Logistics Value Chain Analysis
Diunggah oleh
ChandrasekarHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Logistics Value Chain Analysis
Diunggah oleh
ChandrasekarHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
American Journal of Industrial and Business Management, 2013, 3, 131-135 131
http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ajibm.2013.32017 Published Online April 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ajibm)
Research on Logistics Value Chain Analysis and
Competitiveness Construction for Express Enterprises*
Xingjian Zhou
School of Management, Wuhan Textile University, Research Center of Hubei Logistics Development, Wuhan, China.
Email: wuliuwtu@163.com
Received January 20th, 2013; revised February 28th, 2013; accepted March 20th, 2013
Copyright © 2013 Xingjian Zhou. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which
permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
Through analyzing the value of the activities in the process of express delivery, the model of logistics value chain
analysis (LVCA) of express enterprises is constructed. Using the model, the express enterprises can identify the key
activities from the whole process of express delivery from senders to receivers, and those key activities constitute the
logistics competitiveness of express enterprises. Then a model of logistics competitiveness is established, which in-
cludes four aspects: strategic location, network optimization, value-added services and performance measures. Those
four aspects form the core logistics competitiveness for express enterprises.
Keywords: Logistics Value Chain; Logistics Competitiveness; Express Enterprises
1. Introduction create customer demands, make the express delivery va-
lue-added, and achieve the competitive advantage. We
With about 30 years development, China has formed a
can use the theory of Michael Porter’s value chain (VC)
large-scales express delivery industry. In 2008, the vol-
[4] to help express enterprises to identity the key activi-
ume of express enterprises registration in China has more
ties or business which make logistics value added in the
than 5000, and the express delivery industry has em- express delivery process, and then form their core logis-
ployed about 23.1 million people [1]. However, the tics competitiveness.
competition of express markets becomes fiercer increas-
ingly, more and more express enterprises are required to 2. Logistics Value Chain Analysis of Express
provide the services with faster and safer. A growing Delivery
number of express enterprises began to develop the direct-
service, such as “door to door”, “table to table”. Fur- 2.1. Logistics Value Chain
thermore, some enterprises try to shorten the delivery Value chain is a theoretical tool of analysis the compete-
time, and they began to develop the faster-service, such tive advantage for an enterprise [5]. Introduction the the-
as “next day delivery”, “next morning delivery”. There- ory to logistics area, so-called logistics value chain
fore, it’s very important for express enterprises to form (LVC), refers to the chain with a series of intrinsic logis-
the core competitiveness, so as to win more customers in tics value. Logistics value chain exists in the relationship
express market [2]. of logistics process, from upstream to downstream. Lo-
Consequently, for express enterprises, its core com- gistics value chain reflects the nature of supply chain,
petitiveness is manifested in the implement “customer and shows the origin driving force to form the supply
value strategy”. Customer value strategy is a value-cre- chain. The usual sense of the “logistics contract” is a
ating activity to win the finally success, and win custom- concrete form, and the value chain has been translated
ers’ satisfies by creating more value for them, rather than into supply chain as a constraint. In the traditional struc-
simply improve the services qualities or service tech- ture of value chain, the “logistics” activities were shown
nologies [3]. in internal logistics (i.e., industrial logistics) and external
Therefore, the express enterprises will focus on how to logistics (i.e., business logistics), but all of them are parts
*
Sponsored by the Hubei Provincial Department of Education, and of logistics value chain [6].
Research Center of Hubei Logistics Development. In fact, logistics value chain is one part of the enter-
Copyright © 2013 SciRes. AJIBM
132 Research on Logistics Value Chain Analysis and Competitiveness Construction for Express Enterprises
prise’s value chain, which includes such external logis- value chain of express enterprises is shown in Figure 2.
tics activities as delivery of raw materials and finished
goods, and also involves such internal logistics activities 2.2. Model of Logistics Value Chain Analysis
as production and selling. So we can think that, in the
Value chain reflects the enterprises’ history, strategy, and
supply chain, logistics is used to optimize and integrate tactics. All these activities in the enterprises can be di-
the logistics resources, while logistics value chain is used vided into basic activities and ancillary activities, and the
to design and plan the value-added activities in the logis- basic activities are considered as the key business in the
tics process. Therefore, all those activities constitute a enterprises. Generally, the basic activities include inter-
new chain, that is logistics value chain [7]. The “value nal logistics, production and management, external logis-
flow” in logistics value chain is shown in Figure 1. tics, marketing and service, which lead to better services,
Logistics value chain can be used to optimize logistics and more effectiveness; ancillary activities include de-
system and reconstruct the logistics process of express sign of the system, information sharing between logistics
enterprises, and then make the logistics value maximized. activities, inventory visibility and good coordination of
The express enterprises provide the logistics services, operation, which lead to lower costs, and more efficiency
and there are different levels of value-added activities in [9].
the process of express delivery, which includes recipient, According to above value chain analysis (VCA), the
branch transportation, transit, trunk transportation, transit activities in the logistics enterprises can be also divided
again, branch transportation again, distribution, etc. [8]. into basic activities and ancillary activities. For example,
If the express enterprises want to improve its compete- the basic activities in the process of express delivery:
tiveness, they need the cooperation and synergy from recipients, sorting (including the packaging and receiv-
above activities to get the maximum values. Those values ing), transportation, and distribution. In order to achieve
come from the logistics value chain, which exist in the synergy between the four aspects of the express delivery,
express delivery process and networks. The logistics the express enterprises need to optimize delivery network,
Value Flow
Transportation
Warehousing Distribution Packaging
Suppliers Logistics Customers
Enterprises
Information Loading/unloading Distribution
Handling Process
Material Flow Information Flow Ownership Flow Value Flow
Figure 1. “Value flow” in logistics value chain.
Value Flow Value Flow
Branch Trunk Branch
Transit Transit
Transportation Transportation Transportation
Air Transportation
Recipient Distribution
Figure 2. Logistics value chain of express delivery.
Copyright © 2013 SciRes. AJIBM
Research on Logistics Value Chain Analysis and Competitiveness Construction for Express Enterprises 133
design delivery process, etc. Ancillary activities are be- tegic positioning, network optimization, value-added ser-
yond the basic activities, and extend the basic activities, vices and performance measures, as shown in Figure 4.
such as payment collection, e-commerce, etc., which meet
and create the demands of customers. 3.1. Strategic Positioning
Above logistics value chain analysis (LVCA) help the
Strategic positioning is a competitiveness of the accurate
express enterprises identify the key business, find new
positioning of markets and resources. Strategic position-
profit growth points, make the value of both the enter-
ing refers that how to position the logistics activities in
prises and customers improved, and then get the core
the enterprises from its strategy to structure. Business mar-
logistics competitiveness.
keting strategy, procurement strategy, R & D strategy,
Specifically, for express enterprises, the basic activi-
and logistics strategy are closely linked with each other.
ties include four main aspects: strategic positioning, net-
Logistics organizational structure, personnel structure
work optimization, value-added services and perform-
and logistics network structure, in other words, that all
ance evaluation, such as layout of logistics network, op-
logistics resources are related and integrated with the
timization of delivery process, establish of call centers,
enterprises strategies and department strategies.
evaluation of delivery performance, and so on. The an-
cillary activities include two main aspects: delivery in-
3.2. Network Optimization
frastructure and information platform, such as sharing the
delivery information, construction the delivery network, Network optimization is a competitiveness of achieving
developing e-commerce, collection payment, and so on. synergy effect, which comes from the theory of system.
Basic activities are the fundamental of express enter- Network optimization refers that how to implement the
prises to enhance competitiveness, and the source of lo- logistics strategy. The logistics enterprises need to con-
gistics profits. Ancillary activities support the basic ac- struct a coordination mechanism between internal and
tivities to implement successfully. All those activities external enterprises, and use the mechanism to control
create logistics value from “the third profits resource”. the total cost of logistics, service objectives, logistics
Through above analysis, we can build the model of lo- ideas and cross-functional process.
gistics value chain analysis of express delivery, as shown
in Figure 3. 3.3. Value-Added Services
The logistics value chain of express delivery is a dy- Value-added service is a competitiveness of responding
namic process with creating logistics value for customers. the customers’ demands rapidly, which includes various
In the traditional, the “customer” is the external custom- kinds of business to improve customers’ satisfaction.
ers of an enterprise, and the “service” is the internal “cus- Value-added services come from the idea of logistics sys-
tomers”. In logistics value chain, combining the internal tem. The goal of logistics system is to serve customers,
and external factors, the express enterprises improve the and the only purpose is to create value for customers.
service quality of external and internal customers syn-
chronously, so as to get the fully and continued advantages 3.4. Performance Evaluation
of internal and external resources, and then form the core
logistics competitiveness. Performance evaluation is a necessary factor so that a
3. Logistics Competitiveness Model of
Express Delivery
Based on the model of logistics value chain analysis, the
logistics competitiveness of express enterprises comes
from the process of pursuit the logistics value. The model
of logistics competitiveness for express enterprises is
constructed based on the basic activities, including stra-
Figure 4. Logistics competitiveness model of express deliv-
Figure 3. Model of LVCA for express delivery. ery.
Copyright © 2013 SciRes. AJIBM
134 Research on Logistics Value Chain Analysis and Competitiveness Construction for Express Enterprises
logistics system can fulfill its functions successfully. The 4.1.3. Information Systems
logistics process’s efficiency and effectiveness must be Scalability. Usually, a common demand of the informa-
measurable, so that managers can control and adjust time- tion system or a business function changes will cause to
ly to ensure that the organization goals can be achieved modifications of a number of information subsystems in
with shorter time and lower costs. The logistics enter- a wide range.
prises should have an internal and external “monitor Synergies. The information subsystems of SF are rela-
mode”, which will provide information for strategic posi- tive independent, which form the isolated islands of in-
tioning, network optimization and value-added services. formation. The sharing capability of information is weak.
4. Empirical Research: The Logistics 4.2. Logistics Competitiveness Model of SF
Competitiveness for SF Based on above problems for SF, the logistics compete-
tiveness model of SF is constructed from four aspects:
SF is an express enterprise and as the leader of the ex-
SF’s strategic positioning, SF’s network optimization,
press delivery industry in China. The core value of SF is
SF’s value-added services, and SF’s performance evalua-
“FIRST” (abbreviation of faith, integrity, responsibility,
tion.
service and team). The competitiveness of SF is higher
than other domestic express enterprises in such aspects as
4.2.1. SF’s Strategic Positioning
network architecture, value-added services and informa-
“FIRST” is the strategic positioning of SF. Network op-
tion system. However, for SF, there are also some prob-
timization and value-added services are two important
lems in those three areas.
strategies. So the strategic positioning of SF combines
those two strategies, through optimization of the express
4.1. The Situation of Express Delivery for SF delivery network based on providing value-added ser-
4.1.1. Express Delivery Network vices to add the logistics value in the different levels of
The network of air transportation. At present, SF has own customers’ demands.
cargo aircrafts and airlines, but the coverage of shipping
lines is small and the loading rate is low. Therefore, the 4.2.2. SF’s Network Optimization
delivery volume is not balanced, and lead to high logis- SF need to optimize the air transportation network and
tics costs. road transportation network based on logistics value
The network of road transportation. SF uses informa- chain. The network optimization is used to integrate va-
tion technology to position the vehicles, and ensure the riety resources of express delivery in order to get the
process of road transportation is smooth and effective. synergy effects, form the coordination mechanisms, and
However, in current, the road transportation network is achieve the goal of controlling total cost of delivery, ser-
still unable to meet the increasing of express delivery, vices levels, process optimization and reconstruction.
and the loading rate of road transportation is also low.
The process of express delivery. The delivery speed at 4.2.3. SF’s Value-Added Services
the start and the end of express delivery is slow, because SF should provide value-added services with a variety of
SF does not pay more attention to the links of different marketing methods, which is an important way to im-
parts. SF spent more time in distribution, which leads to prove customers’ satisfaction. SF need to use network to
low efficiency. provide faster and more flexible delivery service, so as to
meet and create customers’ demand constantly.
4.1.2. Value-Added Services
Marketing homogenization. The marketing methods and 4.2.4. SF’s Performance Evaluation
means of SF are similar with other express enterprises, SF should establish a measurable evaluation system and
and imitate each other. process of express delivery, which can be used to control
Marketing activities single. SF’s marketing activities and adjust the strategic positioning, network optimization
are not the target and lacking of innovation. Service mar- and value-added services to achieve goals with the man-
keting and knowledge marketing are used to maintain ner of efficiency and effectiveness.
customer relationships, and then SF failed to develop a
variety of activities based on characteristics of the VIPs.
4.3. Characters of Logistics Competitiveness for
Important clients marketing system. SF did litter to
SF
construct the VIPs marketing system, the marketing or- In the model of logistics value chain analysis, the four
ganizations and staffs are insufficient, and the marketing basic activities, strategic positioning, network optimiza-
policy and design are not reasonable. tion, value-added services and performance evaluation,
Copyright © 2013 SciRes. AJIBM
Research on Logistics Value Chain Analysis and Competitiveness Construction for Express Enterprises 135
each include a series of indicators. Good or bad indica- competitiveness of key activities or business and the
tors show that the express enterprises have or haven’t the management team leadership constitute the core com-
competitive advantages comparative to other competitors. petitiveness, and the core competitiveness is the essential
Those indicators have a broad applicability, and provide part and fundament for the development of the enterprises.
an important basis for SF to find the direction to improve The express enterprises provide high level services to
its logistics competitiveness. meet customers’ demands, develop the customer markets
For SF, the characters of logistics competitiveness and constantly, and then get the chance of growing and being
the indicators of logistics value chain are shown in Table 1. stronger. There are a number of activities in the process
of express delivery, but the different activity contributes
5. Conclusions the different value to the whole process. Through con-
struction the model of logistics value chain analysis, the
The core competitiveness is a system of certain advan-
key activities of express delivery can be identified, which
tages, abilities or knowledge for the enterprises, and
constitute the logistics competitiveness for the express
shown as the key activities or unique business in the en-
enterprises. Then a model of logistics competitiveness is
terprises. The core competitiveness is in relation to the
established, which involves four factors: strategic posi-
enterprises’ surviving and development, and it can make
tioning, network optimization, value-added services and
the enterprises stronger than other competitors. The
performance evaluation. The model helps the express en-
Table 1. Characters of logistics competitiveness. terprises to form the core logistics competitiveness.
Strategic Positioning
REFERENCES
Strategy Network Supply chain Organization
[1] X. Y. Xu, “Report of the Development of Express Deliv-
High level of ery in Chian,” China Social Sciences Publishing House,
Establishment of license, process,
basic services, Partners, strategic Beijing, 2009.
distribution learning,
integration of positioning,
centers and dynamic, team [2] D. P. Wang and Y. F. Yang, “Analysis of the Competition
internal process, organizations
nodes, providing loyalty, of the Express Market in China,” Social Science of Bei-
market expand, influence
solutions possibility jing, Vol. 48, No. 2, 2009, pp. 10-15.
positioning
[3] C. B. Jiang, “Analysis of Market Opportunities for Chi-
Network Optimization
nese Private Express Service,” Logistics Sci-Tech, Vol.
Information 32, No. 8, 2009, pp. 79-81.
Cooperation Standardization Discipline
sharing [4] M. Port, “Competitive Advantage,” Hua Xia Press, Bei-
Information Predictability jing, 1997.
Specialized tasks, Standard
exchange, and accuracy [5] X. J. Zhou, “Logistics: From Supply Chain to Value
criteria, processes,
agreement and of results,
distribution industry standards Chain,” Logistics Sci-Tech, Vol. 30, No. 12, 2007, pp.
methods pay system
48-49.
Information Information
Simplify [6] X. J. Zhou and Q. N. Zhang, “Research on Construction
technology exchange
and Generation of Logistics Value Chain,” China Busi-
IT innovation, Technology, ease Restructuring, ness and Market, Vol. 24, No. 4, 2010, pp. 26-29.
integration or difficult modular
[7] X. J. Zhou and C. H. Huang, “Value Chain Alliance of
Value-added Services Logistics Enterprises Based on Core Competition,” Jour-
Idea Ability to adapt Customer Flexible nal of Wuhan University of Science and Engineering, Vol.
20, No. 9, 2007, pp. 79-81.
Customer service, Comprehensive Procedures,
Synchronization, [8] L. Ma and J. Tang, “Value Chain Analysis and Applica-
satisfaction, services, logistics extension,
order execution tion of Express Enterprises,” Commercial Times, Vol. 22,
success channels lateral supply
No. 24, 2010, pp. 88-89.
Performance Evaluation
[9] X. J. Zhou, J. Z. Li and S. A. Xie, “Optimization of Lo-
Functional Process gistics Value Chain for Cluster Supply Chain,” China
Contrast
assessment evaluation Business and Market, Vol. 25, No. 4, 2011, pp. 34-37.
Internal, Costs, customers,
Range, accuracy
cross-industry channels
Copyright © 2013 SciRes. AJIBM
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Human Person Flourishing in Terms of Science and TechnologyDokumen12 halamanThe Human Person Flourishing in Terms of Science and TechnologyCelhes de leon82% (17)
- Hanuman Mantra For EnemyDokumen8 halamanHanuman Mantra For Enemyanadinath sharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: This Document Consists of 19 Printed PagesDokumen19 halamanCambridge Assessment International Education: This Document Consists of 19 Printed Pagestecho2345Belum ada peringkat
- Scan Sep 2, 2020Dokumen1 halamanScan Sep 2, 2020Taresh MittalBelum ada peringkat
- Government of India Recruits Trainees at Variable Energy Cyclotron CentreDokumen13 halamanGovernment of India Recruits Trainees at Variable Energy Cyclotron Centrenira365Belum ada peringkat
- Operational and PostimplementationDokumen20 halamanOperational and PostimplementationTissyu BasahBelum ada peringkat
- Note 13 - Grievance & DisciplineDokumen3 halamanNote 13 - Grievance & DisciplineVishesh MehtaBelum ada peringkat
- The Flame of Love RosaryDokumen2 halamanThe Flame of Love Rosarygenerose0% (1)
- CBMS consent form for household data collectionDokumen1 halamanCBMS consent form for household data collectionMarjo Ursula50% (2)
- History AssignmentDokumen5 halamanHistory AssignmentVenom ESports100% (1)
- 1st Quarter NCCS Newsletter, 2013Dokumen10 halaman1st Quarter NCCS Newsletter, 2013Heather Pendry MullinsBelum ada peringkat
- Commil USA, LLC v. Cisco Systems, Inc. (2015)Dokumen20 halamanCommil USA, LLC v. Cisco Systems, Inc. (2015)Scribd Government DocsBelum ada peringkat
- John Snow's pioneering epidemiology links Broad Street pump to cholera outbreakDokumen4 halamanJohn Snow's pioneering epidemiology links Broad Street pump to cholera outbreakAngellaBelum ada peringkat
- Democracy in Islam: by - Hassan TahaDokumen35 halamanDemocracy in Islam: by - Hassan TahalaleenmehtaBelum ada peringkat
- PARLE AGRODokumen14 halamanPARLE AGRORakesh RajpurohitBelum ada peringkat
- Saagesh - Concise insights from ancient textsDokumen2 halamanSaagesh - Concise insights from ancient textsChidambaramBelum ada peringkat
- HRM CHAPTER 10 Changes in Personnel StatusDokumen8 halamanHRM CHAPTER 10 Changes in Personnel StatusBen joe CajigalBelum ada peringkat
- Examining Alternative MedicineDokumen288 halamanExamining Alternative Medicinecheeky monkey100% (1)
- Common Terminology in Wireless NetworksDokumen15 halamanCommon Terminology in Wireless Networksabhishek4vishwakar-1Belum ada peringkat
- Agirm Agn 4500210653 Itp 001 02 Kas3 Iso Seawater Strainer Forward Sea ChestDokumen6 halamanAgirm Agn 4500210653 Itp 001 02 Kas3 Iso Seawater Strainer Forward Sea ChestRJS TUTORIALBelum ada peringkat
- Position Paper Michael Lawrence TalaveraDokumen44 halamanPosition Paper Michael Lawrence TalaveraHaroldRamosBelum ada peringkat
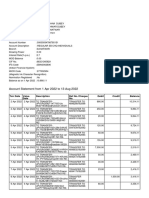
- Account Statement From 1 Apr 2022 To 13 Aug 2022: TXN Date Value Date Description Ref No./Cheque No. Debit Credit BalanceDokumen11 halamanAccount Statement From 1 Apr 2022 To 13 Aug 2022: TXN Date Value Date Description Ref No./Cheque No. Debit Credit BalanceShubham TyagiBelum ada peringkat
- E Business InfrastructureDokumen26 halamanE Business InfrastructureankitjhaBelum ada peringkat
- Case Concerning Delimitation of Maritime Areas Between CanadaDokumen2 halamanCase Concerning Delimitation of Maritime Areas Between CanadaVen BuenaobraBelum ada peringkat
- 13th December 1981 UN Secretary-GenDokumen2 halaman13th December 1981 UN Secretary-GenMason SykesBelum ada peringkat
- Freelancing Success: 101 Questions AnsweredDokumen52 halamanFreelancing Success: 101 Questions AnsweredsdsdsdBelum ada peringkat
- Mouse Pad Bill PDFDokumen1 halamanMouse Pad Bill PDFsuresh kumarBelum ada peringkat
- Aitel Joint Mock Examinations: of East Africa) Paper 2Dokumen2 halamanAitel Joint Mock Examinations: of East Africa) Paper 2Owani JimmyBelum ada peringkat
- The Secret You Need To Know For You To Move ForwardDokumen4 halamanThe Secret You Need To Know For You To Move ForwardBukola BukkyBelum ada peringkat
- Risk and Opportunity Assessment GuideDokumen6 halamanRisk and Opportunity Assessment GuideChandrashekhar ThiramdasuBelum ada peringkat