkat
- Production Planning: It's Meaning and Objectives!Dokumen52 halamanProduction Planning: It's Meaning and Objectives!Gautam KocherBelum ada peringkat
- Material Requirements Planning (MRP) I: Presented by Muhammad Imran Basseri & Muhammad Syafiq MazlanDokumen17 halamanMaterial Requirements Planning (MRP) I: Presented by Muhammad Imran Basseri & Muhammad Syafiq MazlanSyafiq MazlanBelum ada peringkat
- UntitledDokumen112 halamanUntitledvijayBelum ada peringkat
- TutorDokumen6 halamanTutorFitRi EzeryBelum ada peringkat
- Good TreeDokumen1 halamanGood TreeFitRi EzeryBelum ada peringkat
- Business Model CanvasDokumen19 halamanBusiness Model CanvasFitRi EzeryBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 PDFDokumen27 halamanChapter 3 PDFFitRi EzeryBelum ada peringkat
- Importance of Project Management in ConstructionDokumen10 halamanImportance of Project Management in ConstructionNicole SantillanBelum ada peringkat
- Baspelancongan 30 Jun 2015Dokumen1.400 halamanBaspelancongan 30 Jun 2015Mohd Shahlan Sidi AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- Test Bank For Financial Reporting and Analysis 13th Edition Charles H GibsonDokumen36 halamanTest Bank For Financial Reporting and Analysis 13th Edition Charles H Gibsonbdelliumtiliairwoct100% (42)
- Case StudyDokumen4 halamanCase Studychandu1113Belum ada peringkat
- Share Holders Right To Participate in The Management of The CompanyDokumen3 halamanShare Holders Right To Participate in The Management of The CompanyVishnu PathakBelum ada peringkat
- Helmet Jan19 PDFDokumen31 halamanHelmet Jan19 PDFLokeshBelum ada peringkat
- River Eye Fashion CompanyDokumen11 halamanRiver Eye Fashion Companyriver eyeBelum ada peringkat
- Problem Set 2Dokumen2 halamanProblem Set 2Rubab MirzaBelum ada peringkat
- InvoiceDokumen1 halamanInvoicetanya.prasadBelum ada peringkat
- DNV GL enDokumen2 halamanDNV GL enSreegith ChelattBelum ada peringkat
- NAFTA Verification and Audit ManualDokumen316 halamanNAFTA Verification and Audit Manualbiharris22Belum ada peringkat
- Hypothesis Testing For A Single PopulationDokumen37 halamanHypothesis Testing For A Single PopulationAna Salud LimBelum ada peringkat
- Huaman Repite PlatoDokumen2 halamanHuaman Repite PlatoNkma CzrBelum ada peringkat
- The 3CDokumen4 halamanThe 3CPankaj KumarBelum ada peringkat
- B2B E-Marketplace Adoption in Agriculture: Zheng XiaopingDokumen8 halamanB2B E-Marketplace Adoption in Agriculture: Zheng XiaopingNikhil MalhotraBelum ada peringkat
- Entry Modes AnalysisDokumen24 halamanEntry Modes AnalysisShona JainBelum ada peringkat
- Godown Creation in Tally 9 Tutorial Youtube PDFDokumen3 halamanGodown Creation in Tally 9 Tutorial Youtube PDFKristinBelum ada peringkat
- EXPORTDokumen99 halamanEXPORTdhruv81275Belum ada peringkat
- World Airports Freighters: FreighDokumen16 halamanWorld Airports Freighters: FreighBobbie KhunthongchanBelum ada peringkat
- Significance of Cross Elasticity of DemandDokumen4 halamanSignificance of Cross Elasticity of Demandvijay vijBelum ada peringkat
- Braytron Catalogue 2019 PDFDokumen174 halamanBraytron Catalogue 2019 PDFLiviu Cioroianu0% (1)
- Midsemester Practice QuestionsDokumen6 halamanMidsemester Practice Questionsoshane126Belum ada peringkat
- Fuzzy AHPDokumen17 halamanFuzzy AHPmsdpardisBelum ada peringkat
- DO Section 5-6Dokumen46 halamanDO Section 5-6Gianita SimatupangBelum ada peringkat











![Practical Guide To Production Planning & Control [Revised Edition]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/235162742/149x198/2a816df8c8/1709920378?v=1)