ICT Blueprint For Change 2010 V June 2010
Diunggah oleh
TDOttawaDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
ICT Blueprint For Change 2010 V June 2010
Diunggah oleh
TDOttawaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Information Technology Solutions
Towards 2020
Connecting with our Students
VISION
Our vision is one where all staff and students in the Ottawa Catholic School
Board have the skills they need to excel in the 21st century. We will achieve
st
21 Century
Teaching student success by meeting the diverse needs of 21st century learners.
Learning
The Need for Change
Today’s students are different from the students that our system was created to educate.
The new digital learners are immersed in technology and they expect to use
digital tools as part of their educational experience. Brain based research
“As we enter the new
age, the future won’t
provides evidence that today’s generation of students are “wired” differently
just happen. It will than previous generations. Instructional strategies are evolving to reflect the
be created – and needs of 21st century learners. The question we need to ask is not about
primarily by them.” what equipment to purchase or install, but rather what skills do our students
need to succeed. The class of 2020 is currently sitting in our grade 2
Don Tapscott
classrooms (in 2010). These “Lucky 2’s” will graduate from a learning
“Grown Up Digital”
environment and culture that espouses 21st century skill sets and tools.
In order to create a learning environment that engages our students we are in the process
of: updating our infrastructure, introducing new tools, creating professional digital learning
communities, building leadership capacity, and removing procedural barriers (see
appendix one for a list of information technology initiatives).
Information Communication Technology (ICT) Tipping Point
Technology is now reaching the point where it is available almost
everywhere. The cost of technology is rapidly decreasing while the
processing power is increasing. Convergence between a variety of
devices and the Internet is becoming common place. In 2008 the
Media Technology Monitor (MTM) survey examined the media habits
and technology usage of Canadians. The survey found that household
penetration of broadband services continues to grow year after year.
Toward 2020 – Information Technology Blueprint for Change Page 1
The significance for our schools is that more and more students have access to rich media
resources when they are outside of school. Weekly Internet usage by
Canadians has tripled since 2007. According to Internet World Stats,
There are over 300 there were 361 million Internet users in the year 2000; there are now
million searches on over 1.7 billion users accessing over 1 trillion unique URLs.
Google every day!
There are over 300 million searches on Google every day! Over 100
million YouTube videos are watched daily. According to the Social
Media Guide, there are over 247 billion emails sent per day. Blog
Pulse indicates that there are over 126 million blogs available on the Internet. There are
over 37.4 trillion page views on Facebook each year. Over 320 million cell phones were
sold world-wide in the last 3 months of 2009.The increasing prevalence of Smart Phones
is creating opportunities for learning both in and out of school. The iPhone came out in
2007. After just 3 years, there are now over 100,000 apps available, many of them
educational, and many of them free.
Implication
Ubiquitous access to technology cannot (and should not) be stopped. OCSB staff need to
be prepared to leverage technology to engage students and increase student success.
Leaders in the OCSB need to model the use of new technologies and their positive
benefits to both staff and students.
Core Priorities
Technology within the Ottawa Catholic School Board will be viewed as
a tool to support research based instructional strategies. The core
Success for Students priorities of student success, success for staff, and stewardship of
Success for Staff resources, within a Catholic framework will be enhanced by digital
Stewardship of learning opportunities.
Resources
Implication
Interdepartmental relationships and communication are essential to
ensure that stewardship of resources is being achieved. Initiatives that are not supporting
our Board core priorities should be challenged and resources allocated to other areas.
Departmental budgets should include provisions to prioritize 21st century teaching and
learning. The provision of an infrastructure and tools will not result in improved student
success without the alignment of curriculum resources, instructional practices, and
professional learning.
Toward 2020 – Information Technology Blueprint for Change Page 2
Governance
Several Board policies and procedures may have unintentionally restricted students and
staff from accessing digital resources over our secure network (for example, blocking
teacher access to You Tube).
The OCSB will strive to find a balance between safety/security and access to resources.
Procedures will be created that will be flexible in nature to allow for changing technologies
to be readily implemented within the system.
Implication
A new Board policy will be released to clarify how staff can use emerging technologies
such as social media for instructional purposes. The implementation of a wireless
environment throughout the Board will coincide with school practices that allow student
use of devices to connect to the Internet for academic purposes. Teachers will be
encouraged to teach students the appropriate use of social media and safe online activity.
Restrictions blocking teacher access to the Internet will be relaxed with more emphasis on
classroom management. Staff will have more flexibility in bringing Board devices home to
continue their learning by accessing just-in-time online learning modules.
Capacity Building and Teacher Preparation
The new generation of teachers will enter our system with an
Simply inserting understanding of the required changes in instructional practice in order
technology into to relate to today’s digital learners. Problem solving, or discovery
classrooms and learning, with the teacher facilitating individualized student learning will
schools without continued to be emphasized. Differentiated instruction through the use
considering how the
of a variety of technologies and tools should be a standard component
contexts for learning
need to change, will of all teacher preparation programs.
likely fail.
OCSB leaders from all generations need to model the effective use of
Allan Collins
information technology skills with the goal of achieving student
success.
Implication
Board staff will continue to contribute to provincial dialogue around the re-design of
teacher education programs, principal qualification programs, and supervisory officer
qualification programs. A focus on 21st century learning and teaching skills should
become embedded as tools for achieving student and staff success.
Toward 2020 – Information Technology Blueprint for Change Page 3
Standards of basic technology competency should be shared with teachers and
administrators. These standards can then be used as objectives within personal learning
plans.
The OCSB Journey to Leadership program should include technological competencies
that promote the use of digital tools for learning opportunities. Central staff will continue to
use digital tools as a means of modeling to other leaders in the system.
The Catholic Leadership Framework provides a reference for Vice-Principals, Principals,
and Supervisory Officers to set direction and priorities. These leaders should receive
support and training in the use of digital tools to ensure that they can model 21st century
skills.
Devices and Applications
The focus should not be on any particular device or application. Teachers and students
will focus on transferable skill sets as opposed to skills related to
... powerful software learning a particular application.
and hardware often
get used in limited Software and computer devices will continue to change at a rapid
ways to simply
maintain rather than
pace. The OCSB infrastructure should be flexible enough to leverage
transform prevailing advances in technology.
instructional practices
Clayton Christensen
As a starting point, teachers and students need access to a wireless
environment with high speed bandwidth. Teachers should have a
laptop or other device that will allow them to personalize their learning
and instruction. Teachers and students should have access to an
LCD projector and an interactive whiteboard for display and engagement purposes.
Other devices for student and staff access such as netbooks, document cameras,
response systems, voice amplification systems, tablets, iPods, iPads, etc. may
supplement core resources. The continued differentiation of instructional practice should
supplement the use of these resources in order to maximize the impact on student
learning.
Implication
The OCSB infrastructure should be in place in order to leverage the digital resources that
are available to students. This includes a balance between textbooks and digital
resources once access and reliable connectivity is no longer an issue.
Toward 2020 – Information Technology Blueprint for Change Page 4
Learning Environment
The traditional classroom will continue to adapt as the main learning environment for most
students; however, digital tools of the day should expand the learning
Perhaps above all other environment to a more global perspective. Within the changing
aspects of Web classroom, students will participate in learning activities through a
utilization, the power variety of medium. Students will learn the skills to work with partners
of choice is what sets who may not be physically present in the traditional classroom.
the Web of Learning
apart from other forms
of learning. Where possible (recognizing Ministry guidelines), time constraints should
be removed from traditional credit based instruction at the high school
Curtis J. Bonk level. The amount of time that a student should spend in any one
class or required to complete a “course” should change.
Differentiated instruction and individualized learning should lead to anytime learning.
Students should have access to the resources they need in order to meet content
expectations as opposed to timeline expectations. Students should have input into the
speed and pace of their own learning.
Students should have increased choice in the instructional model that best suits their
learning style. Options should include: face to face learning, hybrid or blended learning
opportunities that combine online learning and face to face learning, and virtual learning.
Implication
The Board will develop a secure and stable online learning portal for staff and student
access. The online learning portal shall serve as an object repository that allows the
sharing of resources. The selected platform should be easy for staff to use and flexible
enough to allow for varied levels of staff use (example, virtual learning, blended learning,
credit recovery).
Instructional Practices - Higher Order Thinking Skills
Teachers are changing from a focus on providing facts to a new focus on higher order
thinking skills. Assessment strategies that focus on memorization and recall are
changing to new assessment strategies that focus on higher order thinking skills such as
evaluating and creating. Electronic response systems are being used to provide
immediate feedback and to inform instruction. Student use of digital tools such as social
media will provide them with the opportunity to engage in higher order thinking skills.
There should be a cross-curricular focus on 21st century learning skills including:
communication and collaboration (both with students inside and out of the school),
creativity, problem solving, and critical thinking.
Toward 2020 – Information Technology Blueprint for Change Page 5
Higher Order Thinking Skills Teachers should continue to challenge
beliefs and strategies that have been
based on a left-brain (logical and
Creating analytical) society to one that
Evaluating recognizes and assesses right-brain
Analyzing
(creativity and problem solving)
activities. Bloom’s revised Taxonomy of
Applying Thinking Skills clearly demonstrates the
Understanding required evolution in instruction and
Remembering assessment.
Lower Order Thinking Skills Research indicates that digital learners
are not motivated by a teacher standing
at the front of a classroom lecturing and
requiring students to copy notes. Fortunately this practice is no longer the norm in the
Ottawa Catholic School Board. The majority of digital learners are visual learners who
are “wired” for video and audio engagement.
In an environment where information and facts are readily available, teachers have an
important role to play in helping students challenge, question, and create, based on the
myriad of information available to them.
Implication
OCSB staff should continue to support teachers as they transition away from traditional
skills to higher order thinking and 21st century learning skills. The introduction of the
technological tools without changes in instructional practice will not result in significant
gains in student achievement or engagement. The Student Success Department is
supporting teachers with resources to reflect revised curriculum. These resources
should continue to be aligned with 21st century teaching and learning skills (Information
media and technology skills, learning and innovation skills, life and career skills, core
subjects and 21st century themes).
http://www.21stcenturyskills.org/documents/P21_Framework.pdf
Toward 2020 – Information Technology Blueprint for Change Page 6
Catholicity
In an age where information is readily available, it has become increasingly important for
teachers to guide students towards value based judgments. Students and staff have the
ability to create and add to the wealth of
positive information available on the World
Wide Web.
The Catholic Graduate Expectations will have
an increasingly important place in the
preparation of our students. The Catholic
Graduate Expectations are inherently higher
order, focused on communication,
collaboration, creativity, and lifelong learning.
The OCSB is well positioned to play an
important role in developing comprehensive digital citizens. Safety within digital
environments, Cyberbullying prevention, and healthy relationships are all components of
the Religious and Family Life courses. Teachers will continue to create learning
activities that require students to apply value based judgments and to critically analyze
and validate facts and arguments.
Professional Development – Generation Gaps
As a Board, we need to recognize that the majority of decision makers come from those
who would be considered baby boomers and some who would be considered generation
X. The students that we serve are generation Y, generation Z, and those students who
were born in 2010 and later are being referred to as generation alpha. Our teaching
staff is comprised of individuals from a variety of generations. Job embedded training
and in-service opportunities should be differentiated for our staff in a manner similar to
the differentiated instruction that we provide to our students. Decision makers should
recognize the generational differences when making decisions.
A new phase of digital professional learning communities is being initiated to provide
just-in-time delivery to our new generation of teaching staff. The focus will shift away
from text based instruction and move to media rich environments where staff can refine
their instructional practices both in the classroom and in the new global classroom that
extends beyond traditional classroom walls.
Toward 2020 – Information Technology Blueprint for Change Page 7
It is important to recognize both traditional text based skills that many staff value and
the digital audio and video based skills that many of our students and
The Net Generation, the younger staff value. The achievement chart (Knowledge /
biggest ever, is coming of Understanding; Thinking / Inquiry; Communication, and; Application /
age. As they go to college Making Connections) can be used as a framework to provide a focus
and begin jobs, Net
as part of professional learning opportunities. The four areas of the
Geners are beginning to
use remarkable digital
achievement chart apply regardless of the selected medium.
tools that give individuals
the power that in the past Contrary to statements that we are preparing students for jobs that
was reserved for the don’t exist, we should recognize and validate that we are preparing
authorities. students for both jobs that do exist today and providing our students
with skills for jobs that are yet to be invented.
Don Tapscott
Implication
The OCSB should expand its current online delivery model to include opportunities for
staff to learn and develop 21st century skills. Staff should have opportunities to learn
digital skills that will assist them in engaging their students. Recognition of the varying
needs of different generations of teachers is important in providing a variety of learning
opportunities including just-in-time delivery of resources in rich media formats. The
development of personalized portals, anywhere access, combined with access to
digital devices will support success for staff.
Help desk tools will be developed and support will become available in a timely
manner. As digital tools become key components in achieving our Board core
priorities, it is important that the tools are maintained and supported so that staff can
focus on the instructional strategies and not on the technology.
Libraries and Equity of Access
Today a vast collection of resource materials is available online in a digital format. The
model of collecting information and securing it in a central location is changing.
Libraries will evolve into media centers. Media centers do not need to occupy the
same footprint as libraries. The media center will become a central gathering location
for students and staff to continue learning whether that is text based, or rich media
based. Access to online information and spaces for collaborative and creative work
should be central to the media center.
Toward 2020 – Information Technology Blueprint for Change Page 8
Traditional teacher librarians are refining their skills to become Cybrarians who are
adept at navigating the rich digital resources available on the Internet.
The librarian, or
Cybrarians will serve as digital literacy coaches to support staff and
Cybrarian, may students. Access to digital collections need to be extended beyond the
have the most to traditional school day. Ideally, evening and weekend access to digital
gain from this open tools should be made available in the media center to bridge the digital
learning world: divide for those who do not have the tools in their home.
witness e-books,
online portals, open Implication
access journals, and
online video to
Allowing students to bring their own devices to school will provide
accompany many increased access for those students who do not have their own device
publications. (example – if a class has access to 5 devices, and 10 students bring in
their own device, then the 5 school devices can be shared with those
Curtis J. Bonk who do not have their own).This synergy will provide good stewardship
of resources.
The Board practice of replacing devices needs to be supplemented with additional devices
being introduced into the system. The move to virtualization and web based applications
will allow less powerful and older devices to serve educational purposes.
Learning for all
Investments will be made in technology that provides students with curriculum
modification and accommodations for individualized or personalized learning. Following
the principles outlined in Learning for All, the use of information communication technology
will aim to be provided in an inclusive setting. Technologies that facilitate learning will be
made available to students in system classes. Language based applications will be used
to support ELL and ESL learners.
Implication
Interdepartmental cooperation will ensure that stewardship of resources is focused on
equality of opportunity for all students in our system. Resources should be allocated in
order to provide digital tools to assist with modifications and accommodations to meet
special needs in the system. Staff should stay current with research in the area of
assistive technologies to take advantage of advances in this area. Staff should receive
job embedded learning opportunities in order to provide support to language learners
including ELL and ESL learners.
Toward 2020 – Information Technology Blueprint for Change Page 9
Communication Technology
Parental involvement in education has proven to result in increased student success.
Emerging technologies may be used to supplement traditional communication tools.
Investments may be made to provide a communication channel that is differentiated for
each family (example, email, text message, voice message, etc.). New technologies
should also be used to offer messages in a variety of languages to respect our
increasingly diverse community. Technologies will be explored and used to improve
student safety and security.
Implication
Investments should be made to provide improved communication. The development of a
parental portal should complement the development of a teacher portal. Static website
delivery of information should evolve into interactive web 2.0 and 3.0 technologies along
with mobile access to school and Board information.
Business and Management Applications
New technologies are allowing for easier access to personal data such as payroll and
other human resources information. As access increases it is important that safeguards,
contingency planning, and disaster recovery plans are put in place. Privacy of personal
information must be maintained and communicated across the system.
The design of new learning spaces and schools should take into account current research
on 21st century learning. Introducing digital tools along with flexible learning spaces will
result in the greatest impact on student learning.
Implication
Staff should receive training on the proper storage and access to data.
Disaster recovery systems must be put into place as non-electronic means to accomplish
business tasks are eliminated. Electronic tools should be seen as mission critical as they
contribute to key priorities and, as such, should be kept online with minimal disruption.
Interdepartmental collaboration will contribute to the development of holistic and
comprehensive plans to ensure that each area of the Board is focusing on student
success regardless of job function.
Toward 2020 – Information Technology Blueprint for Change Page 10
Summary
The Ottawa Catholic School Board is a leading school Board in Ontario with a clear focus
on student and staff success. We will continue to innovate and adapt to reflect the
changing needs of 21st Century learners. We recognize that we are no longer preparing
students for the world that we grew up in; we are preparing them to be contributing digital
citizens in a new 21st Century environment.
21st century learning needs to move away from a focus on equipment and technology and
instead focus on our priorities: success for students, success for staff, and stewardship of
resources, all within a Catholic framework.
Digital tools and individualized learning paths will enable us to continue to be a successful
Catholic School Board. As we begin the second decade of the 21st Century we will
implement the necessary changes to ensure that our “Lucky 2’s” are well prepared to be
contributing digital citizens when they graduate in 2020.
Key Resources reviewed in the preparation of this discussion paper
21st Century Fluency Series: http://www.21stcenturyfluency.com
Teaching for Tomorrow, Attributes of Digital Learners, Getting it Right
Understanding Digital Kids I and II, Literacy is Not enough, Living on the Future Edge
International Society for Technology in Education (ISTE)
http://www.iste.org/AM/Template.cfm?Section=NETS
The Partnership for 21st Century Learning
http://www.21stcenturyskills.org/
Bonk, Curtis J.. The World Is Open: How Web Technology Is Revolutionizing Education. New York, NY:
Wiley, 2009. Print.
Christensen, Clayton M., Michael B. Horn, and Curtis W. Johnson. Disrupting Class: How Disruptive
Innovation Will Change the Way the World Learns. 1 ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2008.
Collins, Allan, and Richard Halverson. Rethinking Education in the Age of Technology: The Digital
Revolution and Schooling in America (Technology, Education--Connections (Tec)) (Technology,
Education-Connections the Tec Series). New York: Teachers College Press, 2009.
Tapscott, Don(Author). Grown Up Digital: How the Net Generation Is Changing Your World [GROWN
UP DIGITAL]. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2008.
Toward 2020 – Information Technology Blueprint for Change Page 11
Information Technology Solutions
Appendix One: IT Initiatives
Information Communication Technology
Our vision is one where all staff and students in the Ottawa
Catholic School Board have the skills they need to excel in
the 21st century. We will achieve student success by
meeting the diverse needs of 21st century learners.
VISION
21st Century The use of sound pedagogy combined with technology will create an alignment between 21st
century teaching and 21st century learning. In order to create a learning environment that
Teaching engages our students we are in the process of: updating our infrastructure, introducing new tools,
Learning creating professional learning communities, building capacity, and removing procedural barriers.
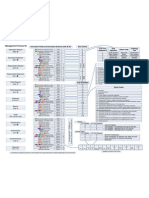
Snapshot of where we’re going…
Board Portal –– Increased Reliable
Wireless
increased bandwidth to network – core
learning
communications process rich switches,
environment at
with parents media storage,
all Board Sites
and between connections backups
staff
Increased
Board Portal Reliable Network Wireless
Bandwidth
eLearning – Creation of a Change in Decreased
Blended data warehouse policies and reliance on
Learning – all to allow all practice – allow computer labs
students users easy social media, and increased
exposed to access to a data and allow use of Internet
blended or dashboard student use of connected
online learning Smart Phones devices
Blended Learning Data Warehouse Remove Barriers Internet Devices
Re-tool our Build Capacity
Google Apps – classrooms - Improved
– job embedded efficiencies –
increased use of Interactive learning,
web based White Boards, workflow,
leaders integrated
applications and LCD projectors, modeling use of
cloud document systems
ICT, online
computing cameras PLCs
Web Apps Re-tool classrooms Build Capacity Improved workflow
Information Technology Solutions
Reliable Network
There is an on-going investment in the network infrastructure to ensure that it is reliable and stable.
Increased Bandwidth
The increased use of media and resources such as video from You Tube and Teacher Tube require increased bandwidth.
Teaching tools such as Skype for online mentoring require reliable and high speed connectivity.
Wireless Learning Environment
The creation of a secure wireless environment at all Board sites will allow for improved student access to educational
resources over the Internet. Students will be permitted to use personal devices to connect to the World Wide Web for
educational purposes. Teachers will be able to work, prepare, and collaborate from any location in the school.
Board Portal
The development of a Board Portal will allow for improved communications with parents and students. Staff will have
single sign-on access to a variety of teaching tools, data, and utilities. The Portal will allow for direct communications
to teachers and/or all staff.
Changing computer labs
The new model of delivery will move away from bringing an entire class to a computer lab. Differentiated instruction
practices will see a more flexible learning environment with technology on-demand in the classroom.
Blended Learning
The use of a learning management system will allow the exchange of resources through a central object repository.
Students may choose to take blended courses that combine face to face instruction with anytime and anywhere learning.
Data Warehouse
The creation of a data-warehouse and a data dashboard in partnership with the Noel-York consortium will allow for
access to data to inform and improve student achievement.
Change in Policy and Practice
Policies and practices that currently create barriers to student engagement will be removed or modified. Students will
be permitted to use Internet connected devises for academic purposes. Staff will be permitted to use social media to
improve communication and enhance professional dialogue.
Web Apps
The use of web-based applications such as Google Apps will promote 21st century skills including: collaboration,
communication, and creativity. Google Apps provides tools such as documents, calendars, voice, and shared groups.
Re-tool our classrooms
Overhead projectors and chalkboards are being replaced with interactive whiteboards, document cameras, and LCD
projectors. All teaching staff will have a Board issued laptop to access the wireless environment at our sites.
Build Capacity
Online user directed PLCs, leader modeling, just in time learning, and job-embedded learning will all be part of a
strategy to increase the use of ICT. Help line and help desk ticket system available to support all employees.
Improved Workflow
Department and school use of digital forms and a centralized searchable document repository will result in efficiencies
and increased work flow.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Vision - Scope. Time-Tracker 2.0Dokumen7 halamanVision - Scope. Time-Tracker 2.0ВиталийВладимирович100% (1)
- Synchronous LearningDokumen6 halamanSynchronous LearningJheng Panimbatan Navera100% (2)
- MIT Report IPRI CIS Critical InfrastructureDokumen49 halamanMIT Report IPRI CIS Critical InfrastructureTechCrunchBelum ada peringkat
- 4 Types of ALVDokumen7 halaman4 Types of ALVlavi2Belum ada peringkat
- 07 WSOS5 FundamentalsDokumen54 halaman07 WSOS5 FundamentalsMiguel Paredes50% (2)
- Harmonic Cable Spectrum MibDokumen4 halamanHarmonic Cable Spectrum MibJohn SmithBelum ada peringkat
- Brand Rex 2016 Catalogue-WebDokumen96 halamanBrand Rex 2016 Catalogue-WebjuliosieteBelum ada peringkat
- ChangelogDokumen11 halamanChangelogKaushikPaulBelum ada peringkat
- Linux For The Real World: Instructor - Shawn PowersDokumen2 halamanLinux For The Real World: Instructor - Shawn PowersAbhinavBelum ada peringkat
- 4th AssessmentDokumen2 halaman4th AssessmentLily CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Atificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Based Software Project TopicsDokumen2 halamanAtificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Based Software Project TopicsEmmanuelOchiiBelum ada peringkat
- Ashish Deshpande: Work ExperienceDokumen2 halamanAshish Deshpande: Work Experiencearun1974Belum ada peringkat
- HS-001A Subject-Verb AgreementDokumen39 halamanHS-001A Subject-Verb AgreementS KohliBelum ada peringkat
- Admission BookletDokumen38 halamanAdmission BookletMmBelum ada peringkat
- English 7 - Q2 - Mod3 - Informationsources - v5Dokumen22 halamanEnglish 7 - Q2 - Mod3 - Informationsources - v5MARYKNOLL PONCEBelum ada peringkat
- Education PortalDokumen41 halamanEducation PortalRaju RamanBelum ada peringkat
- Travel Industry Performance.Dokumen4 halamanTravel Industry Performance.Paolo AbellanosaBelum ada peringkat
- Blue TrackingDokumen5 halamanBlue Trackingpatrick_lloydBelum ada peringkat
- Test Wifi Hotspot-Word ListDokumen4 halamanTest Wifi Hotspot-Word ListM TauhidBelum ada peringkat
- NETGEAR Wireless-N Access Point WN802T v2 Reference ManualDokumen96 halamanNETGEAR Wireless-N Access Point WN802T v2 Reference ManualDavidBelum ada peringkat
- ETutor Self Review FormDokumen3 halamanETutor Self Review FormEMYZULBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Management: Section A1Dokumen10 halamanFundamentals of Management: Section A1Mehak AminBelum ada peringkat
- LHTTP DOC V10 enDokumen28 halamanLHTTP DOC V10 enhdswt_mBelum ada peringkat
- 2Dokumen57 halaman2Anonymous 1gKhjhXt6Belum ada peringkat
- E-Commerce and Operations ManagementDokumen18 halamanE-Commerce and Operations ManagementAnil KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Module 3 DSMMDokumen70 halamanModule 3 DSMMKartika Bhuvaneswaran NairBelum ada peringkat
- Tricks and HacksDokumen12 halamanTricks and HacksHygieia AfBelum ada peringkat
- UIDAI Based Voting Application On ANDROIDDokumen76 halamanUIDAI Based Voting Application On ANDROIDhasan41Belum ada peringkat
- Management FramesDokumen1 halamanManagement Framesapi-3710188100% (1)
- Ais FinalDokumen12 halamanAis Finalsamuel kebedeBelum ada peringkat