Clase Endrino Skincare
Diunggah oleh
Juan AvonHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Clase Endrino Skincare
Diunggah oleh
Juan AvonHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
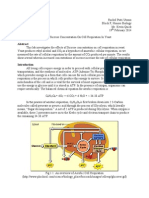
La glandula pituitaria fabrica 7 hormona.
- The pituitary gland is composed of ty=wo (2) different parts: Anterior lobe and posterior
lobe.
- Both are very different; sometimes we considerer that they are 2 different and
independent glands.
- The anterior lobe of Pituitary gland produce 7 main types of hormones. Some of them
are “TROPIC HORMONES” which stimulate other endocrine glands.
- It is not rare to refer to the “ANTERIOR LOBE” as the “MASTER GLAND” because its
hormones control the activities of the thyroids, adrenal cortex, ovaries and testes
glands, and in addition, regulates the growth of the entire body and performs others
important body’s functions.
Growth Hormone:
- Controls general body growth causing body cells to grown. It increments glucose
concentration in blood.
- Secretion of GH does not vary from childhood to adulthood and can be increased or
decreased within minutes in relation to the client’s nutrition status.
- Prolactin: Stimulates breast development during pregnancy and milk secretion of
childbirth.
MELANOCYTES STIMULATING HORMONE: MSH
- Acts on the skin pigmentation, especially after exposure to the sunlight, stimulation
synthesis and dispersion of melanin pigment on the skin.
THYROID STIMULATION HORMONE: TSH (Tropic Hormone)
- Stimulates the thyroid gland to increase secretion of thyroid hormones, which regulate
the body’s metabolism.
ADRENOCORTICOTROPIC HORMONE: ACTH (Tropic Hormone)
- Stimulates the Adrenal Cortex to increase in size and to secrete larger amounts of its
hormones.
FOLLICLE STIMULATING HORMOES: FSH (Tropic Hormone)
- (F) Stimulates ovaries to convert androgen to estrogen. (M) Stimulates testes to grow
and produce sperm.
LUTEINIZING HORMONE: LH (Tropic Hormone- pq estimula otras hormonas del Sistema
endocrino)
- (F) Increased LH secretion results in ovarian hyperactivity thus hyperandrogenism and
the development of hirsutism.
- (M) Stimulates testes to produce testosterone (es el androgeno mas fuerte)
Posterior lobe: Is an hypothalamus’s extension. Contains terminal ends of axons whose cells lie
within hypothalamus. This gland stores and deliveries two (2) hormones which are produced by
the hypothalamic neurons.
- OXYTOCIN: Stimulates uterus contradiction of the pregnant and is believed to initiate
and help maintain labor.
- ADH: Antidiurectic Hormone or Vasopressin: Prevents excessive urine production. ADH
in high concentration has a very potent effect of constricting arteries and increasing
blood pressure. (Ej de su excrecion, es cuando el cuerpo necesita hacer una hemostasia
por Perdida sanguinea para reestablecer la Perdida de presion y sangre)
THYROID GLAND: located in the neck secretes the following types of hormone:
- TRIIODOTYRONINE (T3): Contains 3 atoms of iodine (I) and
- THYROXINE (T4): Contains 4 atoms of Iodine.
T3 y T4 are known as thyroid hormones which have the main function of control the rate of
the all body cells metabolism.
- IODINE: is an essential element that enables the thyroid to produce thyroid hormones.
Especial cells of the thyroid gland, called C-cells, produce another hormone calcitonin, with
reduces the calcium level in the blood when it be too high.
THE PARATHYROID GLANDS
- Are 4 small glands embedded in the posterior of the thyroid gland, 2 on each lobe which
produce Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) or Parathotmone.
- Plays a role in the regulation of calcium levels in the blood. Precise calcium levels are
important in the human body, since small deviations can cause muscle and nerve
deterioration.
- The PTH increases blood calcium level when it be too low.
THE ADRENAL (SUPRARENAL) GLAND:
- Are situated atop each kidney. Composed of the: Medulla and Cortex wich are so
different that often are considered 2 independent glands.
- The ADRENAL MEDULLA is called “The emergency gland”. It performs sympathetic
system’s similar functions.
- The ADRENAL MEDULLA together witch the sympathetic nervous system, control the
blood circulatory system.
- It produces, stores and delivers Epinephrine (Adrenaline – estimula la circulacion de la
sangre en gran medida).
- Adrenaline: is vital to prepare the way for a quick action in case of sudden dangers and
emergencies, prepare the body to fight and flight (pelear y volar). It is a neurohormone.
THE ADRENAL CORTEX:
- Is the outer portion of the adrenal gland and secretes three different types of hormones
called Steroids which are synthesized from cholesterol. They are: -Mineralocorticoids. –
Glucocorticoids and – Sex hormones.
o Mineralocorticoides: Regulate concentration of electrolytes as sodium (NA) and
potassium (K), and – Maintain suitable volume of water in the body. (Main
hormones: Aldosterone – controla el potasio).
o Glucocorticoids: Increase glucose-level in the blood (If stress), - Reduce
inflammation within the body, and – Inhibit allergic responses. (Main hormones:
Cortisone or cortisol).
o Sex Hormones: For both sexes they are a source of estrogen (F hormone) and
androgens (M hormone). The proportion of these hormones determines the
individual’s secondary……….
THE PANCREAS:
- Who is located behind the stomach is a gland organ in the digestive and endocrine
system. Contain the scattered Islets of Langerhans which are microscopic groups of
alpha cells which secrete glucagon and beta cells which secrete insulin. Both the use and
storage of glucose.
- INSULIN is the only hormone that can decrease blood glucose concentation, while: -
Glucagon, - Growth Hormone, and – Cortisone increase it. (Together maintain an
adequate blood glucose level).
Ovaries secrete 2 types of F hormones and 1 type of M hormone:
- ESTROGEN: Primary female sex hormone.
o Female secondary sex characteristics
o Stimulates menstruation and ovulation.
- PROGESTERONE: female sex hormone
o Prepares female body for pregnancy
- ANDROGEN: Male sex hormone in minor quantity.
The testes are located within the scrotum and secrete:
- TESTOSTERONE: the stronges type of androgen, and
- ESTROGEN: in minor cantidad
- ANDROGEN: Circulate in the bloodstream bound mostly to SHBG (Sex Hormone-Binding
Globulin). Only a small fraction is “free”, and is able to activate the cells of the hair
follicle. If concentration of free androgen change, hair pattern change.
Intersticial cells in the testes secrete the male sex hormone called testosterone directly into
the blood. These cells of the testes are therefore the male endocrine glands.
CELULAS DE LEYDIN
- Testosterone production increases rapidly at age 11 – 13 and last throughout the
remainder of adult life.
- Testosterone increases body hair over the pubic region, face, chest, back and in other
places of the body.
- Testosterone decreases the growth of hair on the top of the head. A man who does not
have functioning testes does not usually become bald.
- Testosterone increases the thickness and robustness of the skin over the entire body
and increases the rate of secretion of the sebaceous glands, which may result in acne.
Therefore acne is a common problem in adolescence.
PINEAL GLAND
- Lies at the exact center of the brain which it is associated.
- The pineal gland produces a number of hormones in very small quantities, with
melatonin being the most significant.
- Melatonin: Inhibits the hormones that affect the ovaries (FSH and Lh). Melatonin levels
increase during the day, therefore it helps to regulate the sleep cycles and theses
variations is thourght to be an important timekeeping mechanism for the body’s
internal clock.
The thymus Gland
- Is located atop the heart. This gland plays a critical part in the body’s defendense against
infections, it is composed largely of lymphocytes (white blood cells).
- The homone thymosin has been isolated from thymus tissue and is actually a group of
several hormones that together play an important role in the development and function
of the body’s immune system.
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM DISORDERS
Hyposecretion, Hypersecretion and Abnormal responsiveness from target cells leads to
abnormal concentration of hormones in the blood stream, which may leads to: -health
disorders, - endocrine system imbalances or to, exccesive hair groeth.
(**insulina distribui la glucose en la sangre)
- Glands disorders, hormonal disturbances or endocrine system imbalances are linked to
excessive hair growth.
DISEADE INVOLVING GROWN HORMONE (GH)
- Dwarfism: Patient of age 20 may look like age 7 years. This is caused by under secretion
of growth hormone.
- Gigantism (Symmetric Acromegaly): Caused by over secretion of GH before puberty.
Patients grow to be 8-9 feet tall.
- Acromegaly: (Asymmetric Acromegaly): Caused by over secretion of GH after puberty.
Bones grown in width, not legth. Big hands, feet, face and spine.
Disease involving THYROXINE (T4)
- Hypothyroidism: occurs when the thyroid does not make enough T4. This causes many
of the body’s functions to slow down.
- Most common causes of hypothyroidism: - Deficient intake of iodine (Goiter) and, Low
levels of TSH (no goiter).
- GOITER: is an abnormally enlarged thyroid gland, present in hypothyroidism &
hyperthyroidism resulted from deficiency or excess of iodine in the diet.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Effects of Sucrose Concentration On Cell Respiration in YeastDokumen7 halamanEffects of Sucrose Concentration On Cell Respiration in YeastRachel Utomo83% (23)
- Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 21 The Sensory SystemDokumen34 halamanAnatomy and Physiology Chapter 21 The Sensory SystemThanh Nguyen VanBelum ada peringkat
- List of Personnel Benefits Granted by The SchoolDokumen8 halamanList of Personnel Benefits Granted by The SchoolAspci Assumption Passi100% (1)
- Load Summary for Premise Under 100kVADokumen2 halamanLoad Summary for Premise Under 100kVAMuhammad Zulhelmi ZawawiBelum ada peringkat
- 16 Point Msds Format As Per ISO-DIS11014 PDFDokumen8 halaman16 Point Msds Format As Per ISO-DIS11014 PDFAntony JebarajBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of Hormonal Control SystemDokumen25 halamanPrinciples of Hormonal Control SystemFAHEEM UD DINBelum ada peringkat
- The Endocrine System: Glands and Hormones that Regulate the BodyDokumen27 halamanThe Endocrine System: Glands and Hormones that Regulate the Bodydaphnereeze100% (1)
- Chapter 2Dokumen8 halamanChapter 2melanielampera17Belum ada peringkat
- Sistem Endokrin: Oleh: Dr. Siska Anggreni Lubis, SPKKDokumen25 halamanSistem Endokrin: Oleh: Dr. Siska Anggreni Lubis, SPKKRichas Interisti SumatraBelum ada peringkat
- Behavioural Neuro ScienceDokumen8 halamanBehavioural Neuro ScienceFaisal AwanBelum ada peringkat
- Pa Tho Physiology of SepsisDokumen5 halamanPa Tho Physiology of SepsisMikee Ann ValdezBelum ada peringkat
- Control Our Bodies Homeostasis via Endocrine GlandsDokumen20 halamanControl Our Bodies Homeostasis via Endocrine GlandsJohn Philip VerastigueBelum ada peringkat
- Secretion From The Pineal GlandDokumen8 halamanSecretion From The Pineal GlandVince Laurence BlancaflorBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine System: Almahsud I. Juhassan Shawn Michael M. AwidDokumen13 halamanEndocrine System: Almahsud I. Juhassan Shawn Michael M. AwidAMEER HANAFI JIKIRI. JUL-ASRIBelum ada peringkat
- Illustration of The Endocrine SystemDokumen7 halamanIllustration of The Endocrine SystemMohammed MohammedBelum ada peringkat
- Role of Hormones Endocrine 1Dokumen37 halamanRole of Hormones Endocrine 1zyrle (zayrieeo)Belum ada peringkat
- ENDOCRINE systems ad its disordersDokumen21 halamanENDOCRINE systems ad its disordersAmir PermitivoBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDokumen9 halamanChemical Coordination and IntegrationAjay JamwalBelum ada peringkat
- Bio Psycho HORMONESDokumen24 halamanBio Psycho HORMONESKhel VincentBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine SystemDokumen19 halamanEndocrine Systemethel roseBelum ada peringkat
- The Endocrine System: Regulating Bodily Functions Through HormonesDokumen41 halamanThe Endocrine System: Regulating Bodily Functions Through HormonesAtteya Mogote AbdullahBelum ada peringkat
- Worksheet 1, AnaphyDokumen3 halamanWorksheet 1, AnaphycelynjasminegBelum ada peringkat
- Exp 03Dokumen5 halamanExp 03NaitikBelum ada peringkat
- BioSci LO#2Dokumen16 halamanBioSci LO#2AudzkieBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine System March 5 - 8, 2024Dokumen61 halamanEndocrine System March 5 - 8, 2024Almira ZuñigaBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine GlandsDokumen4 halamanEndocrine GlandsEzeh PrincessBelum ada peringkat
- Dmma College of Southern Philippines Anatomy and Physiology of Endocrine SystemDokumen16 halamanDmma College of Southern Philippines Anatomy and Physiology of Endocrine SystemCandy Penpillo SaldiviaBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine SystemDokumen24 halamanEndocrine Systempromisefo65Belum ada peringkat
- The Endocrine System-JULYDokumen40 halamanThe Endocrine System-JULYKELVINBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine SystemDokumen5 halamanEndocrine SystemMelissa630100% (1)
- Hormones CompleteDokumen30 halamanHormones CompleteAqsa NoorBelum ada peringkat
- M3 Endocrine system. UpdatedDokumen33 halamanM3 Endocrine system. Updatedlalarela.cindyBelum ada peringkat
- Corticotropins and GonadotropinsDokumen39 halamanCorticotropins and GonadotropinsSudhakar LakavathBelum ada peringkat
- Control and Coordination Animal HormonesDokumen46 halamanControl and Coordination Animal HormonesgolaBelum ada peringkat
- The Endocrine System Overview/ Introduction: Nur112: Anatomy and Physiology ISU Echague - College of NursingDokumen6 halamanThe Endocrine System Overview/ Introduction: Nur112: Anatomy and Physiology ISU Echague - College of NursingWai KikiBelum ada peringkat
- Module 9 The Endocrine SystemDokumen15 halamanModule 9 The Endocrine SystemMisha WilliamsBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine Gland - WikipediaDokumen29 halamanEndocrine Gland - WikipediaSumaya FarheenBelum ada peringkat
- The Endocrine System Study Guide 101 PDFDokumen17 halamanThe Endocrine System Study Guide 101 PDFStephanie Kate PelenioBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 11 - HormonesDokumen8 halamanChapter 11 - Hormonesbussniesm05Belum ada peringkat
- EndocrinologyDokumen23 halamanEndocrinologysaikat55Belum ada peringkat
- Endocrine SystemDokumen10 halamanEndocrine SystemSujatha AluguriBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy & Physiology of Endocrine SystemDokumen34 halamanAnatomy & Physiology of Endocrine SystemUzma Khan100% (1)
- Chemical CoordinationDokumen29 halamanChemical Coordinationjackieaj093100% (1)
- Endocrineglands 140817003157 Phpapp01Dokumen61 halamanEndocrineglands 140817003157 Phpapp01Musfira KhalidBelum ada peringkat
- Functions of The Endocrine System: EquilibriumDokumen20 halamanFunctions of The Endocrine System: EquilibriumKumah WisdomBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine System: Adesanya O.A Department of Anatomy Kampala International University, TanzaniaDokumen29 halamanEndocrine System: Adesanya O.A Department of Anatomy Kampala International University, TanzaniaAnnette MhenggaBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Physiology - Endocrine SystemDokumen8 halamanAnatomy and Physiology - Endocrine Systemcn351073Belum ada peringkat
- 10SUMMARYENDOCRINESYSTEMDokumen14 halaman10SUMMARYENDOCRINESYSTEMArvenBitasBelum ada peringkat
- Psychology - Endocrine Glands (SEM - 2 - CC-6)Dokumen7 halamanPsychology - Endocrine Glands (SEM - 2 - CC-6)Srinivasu ChintalaBelum ada peringkat
- Compiled by Howie BaumDokumen40 halamanCompiled by Howie BaumMaría José Castellanos GutiérrezBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine System and Endocrine GlandsDokumen7 halamanEndocrine System and Endocrine GlandsMr.VivStarBelum ada peringkat
- The Structure and Function of Central and Peripheral HormonDokumen34 halamanThe Structure and Function of Central and Peripheral HormonrichardiaBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine System: The Body's Chemical MessengersDokumen27 halamanEndocrine System: The Body's Chemical MessengersJustinn DukessaBelum ada peringkat
- HormonesDokumen29 halamanHormonesCandy Chieng67% (3)
- CBSE Class-11 Biology Chapter-22 Chemical Coordination and Integration NotesDokumen6 halamanCBSE Class-11 Biology Chapter-22 Chemical Coordination and Integration NotesAarav VarshneyBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine SystemDokumen11 halamanEndocrine SystemSarthak AgarwalBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine System Anatomy and PhysiologyDokumen17 halamanEndocrine System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBD0% (1)
- Nervous System ReportDokumen5 halamanNervous System ReportsharkBelum ada peringkat
- Hormones Are Chemical Substances Synthesized From Amino Acids and Cholesterol That Act OnDokumen19 halamanHormones Are Chemical Substances Synthesized From Amino Acids and Cholesterol That Act OnJasminKate SutacioBelum ada peringkat
- Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland Control Endocrine SystemDokumen13 halamanHypothalamus and Pituitary Gland Control Endocrine SystemUmer Shahzad ANSERBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine System Sem2Dokumen14 halamanEndocrine System Sem2chandraboli majumdarBelum ada peringkat
- Thyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedDari EverandThyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (2)
- Balancing Hormones Naturally: A Woman's Guide to Hormonal Harmony: HealthDari EverandBalancing Hormones Naturally: A Woman's Guide to Hormonal Harmony: HealthBelum ada peringkat
- Thyroid Diet : Thyroid Solution Diet & Natural Treatment Book For Thyroid Problems & Hypothyroidism Revealed!Dari EverandThyroid Diet : Thyroid Solution Diet & Natural Treatment Book For Thyroid Problems & Hypothyroidism Revealed!Penilaian: 1 dari 5 bintang1/5 (1)
- New Facility or New Ownership ApplicationDokumen13 halamanNew Facility or New Ownership ApplicationJuan AvonBelum ada peringkat
- 5 Use of Long Pulse ND Yag 1064 NM Laser For Treatment of Rosacea TelangiectaticaDokumen4 halaman5 Use of Long Pulse ND Yag 1064 NM Laser For Treatment of Rosacea TelangiectaticaJuan AvonBelum ada peringkat
- 5 Use of Long Pulse ND Yag 1064 NM Laser For Treatment of Rosacea TelangiectaticaDokumen4 halaman5 Use of Long Pulse ND Yag 1064 NM Laser For Treatment of Rosacea TelangiectaticaJuan AvonBelum ada peringkat
- Clase Endrino SkincareDokumen5 halamanClase Endrino SkincareJuan AvonBelum ada peringkat
- Consent Mesotherapy LipodissolveDokumen2 halamanConsent Mesotherapy LipodissolveJuan AvonBelum ada peringkat
- Skin Care AdvancedDokumen5 halamanSkin Care AdvancedJuan AvonBelum ada peringkat
- Yoga Nidra MethodDokumen13 halamanYoga Nidra MethodPrahlad Basnet100% (2)
- MSDS - ENTEL BatteryDokumen3 halamanMSDS - ENTEL BatteryChengBelum ada peringkat
- CN LSHC The Future of Pharmacy en 031120Dokumen8 halamanCN LSHC The Future of Pharmacy en 031120marina_netBelum ada peringkat
- Pvpsit Department of Mechanical Engineering PVP19Dokumen2 halamanPvpsit Department of Mechanical Engineering PVP19Satya NarayanaBelum ada peringkat
- Plant and Animal Cells Crossword Puzzle: FreebieDokumen5 halamanPlant and Animal Cells Crossword Puzzle: FreebieAref DahabrahBelum ada peringkat
- Asian Organized CrimeDokumen17 halamanAsian Organized CrimeMagr EscaBelum ada peringkat
- Two-day workshop budgetDokumen2 halamanTwo-day workshop budgetVishwanath BaliBelum ada peringkat
- Manual Murray 20Dokumen28 halamanManual Murray 20freebanker777741Belum ada peringkat
- Akron Grad School Statement of Purpose PDFDokumen2 halamanAkron Grad School Statement of Purpose PDFapi-406039291Belum ada peringkat
- Refrigerant Color Code ChartDokumen11 halamanRefrigerant Color Code ChartJeffcaster ComelBelum ada peringkat
- State-of-the-Art Reactor Consequence Analyses (SOARCA) ReportDokumen200 halamanState-of-the-Art Reactor Consequence Analyses (SOARCA) ReportKingba OlayemiBelum ada peringkat
- Assessments and Rubrics For Unit 2Dokumen13 halamanAssessments and Rubrics For Unit 2api-302258576Belum ada peringkat
- Respiration PHYSIODokumen23 halamanRespiration PHYSIOTauseef AfridiBelum ada peringkat
- Barangay Peace and Order and Public Safety Plan Bpops Annex ADokumen3 halamanBarangay Peace and Order and Public Safety Plan Bpops Annex AImee CorreaBelum ada peringkat
- EfAD BenchmarkJune2005 UKDokumen55 halamanEfAD BenchmarkJune2005 UKCristina Dobrin ClaudiaBelum ada peringkat
- SinogramDokumen2 halamanSinogramNguyễn Thành CôngBelum ada peringkat
- Prof Educ 2: Foundation of Special and Inclusive EducationDokumen12 halamanProf Educ 2: Foundation of Special and Inclusive EducationNerissa Custosa BastoBelum ada peringkat
- Tracking SARDO StudentsDokumen2 halamanTracking SARDO StudentsLean ABBelum ada peringkat
- Bhima Devi Poudel Adhikari Year 2 Assignment 1 - 220179000Dokumen10 halamanBhima Devi Poudel Adhikari Year 2 Assignment 1 - 220179000api-525310113Belum ada peringkat
- Port Works Design Manual Part 2 PDFDokumen124 halamanPort Works Design Manual Part 2 PDFhessian123Belum ada peringkat
- HIV Lecture For C I 2006Dokumen181 halamanHIV Lecture For C I 2006Ruth DanielBelum ada peringkat
- CALIS ScoringDokumen2 halamanCALIS ScoringIqbal BaryarBelum ada peringkat
- Colours of the RainbowDokumen16 halamanColours of the RainbowMd A RAZZAKBelum ada peringkat
- Transpo Printable Lecture4Dokumen10 halamanTranspo Printable Lecture4Jabin Sta. TeresaBelum ada peringkat
- Greek God and Goddess ListDokumen3 halamanGreek God and Goddess Listapi-359276609Belum ada peringkat
- Rexnord Thomas Flexible Disc Couplings - Series 71 - 8Dokumen2 halamanRexnord Thomas Flexible Disc Couplings - Series 71 - 8Orlando ReisBelum ada peringkat